H-O-S-Pb ISOTOPIC COMPONENTS OF THE LIANGSHAN MOLYBDENUM DEPOSIT IN XINYU, JIANGXI PROVINCE AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR THE ORE FORMING PROCESS
-
摘要:
在前人研究成果的基础上,对江西新余良山钼矿床的地质特征进行了详细研究,系统测试了矿床中石英脉型钼矿石样品的氢、氧、硫和铅同位素组成,进而探讨钼矿床的成矿流体性质以及成矿物质来源。良山钼矿床δD值变化范围-61‰~ -57.9‰,平均值-59.1‰;δ18OV-SMOW值变化于7.1‰~10.5‰,平均值9.2‰,流体的δ18OH2O值变化于-3.32‰~-0.52‰,平均值-1.52‰,表明成矿流体具有岩浆水和大气降水混合流体特征。硫化物的δ34SV-CDT值为-1.8‰~2.6‰,极差4.4‰,平均值1.12‰,其中黄铁矿δ34SV-CDT值为-1.8‰~2.6‰,辉钼矿δ34SV-CDT值为0.8‰~2.3‰,硫同位素表现为较小的正值特征,具有典型的岩浆硫组成特点。良山钼矿石中的矿石铅同位素206Pb/204Pb值为17.555~19.474,207Pb/204Pb值15.486~15.768,208Pb/204Pb值37.942~39.943,μ值9.35~9.7,ω值37.06~38.31,Th/U值3.8~3.96,矿石铅为混合铅,表明成矿物质为混合来源。良山钼矿床应为岩浆热液型-石英脉型钼矿床,是中生代华南板块板内构造演化区域金属成矿作用大爆发的产物。
Abstract:On the basis of predecessors' research results, We study the geological characteristics of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Jiangxi province and test H-O-S-Pb isotopic components of the molybdenum stone samples in quartz vein systematically, and then discusse the metallogenic fluid properties as well as the source of ore-forming materials of the molybdenum deposit. The δD of the ore-forming fluids are between -61‰~-57.9‰, with the average of -59.1‰; and the δ18OV-SMOW of the ore-forming fluid are between 7.1‰~10.5‰, with the average of 9.2‰; and the δ18OH2O of the ore-foring fluids are between -3.32‰~-0.52‰, with the average of -1.52‰, which indicate that the ore-forming fluid has the characteristics of magmatic water and meteoric water mixed fluid. The δ34SV-CDT of the sulfide mineral are between -1.8‰~2.6‰, with the range of 4.4‰ and the average of 1.12‰, of which the δ34SV-CDT of the pyrite are between -1.8‰~2.6‰ and the δ34SV-CDT of the molybdenite are between 0.8‰~2.3‰. The sulfur isotope values are smaller positive which show the characteristics of typical magmatic sulfur. The values of 206Pb/204Pb of the ore samples are between 17.555~19.474, and the values of 207Pb/204Pb are between 15.486~ 15.768, as well as the values of 208Pb/204Pb are between 37.942~39.943, with the μ values of 9.35~9.7 and the ω values of 37.06~38.31, as well as the Th/U values of 3.8~3.96, which indicate the ore are rich in mixed lead, and the ore-forming material sources are mixed. The Liangshan molybdenum ore should belong to the magmatic hydrothermal type and quartz vein type deposit, which is a product of the metal mineralization outbreak during the intraplate tectonic evolution of south China plate in Mesozoic.
-

-
图 1 江西新余铁矿田地质图(据文献[14]略改)
Figure 1.
图 2 江西新余良山钼矿床地质简图(据文献[12]略改)
Figure 2.
图 4 新余良山钼矿δ18OH2O-δD同位素投影图(底图据文献[21])
Figure 4.
图 5 良山钼矿床H-O同位素组成与天然H-O同位素对比图解(底图据文献[25])
Figure 5.
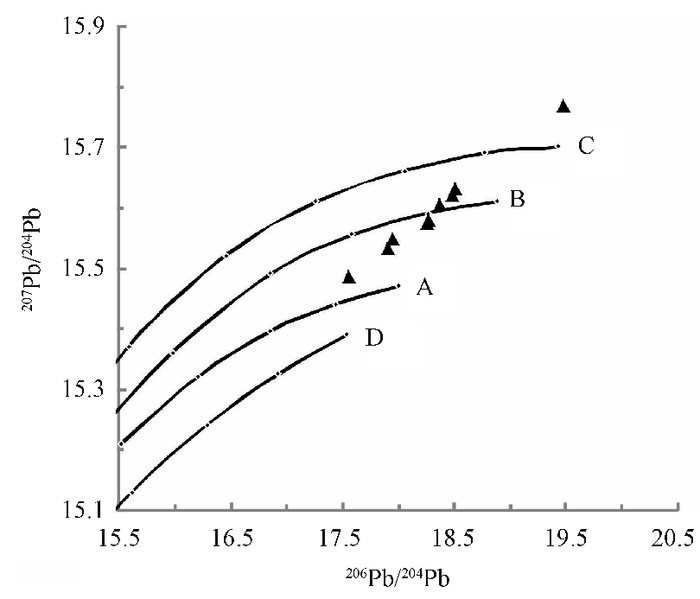
图 7 新余良山钼矿矿床铅同位素207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb模式图(底图据文献[23])
Figure 7.
表 1 江西新余良山钼矿矿床石英氢、氧同位素组成
Table 1. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Xinyu, Jiangxi
样品号 矿物 检测结果 δDV-SMOW/‰ δ18OV-PDB/‰ δ18OV-SMOW/‰ δ18OH2O/‰ Th/℃ JX1-7 石英 -61.0 -19.8 10.5 -0.79 206.5 JX1-8 石英 -59.6 -21.1 9.2 -0.52 234.2 JX1-9 石英 -58.9 -21.5 8.8 -2.01 214.0 JX1-11 石英 -57.9 -23.0 7.1 -0.92 221.4 JX1-12 石英 -58.2 -20.8 9.5 -3.32 221.4 注:样品测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成 表 2 江西新余良山钼矿床硫同位素组成
Table 2. Sulfur isotopic composition of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Xinyu, Jiangxi Province
样品号 矿物 δ34SV-CDT/‰ JX1-7 黄铁矿 2.6 JX1-7-h 辉钼矿 2.0 JX1-8 辉钼矿 2.3 JX1-9 黄铁矿 1.2 JX1-10 辉钼矿 2.1 JX52-3 黄铁矿 1.9 JX52-4B 黄铁矿 0.8 JX52-4C 黄铁矿 -0.3 JX52-5B 黄铁矿 -1.8 JX52-6A 黄铁矿 1.8 JX52-6B 黄铁矿 -0.3 JX52-6B-h 辉钼矿 0.8 JX53-2A 黄铁矿 1.3 JX53-2C 黄铁矿 1.3 注:样品测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成 表 3 中文江西新余良山钼矿床铅同位素组成标题
Table 3. Lead isotopic composition of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Xinyu, Jiangxi Province
样品号 矿物 208Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 206Pb/204Pb t/Ma μ ω Th/U △α △β △γ JX52-3 黄铁矿 38.931 15.630 18.508 133 9.51 38.27 3.89 76.54 19.85 44.79 JX52-4B 黄铁矿 38.672 15.606 18.365 207 9.48 37.78 3.86 73.98 18.61 41.09 JX52-4C 黄铁矿 37.942 15.486 17.555 648 9.35 38.28 3.96 61.97 13.27 41.09 JX52-5B 黄铁矿 38.430 15.580 18.272 243 9.44 37.06 3.80 71.32 17.08 36.14 JX52-6A 黄铁矿 38.722 15.620 18.490 134 9.49 37.42 3.82 75.54 19.20 39.20 JX52-6B 黄铁矿 39.943 15.768 19.474 -399 9.70 38.31 3.82 122.10 28.32 65.98 JX52-6B-h 辉钼矿 38.503 15.574 18.257 246 9.43 37.39 3.84 70.72 16.70 38.26 JX53-2A 黄铁矿 38.200 15.548 17.945 441 9.42 37.66 3.87 67.94 16.01 38.71 JX53-2C 黄铁矿 38.149 15.532 17.913 444.6 9.39 37.47 3.86 66.37 14.99 37.51 注:样品测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成;μ=w(238U)/w(204Pb),ω=w(232Th)/w(204Pb);计算结果由Geokit软件计算所得;t为硫化物模式年龄 -
[1] 浙江之源矿产评估有限公司. 江西省新余良山矿区铁矿采矿权评估报告[R]. 2013.
Zhejiang Zhiyuan Mineral Resource Estimation Co., Ltd. The assessment report of mining concession in Liangshan iron mine, Xinyu city, Central Jiangxi Province [R]. 2013.
[2] Rye R O, Ohmoto H. Sulfer and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: A review [J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69: 826~842. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.826 https://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/4284421-sulfur-carbon-isotopes-ore-genesis-review
[3] Ohmoto H. Stable isotope geochemistry of ore deposits [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1986, 6: 491~559. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199304008.htm
[4] Hoefs J. Stable isotope Geochemistry [M]. Berlin: Sprinter Verlag, 1997: 201.
[5] Jiang S Y, Han F, Shen J Z. Chemical and Sr-Nd isotopic systematics of tourmaline from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit, Guangxi Province, China [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157: 49~67. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00200-9 http://www.geol.lsu.edu/henry/Research/tourmaline/bibliography/TourmalineOreDeposits.htm
[6] Ding T P, Jiang S Y. Stable isotope study of the Langshan polymetallic mineral district, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Resource Geology, 2000, 50: 25~38. doi: 10.1111/rge.2000.50.issue-1 https://core.ac.uk/display/45851511
[7] 李文博, 黄智龙, 张冠.云南会泽铅锌矿田成矿物质来源:Pb, S, C, H, O, Sr同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(10):2567~2580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.10.018
LI Wen-bo, HUANG Zhi-long, ZHANG Guan. Sources of the ore metals of the Huize ore field in Yunnan province: constraints from Pb, S, C, H, O and Sr isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 2006, 22(10): 2567~2580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.10.018
[8] 林芳梅. 湘中锡矿山锑矿床成矿流体研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014.
LIN Fang-mei. On the ore-forming fluid in the Xikuangshan antimony deposit, central Hunan [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014.
[9] 侯林, 彭惠娟, 丁俊.云南武定逸纳厂铁-铜-金-稀土矿床成矿物质来源——来自矿床地质与S, Pb, H, O同位素的制约[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(2):205~218.
HOU Lin, PENG Hui-juan, DING Jun. Sources of the ore-forming materials for the Yinachang Fe-Cu-Au-REE deposit, Wuding, Yunnan Province: Constraints from the ore geology and the S, Pb, H, O isotope geochemistry [J]. Acta petrological Et mineralogical, 2015, 34(2): 205~218.
[10] 杨明桂, 王昆.江西省地质构造格架及地壳演化[J].江西地质, 1994, 8(4):239~251. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXDZ404.000.htm
YANG Ming-gui, WANG Kun. The geological tectonic framework and the crustal evolution in Jiangxi province [J]. Geology of Jiangxi, 1994, 8(4): 239~251. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXDZ404.000.htm
[11] 戴元裕.江西省新余太平山铁矿区叠加褶皱构造解析并论恢复复杂褶皱系的包络面的意义[J].地质找矿论丛, 1986, 1(2):13~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK198602001.htm
DAI Yuan-yu. A structural analysis of super imposed folds at Taipingshan iron mine, Xinyu County, Jiangxi Province, and the significance of reconstructing envelopes in the complicated fold system [J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1986, 1(2): 13~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK198602001.htm
[12] 肖光荣, 姚琪.江西省新余式铁矿中深部铁矿勘查探讨[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):305~311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304031.htm
XIAO Guang-rong, YAO Qi. A study of the exploration of middle and deep mine of Xinyu type of iron deposits [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 305~311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304031.htm
[13] 江西省地质矿产勘查开发局赣西地质调查大队. 江西省新余市太平山—松山矿区铁矿接替资源勘查项目总体设计[R]. 2013.
http://www.doc88.com/p-8728052652268.html Ganxi Geological Survey Brigade, Jiangxi Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development. The project overall design of mine resource probing projects at Taipingshan-Songshan iron mining in Xinyu County, Central Jiangxi Province [R]. 2013.
[14] 曾书明, 周建廷, 王学平, 等.江西新余铁矿田铁矿成矿地质特征与成因分析[J].地质与勘探, 2011, 47(2):187~196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201102008.htm
ZENG Shu-ming, ZHOU Jian-ting, WANG Xue-ping, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and analysis of iron ore deposit in the Xinyu iron orefield [J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2011, 47(2): 187~196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201102008.htm
[15] 李吉人. 江西峡江铀矿区金滩花岗岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011.
http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20131220&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2013 LI Ji-ren. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Jintan granites from the Xiajiang uranium ore district, Jiangxi [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011.
[16] 刘亚光.江西省地层多重划分对比研究[J].江西地质科技, 1996, 23(2):51~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXZK199602000.htm
LIU Ya-guang. The multiple stratigraphic division in Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology of Jiangxi, 1996, 23(2): 51~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXZK199602000.htm
[17] 杨明桂, 刘亚光, 黄志忠, 等.江西中新元古代地层的划分及其与邻区对比[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(1):43~53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201201006.htm
YANG Ming-gui, LIU Ya-guang, HUANG Zhi-zhong, et al. Subdivision of Meso-Neoproterozoic strata in Jiangxi and a correlation with the neighboring areas[J]. Chinese Geology, 2012, 39(1): 43~53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201201006.htm
[18] 伍俊杰, 付蕾, 潘家永, 等.江西新余良山铁矿区钼矿体的特征及意义[J].低碳世界, 2016, 18:1~2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DTSJ201618031.htm
WU Jun-jie, FU Lei, PAN Jia-yong, et al. Characteristic and significance of the molybdenum mineralization bodies in Liangshan area of Xinyu County, Jiangxi Province [J]. Low Carbon World, 2016, 18: 1~2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DTSJ201618031.htm
[19] 张大椿, 穆治国, 黄福生, 等.江西阳储岭钨钼矿床稳定同位素组成特征的研究[J].矿床地质, 1984, 3(2):49~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198402005.htm
ZHANG Da-chun, MU Zhi-guo, HUANG Fu-sheng, et al. Stable isotope studies of the Yangchuling tungsten-molybdenum ore deposit, Jiangxi Province [J]. Mineral Deposits, 1984, 3(2): 49~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198402005.htm
[20] 汪在聪, 刘建明, 刘红涛, 等.稳定同位素热液来源示踪的复杂性和多解性评述——以造山型金矿为例[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(5):577~590. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201005013.htm
WANG Zai-cong, LIU Jian-ming, LIU Hong-tao, et al. Complexity and uncertainty of tracing fluid sources by means of H-O, C, S, N isotope systems: A case study of orogenic lode gold deposits [J]. Acta Petrological Et Mineralogica, 2010, 29(5): 577~590. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201005013.htm
[21] Clayton R N, Onnma N, Mayeda T K. Oxygen isotope temperatures of 'equilibrated' ordinary chondrites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1972, 36(2): 157~168. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(72)90004-X http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001670377290004X
[22] 张理刚.稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用:金属活化热液成矿作用及找矿[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1985.
ZHANG Li-gang. Stable isotope application in geological sciences: Metal activation hydrothermal mineralization and prospecting [M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 1985.
[23] 宜昌地质矿产研究所. 铅同位素地质研究的基本问题[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1979: 1~246.
http://www.oalib.com/paper/4764294 Yichang Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources. The fundamental problem of the lead isotope geological research [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1979: 1~246.
[24] Taylor H P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition [J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69(6): 843~883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00375296
[25] 李永胜, 吕志成, 严光生, 等. 西藏甲玛铜多金属矿床S、Pb、H、O同位素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(4): 72~81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201204008.htm
LI Yong-sheng, LV Zhi-cheng, YAN Guang-sheng, et al. Isotopic characteristics of S, Pb, H and O of Jiama copper-polymetallic ore deposit, Tibet and their significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(4): 72~81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201204008.htm
[26] Rollinson H R. Using Ueochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation Interpretation [M]. New York; John Wiley and Sons, Inc, 1992: 1~343.
[27] 刘英超, 杨竹森, 侯增谦, 等. 青海玉树东莫扎抓铅锌矿床地质特征及碳氢氧同位素地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(6): 770~784. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200906005.htm
LIU Ying-chao, YANG Zhu-sen, HOU Zeng-qian, et al. Geology and hydrogen, oxygen and carbon isotope geochemistry of Dongmozhazhua Pb-Zn ore deposit, Yushu area, Qinghai Province [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(6): 770~784. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200906005.htm
[28] Ohmoto H, Rye R O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon[C]//Barnes H L. Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1979: 509~567.
[29] Staecy J S, Kramers J D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two stage model [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 26(2): 207~221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6 http://www.academia.edu/999883/Approximation_of_terrestrial_lead_isotope_evolution_by_a_two-stage_model
[30] 张乾, 潘家永, 邵树勋.中国某些金属矿床矿石铅来源的铅同位素诠释[J].地球化学, 2000, 29(3):231~238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200003003.htm
ZHANG Qian, PAN Jia-yong, SHAO Shu-xun. An interpretation of ore lead sources from lead isotopic compositions of some ore deposits in China[J]. Geochimica, 2000, 29(3): 231~238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200003003.htm
[31] Zartman R E, Doe B R. Plumbotectonics: The model [J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(1/2): 135~162. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00321987
[32] 付伟, 柴明春, 杨启军, 等.广西佛子冲大型铅锌多金属矿床的成因:流体包裹体和H-O-S-Pb同位素地球化学约束[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(12):4136~4150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201312007.htm
FU Wei, CHAI Ming-chun, YANG Qi-jun, et al. Genesis of the Fozichong Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit: Constraints from fluid inclusions and H-O-S-Pb isotopic evidences [J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 2013, 29 (12): 4136~4150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201312007.htm
[33] 胡瑞忠, 毛景文, 范蔚茗, 等.华南陆块陆内成矿作用的一些科学问题[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(2):13~26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002006.htm
HU Rui-zhong, MAO Jing-wen, FAN Wei-ming, et al. Some scientific questions on the intra-continental metallogeny in the South China continent[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 2010, 17(2): 13~26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002006.htm
[34] Hu R G, Zhou M F. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China: An introduction to the thematic issue [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6): 579~588. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0431-6
[35] Mao J W, Cheng Y B, Chen M H, et al. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2013, 48: 267~294. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z https://rd.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs00126-012-0446-z.pdf
[36] 周新民.南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007:1~691.
ZHOU Xin-min. Genesis of the Late Mesozoic granite and dynamic evolution of the lithosphere in Nanling region[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 1~691.
-




 下载:
下载: