The ore-controlling tectonic patterns and tectono-geochemical prospecting in the Gaojiajing exploration area, the periphery of the Huize lead-zinc deposit, Yunnan
-
摘要:
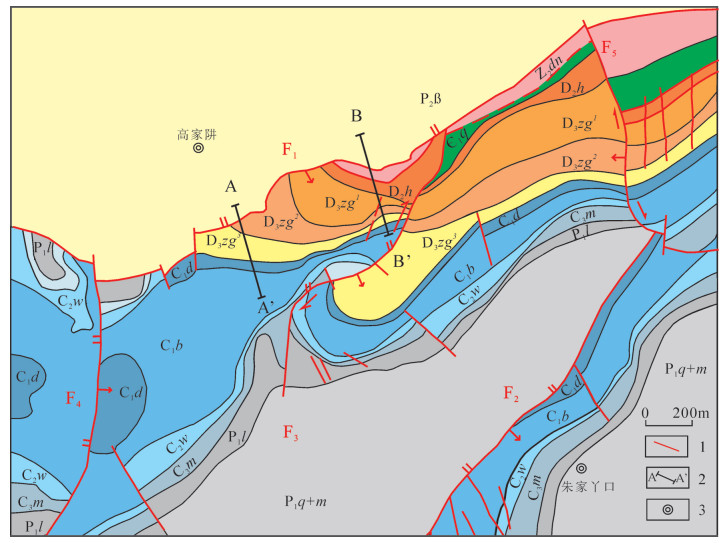
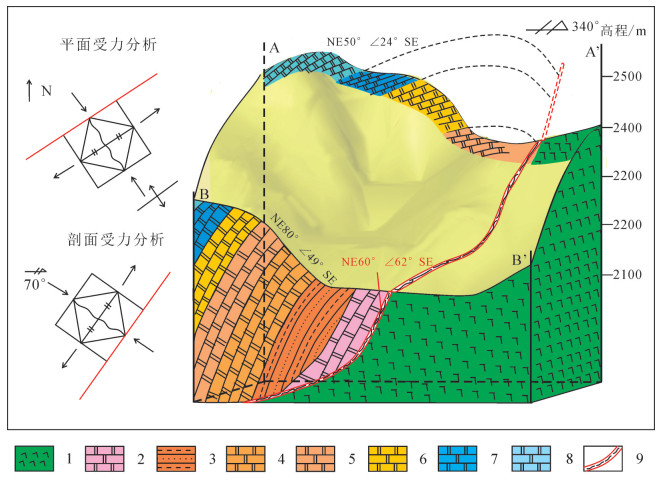
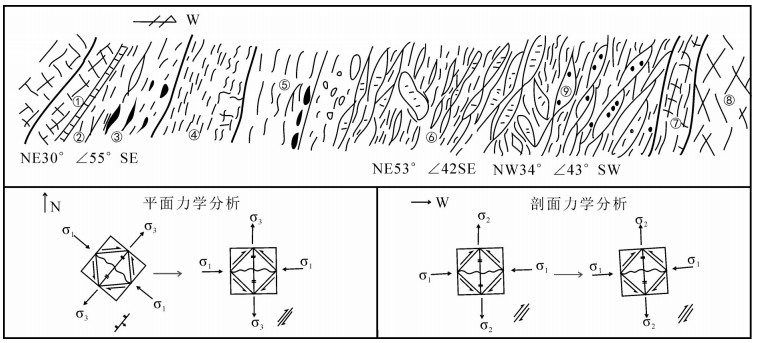
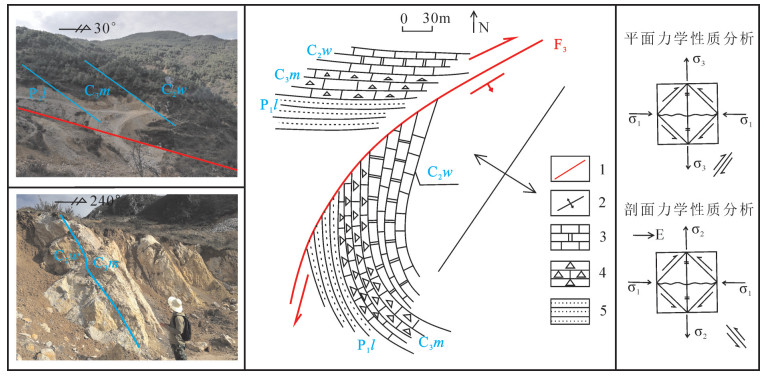
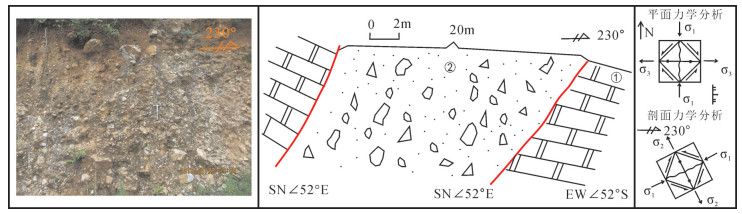
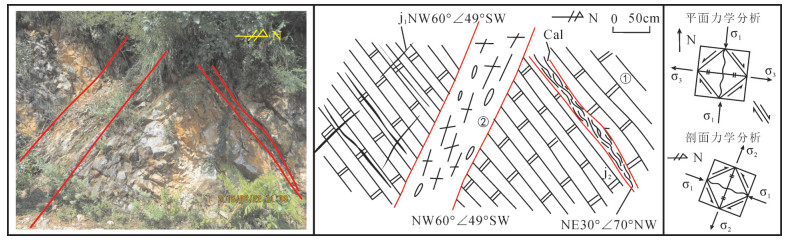
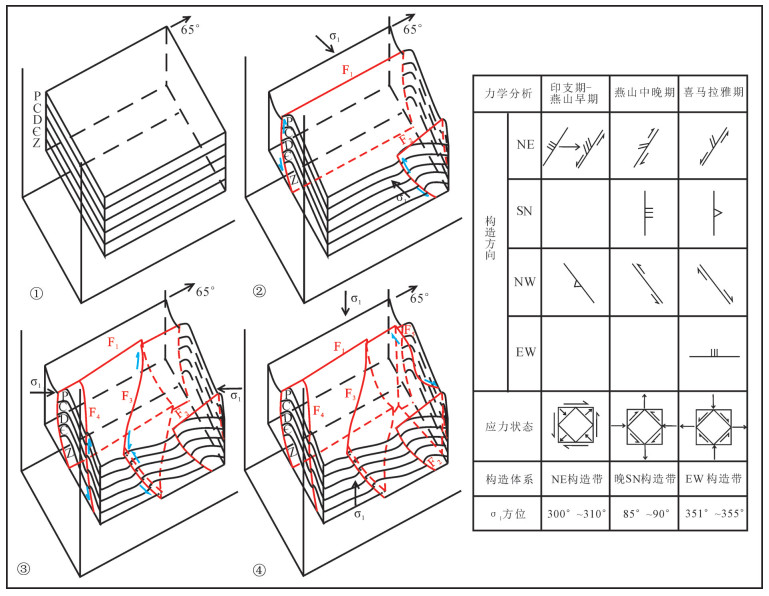
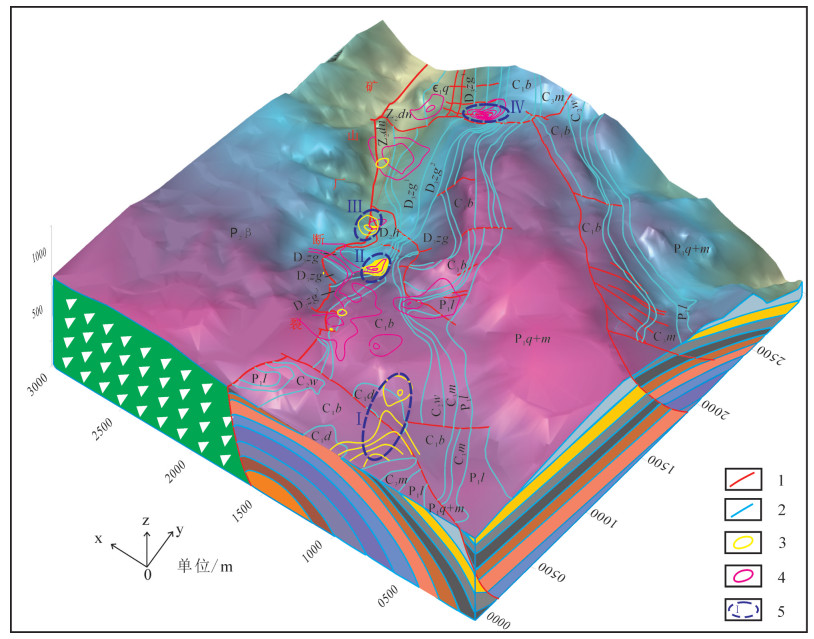
高家阱勘查区位于云南会泽铅锌矿床北东侧,是矿山厂断裂NE向延伸的有利成矿地段。在1:5000构造地质填图基础上,结合典型构造面力学性质分析,认为高家阱勘查区受NE向矿山厂背斜、矿山厂断裂控制,NE向左行压扭性层间断裂是矿体赋存的有利部位。印支晚期,在NW-SE向应力持续作用下,形成NE向牵引褶皱,构成高家阱控岩控矿构造格架——逆冲推覆构造,为成矿流体的运移提供通道。通过蚀变指数计算,提取肉红色粗晶白云岩、米黄色粗晶白云岩、灰白色粗晶白云岩蚀变信息,划定3个强蚀变地段。通过构造地球化学因子分析,绘制Pb-Zn-Cd-Ag、As-Sb-Hg元素组合异常图,提取异常信息并圈定4个主要异常区。除石炭系外,异常还分布在震旦系、泥盆系,具多层位找矿潜力。综合控矿构造-矿化蚀变-构造地球化学勘查技术组合,提出找矿方向。
Abstract:Located in the northeast of the Huize lead-zinc deposit, the Gaojiajing exploration area is a favorable ore-forming area located on the northeast side of the Kuangshanchang faults. On the basis of the 1:5000 structure geological mapping, the authors studied and summarized the structural styles based on an analysis of the mechanical properties of typical structural surfaces, and consider that the Gaojiajing exploration area is controlled by the thrust-fold structures, NE-trending left-slip compression torsion interlayer faults and NW-trending transtensional faults and is the favorable place in search for ore bodies. In late Indosinian period, Permian-Sinian strata were reversed and the NE-trending drag fold was formed under the action of the NE-striking stress. These factors constituted the tectonic framework of the Gaojiajing exploration area and provided passage and storing space for the flowing metallogenic fluids. The authors extracted alteration information by calculating chemical index of alteration, and delineated three strongly altered places. The authors extracted the combined anomalies of Pb-Zn-Cd-Ag and As-Sb-Hg by using factor analysis method, and delineated four anomaly areas. The abnormal distribution which reflects the "multi-layer" mineral exploration potential was found in Sinian, Devonian and Carboniferous strata. The ore-prospecting direction and the prospecting target are proposed by synthesizing the exploration technology of ore-control structure, mineralized alteration and tectono-geochemistry.
-

-
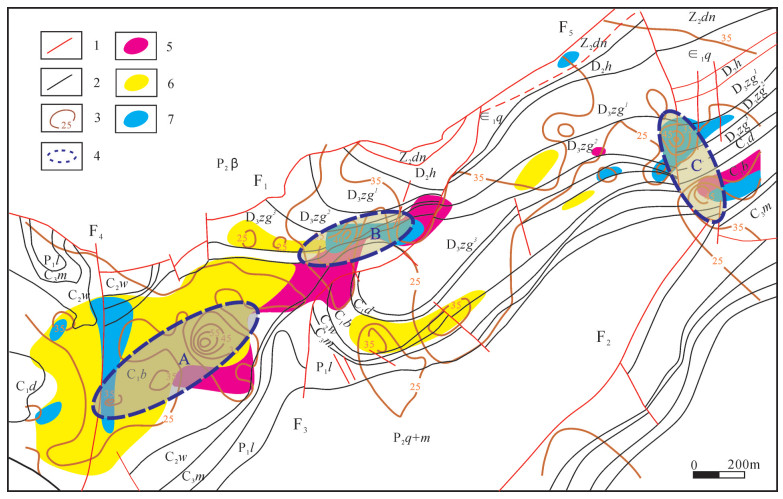
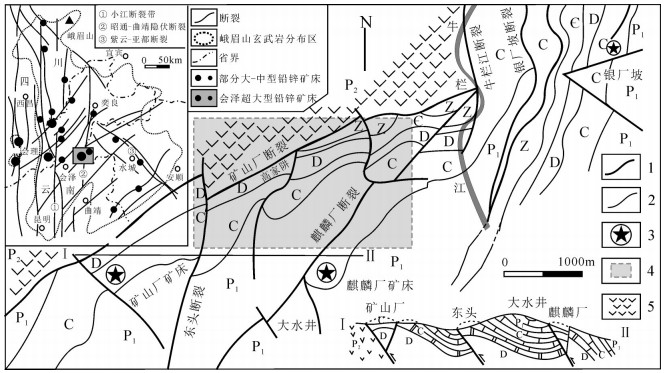
图 1 会泽铅锌矿区地质简图[27]
Figure 1.
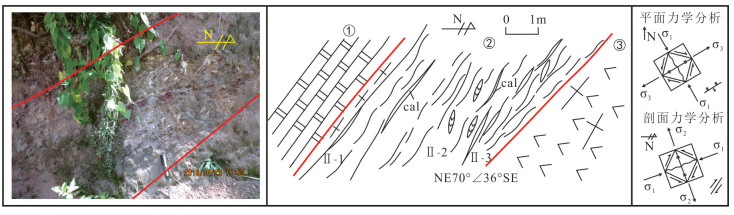
图 5 HQ2麒麟厂斜冲断裂带剖面素描图[41]
Figure 5.
表 1 高家阱勘查区构造地球化学R型因子分析方差极大旋转载荷矩阵
Table 1. Varimax rotation factor load matrix for tectonites of the Gaojiajing exploration area
元素 Factor 1 Factor 2 Factor 3 Factor 4 Factor 5 Factor 6 Al2O3 0.84 -0.06 0.27 0.02 0.20 0.01 TFe2O3 0.79 0.01 0.34 0.02 0.28 0.29 MgO -0.24 0.03 0.08 0.55 0.05 0.42 CaO -0.79 0.05 -0.10 -0.31 0.07 -0.01 Na2O 0.30 -0.13 0.67 -0.23 0.02 0.24 K2O 0.78 -0.08 0.36 0.05 0.18 -0.12 MnO 0.06 0.19 0.03 -0.03 0.04 0.74 P2O5 0.61 0.04 0.02 0.17 -0.06 0.58 TiO2 0.92 -0.03 0.28 -0.14 0.05 0.08 Ba 0.33 -0.15 0.74 -0.02 0.18 0.07 Sr -0.13 -0.02 0.16 -0.81 0.02 0.10 Cu 0.62 -0.01 0.34 -0.30 0.16 0.23 Zn 0.09 0.78 0.34 -0.01 0.10 0.22 Cr 0.69 -0.07 0.44 -0.18 0.33 -0.09 Co 0.73 -0.01 0.52 -0.19 -0.01 0.17 Ni 0.50 0.04 0.61 -0.24 0.17 0.06 V 0.63 -0.03 0.62 -0.12 0.22 0.14 Li 0.83 -0.03 0.39 0.09 0.10 -0.07 Be 0.58 0.02 0.64 0.05 -0.10 -0.13 Sc 0.78 0.03 0.52 -0.08 -0.11 -0.05 Ga 0.78 0.05 0.56 -0.05 -0.08 -0.05 Ge 0.89 0.01 0.12 0.04 0.20 0.15 Rb 0.81 0.02 0.43 0.12 0.11 -0.21 Zr 0.93 0.05 -0.21 0.07 -0.07 0.06 Nb 0.76 -0.02 0.54 0.01 -0.14 0.03 Mo 0.64 -0.10 0.37 0.16 0.34 0.07 Ag -0.01 0.52 -0.02 0.07 0.06 0.06 Cd -0.31 0.72 -0.18 -0.22 -0.01 -0.05 In 0.32 0.19 0.58 0.05 -0.32 -0.09 Sn 0.23 0.14 0.58 0.14 -0.49 -0.22 Cs 0.63 0.00 0.55 0.12 0.00 -0.38 Hf 0.93 -0.01 0.27 -0.05 0.02 0.01 Ta 0.78 -0.07 0.36 0.00 0.04 0.00 W 0.44 -0.09 0.39 0.00 0.27 -0.11 Tl 0.71 0.06 0.38 0.23 0.12 -0.31 Pb -0.01 0.82 -0.16 0.09 0.16 0.05 Bi 0.45 0.00 0.27 0.09 0.15 -0.36 Th 0.77 -0.01 0.49 0.06 0.09 -0.24 U 0.77 -0.15 0.42 0.00 0.25 -0.07 As 0.34 0.27 0.08 0.18 0.66 0.02 Sb 0.05 0.17 -0.05 -0.06 0.75 0.01 Hg 0.16 0.42 0.10 -0.04 0.47 -0.11 ΣLREE 0.85 -0.02 0.34 -0.26 0.06 -0.05 ΣHREE 0.87 0.19 0.10 -0.27 -0.01 0.03 解释方差 17.47 2.59 6.88 1.81 2.42 2.03 总百分比 0.40 0.06 0.16 0.04 0.06 0.05 -
[1] 张位及.试论滇东北铅锌矿床的沉积成因和成矿规律[J].地质与勘探, 1984, (7):13-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKT198407002.htm
[2] 陈士杰.黔西滇东北铅锌矿成因探讨[J].贵州地质, 1986, (3):3-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfd1986-gzdz198603000.htm
[3] 柳贺昌.滇、川、黔铅锌成矿区的构造控矿[J].云南地质, 1995, (3):173-189. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500584750
[4] 刘文周, 徐新煌.论川滇黔铅锌成矿带矿床与构造的关系[J].成都理工大学学报(自科版), 1996, (1):71-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600193278
[5] 韩润生, 刘丛强.云南会泽铅锌矿床构造控矿及断裂构造岩稀土元素组成特征[J].矿物岩石, 2000, 20(4):11-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys200004003
[6] 周云满.乐马厂银矿逆冲推覆构造特征及控矿作用.矿床地质, 2001, 20(3):271-278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200103011
[7] Han R S, Liu C Q, Huang Z L, et al. Geological features and origin of the Huize carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-(Ag) District, Yunnan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1):360-383. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.oregeorev.2006.03.003/
[8] 韩润生, 刘从强, 马德云, 等.铜石矿田陈家坝地区断裂构造地球化学特征及定位预测[J].地质与勘探, 2000, 36(5):66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2000.05.018
[9] 韩润生, 陈进, 李元, 等.云南会泽麒麟厂铅锌矿床构造地球化学及定位预测[J].矿物学报, 2001, 21(4):667-673. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb200104017
[10] 韩润生.隐伏矿定位预测的矿田(床)构造地球化学方法[J].地质通报, 2005, 24(10):978-984. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2005010192&flag=1
[11] 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 等.会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4):758-771. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201404003
[12] 韩润生, 吴鹏, 王峰, 等.论热液矿床深部大比例尺"四步式"找矿方法——以川滇黔接壤区毛坪富锗铅锌矿为例[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(2):246-257. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90781X/201902/7001807423.html
[13] 韩润生, 张艳, 王峰, 等.滇东北矿集区富锗铅锌矿床成矿机制与隐伏矿定位预测[M].北京:科学出版社, 2017.
[14] 陈国达, 黄瑞华.关于构造地球化学的几个问题[J].大地构造与成矿学, 1984, 3(1):3-4. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001900776
[15] 孙岩, 戴春森.论构造地球化学研究[J].地球科学进展, 1993, 8(3):1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201702006
[16] 孙家骢, 江祝伟, 雷跃时.个旧矿区马拉格矿田构造-地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 1987, (4):303-311. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/58252
[17] 钱建平.构造地球化学浅议[J].地质地球化学, 1999, 27(3):94-101. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900079530
[18] 吴鹏, 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 等.云南楚雄红层盆地六苴砂岩铜矿区断裂的地质特征及其与成矿的关系[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(5):618-625. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200805005
[19] 戢兴忠, 陈懋弘, 刘旭, 等.构造-蚀变填图在贵州泥堡金矿床的初步实践[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3):193-204. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020306&flag=1
[20] 张进, 曲军峰, 张庆龙, 等.基岩区构造地质填图方法思考、实践、探索[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3):192-221. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020302&flag=1
[21] 贾福东, 张长青, 娄德波, 等.朱乔乔云南北衙地区矿产地质专题填图方法初探[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3):254-261. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020305&flag=1
[22] 李欢, 徐国志, 孙璐, 等.化探综合异常图定量编制方法及应用[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(6):1062-1070. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190616&flag=1
[23] Han R S, Chen J, Wang F, et al.Analysis of metal-element association halos within fault zones for the exploration of concealed ore-bodies-Acase study of the Qilinchang Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposit in the Huizemine district, northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159:62-78. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.08.006
[24] 王雷, 韩润生, 黄建国, 等.云南易门凤山铜矿床59~#矿体分布区断裂构造地球化学特征及成矿预测[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(2):233-238. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201002009
[25] 吴鹏, 韩润生, 冉崇英, 等.云南易门凤山铜矿床"阶梯空当"定位矿体及其构造地球化学异常证据[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4):879-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201404013
[26] 李波, 韩润生, 文书明, 等.滇东北巧家松梁铅锌矿床构造特征及构造地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4):129-139. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201404011
[27] 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 等.滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(2):280-294. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201202007
[28] 王小春.天宝山铅锌矿床成因分析[J].成都理工大学学报(自科版), 1992, (3):10-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CDLG199203001.htm
[29] Zheng M H, Wang X C. Genesis of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Sichuan, China[J]. Economic Geology, 1991, 86(4):831-846. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.86.4.831
[30] 刘文周.茂租铅锌矿床地质特征及其成因探讨[J].矿床地质, 1998, 17(Z4):637-640. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/34078
[31] 刘文周.云南茂租铅锌矿矿床地质地球化学特征及成矿机制分析[J].成都理工大学学报(自科版), 2009, 36(5):480-486. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdlgxyxb200905004
[32] Wang X C, Zhang Z R, Zheng M H, et al. Metallogenic Mechanism of the Tianbaoshan Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2000, 19(2):121-133. doi: 10.1007/BF03166867
[33] Huang Z L, Chen J, Liu C Q, et al. A preliminary discussion on the genetic relationship between Emeishan basalt and deposits as exemplifide by Huize Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2001, 55(10):1300-1310.
[34] Huang Z L, Li W B, Chen J, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotope constraints on mantle fluidinvolvement in the mineralization of the Huize super-large Pb-Zn deposits, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 78/79(3):637-642. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c0e223c827ba42f3dcb6650bde996266&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[35] Li B, Han R S, Zou H J, et al. Tectono-geochemical Characteristics at 1260m Level in the Songliang Zn-Pb Deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta Supplement, 2008, 72(12):A540. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/252801703_Tectono-geochemical_Characteristics_at_1260m_Level_in_the_Songliang_Zn_Pb_Deposit_Yunnan_China
[36] 周家喜, 黄智龙, 高建国, 等.滇东北茂租大型铅锌矿床成矿物质来源及成矿机制[J].矿物岩石, 2012, 32(3):62-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201203009
[37] Zhou J X, Gao J G, Chen D, et al. Ore genesis of the Tianbaoshan carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Southwest China:geologic and isotopic (C-H-O-S-Pb) evidence[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(10):1300-1310. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.782973
[38] Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Yan Z F. The origin of the Maozu carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China:Constrained by C-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions and Sm-Nd isotopic age[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 73(5):39-47. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=445e689479ed5ad175d85c46796e8abf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[39] Zhou J X, Bai J H, Huang Z L, et al. Geology, isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Jinshachang carbonatehosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 98(1):272-284. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262963733_Ore_genesis_of_the_Tianbaoshan_carbonate-hosted_Pb-Zn_deposit_Southwest_China_Geologic_and_isotopic_C-H-O-S-Pb_evidence
[40] 柳贺昌, 林文达.滇东北铅锌银矿床规律研究[M].昆明:云南大学出版社, 1999.
[41] 韩润生.构造成矿动力学及隐伏矿定位预测[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006.
[42] 张乐骏, 周涛发, 袁峰, 等.热液矿床中蚀变强度的化学估计及其对找矿勘探的指示[C]//全国矿床会议, 2008: 592-593.
[43] 陈随海, 韩润生, 申屠良义, 等.滇东北矿集区昭通铅锌矿区蚀变岩分带及元素迁移特征[J].吉林大学学报(地), 2016, 46(3):711-721. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201603009
[44] Haeussinger H, Okrusch M, Scheepers D. Geochemistry of premetamorphic hydrothermal alteration of metasedimentary rocks associated with the Gorob massive sulfide prospect, Damara Orogen, Namibia[J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(1):72-90. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.1.72
[45] 文德潇, 韩润生, 吴鹏, 等.云南会泽HZT型铅锌矿床蚀变白云岩特征及岩石-地球化学找矿标志[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(1):235-245. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201401019
-



 下载:
下载: