LITHOSPHERIC THERMAL-RHEOLOGICAL STRUCTURE AND DEEP GEODYNAMICS IN THE YANGTZE RIVER ECONOMIC BELT
-
摘要:
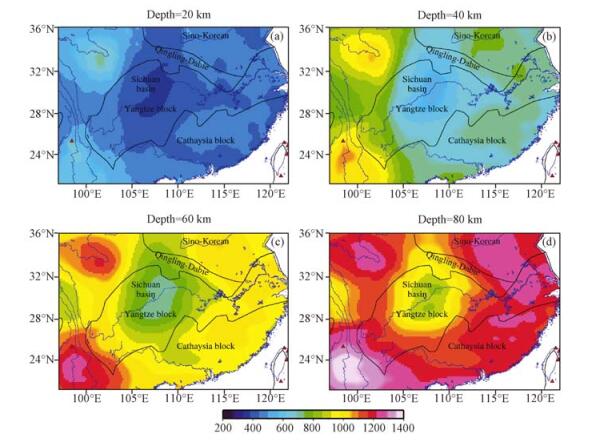
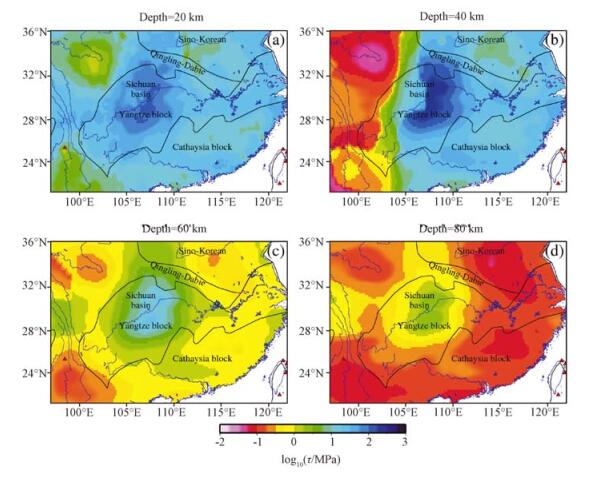
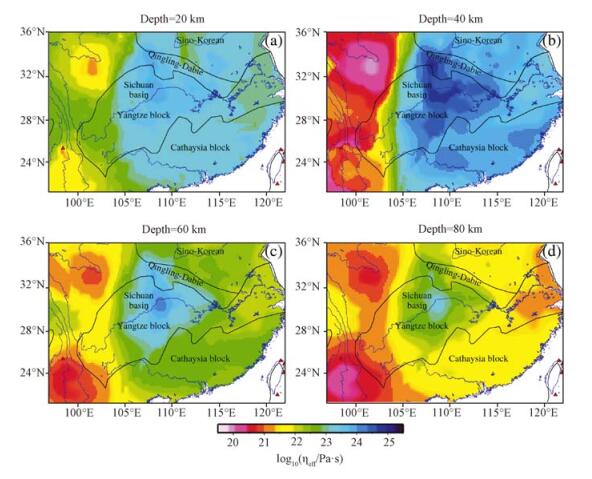
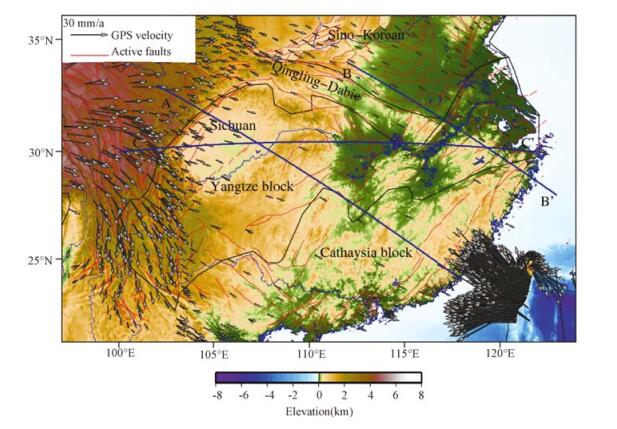
通过Crust 2.0模型构建有限元三维数值模型,以地表观测温度、深部反演温度和地表热流作为约束,计算了长江经济带地区岩石圈温度结构;在温度结构的基础上,通过GPS观测数据得到的地表应变率和选取代表性岩石物性,计算了长江经济带岩石圈流变强度和等效粘滞性系数。结果表明:长江经济带地区岩石圈表现出明显的横向不均匀性,其中四川盆地表现为低温、高强度和高粘滞性的特征,相同深度,四川盆地核心区比周围地块的温度低100~300℃,强度和粘滞性分别比周缘高1~2个数量级;在温度、强度和粘滞性的过渡地带构造活动性比较强烈。结合深部地球物理观测综合分析认为,长江经济带东、西部分别受到太平洋板块深俯冲和印度-欧亚大陆板块碰撞的影响,其深部影响范围分别达到四川盆地的东、西边界,深部动力学过程可能导致了岩石圈的横向不均匀性。
Abstract:Constructing the finite three-dimensional numerical model through Crust 2.0, under constraints of the surface temperature, deep inversion temperature and surface heat flow, we have calculated the thermal structure of the continental lithosphere beneath Yangtze River Economic Belt and adjacent regions. On the basis of 3D thermal structure, deriving surface strain rates from GPS observation, and selecting representative rock physical properties, we have calculated the strength and effective viscosity of the continental lithosphere. The results show that there is obvious lateral heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The Sichuan basin has low temperature, high strength and high viscosity. In the same depth, temperature beneath the Sichuan basin is lower than ambient region for 100~300℃. Strength and viscosity is lower for 1~2 orders of magnitude. The transition zone of temperature, strength and viscosity has strong active tectonics. Combining with deep geophysical observation, the study proposed that the Pacific Plate subduction and India-Eurasia Plate collision played important roles in the deep dynamic process respectively in the eastern and western parts of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The effective sphere reach the eastern and western boundaries of Sichuan basin, deep dynamic process may lead to the horizontal heterpgeneity of the lithosphere.
-

-
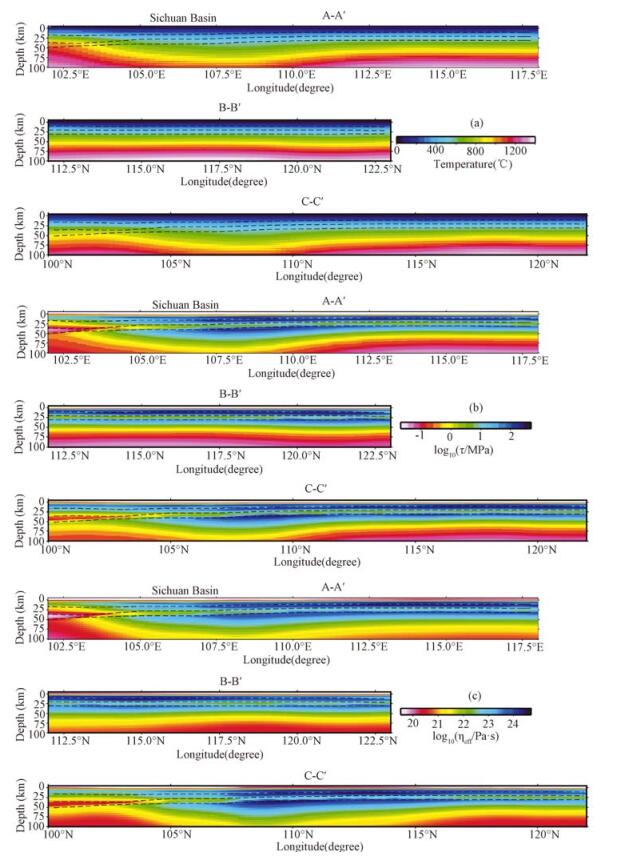
图 3 长江经济带地区各个剖面岩石圈温度、强度和等效粘滞性系数分布(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 3.
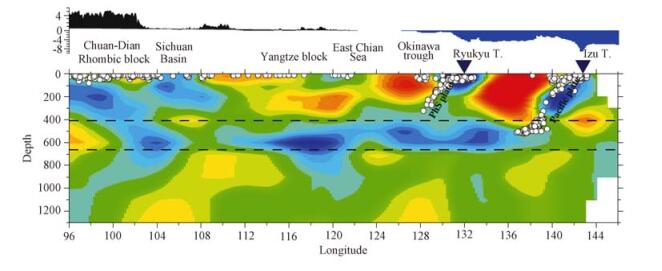
图 6 长江经济带地区及周缘深部地震层析成像结果[25](剖面沿着北纬30°)
Figure 6.
-
[1] 舒良树.华南构造演化的基本特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035~1053 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201207004.htm
SHU Liang-shu. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(7):1035~1053. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201207004.htm
[2] 张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等.中国华南大陆构造与问题[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(10):1553~1582 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201310003.htm
ZHANG Guo-wei, GUO An-lin, WANG Yue-jun, et al. Tectonics of South China continent and its implications[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2013, 43(10):1553~1582. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201310003.htm
[3] 张岳桥, 徐先兵, 贾东, 等.华南早中生代从印支期碰撞构造体系向燕山期俯冲构造体系转换的形变记录[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(1):234~247 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200901033.htm
ZHANG Yue-qiao, XU Xian-bing, JIA Dong, et al. Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic systemin South China during the Early Mesozoic[J]. Earth Sciences Frontiers, 2009, 16(1):234~247. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200901033.htm
[4] Gan W, Zhang P, Shen Z-K, et al. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan Plateau inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112:B08416. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005JB004120/references
[5] Kreemer C, Blewitt G, Klein E C. A geodetic plate motion and Global Strain Rate Model[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(10):3849~3889. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005407
[6] Deng Q, Zhang P, Ran Y, et al. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China[J]. Science in China:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(4):356~372. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1360%2F03yd9032.pdf
[7] Goes S, Govers R, Vacher P. Shallow mantle temperatures under Europe from P and S wave tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(B5):11153~11169. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900300
[8] Goes S, Lee S v d. Thermal structure of the North American uppermost mantle inferred from seismic tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(B3):2050. doi: 10.1029/2000JB000049
[9] An M, Shi Y. Lithospheric thickness of the Chinese continent[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2006, 159(3/4):257~266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031920106002494
[10] An M, Shi Y. Three-dimensional thermal structure of the Chinese continental crust and upper mantle[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2007, 50(10):1441~1451. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0071-3
[11] Hu S, He L, Wang J. Heat flow in the continental area of China:a new data set[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 179:407~419. doi: 10.1016/S0012~821X(00)00126~6
[12] Sun Y, Dong S, Zhang H, et al. 3D thermal structure of the continental lithosphere beneath China and adjacent regions[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62:697~704. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.020
[13] Kohlstedt D L, Evans B, Mackwell S J. Strength of the lithosphere:Constraints imposed by laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B9):17587~17602. doi: 10.1029/95JB01460
[14] 臧绍先, 李昶, 魏荣强.岩石圈流变机制的确定及影响岩石圈流变强度的因素[J].地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1):50~60 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200201007.htm
ZANG Shao-xian, LI Chang, WEI Rong-qiang. The determination of the deformational mechanism of the lithosphere and the factors influenced the lithospheric rheological strength[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(1):50~60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200201007.htm
[15] Zang S X, Wei R Q, Liu Y G. Three-dimensional rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Ordos block and its adjacent area[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 163(1):339~356. doi: 10.1111/gji.2005.163.issue-1
[16] Zang S X, Wei R Q, Ning J Y. Effect of brittle fracture on the rheological structure of the lithosphere and its application in the Ordos[J]. Tectonophysics, 2007, 429:267~285. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2006.10.006
[17] 魏荣强, 臧绍先.岩石破裂强度的温度和应变率效应及其对岩石圈流变结构的影响[J].地球物理学报, 2006, 49(6):1730~1737 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200606019.htm
WEI Rong-qiang, ZANG Shao-xian. Effects of temperature and strain rate on the fracture strength of rock and their influences on the rheological structure of the lithosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(6):1730~1737. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200606019.htm
[18] Shimada M. Lithosphere strength inferred from fracture strength of rocks at high confining pressures and temperatures[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993, 217:55~64. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(93)90202-U
[19] Kirby S H. Rheology of the lithosphere[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 1983, 21(6):1458~1487. doi: 10.1029/RG021i006p01458
[20] Ranalli G, Murphy D C. Rheological stratification of the lithosphere[J]. Tectonophysics, 1987, 132:281~295. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(87)90348-9
[21] Weertman J. The creep strength of the Earth's mantle[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 1970, 8(1):145~168. doi: 10.1029/RG008i001p00145
[22] Kirby S H, Kronenberg A K. Rheology of the lithosphere:Selected topics[J]. Review of Geophysics, 1987, 25(6):1219~1244. doi: 10.1029/RG025i006p01219
[23] Zhu S, Shi Y. Estimation of GPS strain rate and its error analysis in the Chinese continent[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 40(1):351~362. http://www.escience.cn/system/download/71645
[24] 孙玉军, 董树文, 范桃园, 等.中国大陆及邻区岩石圈三维流变结构[J].地球物理学报, 2013, 56(9):2936~2946 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201309008.htm
SUN Yu-jun, DONG Shu-wen, FAN Tao-yuan, et al. 3D rheological structure of the continental lithosphere beneath China and adjacent regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(5):546~558. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201309008.htm
[25] Huang J, Zhao D. High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006, 111(B9):B09305. http://www.oalib.com/references/15772398
[26] Wei W, Xu J, Zhao D, et al. East Asia mantle tomography:New insight into plate subduction and intraplate volcanism[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 60:88~103. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.001
-



 下载:
下载: