The great differences between the Archean and modern times: Could there have been plate tectonics in the Archean?
-
摘要:
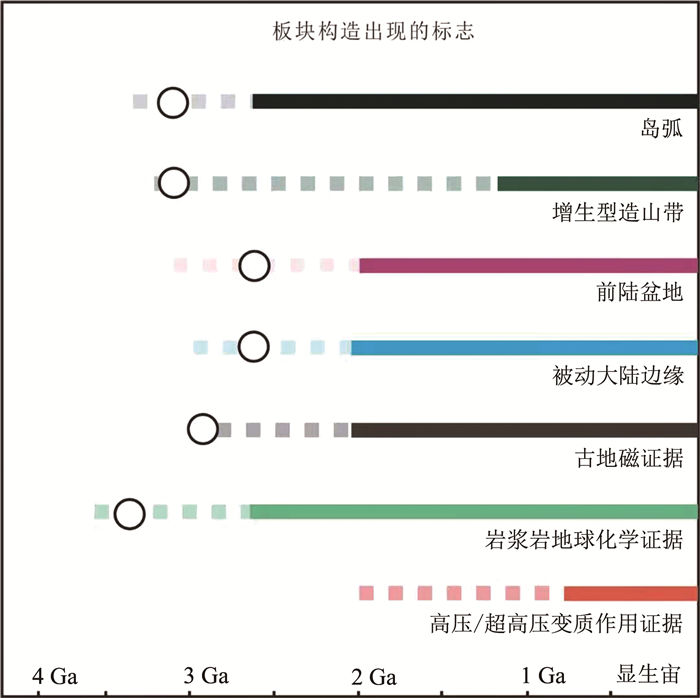
太古宙出露的岩石(如TTG、科马提岩、绿岩带)大多与现代不同,故"将今论古"的思想不适合推演到太古宙,也不能把太古宙TTG对比为现今的埃达克岩。TTG与俯冲无关,也不是地壳加厚形成的,而可能是在停滞盖层构造背景下初始地壳内富钠玄武岩部分熔融形成的。地球演化是一个不断散热的过程,太古宙属于热球阶段,元古宙以后可能才进入冷球阶段。因此,太古宙可能主要表现为停滞盖层构造,元古宙以后可能才出现板块构造。板块热俯冲的可能性很小,只有当岩石圈足够冷且具有一定的刚性和浮力时,板块才可能俯冲;而查明板块构造的地质记录(如蛇绿岩、蓝片岩、混杂堆积、深海沉积等)才能知道板块构造启动的时间。
Abstract:Most outcropped Archean rocks(such as TTG, komatiite and greenstone belt) are different from the modern ones.Therefore, the idea of "the present is the key to the past" is not suitable to be extended to the Archean Eon, nor can the Archean TTG be compared to the present adakites.TTG had nothing to do with subduction, and might be formed by partial melting of sodium-rich basalts in the initial crust under the tectonic setting of the stagnant lid instead of by crustal thickening.The earth is a process of continuous heat dissipation.The Archean Eon belongs to the hot sphere stage, and the earth might enter the cold sphere stage after the Proterozoic Eon.Therefore, the Archean might be mainly characterized by stagnant lid tectonics, and plate tectonics might have appeared after the Proterozoic.As possibility of plate thermal subduction is small, only when the lithosphere is cold enough and has certain rigidity and buoyancy, can the plate subduction occur.Only by establishing the geological record of plate tectonics(such as ophiolite, blueschist, melanges, deep-sea deposits, etc.) can we know when plate tectonics began.
-

-
[1] Salop L I. Two types of Precambrian structures: Gneisses, folded ovals and gneiss domes[J]. Int. Geol. Rev., 1972, 14: 1209-1228. doi: 10.1080/00206817209475823
[2] 翟明国. 华北前寒武纪成矿系统与重大地质事件的联系[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1759-1773. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305023.htm
[3] Martin H. Effect of steeper Archean geothermal gradient on geochemistry of subduction-zone magmas[J]. Geology, 1986, 14: 753-756. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<753:EOSAGG>2.0.CO;2
[4] Martin H. Adakitic magmas: modern analogues of Archean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46: 411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
[5] Drummond M S, Defant M J. A model for trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite genesis and crustal growth via slab melting: Archean to modern comparison[J]. Journal of Geophysics Research, 1990, 95: 21503-21521. doi: 10.1029/JB095iB13p21503
[6] Foley S, Tiepolo M, Vanucci R. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones[J]. Nature, 2002, 417: 837-840. doi: 10.1038/nature00799
[7] Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D. Growth of early continental crust by partial melting of eclogite[J]. Nature, 2003, 425: 605-609. doi: 10.1038/nature02031
[8] Smithies R H, Champion D C. Adakite, TTG and Archaean crustal evolution[C]//Geophysical Research Abstracts, 2003, 5: 01630.
[9] Steenfelt A, Garde A A, Moyen J F. Mantle wedge involvement in the petrogenesis of Archaean grey gneisses in West Greenland[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79: 207-228. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.054
[10] Smithies R H, Champion D C. The Archaean high-Mg dioritesuite: Links to tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite magmatism and implications for Early Archaean crustal growth[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41: 1653-1671. doi: 10.1093/petrology/41.12.1653
[11] Condie K C. TTGs and adakites: are they both slab melts?[J]. Lithos, 2005, 80: 33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2003.11.001
[12] 张旗, 翟明国. 太古宙TTG岩石是什么含义?[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(11): 3446-3456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201211004.htm
[13] Palin R M, Santosh M, Cao W, et al. Secular metamorphic change and the onset of plate tectonics[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103172.
[14] Condie K C, Kröner A. When did plate tectonics begin? Evidence from the geologic record[J]. Geological Society of America, Special Paper, 2008, 440: 281-294. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313576739_When_did_plate_tectonics_begin_on_planet_Earth?ev=auth_pub
[15] Rapp R P, Watson E B, Miller C F. Partial melting of amphibolite eclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalites[J]. Precamb. Res., 1991, 51: 1-25. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(91)90092-O
[16] Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36: 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[17] Schmidt M W, Dardon A, Chazot G, et al. The dependence of Nb and Ta rutile-melt composition and Nb/Ta fractionation during subduction processes[J]. Earth Plant. Sci. Lett., 2004, 226: 415-432. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.08.010
[18] Klemme S, Prowatke S, Hametner K, et al. Partitioning of trace elements between rutile and silicate melts: implications for subduction zones[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2005, 49: 2361-2371. http://www.geos.ed.ac.uk/homes/sklemme/publications/Klemme_etal_2005.pdf
[19] Xiong X L, Xia B, Xu J F, et al. Na depletion in modern adakites via melt/rock reaction within the sub-arc mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 229: 273-292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.008
[20] Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subduction lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[21] Smithies R H, Champion D C, van Kranendonk M J. Formation of Paleoarchean continental crust through infracrustal melting of enriched basalt[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 281: 298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.03.003
[22] Kusky T M. Accretion of the Archean Slave Province[J]. Geology, 1989, 17: 63-67. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0063:AOTASP>2.3.CO;2
[23] Kusky T M, Polat A. Growth of granite-greenstone terranes at convergent margins, and stabilization of Archean cratons[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 305: 43-73. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00014-1
[24] Kusky T M. 板块构造与地幔温度和变质属性之间的关系[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50: 635-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202005005.htm
[25] Komiya T. Material circulation through time: Chemical differentiation within the mantle and secular variation of temperature and composition of the mantle[C]//Yuen D, Maruyama S, Karoto S, et al. Superplumes: Beyond Plate Tectonics. Springer, 2007: 187-234.
[26] Greber N D, Dauphas N, Bekker A, et al. Titanium isotopic evidence for felsic crust and plate tectonics 3.5 billion years ago[J]. Science, 2017, 357: 1271-1274. doi: 10.1126/science.aan8086
[27] Ge R, Zhu W, Wilde S A, et al. Remnants of Eoarchean continental crust derived from a subducted proto-arc[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(2): eaao3159. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao3159
[28] Deng Z, Chaussidon M, Savage P, et al. Titanium isotopes as a tracer for the plume or island arc affinity of felsic rocks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 01809164. http://www.pnas.org/highwire/filestream/843484/field_highwire_adjunct_files/0/pnas.1809164116.sapp.pdf
[29] Dhuime B, Wuestefeld A, Hawkesworth C J. Emergence of modern continental crust about 3 billion years ago[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8: 552-555. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2466
[30] Næraa T, Schersten A, Rosing M T, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for a transition in the dynamics of continental growth 3.2 Gyr ago[J]. Nature, 2012, 485: 627-630. doi: 10.1038/nature11140
[31] Tang M, Chen K, Rudnick R L. Archean upper crust transition from mafic to felsic marks the onset of plate tectonics[J]. Science, 2016, 351: 372-375. doi: 10.1126/science.aad5513
[32] Smit K V, Shirey S B, Hauri E H, et al. Sulfur isotopes in diamonds reveal differences in continent construction[J]. Science, 2019, 364: 383-385. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000042302748099_26dc.html
[33] Zheng Y F, Zhao G. Two Styles of plate tectonics in Earth's history[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65: 329-334. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.12.029
[34] Condie K C, O'Neill C, Aster R C. Evidence and implications for a widespread magmatic shutdown for 250 My on Earth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 282: 294-298. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.03.033
[35] Brown M. Metamorphic conditions in orogenic belts: A record of secular change[J]. Int. Geol. Rev., 2007, 49: 193-234. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.3.193
[36] Brown M, Johnson T, Gardiner N J. Plate tectonics and the Archean Earth[J]. Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2020, 48: 12.1-12.30. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-071719-054845
[37] Herzberg C, Condie K, Korenaga J. Thermal history of the Earth and its petrological expression[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 292: 79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.01.022
[38] Korenaga J. Initiation and evolution of plate tectonics on Earth: theories and observations[J]. Annual Reviewof Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2013, 41: 117-151. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-050212-124208
[39] Moyen J F, Laurent O. Archaean tectonic systems: A view from igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 2018, 302/303: 99-125. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.11.038
[40] 张旗, 王焰, 熊小林, 等. 埃达克岩和花岗岩: 挑战与机遇[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008.
[41] Lenardic A. The diversity of tectonic modes and thoughts about transitions between them[J]. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A., 2018, 376: 20170416. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2017.0416
[42] Hamilton W B. Archean magmatism and deformation were not products of plate tectonics[J]. Precambrian Research, 1998, 91: 143-179. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926898000424
[43] Davies G F. On the emergence of plate tectonics[J]. Geology, 1992, 20: 963-966. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0963:OTEOPT>2.3.CO;2
[44] Arndt N T. Formation and evolution of the continental crust[J]. Geochemical Perspectives, 2014, 2(3): 436-504. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/273042540_Formation_and_Evolution_of_the_Continental_Crust
[45] Stern R J. 板块构造启动的时间和机制: 理论和经验探索[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(5): 489-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.05.001
[46] Van Hunen J. Onset and evolution of plate tectonics: Geodynamical constraints[J]. Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/13978-0-12-409548-9.10861-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/13978-0-12-409548-9.10861-9.
[47] Zhai M G, Peng P. Origin of early continents and beginning of plate tectonics[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65: 970-973. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.03.022
[48] Moyen J F, van Hunen J. Short term episodicity of Archaean subduction[J]. Geology, 2012, 40: 451-454. doi: 10.1130/G322894.1
[49] Sleep N H. Evolution of the mode of convection within terrestrial planets[J]. Journal of Geophyical Research: Planets(1991-2012), 2000, 105(E7): 17563-17578. doi: 10.1029/2000JE001240
[50] Frisch W, Meschede M, Blakey R. Plate tectonics[M]. Springer, 2011.
[51] 翟明国, 赵磊, 祝禧艳, 等. 早期大陆与板块构造启动——前沿热点介绍与展望[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(8): 2249-2275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202008002.htm
[52] Peacock S M. Thermal structure and metamorphic evolution of subducting slabs[J]. American Geophysical Union, 2003, 138: 7-22.
[53] 赵振华. 地质历史中板块构造启动时间[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(1): 1-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201701001.htm
[54] Peltonen P, Kontinen A, Huhma H. Petrology and geochemistry of metabasalts from the 1.95 Ga Jormua ophiolite, northeastern Finland[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37: 1359-1383. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036555276110_9787.html
[55] Scott D J, Helmstaedt H, Bickle M J. Purtuniq ophiolite, Cape Smith belt, northern Quebec, Canada: A reconstructed section of early Proterozoic oceanic crust[J]. Geology, 1992, 20: 173-176. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039833809810_343e.html
-



 下载:
下载: