The discovery of Thalattosauria (Reptilia:Diapsida) from the Late Triassic strata of Luxi County, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
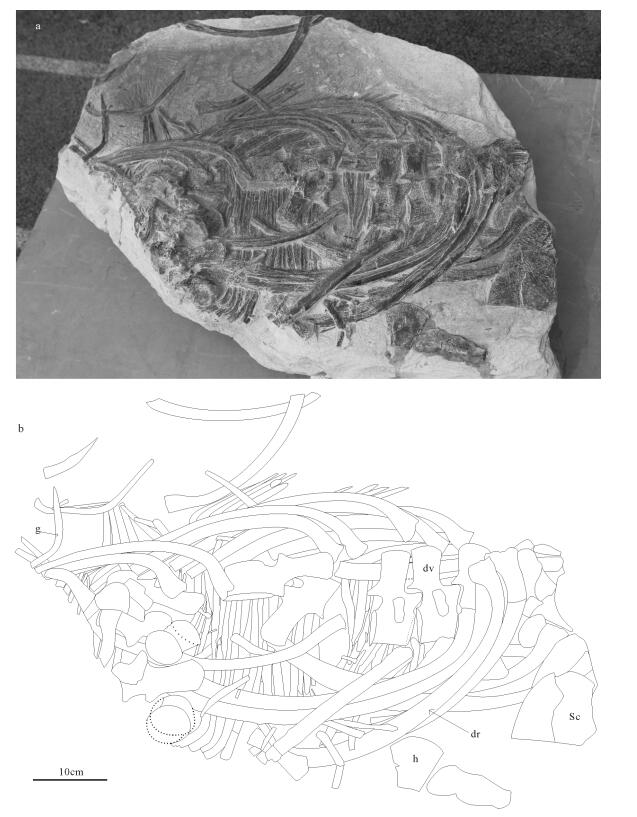
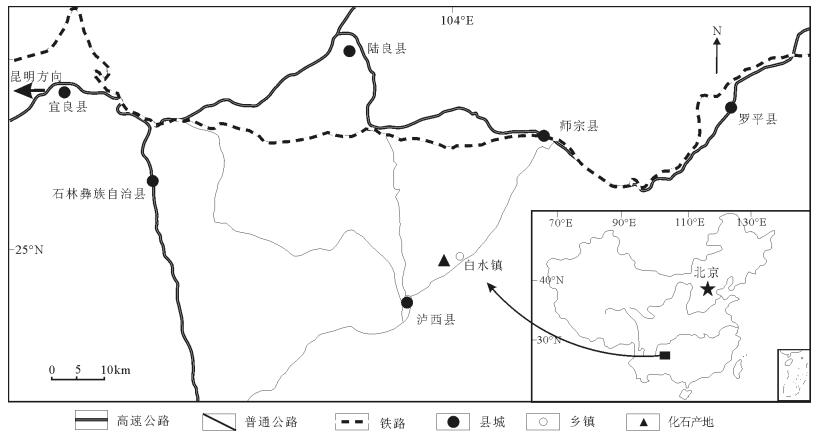
采自云南泸西县城附近小兴安村晚三叠世卡尼期小凹组的海龙化石,是关岭生物群海龙类化石在贵州关岭之外地区的首次发现。该化石标本共保存有9枚较好的背椎骨,21条完好的肋骨及若干腹肋。靠近头部的4枚背椎骨为有次序的自然排列。背椎椎体长约12cm,椎体横突发育,椎体腹侧轻微凹入,呈双凹形,近似圆形。这一特征与鱼龙类脊椎骨明显的双凹特征有所区别,故暂且将其归于海龙类。新采集的该化石标本为探讨海龙类的古地理分布,以及寻找规律生物群新化石产地提供了信息。
Abstract:This paper reposts a thalattosaur specimen collected from the Late Triassic Xiaowa Formation in Xiaoxingan Village, Luxi County, Yunnan Province.It is the first record of Thalattosauria fossil outside Guanling, Guizhou Province.The specimen consists of 9 well preserved dorsal vertebrae, 21 dorsal ribs, and several gastralia.4 dorsal vertebrae are present and arranged as a sequence of natu-ral order.The length of dorsal vertebrae is about 12cm.The transverse process is well developed.The two ends of the dorsal verte-brae are slightly biconcave, distinctly different from ichthyosauria vertebrae with obvious biconcave.The specimen is tentatively as-signed to the Thalattosauria.The new discovery provides new information for paleobiographic distribution of the Thalattosauria and the search for new fossil localities of the Guangling biota.
-
Key words:
- Thalattosauria /
- Late Triassic /
- Xiaowa Formation /
- Luxi County, Yunnan
-

-
[1] Rieppel O. Clarazia and Hescheleria: a reinvestigation of two problematical reptiles from the Middle Triassic of Monte SanGiogio(Switzerland)[J]. Palaeontographica, Abcellung A, 1987, 195: 101-129. http://www.mendeley.com/research/clarazia-hescheleria-reinvestigation-problematical-reptiles-middle-triassic-monte-san-giorgio-switzerland-4/
[2] Nicholls E L. A reexamination of Thalattosaurus and Nectosaurus and the relationships of Thalattosauria(Reptilia: Diapsida)[J]. PaleoBios, 1999, 19: 1-29. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285744853_A_reexamination_of_Thalattosaurus_and_Nectosaurus_and_the_relationships_of_the_Thalattosauria_Reptilia_Diapsida
[3] Müller J. A revision of Askeptosaurusitalicus and other thalattosaurs from the European Triassic, the interrelationships of thalattosaurs, and their phylogenetic position within diapsida reptiles(Amniota, Eureptilia) [D]. Ph. D. thesis, Johannes Gutenberg Universitat, Mainz, 2002.
[4] Müller J. The anatomy of Askeptosaurusitalicus from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio and the interrelationships of thalattosaurs (Reptilia: Diapsida)[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2005, 79 (12): 1347-1367. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Johannes_Mueller9/publication/237169287_The_anatomy_of_Askeptosaurus_italicus_from_the_Middle_Triassic_of_Monte_San_Giorgio_and_the_interrelationships_of_thalattosaurs_Reptilia_Diapsida/links/56268ed508aed3d3f1389ed6/The-anatomy-of-Askeptosaurus-italicus-from-the-Middle-Triassic-of-Monte-San-Giorgio-and-the-interrelationships-of-thalattosaurs-Reptilia-Diapsida.pdf
[5] Kuhn E. Die Triasfauna der Tessiner Kalkalpen. XVII: Askeptosaurus italicus Nosika[J]. Schweizerrische Paläontologische Abhandlungen, 1952, 69:1-73.
[6] Kuhn-Schnyder E. Über einen Schädel von Askeptosaurus italicus Nopsca aus der mittleren Trias des Monte San Giorgio (Kt. Tessin, Schweiz)[J]. Albhandlungen des Hessischen Landesamtes für Bodenforschung, 1971, 60: 89-98.
[7] Merriam J C. Notes on the osteology of the thalattosaurian genus Nectosaurus[J]. University of California Department of Geology Bulletin, 1908, 5: 217-223. http://www.worldcat.org/title/notes-on-the-osteology-of-the-thalattosaurian-genus-nectosaurus/oclc/4911129
[8] Nicholls E L, Brinkman D. New thalattosaurs (Reptilia: Diapsida) from the Triassic Sulphur Formation of Wapiti Lake, British Columbia[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 1993, 67: 263-278. doi: 10.1017/S0022336000032194
[9] Rieppel O, Liu J, Bucher H. The first record of a thalattosaur reptile from the Late Triassic of South China[J]. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 2000, 20(3): 507-514. doi: 10.1671/0272-4634(2000)020[0507:TFROAT]2.0.CO;2
[10] Liu J. New discovery of sauropterygian from Triassic of Guizhou, China[J].Chinese Sci. Bull., 1999, 13:1312-1315. http://www.academia.edu/1882074/Sauropterygian_from_Triassic_of_Guizhou_China
[11] Liu J, Rieppel O. Restudy of Anshunsaurus huangguoshuensis (Reptilia: Thalattosauria) from the Middle Triassic of Guizhou, China[J]. American Museum Novitiates, 2005, (3488): 1-34. http://www.bioone.org/doi/abs/10.1206/0003-0082(2005)488%5B0001:ROAHRT%5D2.0.CO%3B2
[12] 尹恭正, 周修高, 曹泽田, 等.贵州关岭晚三叠世早期海生爬行动物的初步研究[J].地质地球化学, 2000, 28(3): 1-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200003000.htm
[13] Liu J, Rieppel O. The second thalattosaur from the Triassic of Guizhou, China[J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2001, 39(2):77-87. http://www.academia.edu/1882094/The_second_thalattosaur_from_the_Triassic_of_Guizhou_China
[14] 程龙.贵州关岭三叠纪海龙类化石一新种[J].地质通报, 2003, 22 (4):274-277. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20030453&journal_id=gbc
[15] Jiang D Y, Maisch M W, Sun Y L, et al. A new species of Xinpusaurus (Thalattosauria) from the Upper Triassic of China[J]. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 2004, 24(1): 80-88. doi: 10.1671/1904-7
[16] Cheng Y N, Wu X C, Sato T. A new thalattosaurian (Reptilian: Diapsida) from the upper Triassic of Guizhou, China[J]. Vert Pal Asiat, 2007, 45(3): 246-260. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.517.5666&rep=rep1&type=pdf
[17] 吴肖春, 程延年, 佐藤环, 等.短吻贫齿龙(双孔亚纲:海龙目)头后骨骼及系统关系研究[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2009, 47 (1): 1-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZD200901002.htm
[18] 赵丽君, 佐藤环, 刘俊, 等.短吻贫齿龙(双孔亚纲:海龙目)的新材料及补充研究[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2010, 48 (1): 1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZD201001001.htm
[19] Zhao L J, Liu J, Li C, et al. A new thalattosaur, Concavispina biseridens gen. et sp.nov. from Guanling, Guizhou, China[J]. Vert Pal Asiat(古脊椎动物学报), 2013, 51(1):24-28. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GJZD201301006.htm
[20] Rieppel O, Liu J, Li Cn. A new species of the thalattosaur genus Anshunsaurus(Reptilia: Thalattosauria) from the Middle Triassic of Guizhou Province, Southwestern China[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2006, 44(4): 285-296. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257931593_A_new_species_of_the_Thalattosaur_genus_Anshunsaurus_Reptilia_Thalattosauria_from_the_Middle_Triassic_of_Guizhou_Province_southwestern_China
[21] 程龙, 陈孝红, 王传尚.贵州晚三叠世安顺龙(爬行纲:海龙目)一新种[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(10): 1345-1351. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.10.005
[22] Liu J. A juvenile specimen of Anshunsaurus (Reptilia: Thalattosauria)[J]. Am. Mus. Novit., 2007, (3582): 1-9 http://www.bioone.org/doi/abs/10.1206/0003-0082(2007)3582%5B1:AJSOAR%5D2.0.CO%3B2
[23] Sun Z Y, Maisch M W, Hao W C, et al. A Middle Triassic thalattosaur(Reptilia: Diapsida) from Yunnan(China) [J]. N. Jb. Geol. Paläont. Mh., 2005, 4: 193-206. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260273420_A_Middle_Triassic_thalattosaur_Reptilia_Diapsida_from_Yunnan_China
[24] 程龙, 陈孝红, 张保民, 等.云南罗平中三叠统海龙类新材料[J].中国地质大学学报(地球科学), 2010, 35(4): 507-511. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201004002.htm
[25] 刘俊.新铺龙(爬行纲:海龙目)的分类[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2013, 51(1): 17-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZD201301005.htm
[26] Jiang D Y, Motani R, Li C, et al. Guanling Biota: A marker of Triassic biotic recovery from the end-Permian extinction in the Ancient Guizhou Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(6): 729-738. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2005.79.issue-6
[27] Benton M J, Zhang Q, Hu S, et al. Exceptional vertebrate biotas from the Triassic of China, and the expansion of marine ecosystems after the end-Permian mass extinction[J]. Earth-Science reviews, 2013, 125: 199-243. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.05.014
-



 下载:
下载: