SUMMARY ON THE PREVENTION PROGRESS OF ENGINEERING SLOPE IN HONG KONG
-
摘要:
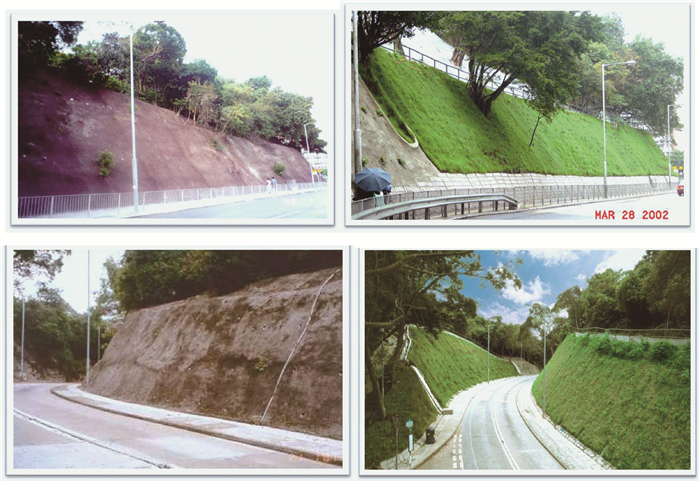
受特殊的丘陵地形、强风化岩石以及季节性强降雨的影响, 香港滑坡时有发生。根据香港土木工程拓展署(CEDD)土力工程处(Geotechnical Engineering Office, GEO)的相关资料, 梳理了香港工程边坡防治进展的历史进程和关键防治技术, 对我国大陆相关工程边坡防治具有一定的参考价值。
Abstract:Due to the special hilly terrain, strongly weathered rock and the seasonal rainfall, landslide occurs frequently in Hong Kong. According to the relevant data collected from Hong Kong civil Engineering development board (CEDD), the GEO Geotechnical Engineering Office (GEO), the historical process and the key prevention and control technology of engineering slope in Hong Kong are summarized in this paper, which will be valuable to the relevant prevention and control of slope engineering in mainland China.
-
Key words:
- Hong Kong /
- rainfall /
- engineering slope /
- prevention and control technology
-

-
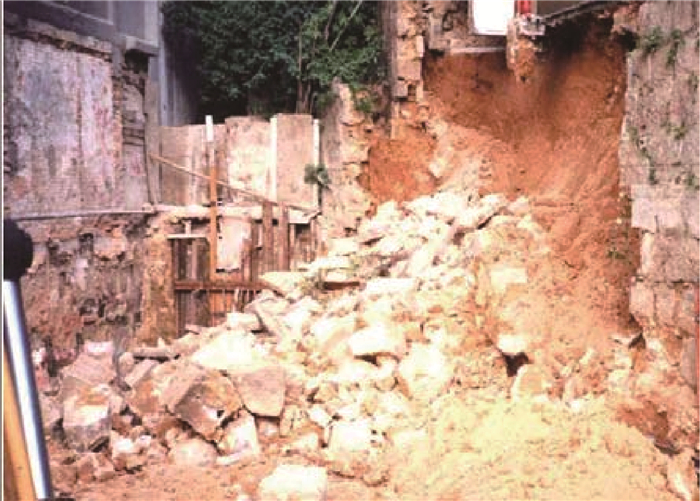
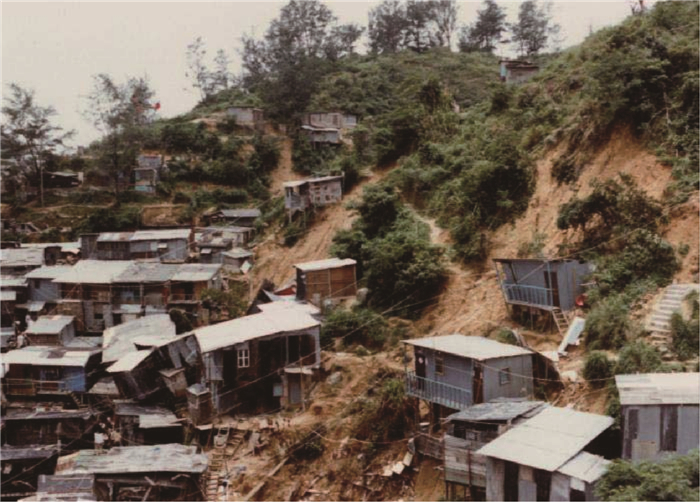
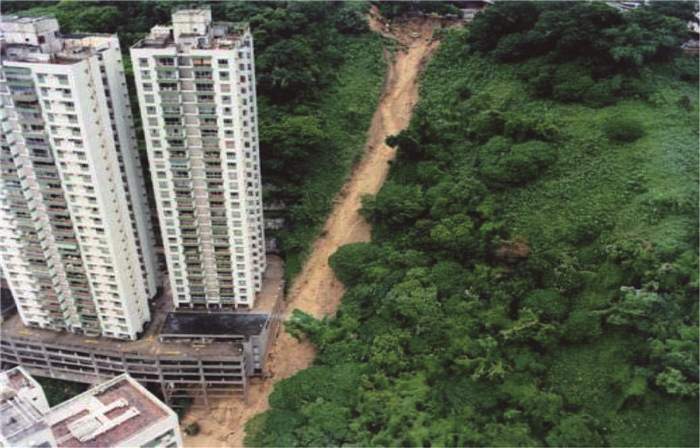
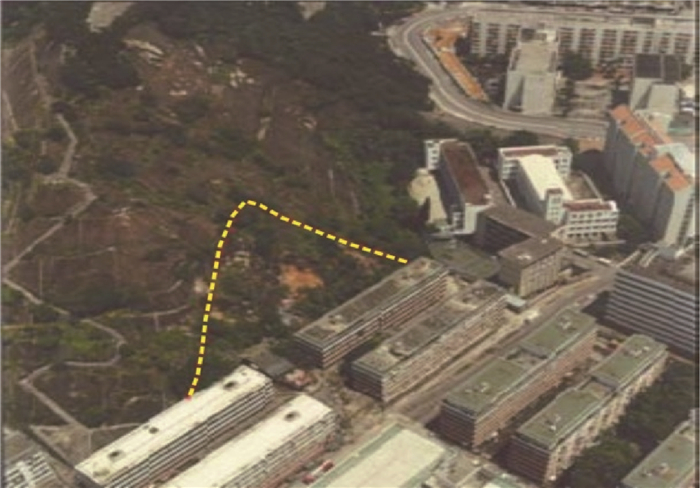
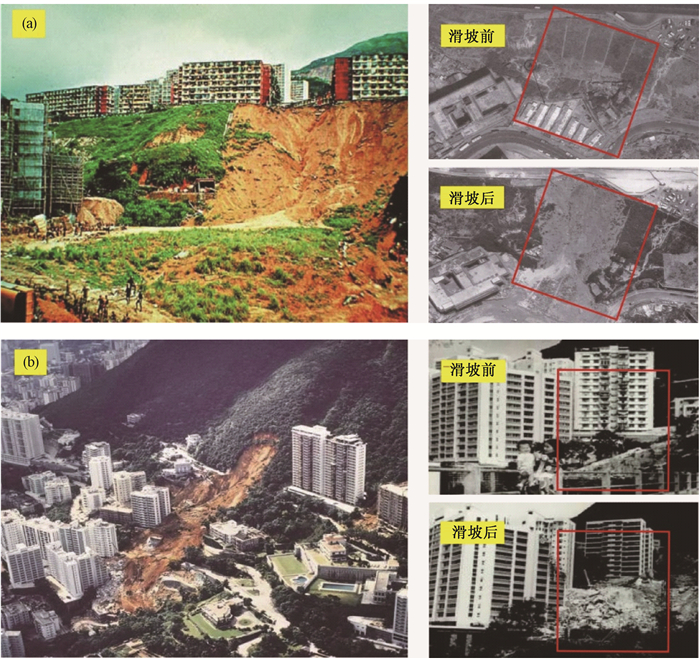
图 1 秀茂坪滑坡和宝珊道滑坡[3]
Figure 1.
-
[1] Chan R K S. Hong Kong slope safety management system[C]//Proceedings of the Symposium on Slope Hazards and Their Prevention. Hong Kong, 2000: 1~16.
[2] Chan R K S. Safe and green slopes: The holistic Hong Kong approach[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 HKIE Geotechnical Division Annual Seminar. Hong Kong: HKIE, 2005: 1~26.
[3] Chan R K S. Evolution of LPM policy in the past thirty five years: Landslide risk reduction through works[C]//35 Years of Landslip Preventive Measures Programme and Beyond. Hong Kong, 2011: 1~14.
[4] Lam B M T. An appraisal of the landslide preventive works to fill slopes in Hong Kong[M]. MSc Dissertation, Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, the University of Hong Kong, 1980: 1~80.
[5] Chan Y C. Study of old masonry retaining walls in Hong Kong: GEO report No. 31[M]. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong Government, 1982.
[6] Brand E W, Hudson R R. CHASE: An empirical approach to the design of cut slopes in Hong Kong[C]//Proceedings of the 7th Southeast Asian Geotechnical Conference. Hong Kong, 1982: 1~16.
[7] HAP (Halcrow Asia Partnership Ltd.). Report on the Ching Cheung Road Landslide of 3 August 1997[C]//GEO Report No. 78. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong SAR Government, 1998.
[8] Fugro Maunsell Scott Wilson Joint Venture. Report on the Shek Kip Mei Landslide of 25 August 1999: Vol. 1-Findings of the Landslide Investigation[M]. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong SAR Government, 2000.
[9] Cheung W M, Shiu Y K. Assessment of global landslide risk posed by pre-1978 man-made slope features: Risk reduction from 1977 to 2000 achieved by the LPM Programme[C]//Special Project Report No. SPR 6/2000. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong SAR Government, 2000.
[10] Shiu Y K, Chang G W K. Effects of inclination, length pattern and bending stiffness of soil nails on behaviour of nailed structures[C]//Geotechnical Engineering Office, Hong Kong. GEO Report No. 197. Hong Kong: Geotechnical Engineering Office, 2005: 1~116.
[11] Pun W K, Urciuoli G. Soil nailing and subsurface drainage for slope stabilization[J]. Landslides and Engineered Slopes: From the Past to the Future, 2008, (1): 85~126. http://www.crcnetbase.com/doi/pdf/10.1201/9780203885284-c6
[12] Cheung W M, Shum K W, Pun W K. Review of the approach for estimation of pullout resistance of soil nails[C]//Proceedings of HKIE Geotechnical Division Annual Seminar on Applications of Innovative Technologies in Geotechnical Works, Hong Kong, 2008: 95~100.
[13] Shiu Y K, Cheung W M. Long-term durability of steel soil nails (HKIE Transactions Prize 2009)[J]. HKIE Transactions, 2008, 15(3): 1~9.
[14] Cheung W M. Non-destructive tests for determining the lengths of installed steel soil nails[C]//GEO Report No. 133. Geotechnical Engineering Office, Hong Kong, 2003: 1~54.
[15] Mott Connell Ltd. Review of stepped drainage channels: Report prepared under Agreement No. CE 10/2004(GE)[M]. Mott Connell Ltd., 2006: 1~69.
[16] Chanson H. Hydraulic design of stepped cascades, channels, weirs and spillways[M]. Oxford: Pergamon, 1994: 1~261.
[17] Tang C S C, Cheung S P Y. Frequency analysis of extreme rainfall values: Technical Note No. 1/2011[M]. Hong Kong: Geotechnical Engineering Office, 2011: 1~208.
-




 下载:
下载: