The sedimentary environment of Early Cretaceous dinosaur tracks in Longzhou Danxia Landform of Jingbian County, Shaanxi Province
-
摘要:
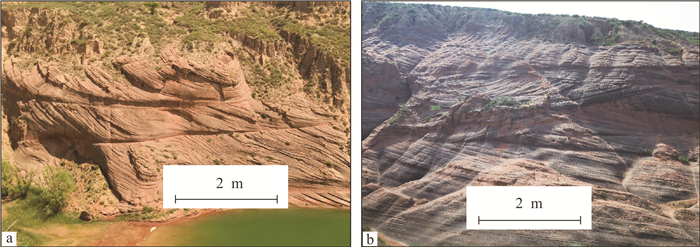
2019年在陕西靖边龙洲下白垩统洛河组紫红色砒砂岩中发现多处恐龙足迹,实属罕见。含恐龙足迹地层岩石组合为一套典型沙漠相"红色砒砂岩"系,岩石组合以紫红色-暗紫红色薄层中-粗粒长石石英砂岩、石英砂岩夹灰黄色-浅紫红色块状粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩为主。发现识别出恐龙足迹行迹9处。根据足迹形态对比,推断其类型为兽脚类恐龙足迹。根据足迹产地地层剖面的研究,推断恐龙足迹分布在沙丘湖岸附近。本次发现的恐龙足迹与2017年在陕西神木中鸡发现的恐龙足迹差异明显,为陕北鄂尔多斯盆地恐龙研究提供了珍贵的研究资料。由于靖边龙洲丹霞地貌恐龙足迹产地的地层研究程度较低,因此,对恐龙足迹的研究在地层年代确定,特别是恢复岩相古环境具有重大意义。
Abstract:During the extensive survey on Longzhou Danxia Landform in Jingbian County of Northern Shaanxi in July 2019, Shaanxi Institute of Geological Survey found several dinosaur track sites in the purple sandstone of Early Cretaceous Luohe Formation.The dinosaur track-bearing formation belongs to a typical red arsenic sandstone of desert facies, which is mainly composed of purplish red to dark purplish red medium to coarse grained feldspathic quartz sandstone, and quartz sandstone intercalated with grayish yellow-pale purple red massive silty mudstone and argillaceous stone, constituting the typical Danxia Landform scene.Altogether 9 dinosaur trackway sites were identified.Based on the comparison of morphological features and the field survey, it can be inferred that the dinosaur trackmakers were theropod.Based on the research on the sequence of around this area, it can be inferred that these dinosaur tracks were preserved near the shoreside of a desert lake.The dinosaur tracks found in Jingbian are distinctly different from those found in Zhongji Town, Shenmu City in 2017 and can provide rare research materials for the dinosaur research in the Ordos Basin.Moreover, the dinosaur track-bearing formation is less well studied, thus the study of the dinosaur tracks will contribute greatly to ascertaining the stratigraphic age and reconstructing the paleoenvironment.
-
Key words:
- Longzhou Danxia Landform /
- dinosaur tracks /
- desert facies /
- sedimentary environment /
- Cretaceous
-

-
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地沙漠相亚相划分
Table 1. Classification of subfacies of desert facies in the Ordos Basin
沉积相 沉积亚(微)相 地质营力 沉积构造及粒度 发育情况 沙漠相 戈壁亚相 风力为主 平行层理、沙丘;粗砂、砾石 少见 旱谷亚相 旱谷 水力为主 块状、斜层理;粗砂、细砾 常见 沙漠平原 风力为主 水平层理;细砂、粉砂 常见 沙丘亚相 小型沙丘 风、水交错 小型沙丘、斜层理;细、粉砂 广泛 大型沙丘 风力为主 大型板状、交错层;细、粗砂 广泛 丘间亚相 干丘间 风、水交错 大型交错层;细、粗砂 广泛 湿丘间 水力为主 小型沙丘、平行层理;细粉砂 常见 沙漠湖亚相 水力为主 水平层理;细砂、粉砂、泥 常见 -
[1] 唐永忠, 邢立达, 徐涛, 等.陕西中鸡发现白垩纪恐迹龙足群[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(7):1193-1196. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180703&flag=1
[2] 唐永忠, 徐涛, 邢立达, 等.陕西神木白垩纪恐龙足迹沉积环境与时代研究[J].矿产勘查, 2018, 5(5):793-802. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.05.003
[3] 张玉光, 李建军, 胡松梅, 等.陕西神木侏罗纪恐龙足迹的新发现及其地层学意义[J].地层学杂志, 2012, 36(1):60-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz201201009
[4] 谢渊, 王剑, 江新胜, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地白垩系沙漠相沉积特征及其水文地质意义[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(1):73-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.010
[5] 齐骅, 李国栋.鄂尔多斯盆地志丹群沉积时期的古沙漠盆地体系[J].西北地质科学, 1996, 17(1):63-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBFK601.002.htm
[6] 郭庆银, 李子颖, 杨圣彬, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地西北部白垩系沉积特征[J].铀矿地质, 2006, 22(3):143-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2006.03.003
[7] 江新胜, 徐金沙, 潘忠习.鄂尔多斯盆地白垩纪沙漠石英沙颗粒表面特征[J].沉积学报, 2003, 21(3):416-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.008
① 王洪亮, 李维均.陕西省神木大柳塔—孙家岔地区1: 5万区调报告.陕西省地质调查院, 1999.
-




 下载:
下载: