3D characteristics of primary halo and deep prospecting prediction in the Zaozigou gold deposit, Hezuo City, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
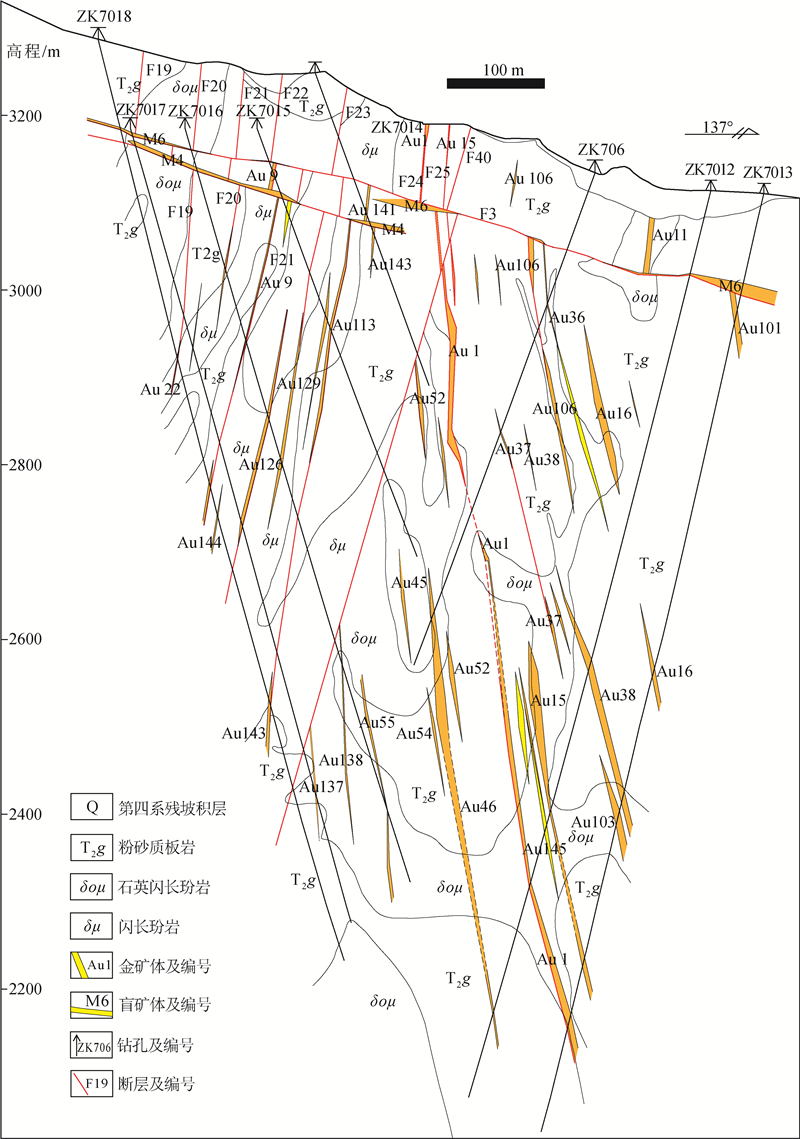
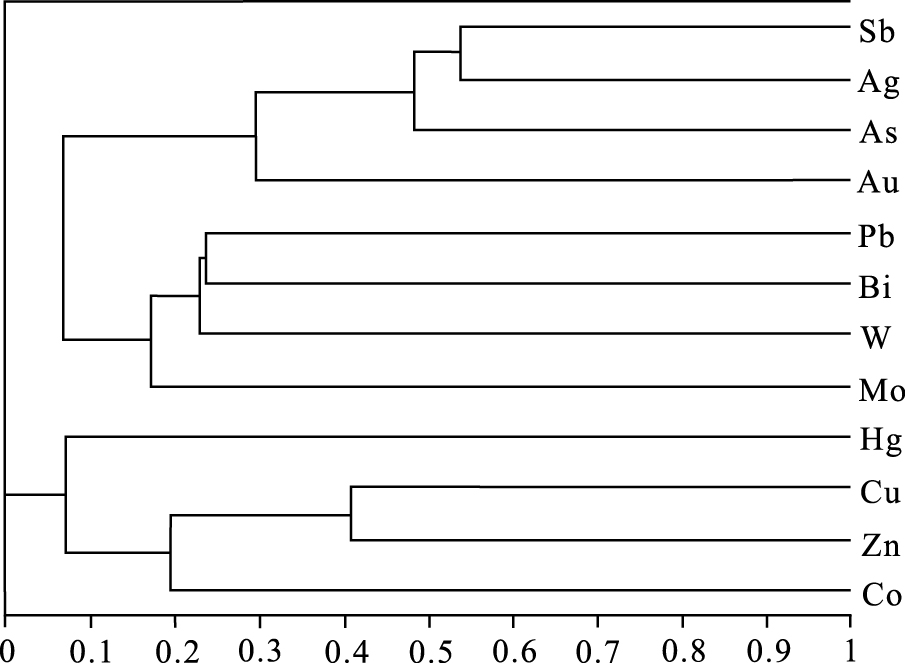
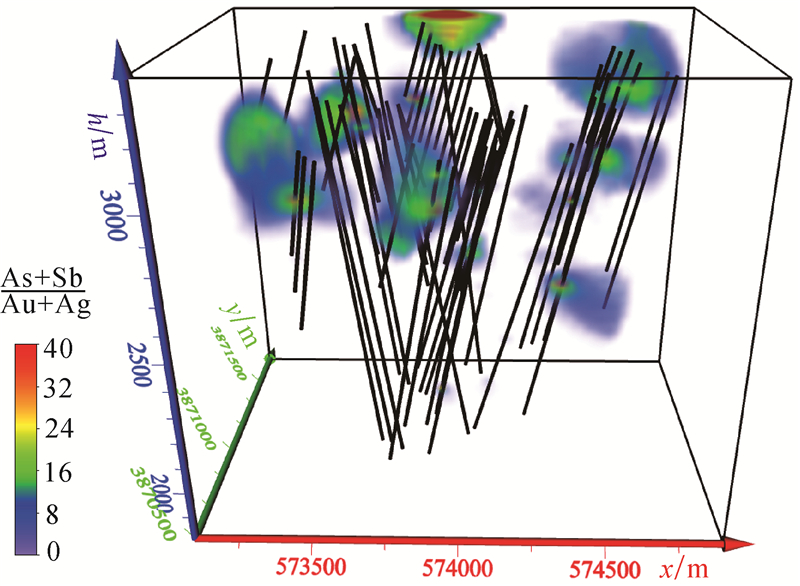
为了评价早子沟金矿深部找矿潜力和找矿方向,以早子沟金矿61个钻孔为研究对象,对矿体出露较厚大的70勘查线原生晕数据进行多元统计分析和三维空间分布特征研究。研究表明:①相关分析和聚类分析结果反映,与主成矿元素Au相关性最密切的元素为As、Ag;②原生晕的形态特征和空间分布特征显示,矿体原生晕发育,且分带明显,矿床的前缘晕元素为As、Sb、Hg,近矿晕元素为Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn,尾晕元素为W、Mo、Bi;③对原生晕数据进行三维插值分析,构建了早子沟金矿各元素原生晕三维模型。Au、As、Sb、Ag等指示元素和As+Sb/Au+Ag元素异常累加比值的异常模型显示,在2500 m以浅,异常规模较小;在2500 m以深,异常规模呈现出向深部越来越大,且延伸稳定。结合异常元素的空间分布特征,提出早子沟金矿78~85勘查线2000 m以深仍有较大的找矿潜力。
Abstract:In order to evaluate the prospecting potential and direction in the depth of the Zaozigou gold deposit, the authors selected 61 drill holes in the Zaozigou gold deposit as the research objects, conducted multivariate statistical analysis and 3D spatial distribution characteristics study of the primary halo data along No.70 exploration line with thick orebodies exposed.The results are as follows:① Correlation analysis and cluster analysis indicate that the elements most closely related to Au are As and Ag.② The morphological characteristics and spatial distribution characteristics of the primary halo show that the ore- and halos- forming elements exhibit a clear zonation.The primary halo is characterized by the front halo elements of As, Sb, Hg, the near-ore halo elements of Au, Ag, Cu, Pb, Zn and the rear halo elements of W, Mo, Bi.③ Based on the 3D interpolation analysis of the primary halo data, a 3D model of each element primary halo in the Zaozigou gold deposit was constructed.The anomaly model of indicator elements such as Au, As, Ag and the anomaly accumulation ratio of As+Sb/Au+Ag show that the anomaly scale is small when the anomaly is shallower than 2500 meters.In the depths greater then 2500 meters, the anomaly scale seems to be larger and larger toward the depth, and the extension is stable.Combined with the spatial distribution characteristics of anomaly elements, it is proposed that the place along No.78 line-No.85 exploration line of the Zaozigou gold deposit still has great prospecting potential in the depths greater than 2000 m.
-
Key words:
- deep prospecting prediction /
- 3D visualization /
- primary halo /
- Zaozigou gold deposit /
- Gansu Province
-

-
表 1 早子沟金矿钻孔原生晕数据参数统计
Table 1. Data parameter statistics table of drilling primary halo in the Zaozigou gold deposit
元素 最小值 最大值 几何平
均值算术平
均值中位数 标准
离差浓集
系数变异
系数Au 1.80 24900 49.4 249.40 45.20 1097.40 293.47 4.40 As 1.10 12322.9 206.7 695.50 180.10 1417.30 158.07 2.04 Sb 1.98 93471.8 49.83 775.81 41.49 6112.53 2281.80 7.88 Hg 4.00 94931.0 37.00 209.00 31.00 3785.00 17.38 18.15 Cu 1.70 121.2 18.90 23.50 17.40 17.50 1.38 0.74 Pb 1.90 381.8 23.60 28.50 22.30 25.40 1.5 0.89 Zn 22.50 307.1 77.30 82.00 86.20 27.30 1.21 0.33 Co 1.90 54.9 14.30 15.90 16.70 6.20 1.59 0.39 Ag 0.045 2.86 0.107 0.151 0.09 0.255 2.52 1.69 Bi 0.08 203.92 0.61 1.64 0.51 8.94 9.1 5.45 W 0.18 1639.75 6.79 17.01 6.73 87.04 17.54 5.12 Mo 0.16 304.05 1.27 4.02 0.89 14.19 6.48 3.53 注:浓集系数为算术平均值与丰度值[33]的比值,变异系数为标准离差与算术平均值的比值。Au、Hg元素单位为10-9,其余元素为10-6 表 2 早子沟金矿70勘查线原生晕样品正交旋转载荷矩阵
Table 2. Orthogonal rotational load matrix of primary halo samples in No.70 exploration line from the Zaozigou gold deposit
因子 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Au 0.460 0.086 -0.036 -0.170 0.068 As 0.799 -0.096 -0.056 -0.062 0.016 Sb 0.567 -0.088 0.078 0.540 -0.280 Hg -0.006 -0.087 0.001 0.442 0.878 Cu 0.274 0.761 -0.044 -0.035 0.170 Pb -0.026 -0.02 0.778 -0.032 -0.051 Zn -0.145 0.784 0.161 -0.053 -0.027 Co -0.401 0.298 0.213 0.548 -0.128 Ag 0.823 0.137 0.156 0.238 -0.025 Bi 0.049 0.026 0.571 0.126 -0.052 W 0.128 -0.112 0.497 -0.476 0.293 Mo -0.064 -0.469 0.302 -0.022 -0.030 主因子方差 2.128 1.566 1.376 1.124 0.993 累积方差贡献/% 17.840 31.078 42.493 51.612 60.886 表 3 早子沟金矿各元素临界值
Table 3. The critical value of elements in the Zaozigou gold deposit
元素 Au As Sb Hg Ag Co Cu Pb Zn W Mo Bi 插值 0.12 800 130 0.08 0.18 20 48 30 100 25 2.8 1.2 -
[1] Beus A A, Grigorian S V.Geochemical Exploration Methods for Mineral Deposits [M].Illinois:Applied Publishing Ltd, 1977:1-287.
[2] 刘崇民.金属矿床原生晕研究进展[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(10):1528-1538. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200610006
[3] 邵跃.热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法)找矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1997:1-142.
[4] 欧阳宗圻, 李惠, 刘汉忠.典型有色金属矿床地球化学异常模式[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990:1-75.
[5] 李惠, 张文华, 刘宝林, 等.中国主要类型金矿床的原生晕轴向分带序列研究及其应用准则[J].地质与勘探, 1999, 35(1):32-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt199901009
[6] 孙保平, 王宗炜, 王云.河南桐柏破山银矿床原生地球化学异常模式[J].西北地质, 2007, 40(1):61-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200701005
[7] 陈永清, 韩学林, 赵红娟, 等.内蒙花敖包特Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿床原生晕分带特征与深部矿体预测模型[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(2):236-246. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201102006
[8] 邢利琦, 刘炳璋.矿床原生地球化学晕分带性研究[J].四川地质学报, 2011, 31(4):489-492, 495. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=scdzxb201104028
[9] 方贵聪, 赵正, 陈伟, 等.赣南长流坑钨矿年代学与原生晕地球化学[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(5):149-158. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201705014
[10] 李昌明, 陈远荣, 陈晓雁, 等.广西南丹县大厂矿田铜坑锡矿成矿地球化学模型和找矿预测标志[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(1):136-142. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120117&flag=1
[11] 陈国忠, 梁志录, 王建龙, 等.甘肃合作早子沟金矿原生叠加晕特征及深部预测[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(2):268-277. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtyht201402013
[12] 林成贵, 程志中, 吕志成, 等.甘肃省早子沟金矿原生晕分带特征及深部找矿预测[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(1):70-84. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb202001006
[13] 吴俊华, 龚敏, 龚鹏, 等.江西九江城门山铜矿三维地质地球化学特征与成矿预测[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(6):925-932. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100615&flag=1
[14] 肖克炎, 陈学工, 李楠, 等.地质矿产勘探评价三维可视化技术及探矿者软件开发[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(S1):758-760. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7413152
[15] 向中林, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等.基于三维地质建模及可视化的大比例尺深部找矿预测研究及应用:以内蒙古柳坝沟矿区为例[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(5):227-235. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201405018
[16] Wang G W, Li R X, Carranza E J M, et al.3D geological modeling for prediction of subsurface Mo targets in the Luanchuan district, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:592-610. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.002
[17] Wang G W, Feng Y, Carranza E J M, et al.Typomorphic characteristics of pyrite:Criteria for 3D exploration targeting in the Xishan gold deposit, China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 164:136-163. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.003
[18] 郭福生, 吴志春, 李祥, 等.江西相山火山盆地三维地质建模的实践与思考[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3):421-434. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020320&flag=1
[19] 向杰, 陈建平, 肖克炎, 等.基于机器学习的三维矿产定量预测——以四川拉拉铜矿为例[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(12):2010-2021. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20191209&flag=1
[20] 王润怀, 李永树, 刘永和, 等.三维地质建模中虚拟钻孔的引入及其确定[J].地质与勘探, 2007, 43(3):102-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt200703021
[21] 曹晓峰, Mohamed L S S, 吕新彪, 等.甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿过程分析——来自矿床地质特征、金的赋存状态及稳定同位素证据[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(4):1039-1054. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201204020.htm
[22] Sui J X, Li J W, Hofstra A H, et al.Genesis of the Zaozigou gold deposit, West Qinling orogen, China:constraints from sulfide trace element and stable isotope geochemistry[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 103477.doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103477
[23] Yu H C, Guo C A, Qiu K F, et al.Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the formation of the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China[J].Minerals, 2019, 9(1):1-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=MDPI000000188796
[24] Mohamedl S S, Lv X B, Cao X F, et al.Geology, petrography and structural characteristics of Zaozigou gold deposit[J].Research Journal of Applied Sciences, 2008, 3(3):206-215. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Open J-Gate000001048280
[25] 钱建平, 张果, 漆炜博, 等.甘肃早子沟金矿复合成矿构造系统的构成、样式、时间演化和控矿规律[J].大地构造与成矿学, .https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.02.018. https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.02.018.
[26] 李伟, 陈建平, 贾玉乐, 等.甘肃早子沟金矿三维建模与综合成矿预测[J].地球学报, 2020, 41(2):144-156. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb202002005
[27] 代文军, 陈耀宇, 金鼎国, 等.甘肃枣子沟金矿床控矿因素及找矿标志[J].黄金, 2012, 33(8):17-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJZZ201208005.htm
[28] 王涛.甘肃夏河-合作矿集区早子沟金矿成矿作用与找矿预测地质模型研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2018.
[29] 陈瑞莉, 陈正乐, 伍俊杰, 等.甘肃合作早子沟金矿床流体包裹体及硫铅同位素特征[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(1):87-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201801007
[30] 韦良喜, 陈正乐, 庞振山, 等.甘肃省合作市早子沟金矿床构造应力场分析[J].地球学报, 2018, 39(1):79-93. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201801009
[31] 刘春先.甘肃枣子沟金矿矿石特征[J].甘肃科技, 2011, 27(22):55-57, 7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gskj201122020
[32] 付男, 陈耀宇, 金鼎国, 等.早子沟金矿格娄昂矿段原生晕异常特征[J].地球科学进展, 2012, 27(S1):518-521. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7955988
[33] 迟清华, 鄢明才.应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:1-148.
[34] 于皓丞, 李俊, 邱昆峰, 等.西秦岭甘南早子沟金锑矿床白云石Sm-Nd同位素地球化学及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2019, 35(5):1519-1531. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201905014
-



 下载:
下载: