The discovery of Longyasongduo eclogite from Gongbujiangda County, Tibet, and its significance
-
摘要:
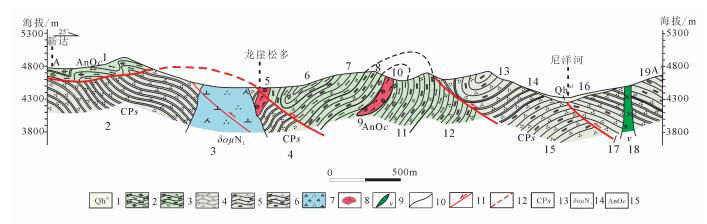
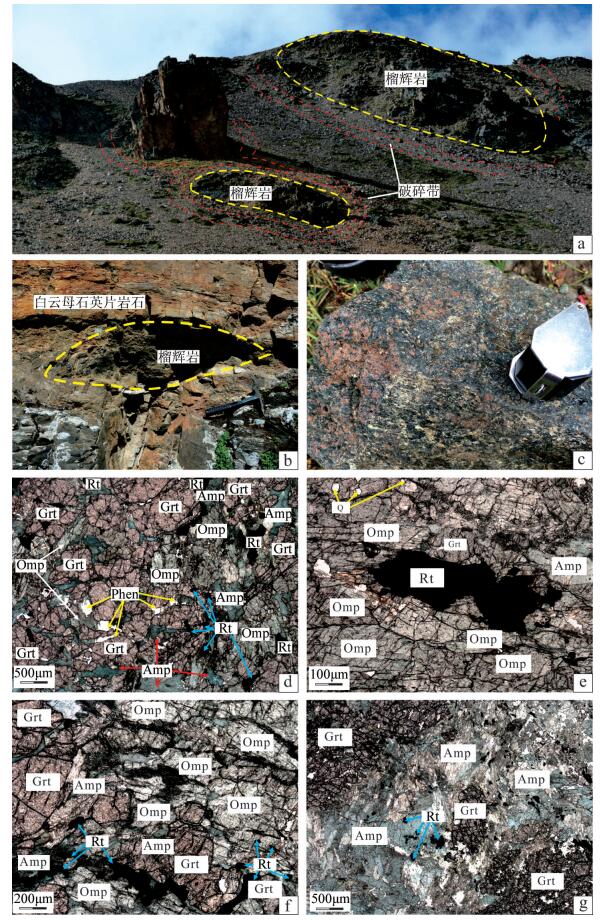
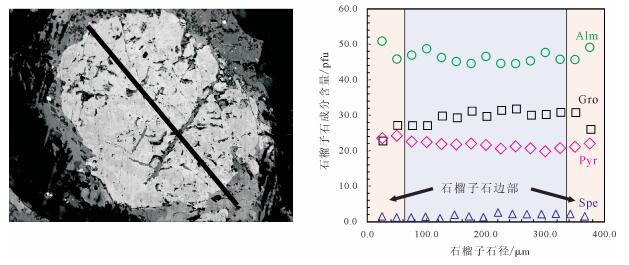
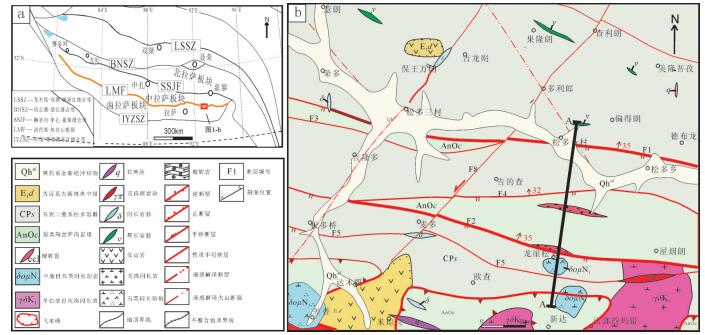
唐加-松多榴辉岩高压变质带位于冈底斯板块中部,对研究古特提斯构造演化具有至关重要的意义,但是榴辉岩的出露范围和规模尚不清楚。在龙崖松多地区新发现榴辉岩的出露点,通过详细的野外地质调查、岩石学及矿物学研究,发现其岩性为金红石榴辉岩和石英榴辉岩,以透镜体的形式产出,围岩以低绿片岩相岩石为主,少部分为石英白云母片岩。龙崖松多榴辉岩的主要矿物组合为石榴子石、绿辉石、多硅白云母、角闪石、金红石、石英及少量榍石、钛铁矿等,石榴子石的电子探针分析结果显示,从核部到边部,镁铝榴石和铁铝榴石含量逐渐增加,锰铝榴石含量显著减少,具有典型的进变质环带特征,同时榴辉岩边部石榴子石角闪岩的发现,说明该露头的榴辉岩可能经历了后期退变质作用改造。该榴辉岩的发现对探讨唐加-松多蛇绿混杂带的构造演化具有重要意义。
Abstract:Located in the central part of Gangdise plate, the Tangjia-Sumdo eclogite-bearing metamorphic belt played an important role in the evolution of the Paleo Tethys Ocean. However, the exposed scale of eclogites is still unclear. In this study, the authors found a new site of eclogite in Longyasongdo area. The detailed field survey and petrographic and mineralogical study show that the lithology of Longyasongduo eclogite includes rutile eclogite and quartz eclogite. The eclogite is in the form of lens. The surrounding rock of Longyasongduo eclogite is mainly greenschist, with a small part being muscovite quartz schist. The general mineral assemblage of eclogite is garnet+omphagite+phengite+amphibole+rutile+quartz, with minor sphene and ilmenite. The analysis of the EMPA composition profile of the garnet shows typical growth zoning, with Xpyr and Xalm increasing from core to rim but Xspe showing a tendency of decrease. Meanwhile, according to the discovery of garnet amphibolite from the edge of eclogite, it is inferred that Longyasongduo eclogite might have undergone retrograde process. The discovery of Longyasongduo eclogite is of great importance for the study of the tectonic evolution of the Tangjia-Sumdo ophiolite belt.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- Longyasongduo /
- Gangdise plate /
- eclogite /
- petrography
-

-
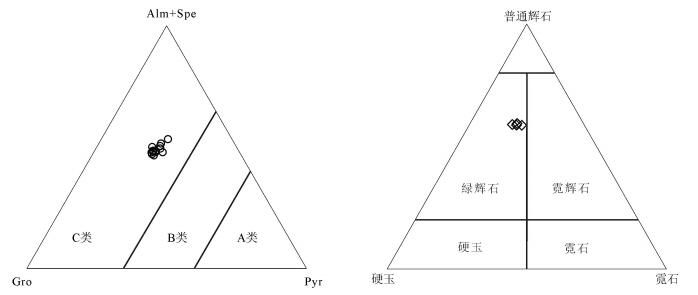
图 3 龙崖松多金红石榴辉岩石榴子石成分(分类据参考文献[18])和单斜辉石三元成分图解
Figure 3.
表 1 龙崖松多榴辉岩石榴子石(S17T3T4)剖面化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of garnet(S17T3T4)from Longyasongduo eclogite in Tibet
测试点 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 SiO2 38.962 38.291 38.711 38.518 38.568 38.49 38.103 37.873 38.327 37.762 38.54 38.029 36.691 38.47 38.078 TiO2 0.0 0.034 0.011 0.078 0.169 0.169 0.101 0.101 0.169 0.135 0.135 0.0 0.157 0.158 0.224 Al2O3 21.739 22.128 21.682 22.082 21.966 21.771 22.007 21.795 21.576 21.686 21.629 21.692 21.384 21.979 21.782 Cr2O3 0.02 0.025 0.006 0.0 0.0 0.024 0.0 0.0 0.032 0.039 0.007 0.0 0.131 0.028 0.004 FeO 24.305 22.448 22.891 23.129 22.253 21.887 21.296 22.104 20.913 20.704 21.874 22.104 20.981 21.508 23.497 MnO 0.674 0.535 0.538 0.631 0.441 0.898 0.68 0.565 1.168 0.983 0.955 0.958 0.989 0.989 0.678 MgO 6.151 6.468 5.937 5.891 5.766 5.726 5.793 5.641 5.313 5.473 5.4 5.108 5.281 5.518 5.76 CaO 8.828 10.758 10.798 10.122 11.393 11.467 11.741 11.159 11.657 11.574 11.686 10.955 11.166 11.355 10.03 Si 2.9948 2.9374 2.9752 2.9669 2.9630 2.9624 2.9498 2.9527 2.9842 2.9640 2.9744 2.9804 2.9382 2.9716 2.9523 Ti 0.0 0.0020 0.0006 0.0045 0.0098 0.0098 0.0059 0.0059 0.0099 0.0080 0.0078 0.0 0.0095 0.0092 0.0131 Al 1.9693 2.0006 1.9640 2.0046 1.9889 1.9749 2.0080 2.0026 1.9799 2.0061 1.9673 2.0036 2.0182 2.0009 1.9904 Cr 0.0012 0.0015 0.0004 0.0 0.0 0.0015 0.0 0.0 0.0020 0.0024 0.0004 0.0 0.0083 0.0017 0.0003 Fe3+ 0.0329 0.0383 0.0517 0.0144 0.0293 0.0422 0.0216 0.0249 0.0221 0.0102 0.0441 0.0095 0.0084 0.0102 0.0325 Fe2+ 1.5295 1.4019 1.4197 1.4756 1.4004 1.3666 1.3572 1.4163 1.3397 1.3489 1.3677 1.4393 1.3968 1.3793 1.4911 Mn 0.0439 0.0348 0.0350 0.0412 0.0287 0.0585 0.0446 0.0373 0.0770 0.0654 0.0624 0.0636 0.0671 0.0647 0.0445 Mg 0.7048 0.7397 0.6802 0.6765 0.6604 0.6570 0.6686 0.6556 0.6167 0.6404 0.6213 0.5968 0.6305 0.6354 0.6658 Ca 0.7270 0.8843 0.8892 0.8354 0.9378 0.9456 0.9739 0.9322 0.9725 0.9734 0.9663 0.9199 0.9581 0.9398 0.8332 Ura 0.06 0.07 0.02 0.0 0.0 0.07 0.0 0.0 0.10 0.12 0.02 0.0 0.41 0.08 0.01 And 1.64 1.88 2.57 0.71 1.45 2.09 1.06 1.23 1.10 0.50 2.19 0.47 0.41 0.50 1.60 Pyr 23.45 24.17 22.49 22.34 21.81 21.70 21.96 21.56 20.52 21.15 20.59 19.76 20.65 21.05 21.94 Spe 1.46 1.14 1.16 1.36 0.95 1.93 1.46 1.23 2.56 2.16 2.07 2.11 2.20 2.14 1.47 Gro 22.49 26.94 26.82 26.87 29.53 29.07 30.93 29.42 31.15 31.52 29.81 30.00 30.57 30.54 25.84 Alm 50.89 45.81 46.94 48.72 46.26 45.14 44.58 46.57 44.57 44.55 45.32 47.67 45.76 45.68 49.14 注:氧化物含量单位为%,其他为阳离子数 表 2 龙崖松多榴辉岩绿辉石、多硅白云母化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of omphacite and pehngite from Longyasongduo eclogite in Tibet
样品号 S17T3T1-2 S17T3T1-3 矿物名称 多硅白云母 多硅白云母 绿辉石 绿辉石 多硅白云母 多硅白云母 多硅白云母 绿辉石 SiO2 54.260 54.462 52.151 53.492 53.489 50.437 53.395 53.069 TiO2 0.081 0.116 0.186 0.116 0.151 0.266 0.081 0.046 Al2O3 27.085 25.685 7.533 7.085 25.550 30.019 6.839 6.477 Cr2O3 0.016 0.039 0.016 0.039 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.022 FeO 2.228 2.155 8.028 7.989 2.425 2.721 7.121 7.216 MnO 0.031 0.000 0.034 0.027 0.021 0.010 0.000 0.010 MgO 3.959 4.357 9.492 9.551 4.255 3.140 10.006 10.121 CaO 0.018 0.035 16.080 16.112 0.011 0.032 16.296 15.910 Na2O 0.433 0.390 6.148 5.978 0.378 0.686 6.185 6.358 K2O 8.480 8.437 0.013 0.006 8.808 8.942 0.000 0.013 Si 3.5076 3.5533 1.931 1.960 3.5282 3.3081 1.961 1.965 AlⅣ 0.4924 0.4467 0.069 0.040 0.4718 0.6919 0.039 0.035 AlⅥ 1.5711 1.5283 0.260 0.266 1.5145 1.6286 0.258 0.248 Al 2.0635 1.9750 0.000 0.000 1.9863 2.3205 0.000 0.000 Ti 0.0039 0.0057 0.005 0.003 0.0075 0.0131 0.002 0.001 Cr 0.0000 0.0000 0.000 0.001 0.0000 0.0000 0.000 0.001 Fe3+ 0.1205 0.1176 0.349 0.280 0.1338 0.1493 0.317 0.351 Mn 0.0017 0.0000 0.001 0.001 0.0012 0.0006 0.000 0.000 Mg 0.3815 0.4238 0.524 0.522 0.4184 0.3070 0.548 0.559 Ca 0.0012 0.0024 0.638 0.633 0.0008 0.0022 0.641 0.631 Na 0.0543 0.0493 0.441 0.425 0.0483 0.0872 0.441 0.456 K 0.6993 0.7022 0.0006 0.0003 0.7412 0.7482 0.000 0.001 注:氧化物含量单位为%,其他为离子数 表 3 龙崖松多榴辉岩(S17T3T1)金红石、钛铁矿化学成分
Table 3. Chemical compositions of rutile and ilmenite from Longyasongduo eclogite in Tibet
% 矿物名称 金红石 金红石 钛铁矿 钛铁矿 SiO2 0.065 0.065 0.016 0.044 TiO2 98.973 99.381 51.426 51.243 Al2O3 0.001 0.008 0.026 0.014 Cr2O3 0.031 0 0.038 0.024 FeO 0.322 0.348 44.459 44.912 MnO 0 0.003 3.051 3.249 MgO 0 0.007 0.014 0.043 CaO 0.077 0.076 0.044 0.039 K2O 0.034 0.01 0 0.013 Na2O 0.079 0.008 0.066 0.055 总量 99.582 99.906 99.14 99.636 注:单矿物化学成分分析在中国地质科学院(北京)地质与矿物资源研究所,使用的电子探针型号为JXA-8800,分析条件为放射束电流的加速电压20kV、电流20nA、探针束斑直径5μm,石榴子石中的Fe3+依照Droop[20]计算,标准辉石各端元组分计算方法根据Morimoto[21],硬玉(XJd)=AlⅥ/(Na+Ca), 霓石(XAe) = (Na-AlⅥ)/(Na+Ca),普通辉石(XAu) = (Ca+Mg+Fe2+)/2,详细分析方法步骤参照Zhai等[22] -
[1] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 张建新, 等.中国主要高压-超高压变质带的大地构造背景及俯冲/折返机制的探讨[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(7):1529-1560. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200907001
[2] Chopin C. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism; tracing continental crust into the mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 212:1-14. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00261-9
[3] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等.造山的高原——青藏高原的地体拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:1-458.
[4] 李才.龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与石炭二叠纪冈瓦纳北界[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 1987, (2):155-166. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001164867
[5] 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部榴辉岩的发现及其意义[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(1):70-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.01.014
[6] 王保弟, 王立全, 许继峰, 等.班公湖-怒江结合带洞错地区舍拉玛高压麻粒岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(9):1605-1616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.002 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150902&flag=1
[7] Dong Y L, Wang B D, Zhao W X, et al. Discovery of eclogite in the Bangong Co-Nujiang ophiolitic mélange, central Tibet, and tectonic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 35:115-123. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.010
[8] Zhang X Z, Wang Q, Dong Y S, et al. High-Pressure Granulite Facies Overprinting During the Exhumation of Eclogites in the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone, Central Tibet:Link to Flat-Slab Subduction[J]. Tectonics, 2017, 36(12):1-18. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=76a2f8887865091798d5fe1cf4d60f63&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] Zhang Y X, Li Z W, Zhu L D, et al. Newly discovered eclogites from the Bangong Meso-Tethyan suture zone (Gaize, central Tibet, western China):mineralogy, geochemistry, geochronology, and tectonic implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 58(5):574-587. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=04aa3f2fd15ec5bc4cfd266de6653f25&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] 陈松永, 杨经绥, 罗立强, 等.西藏拉萨地块MORB型榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(10):1327-1339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.011 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2007010213&flag=1
[11] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 耿全如, 等.中国境内可能存在一条新的高压/超高压(?)变质带——青藏高原拉萨地体中发现榴辉岩带[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(12):1787-1792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.001
[12] Yang J, Xu Z, Li Z, et al. Discovery of an eclogite belt in the Lhasa block, Tibet:A new border for Paleo-Tethys?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(1):76-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.04.001
[13] 陈松永.西藏拉萨地块中古特提斯缝合带的厘定[D].中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2010: 29-50.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-2011012318.htm [14] Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort J D, et al. Zircon U-Pb and garnet Lu-Hf geochronology of eclogites from the Lhasa Block, Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2012, 155(1):341-359. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0228580005
[15] Cheng H, Liu Y, Vervoort J D, et al. Combined U-Pb, Lu-Hf, Sm-Nd and Ar-Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(4):1482-1499. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.017
[16] 郭倩, 赵文霞, 陈建林, 等.西藏松多榴辉岩矿物出溶体研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1689-1696. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201205028
[17] 张丁丁, 张立飞, 赵志丹.西藏松多榴辉岩变质作用研究[J].地学前缘, 2011, 18(2):116-126. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201102010
[18] Coleman R G, Lee D E, Beatty L B, et al. Eclogi te and eclogites:Their differences and similarities[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1965, 76:483-508. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[483:EAETDA]2.0.CO;2
[19] Spear F S. On the interpretation of peak metamorphic temperature in light of garnet diffusion during cooling[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1991, 9:379-388. doi: 10.1111/jmg.1991.9.issue-4
[20] Droop G T R. A general equation for estimating 3+Fe concentrations in ferromagnesian silicates and oxides from microprobe analyses, using stoichiometric criteria[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1987, 51(361):431-435. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1987.051.361.10
[21] Morimoto N. Nomenclature of pyroxenes[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988, 39(1):55-76. doi: 10.1007/BF01226262
[22] Zhai Q G, Zhang R Y, Jahn B M, et al. Triassic eclogites from central Qiangtang, northern Tibet, China:Petrology, geochronology and metamorphic P-T, path[J]. Lithos, 2011, 125(1/2):173-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0221785090/
-



 下载:
下载: