Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and geological signifi-cance of high Nb-Ta acid volcanic rocks from Meisu Formation, Bieruo-Zecuo area, Gangdise belt
-
摘要:
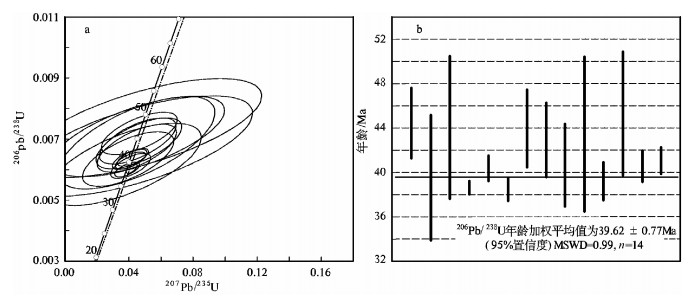
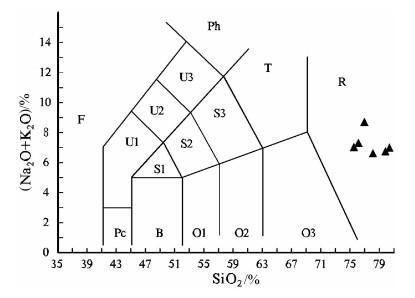
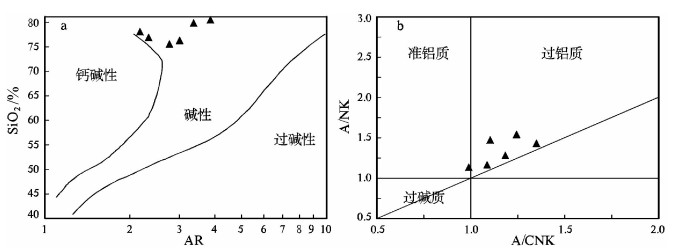
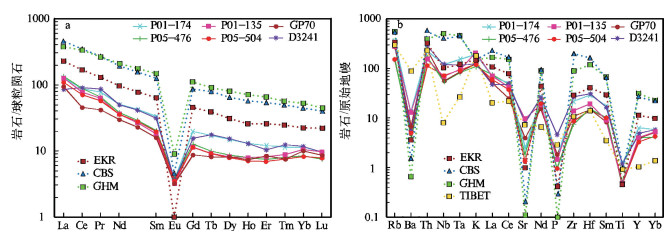
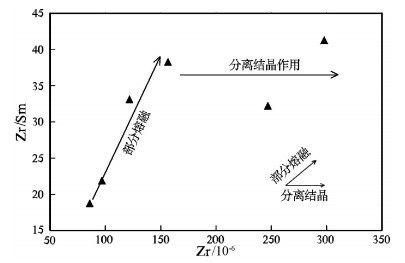
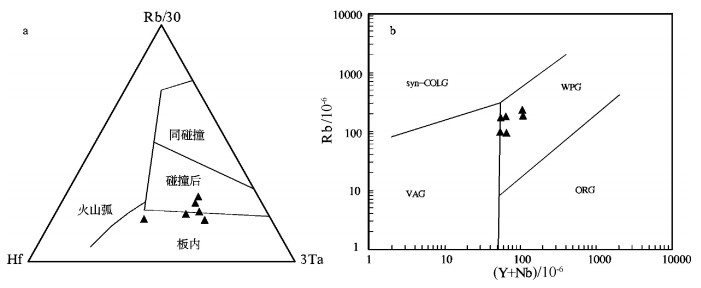
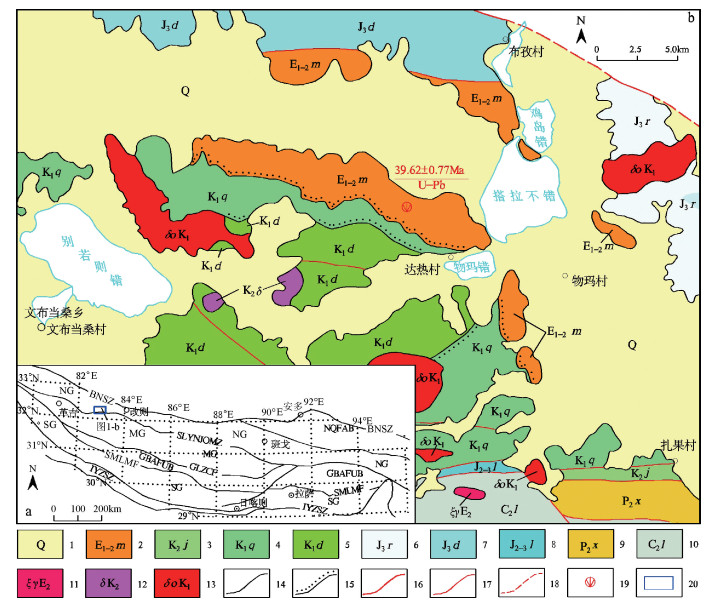
别若则错地区美苏组构造上处于北冈底斯南缘,其中流纹岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石206Pb/238U年龄为39.62±0.77Ma,时代为晚始新世。岩石具高SiO2(72.85%~78.54%)、富碱(Alk=6.36%~8.47%)、贫CaO(0.33%~1.56%)和MgO(0.08%~0.58%)特征,A/CNK=0.99~1.35,属于弱铝质-过铝质碱性系列。稀土元素总量为122.52×10-6~208.35×10-6,(La/Yb)N值为7.27~16.11,δEu=0.13~0.26,在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布模式上表现为Eu的右倾V字形。微量元素Nb(38.1×10-6~88.7×10-6)、Ta(3.36×10-6~6.35×10-6)高,Rb、K、Th、Ce、Zr、Hf相对富集,Ba、Sr、P、Ti强烈亏损。岩石地球化学特征表明,别若则错地区美苏组酸性火山岩“集壳幔特性于一身”,是初始熔体为富碱和富Nb、Ta的幔源玄武质岩浆与壳源岩浆以某一特定比例混合/混染的产物。初步认为,美苏组酸性火山岩产出于大陆板内伸展(裂谷)环境,其地球动力学背景与南侧新特提斯洋壳向北俯冲,导致高原内部的陆内俯冲、走滑剪切与地壳缩短有关。
Abstract:Meisu Formation in Bieruo-Zecuo area is tectonically located on the south margin of north Gangdise belt. LA-ICP-MS zircon 206Pb/238U dating shows that rhyolite from Meisu Formation has an age of 39.62±0.77Ma (n=14, MSWD=0.99), corresponding to Late Eocene. Geochemistry shows that the rhyolite belongs to weakly aluminous to peraluminous alkaline series (A/CNK=0.99~1.35) with characteristics of high SiO2 (72.85%~78.54%), high alkali (Alk=6.36%~8.47%), low CaO (0.33%~1.56%) and low MgO (0.08%~0.58%). The chondrite-normalized REE patterns are characterized by the significant enrichment of LREE (LaN/YbN=7.27~16.11) and strong negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.13~0.26) with total REE content of 122.52×10-6~208.35×10-6. The primitive man-tle-normalized trace element spider diagram shows high content of Nb (38.1×10-6~88.7×10-6) and Ta (3.36×10-6~6.35×10-6), rela-tive enrichment of Rb, K, Th, Ce, Zr and Hf and strong depletion of Ba, Sr, P and Ti. These geochemical characteristics show that the Meisu rhyolite is the product of mixing/contamination by a specific proportion of alkali-rich, Nb-Ta enriched, mantle-derived basaltic magma and crust-derived magma. The authors hold that the Meisu rhyolite was formed in an intraplate extension environ-ment (rift). Geodynamically, the formation of those rocks was associated with the on-plateau intracontinental subduction, strike-slip shear, and crust shortening triggered by northward subduction of Tethys Oceanic crust on the southern side.
-
Key words:
- Gangdise belt /
- Bieruo-Zecuo area /
- Meisu Formation /
- high Nb-Ta /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating /
- geochemistry
-

-
图 4 美苏组酸性火山岩TAS分类图解[11]
Figure 4.
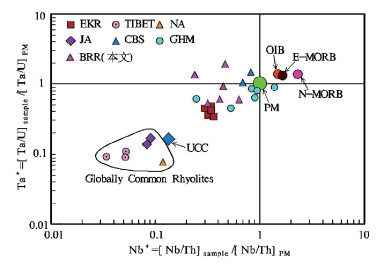
图 7 Nb*-Ta*异常图(除BRR数据外,底图及其他数据均据参考文献[10])
Figure 7.
表 1 美苏组流纹岩(P01(179))LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analyses of Meisu Formation rhyolite (P01(179))
测点 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 206Pb/38U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 1 0.00649 0.00016 0.09509 0.0067 0.10627 0.00837 0.00249 0.00007 41.7 1.0 92.2 6.2 50.3 1.4 2 0.00705 0.00016 0.14056 0.00768 0.14458 0.00930 0.00368 0.00011 45.3 1.0 133.5 6.8 74.3 2.2 3 0.00693 0.00050 0.04572 0.01574 0.04783 0.01684 0.00286 0.00028 44.5 3.2 45.4 15.3 57.7 5.7 4 0.00616 0.00089 0.03751 0.03158 0.04416 0.03769 0.00161 0.00039 39.6 5.7 37.4 30.9 32.4 7.9 5 0.01257 0.00071 0.83390 0.06569 0.48128 0.04763 0.01336 0.00065 80.5 4.5 615.8 36.4 268.2 12.9 6 0.00687 0.00100 0.04494 0.03232 0.04747 0.03481 0.00322 0.00078 44.1 6.4 44.6 31.4 65.1 15.7 7 0.00914 0.00020 0.42774 0.01499 0.33927 0.01643 0.00857 0.00019 58.7 1.3 361.6 10.7 172.4 3.8 8 0.00602 0.00010 0.04187 0.00225 0.05043 0.00312 0.00186 0.00003 38.7 0.6 41.7 2.2 37.6 0.7 9 0.00720 0.00017 0.19359 0.00937 0.19487 0.01157 0.00470 0.00013 46.3 1.1 179.7 8.0 94.8 2.5 10 0.00629 0.00018 0.04126 0.00621 0.04754 0.00738 0.00214 0.00010 40.4 1.2 41.1 6.1 43.2 2.1 11 0.00885 0.00020 0.35398 0.01403 0.2902 0.01516 0.00866 0.00021 56.8 1.3 307.7 10.5 174.3 4.3 12 0.00599 0.00016 0.03905 0.00508 0.04727 0.00638 0.00210 0.00008 38.5 1.0 38.9 5.0 42.4 1.6 13 0.00685 0.00055 0.04638 0.01763 0.04907 0.01907 0.00271 0.00034 44.0 3.5 46 17.1 54.8 6.9 14 0.00669 0.00052 0.04518 0.01635 0.04896 0.01814 0.00185 0.00024 43.0 3.3 44.9 15.9 37.3 4.8 15 0.00633 0.00059 0.03968 0.01884 0.04543 0.02198 0.00245 0.00042 40.7 3.8 39.5 18.4 49.4 8.5 16 0.00676 0.00109 0.04464 0.04805 0.04787 0.05206 0.00224 0.00056 43.5 7.0 44.3 46.7 45.3 11.3 17 0.00611 0.00027 0.04128 0.00827 0.04898 0.01012 0.00197 0.00010 39.3 1.7 41.1 8.1 39.8 2.1 18 0.00787 0.00111 0.13800 0.05582 0.12715 0.05431 0.00265 0.00054 50.5 7.1 131.3 49.8 53.5 10.8 19 0.00707 0.00087 0.04625 0.03535 0.04744 0.03672 0.00286 0.00059 45.4 5.6 45.9 34.3 57.8 11.9 20 0.00632 0.00022 0.04044 0.00711 0.04640 0.00840 0.00210 0.00014 40.6 1.4 40.3 6.9 42.5 2.9 21 0.00639 0.00019 0.04269 0.00639 0.04842 0.00748 0.00223 0.00012 41.1 1.2 42.4 6.2 45 2.4 22 0.01918 0.00072 1.48434 0.07226 0.56111 0.0364 0.02164 0.00066 122.5 4.6 924 29.5 432.8 13.2 23 0.00719 0.00046 0.04674 0.01563 0.04711 0.01607 0.00305 0.00035 46.2 2.9 46.4 15.2 61.5 7.0 24 0.00735 0.00107 0.04872 0.04896 0.04808 0.04881 0.00356 0.00058 47.2 6.9 48.3 47.4 71.9 11.7 表 2 美苏组酸性火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2. Major, trace elements and REE analyses of acid volcanic rocks from Meisu Formation
样品 流纹岩 流纹质凝灰岩 P01(174) D3241☆ P05(504) P01(135) GP70☆ P05(476) SiO2 72.85 74.04 78.54 74.82 75.60 77.48 Al2O3 12.39 14.25 10.76 12.03 12.83 11.34 Fe2O3 1.23 1.42 0.69 0.67 0.37 0.55 FeO 0.16 0.54 0.10 0.10 0.44 0.09 CaO 1.56 0.33 0.37 0.86 1.09 0.40 MgO 0.22 0.55 0.31 0.20 0.08 0.58 K2O 5.47 2.25 3.56 5.87 3.77 3.33 Na2O 1.52 4.59 3.28 2.60 2.59 3.19 TiO2 0.25 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.11 P2O5 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.02 MnO 0.09 0.02 0.02 0.11 0.03 0.09 灼失 4.15 1.20 2.22 2.53 2.31 2.79 H2O+ 2.46 0.92 1.78 1.85 1.72 2.16 H2O- 0.44 0.12 0.73 1.16 0.18 1.31 CO2 1.67 ― 0.19 0.71 - 0.68 总和 99.92 99.32 99.97 99.92 99.25 99.97 AR 3.01 2.77 3.87 2.35 2.19 3.38 NK/A 0.68 0.70 0.86 0.88 0.65 0.78 A/CNK 1.10 1.35 1.08 0.99 1.24 1.18 Cr 4.29 11.00 5.72 4.96 1.00 5.32 Ni 2.26 16.00 2.72 1.56 13.4 2.44 Co 3.67 4.80 8.34 3.78 1.00 6.36 Rb 228 185 94.2 176 174 98 Cs 5.05 5.00 21.60 7.76 8.50 15.90 W 44.5 1.8 82.1 35.8 2.2 55.5 Sr 51.6 170 28.8 203 84.4 38 Ba 94.8 38 35.1 90.1 48.2 28.1 V 8.18 4.4 5.01 4.21 1.36 8.41 Nb 80.7 88.7 51.0 48.1 40.0 38.1 Ta 6.35 4.97 3.36 3.96 3.54 3.54 Zr 247 298 97.2 156 122 85.4 Hf 8.96 9.40 4.38 5.84 4.71 4.66 U 1.69 4.18 2.91 2.20 1.34 3.39 Th 20.5 25.7 9.86 13.1 20.4 14.4 La 47.9 32.0 41.4 47.8 35.4 51.6 Ce 84.6 88.0 68.0 74.9 43.9 86.6 Pr 10.60 12.00 7.96 8.51 5.80 8.96 Nd 36.4 36.0 25.6 25.3 21.2 27.2 Sm 7.70 7.20 4.43 4.08 3.68 4.59 Eu 0.31 0.32 0.3 0.27 0.28 0.34 Gd 6.19 4.80 3.53 3.46 2.74 3.97 Tb 0.98 1.00 0.51 0.51 0.46 0.56 Dy 5.83 6.00 3.04 3.11 3.14 3.32 Ho 1.13 1.10 0.61 0.67 0.64 0.68 Er 2.99 2.6 1.74 2.02 2.16 1.89 Tm 0.45 0.50 0.30 0.35 0.30 0.31 Yb 2.90 2.90 2.07 2.56 2.49 2.11 Lu 0.37 0.37 0.30 0.37 0.33 0.29 Y 27.7 22.0 15.2 17.9 17.6 17.7 ∑REE 208.35 194.79 159.79 173.91 122.52 192.42 δEu 0.13 0.16 0.23 0.22 0.26 0.24 (La/Yb)N 10.88 7.27 13.17 12.3 9.37 16.11 注:☆样品据参考文献①;AR=(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O+K2O)/(Al2O3+CaO-Na2O-K2O);NK/A=(Na2O+K2O)/Al2O3(摩尔比); A/CNK=Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O)(摩尔比);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 -
[1] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯带侏罗纪岩浆作用的时空分布及构造环境[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(4):458-468. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080403&flag=1
[2] 鲍春辉, 丁枫, 王乾, 等.西藏措勤县雄玛地区始新统林子宗群帕那组火山地球化学特征及构造背景[J].地质论评, 2014, 60(2):275-284.
[3] 王立全, 潘桂棠, 丁俊, 等.青藏高原及邻区地质图及说明书(1:500000)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013.
[4] 谢国刚, 廖思平, 罗小川, 等.西藏尼玛地区古近纪美苏组的建立[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(5):341-345. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030564&flag=1
[5] 谢国刚, 邹爱建, 袁建芽, 等.邦多区幅、措麦区幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(5/6):498-505. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040589&flag=1
[6] 西藏自治区地质矿产局.西藏自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1997.
[7] Ludwig K R. Isoplot 2.49:A Geochronnlogical Toolkit forMicro-soft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center:Special Publication, 2001:1-58.
[8] Gunnarsson B, Marsh B D, Taylor J H P. Generation of Icrlandic rhyolites:Silicic lavas from the Torfajo Kull central volcano[J]. Jour-nal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1998, 83:1-45. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(98)00017-1
[9] Thy P, Beard J S, Lofgren G E. Experimental constraints on the ori-gin of Icelandic rhyolites[J].The Journal of Geology, 1990, 98:417-421. doi: 10.1086/629413
[10] 丁烁, 黄慧, 牛耀龄, 等.东昆仑高Nb-Ta流纹岩的年代学、地球化学及成因[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(12):3603-3614. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB201112009.htm
[11] Rollison H R (著), 杨学明(等译). 岩石地球化学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2000.
[12] 周刚.新疆吉木乃县阔依塔斯花岗岩的地球化学及构造意义[J].新疆地质, 1999, 17(2):179-187. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98491X/200601/21099720.html
[13] 庞振甲, 李永军, 赵玉梅, 等.西准阿克巴斯陶铝质A型花岗岩厘定及意义[J].新疆地质, 2010, 28(2):119-124. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200504001088.htm
[14] 何峻岭, 廖群安, 刘跃飞, 等.哈密头苏泉哈尔欣巴A型花岗岩厘定[J].新疆地质, 2013, 31(2):124-128.
[15] Middlemost E A K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks:An Introduction to Igneous Petrology[M]. London:Longman, 1986:1-26.
[16] Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3):605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
[17] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G.Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Joumal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[18] Pearce J A. The role of sub-continental lithosphere in magma gene-sis at destructive plate margins[C]//Hawkesworth et al. Continental Basalts Mantle Xenoliths. Nantwich, Shiva, 1983: 230-249.
[19] 赖绍聪, 张国伟, 秦江锋, 等.青藏高原东北缘伯阳地区第三系流纹岩地球化学及岩石成因[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):212-220. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX201501004.htm
[20] Wilson M. Igneous petrogenesis[M].London:Unwin Hyman Press, 1989:295-323.
[21] 王立强, 唐菊兴, 王登红, 等.西藏墨竹工卡县帮浦泪(铜)矿床辉钼矿稀土-微量元素特征及对成矿流体性质的指示[J].地质论评, 58(5):887-892.
[22] Masuda A, Nakamura N, Tanaka T. Fine structures of mutually normalized rare-earth patterns of chondrites[J].Geochimica et Cos-mochimica Acta, 1973, 37(2):239-248. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90131-2
[23] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Saunders A D, Norry M J. Geo-logical Society, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[24] 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 高永丰, 等.印度大陆与亚洲大陆早期碰撞过程与动力学模型——来自西藏冈底斯新生代火成岩证据[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(9):1233-1248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609001.htm
[25] 鲍春辉, 丁枫, 王乾, 等.西藏措勤县雄玛地区始新统林子宗群帕那组火山岩地球化学特征及构造背景[J].地质论评, 2014, 60(2):275-284.
[26] Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The geochemical evolution of the con-tinental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2):241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[27] Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geo-chim Cosmochim Acta, 1995, 59:1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
[28] Barth M G, McDonough W F, Rudnick R L.Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 165(3):197-213.
[29] Pfander J A, Muinker C, Stracke A, et al. Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf in ocean island basalts-implications for crust-mantle differentiation and the fate of Niobium[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254(1):158-172.
[30] Green T H.Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3):347-359.
[31] Flower M F J, Tamaki K, Hoang N. Mantle Extrusion, A model for Dispersed Volcanism and DUPAL-like Asthenosphere in East Asia and the Western Pacific[M].Washington:American Geophysi-cal Union, 1998:67-88.
[32] Mo X X, Zhao Z D, Zhou S, et al. Evidencefortiming of the initia-tion of India-Asia collision from igneous rocks in Tibet[J]. EOS Transactions, American Geophysical Union, Fall meeting abstract, 2002, 83(47):s628-1201.
[33] Wan X, Jansa L F, Sarti M.Cretaceous and Tertiary boundary stra-ta in southern Tibet and their implication for India-Asia colli-sion[J]. Lethaia, 2002, 35(2):131-146. doi: 10.1080/002411602320183999
[34] Ding L, Paul K, Zhong D, et al. Evidence for a transition from oce-anic to eontinental subduction:Cenozoic Volcanism in Tibet[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(10):1833-1865. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egg061
[35] 李再会, 郑来林, 李军敏, 等.冈底斯中段林子宗火山岩40Ar-39Ar年龄及其意义[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(3):223-227.
[36] 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 杨志明, 等.青藏高原碰撞造山带成矿作用:构造背景、时空分布和主要类型[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(2):348-359. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200602013.htm
[37] Harris N B W, Pearce J A, Tindle A G.geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society London Spe-cial Publications, 1986, 19(5):67-81.
① 四川省地质调查院. 1: 25万物玛幅区域地质调查报告. 2005.
② 西藏自治区地质局区域地质调查大队. 1: 100万区域地质调查报告(日喀则幅H-45、亚东幅G-45). 1983.
③ 石油勘探开发局科学研究院遥感地质研究所.西藏措勤盆地它日错深凹陷区域石油地质调查报告.1998.
④ 甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院1: 5万撞多勒幅、物玛乡幅、扎琼幅、本庆错幅地质矿产调查报告. 2015.
⑤ 西藏自治区地质局. 1: 100万日土幅区域地质调查报告. 1979.
-



 下载:
下载: