The structure-controlled geological interpretations:A consideration for special mapping of intrusive rocks
-
摘要:
火成岩及其组合的性质不仅受岩浆系统本身性质的约束,也受到成岩环境的控制。因此,火成岩分布区的地质填图应当立足于结构可控的地质解释。基于这种认识,建议侵入岩专题填图按照岩浆系统的几何尺度及其与动力系统的关系划分填图单位。一级岩浆系统受控于全球动力学系统,具有最大的几何尺度;二级岩浆系统与区域地质历史有关,是全球动力系统与岩石圈系统相互作用的产物;三级岩浆系统受控于局部动力系统,与全球动力系统没有直接联系;四级岩浆系统受控于岩浆动力系统与围岩动力系统的相互作用,通常与岩浆产量和通道条件紧密联系在一起;五级岩浆系统受控于具体的岩浆过程,通常是侵入岩区的最小填图单位。但是,岩浆系统具有可无限细分的特点,填图过程中可根据具体情况进一步划分更次级的岩浆系统。对于几何尺度小于地质图表述能力的岩浆系统,建议制作局部放大的专题地质图件,以展示特定岩浆系统的地质特征。
Abstract:The development of earth sciences and determining technologies calls for adopting new methods in regional geological mapping. Recently, it has been recognized that the magmatic system is complex, which implies that the features of igneous rocks and their assemblages are controlled not only by the magmatic system itself but also by the rock-forming environments. Therefore, the mapping of igneous rocks should be based on the structure-controlled geological interpretations. Accordingly, the authors propose that the mapping units division should be based on the relationship between geometric scale and dynamic system in special mapping of intrusive rocks. The first grade of magmatic system is controlled by the global dynamic system, and has the maximum scale. The second grade is related to the regional geological history, and results from the interaction between the global dynamic system and the regional lithosphere system. The third grade is controlled by the local dynamic systems such as lithosphere delimination, and is not related to the global dynamic system. The fourth grade is controlled by interaction between the magmatic system and wall rock dynamic system, which is commonly related to the magma production and the conduit conditions. The fifth grade may be the minimum mapping unit in the area of intrusive rocks, and its features are decided by the specific magmatic processes. However, the magmatic system can be divided infinitely. One may divide the system into more secondary magmatic systems according to the local situations in geological mapping. The authors hold that a special geological map should be compiled to show the geological characteristics of the special magmatic system if they are too small to be seen.
-

-
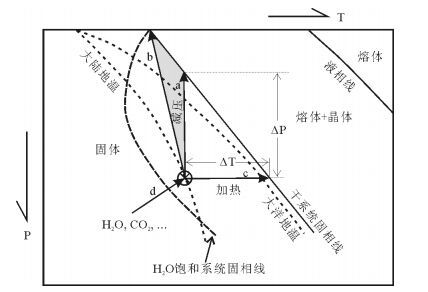
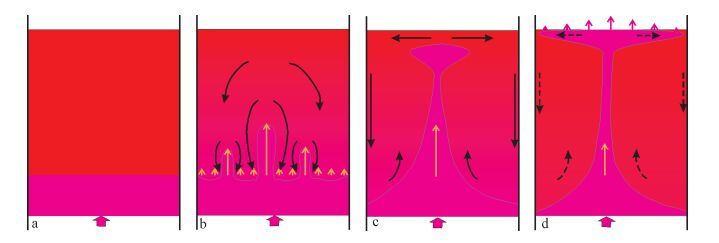
图 3 拉斑玄武质岩浆的固结前锋剖面[9]
Figure 3.
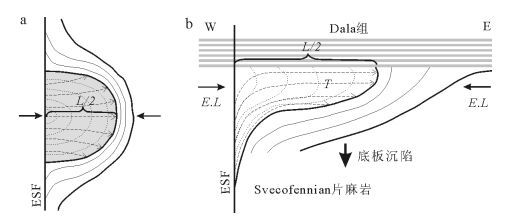
图 4 Ljugaren花岗岩侵位模型[13]
Figure 4.
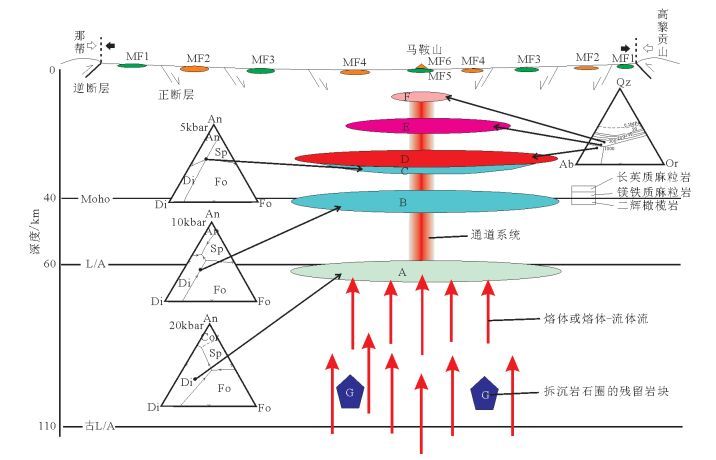
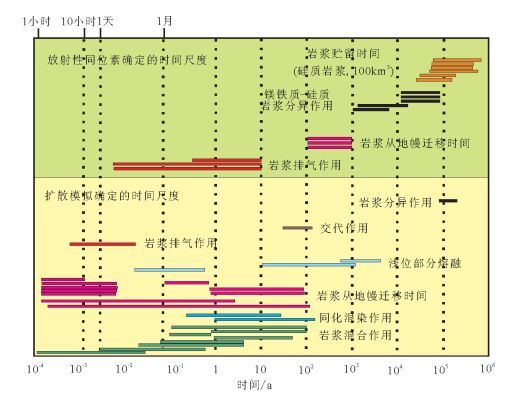
图 7 岩浆过程的时间尺度[25]
Figure 7.
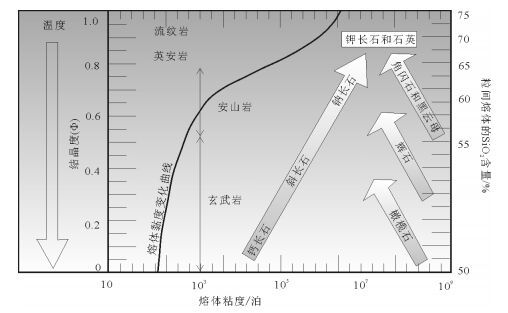
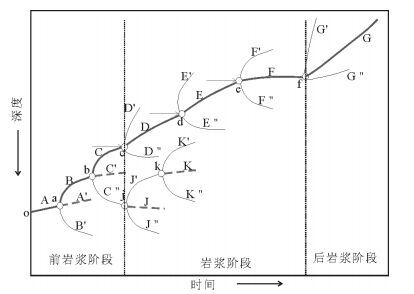
图 8 岩浆系统的成熟度(据参考文献[32]修改)
Figure 8.
表 1 岩浆系统的初步划分方案
Table 1. Preliminary scheme of magmatic system
岩浆系统 相应构造系数 形成动力学条件 基本特征 一级 一级 受控于全球动力学系统,即对流地幔动力系统与岩石圈动力系统强相互作用 时空尺度大,时间上常延续数十个百万年,空间上可延伸数千千米(造山带系统)或数百万平方千米(地幔柱系统),可横跨不同性质的构造板块 二级 二级 受控于区域动力学系统或对流地幔动力系统与岩石圈动力系统强相互作用,但岩石圈结构性质起关键作用 时间尺度与一级岩浆系统相近或较小,但空间尺度明显较小,可延伸数百千米(造山带系统),限于一个构造块体之内 三级 三级 局部动力系统有关,与全球动力系统没有直接关系 时空尺度取决于局部动力系统的辐射范围和持续时间,往往形成规模较小的火成岩聚集区 四级 四级 岩浆动力系统与围岩动力系统的相互作用 火成岩形成复式杂岩体,其规模可达数千平方千米,延续时间往往小于10Ma。杂岩体的结构特征与岩浆产量、通道条件和侵位条件有关 五级 五级 岩浆体内部的动力学过程 侵入体的性质与岩浆侵位条件、固结条件、岩浆供给速率、挥发分含量和岩浆系统的结构有关 -
[1] 於崇文.地质系统的复杂性(上、下册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003:1-1135.
[2] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 刘翠, 等.岩浆热液成矿理论的失败:原因和出路[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(1):1-11. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2011.01.001
[3] 於崇文.固体地球系统的复杂性与自组织临界性[J].高校地质学报, 1998, 4(4):361-368. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/199803/3216489.html
[4] Baker D R. Granitic melt viscosity and dike formation[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1998, 20(9/10):1395-1404. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=10675730
[5] King S D, Anderson D L. Edge-driven convection[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 160:289-296. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00089-2
[6] Tackley P J. Mantle convection and plate tectonics:toward an integrated physical and chemical theory[J]. Science, 2000, 288:2002-2007. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5473.2002
[7] 罗照华, 周久龙, 黑慧欣, 等.超级喷发(超级侵入)后成矿作用[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3131-3154.
[8] Marsh B D. Solidification fronts and magmatic evolution[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1996, 60:5-40. doi: 10.1180/minmag
[9] Marsh B D. On some fundamentals of igneous petrology[J]. Contrib Mineral Petrol. 2013, 166:665-690. doi: 10.1007/s00410-013-0892-3
[10] Latypov R, Morse T, Robins B, et al. A fundamental dispute:A discussion of "On some fundamentals of igneous petrology" by Bruce D. Marsh, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology (2013) 166:665-690[J]. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 2015, 169:20. doi: 10.1007/s00410-015-1108-9
[11] Gutiérrez F, Parada M A. Numerical modeling of time-dependent fluid dynamics and differentiation of a shallow basaltic magma chamber[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(3):731-762, doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp101
[12] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 陈必河, 等.透岩浆流体成矿作用导论[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009:1-177.
[13] Cruden A R. On the emplacement of tabular granites[J]. Journal of the Geological society London, 1998, 155:853-862 doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.155.5.0853
[14] Egorova V, Latypov R. Mafic-ultramafic sills:New insights from M-and S-shaped mineral and whole-rock compositional profiles[J]. Journal of Petrology. 2013, 54(10):2155-2191. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egt045
[15] Best M G. Igneous and metamorphic petrology, second edition[M]. Blackwell Publishing, 2003:1-729.
[16] 罗照华, 邓晋福, 韩秀卿.太行山造山带岩浆活动及其造山过程反演[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999:1-124.
[17] 魏文博, 叶高峰, 金胜, 等.华北地区东部岩石圈导电性结构研究——减薄的华北岩石圈特点[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(4):204-216. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5181cdd376a20029bd642d04-2.html
[18] 梁涛. 安妥岭斑岩钼矿的成因及其深部约束[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2010: 1-183.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2010086011.htm [19] 罗照华, 黄忠敏, 柯珊.花岗质岩石的基本问题[J].地质论评, 2007, 53(增刊):180-226. http://www.doc88.com/p-9079092434987.html
[20] 罗照华, 刘翠, 苏尚国.理解岩浆系统的物理过程[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3113-3119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411002.htm
[21] Weinberg R F, Hasalová P. Water-fluxed melting of the continental crust:a review[J]. Lithos, 2015, 212/215:158-188. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.08.021
[22] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 许俊玉, 等.成矿侵入体的岩石学标志[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(8):2247-2254. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=...
[23] Burgisser A and Bergantz G W. A rapid mechanism to remobilize and homogenize highly crystalline magma bodies[J]. Nature, 2011, 471:212-215. doi: 10.1038/nature09799
[24] Petford N, Cruden A R, McCaffrey K J W, et al. Granite magma formation, transport and emplacement in the Earth's crust[J]. Nature, 2000, 408(7):669-673. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12199000_Granite_magma...
[25] Turner S, Costa F. Measuring timescales of magmatic evolution[J]. Elements, 2007, 3:267-272. doi: 10.2113/gselements.3.4.267
[26] Sparks R S J, Baker L, Brown R J, et al. Dynamical constraints on kimberlite volcanism[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2006, 155:18-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.02.010
[27] Rutherford M J. Magma ascent rates[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2008, 69:241-271. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.7
[28] Coleman D S, Gray W, Glazner A F. Rethinking the emplacement and evolution of zoned plutons:Geochronologic evidence for incremental assembly of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, California[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(5):433-436. doi: 10.1130/G20220.1
[29] 罗照华, 苏尚国, 刘翠.岩浆成矿系统的尺度效应[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1):1-9. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DQHJ201404002003.htm
[30] 郭少丰. 岩基后金矿的成矿作用——以都山岩体为例[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2010: 1-101.
[31] 苏尚国, 汤中立, 罗照华, 等.岩浆通道成矿系统[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3120-3130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411003.htm
[32] Zellmer G F, Annen C. An introduction to magma dynamics[C]//Annen C, Zellmer G F. Dynamics of Crustal Magma Transfer, Storage and Differentiation. Geological Society Special Publication, 2008, 304:1-13.
[33] 汤中立.中国的小岩体岩浆矿床[J].中国工程科学, 2002, 4(6):9-12. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/0c91b958a417866fb84a8eef.html
[34] 罗照华, 魏阳, 辛厚田, 等.造山后脉岩组合的岩石成因——对岩石圈拆沉作用的约束[J], 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6):1672-1684. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=...
[35] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 王秉璋, 等.造山后脉岩组合与内生成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(4):1-12. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=...
[36] 杨宗锋, 罗照华, 卢欣祥.定量化火成岩结构分析与岩浆固结的动力学过程[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):246-266. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201001021
[37] Bachmann O, Bergantz G W. Gas percolation in upper-crustal silicic crystal mushes as a mechanism for upward heat advection and rejuvenation of near-solidus magma bodies[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2006, 149:85-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2005.06.002
[38] 朱训.从矿产勘查过程看认识运动的"阶梯式发展"[J].自然辩证法研究, 1991, 7(10):7-11. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92803X/199110/1000019456.html
[39] 朱训.阶梯式发展是物质世界运动和人类认识运动的重要形式[J].自然辩证法研究, 2012, 28(12):1-8. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/89537X/201304/1005372214.html
-



 下载:
下载: