Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil and Rice in Farmland around the Copper-Lead-Zinc Tailing, Western Hubei Province
-
摘要:
农田土壤污染导致的粮食安全问题已引起广泛关注,客观评价尾矿库周边农田土壤和农作物污染状况对后期土壤污染防治和安全利用具有重要意义。为研究鄂西某铜铅锌尾矿库周边农田土壤-水稻重金属污染状况及风险,本文同步采集50个点位农田土壤及水稻稻穗样品,应用电感耦合等离子体质谱/发射光谱、原子荧光光谱等方法测定As、Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn、Hg、Ni和Cr八种重金属含量及土壤pH值,采用潜在生态风险指数法和健康风险评估模型评价生态风险和健康风险。结果表明:①研究区土壤As、Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn存在超标,Cd超标率20%最大。水稻仅Cd超标,超标率14%。②相关性分析显示土壤重金属有相同的污染源,渗滤液泄漏是可能的污染源;水稻重金属与土壤具有正相关性,Cd元素相关性最强,可能由于水稻对土壤Cd吸收能力强。③潜在生态风险评价结果表明土壤Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu显著富集,Cd富集系数达4.41,研究区处于中度风险,6%点位具有极强风险。④健康风险评价结果表明几乎全部点位土壤总致癌风险和总非致癌风险大于可接受水平,存在重金属致癌风险,As和Cd致癌风险较大。水稻总致癌风险全部大于可接受水平,最大贡献者为Cd;总非致癌风险全部在可接受水平内。综上,该尾矿库周边农田土壤和水稻已受到重金属污染,存在一定的生态风险,对当地居民健康造成的风险值得重视。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The food security problem caused by heavy metal pollution in farmland soil has attracted widespread attention. Objective pollution investigation and evaluation work is of great significance for the later pollution prevention and safe utilization of soil.
OBJECTIVES To fully understand the heavy metal contamination condition, ecological risk and human health risk of soil and rice in the farmland around the copper-lead-zinc tailing pond in Western Hubei Province.
METHODS 50 sites of topsoil and rice were investigated systematically. ICP-MS, ICP-OES and AFS were used to determine the contents of eight heavy metals (As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Hg, Ni, Cr), as well as the pH value of the soil. The potential ecological risk index method and human health risk assessment model were used to evaluate the potential ecological risk and health risk of soil and rice.
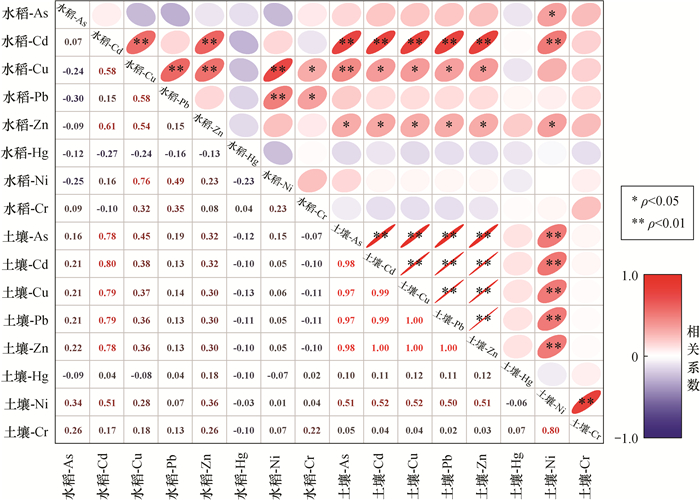
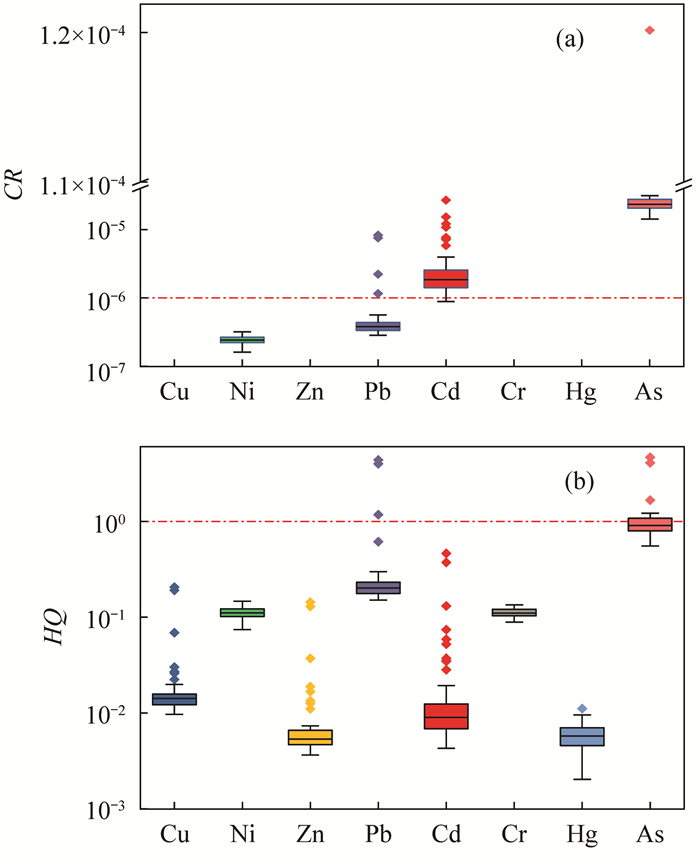
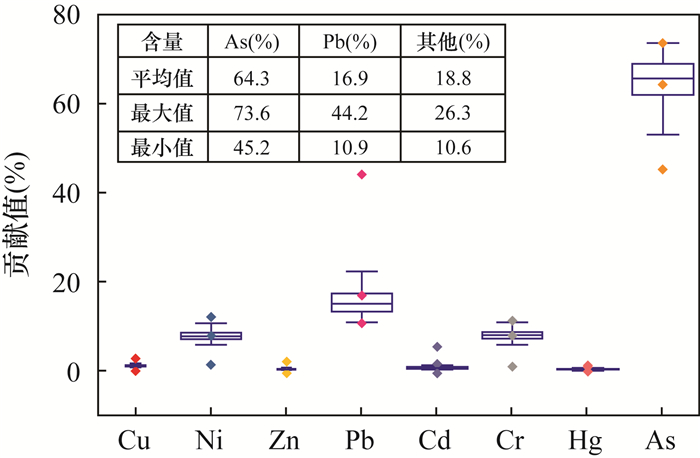
RESULTS The results indicate that: (1) The contents of As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the soil exceed the standard, with the maximum exceedance rate of Cd being 20%. Only Cd in rice exceeds the standard with the exceedance rate of 14%. (2) Correlation analysis shows that soil heavy metals have the same pollution source, and leachate leakage is a possible source of pollution. There is a positive correlation between the heavy metals in rice and the surface soil, with the strongest correlation for Cd, which may be related to the strong absorption capacity of rice for soil Cd. (3) The evaluation results of potential ecological risk index show that Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu are significantly enriched in the soil, with the Cd enrichment coefficient of 4.41. The overall ecological risk is moderate, with 6% of the sites having very strong potential ecological risk. (4) The results of the health risk assessment indicate that the total and non-total carcinogenic risks are greater than the acceptable level at almost all sites. There is an overall risk of heavy metal carcinogenicity in the soil, with As and Cd being the major contributors. The total non-carcinogenic risk for rice at almost all sites in the study area is greater than the acceptable level, with Cd being the largest contributor. The total non-carcinogenic risk for rice at all sites is within the acceptable level.
CONCLUSIONS The soil and rice in the vicinity of the tailings pond have been contaminated by heavy metals, posing a certain ecological risk, and the risks to the health of the local population should be taken into account.
-

-
表 1 健康风险评价模型计算公式
Table 1. Calculation formula of health risk assessment model
参数 计算公式 经口摄入 $ C D I_{\text {ingestion-soil }}=\frac{C_{\mathrm{i}} \times I R_{\text {soil }} \times C F \times E F \times E D}{B W \times A T}$ 皮肤接触 $ C D I_{\text {dermal-soil }}=\frac{C_{\mathrm{i}} \times S A \times A F \times A B S_{\mathrm{d}} \times C F \times E F \times E D}{B W \times A T}$ 呼吸摄入 $ C D I_{\text {inhale-soil }}=\frac{C_{\mathrm{i}} \times I R_{\text {air }} \times E F \times E D}{P E F \times B W \times A T}$ 食物摄入 $ C D I_{\text {oral }-\text { crop }}=\frac{C_{\mathrm{i}} \times I R_{\text {crop }} \times C F \times E F \times E D}{B W \times A T}$ 致癌风险 $ C R_{\mathrm{i}}=\sum\limits_{j=1}^3 C D I_{\mathrm{ij}} \times S F_{\mathrm{ij}}$ $ T C R=\sum\limits_{i=1} C R_{\mathrm{i}}$ 非致癌风险 $ H Q_{\mathrm{i}}=\sum\limits_{\mathrm{j}=1}^3 C D I_{\mathrm{ij}} / R f D_{\mathrm{ij}}$ $ H I=\sum\limits_{\mathrm{i}=1} H Q_{\mathrm{i}}$ 表 2 健康风险评价暴露参数
Table 2. Health risk assessment exposure parameters
参数 参数含义 成人 儿童 BW 平均体重(kg) 61.8 19.2 IRsoil 经口摄入速率(mg/d) 100 200 IRair 空气摄入速率(m3/d) 14.5 7.5 IRcrop 食物摄入速率(mg/d) 328 198 CF 转换因子(kg/mg) 1.00×10-6 1.00×10-6 EF 暴露频率(d/a) 350 350 ED 暴露年限(a) 24 6 SA 暴露皮肤表面积(cm2) 5374 2484 AF 皮肤对土壤黏附系数(mg·cm2) 0.07 0.2 PEF 土壤颗粒物扩散因子(m3/kg) 1.55×107 1.55×107 ABSd 皮肤吸收因子 As(0.03), Cd(0.001) AT 平均暴露时间(d) 27740(致癌), 2190(非致癌) 注:IRcrop参数来源于Mao等[34],其他参数均来源于HJ 25.3—2019。 表 3 重金属不同暴露途径参考计量(RfD)和致癌斜率因子(SF)
Table 3. Reference dose (RfD) and cancer slope factor (SF) of heavy metals by different exposed ways
暴露途径 参数 非致癌暴露参考剂量和致癌斜率因子 Cu Ni Zn Pb Cd Cr Hg As 经口摄入 RfD[mg/(kg·d)] 4.00×10-2 2.00×10-2 3.00×10-1 3.50×10-3 1.00×10-3 3.00×10-3 3.00×10-4 3.00×10-4 SF[kg·d/mg] / / / 8.50×10-3 6.10 5.00×10-1 / 1.50 皮肤接触 RfD[mg/(kg·d)] / / / 2.50×10-5 / / 3.00×10-4 SF[kg·d/mg] / / / 8.50×10-3 2.44×102 2.00 / 1.50 呼吸摄入 RfD [mg/(kg·d)] 1.20×10-2 2.11×10-5 3.00×10-1 2.89×10-3 2.35×10-6 2.35×10-5 7.04×10-5 3.52×10-6 SF [kg·d/mg] 1.11 / / 7.67 5.11×101 / 1.83×101 食物摄入 RfD [mg/(kg·d)] 4.00×10-2 2.00×10-2 3.00×10-1 3.50×10-3 1.00×10-3 3.00×10-3 3.00×10-4 3.00×10-4 SF [kg·d/mg] / / / 8.50×10-3 6.10 5.00×10-1 / 1.50 注:“/”表示HJ 25.3—2019暂无参考值及相应计算值。 表 4 研究区土壤重金属含量和pH值结果统计
Table 4. Statistics of heavy metals content and pH of farmland soil from the study area
参数 pH(无量纲) As Cd Cu Pb Zn Hg Ni Cr 平均值(mg/kg) 6.98 12.3 0.76 46.2 68.1 182 0.057 33.9 74.8 中位数(mg/kg) 7.02 10.6 0.21 28.2 35.2 80.2 0.057 33.6 74.2 最大值(mg/kg) 8.15 54.1 10.8 409 763 2151 0.109 44.5 90.3 最小值(mg/kg) 4.97 6.41 0.10 19.3 26.3 54.7 0.020 22.5 59.6 湖北省背景值[32](mg/kg) / 12.3 0.172 30.7 26.7 83.6 0.08 37.3 86.0 超筛选值点位数 / 2 10 4 4 5 0 0 0 超标率% / 4 20 8 8 10 0 0 0 注:“/”表示无标准限值及相应计算值。 表 5 研究区水稻重金属含量特征
Table 5. Characteristics of heavy metal contents in rice from the study area
参数 As(mg/kg) Cd (μg/kg) Cu (mg/kg) Pb(mg/kg) Zn (mg/kg) Hg (μg/kg) Ni (mg/kg) Cr (mg/kg) 标准限值 0.5 200 / 0.2 / 20 / 1.0 平均值 0.29 197 3.85 0.075 22.2 3.48 0.26 0.18 中位值 0.31 60.7 3.59 0.077 21.8 3.60 0.22 0.15 最大 0.46 2078 8.95 0.196 34.3 6.27 0.78 0.58 最小值 0.13 10.3 2.18 0.050 15.1 0.50 0.11 0.11 超标数 0 7 / 0 / 0 / 0 超标率(%) 0 14.0 / 0 / 0 / 0 注:“/”表示无标准限值及相应计算值。 表 6 农田土壤不同重金属富集系数(Cif)和潜在生态风险(Ei)评价结果
Table 6. Assessment of enrichment factor (Cif) and potential ecological risk (Ei) of different heavy metals in farmland soil
参数 As Cd Cu Pb Zn Hg Ni Cr 富集系数(Cif) 平均值 1.00 4.41 1.50 2.55 2.17 0.72 0.91 0.87 中位数 0.86 1.22 0.92 1.32 0.96 0.71 0.90 0.86 最大值 4.40 62.8 13.3 28.6 25.7 1.36 1.19 1.05 最小值 0.52 0.58 0.63 0.99 0.65 0.25 0.60 0.69 潜在生态风险(Ei) 平均值 10.0 132 7.52 12.8 2.17 28.7 4.54 1.74 中位数 8.58 36.6 4.59 6.58 0.96 28.3 4.50 1.73 最大值 44.0 1884 66.6 143 25.7 54.5 5.97 2.10 最小值 5.21 17.4 3.14 4.93 0.65 10.0 3.02 1.39 表 7 农田土壤和水稻中不同暴露途径重金属致癌风险和非致癌风险
Table 7. Carcinogenic risk and non-carcinogenic risk of heavy metals via different pathways in farmland soil and rice
风险类别 暴露途径 Cu Ni Zn Pb Cd Cr Hg As 合计 致癌风险(CR) 经口摄入 / / / 7.40×10-7 5.92×10-6 / / 2.36×10-5 3.02×10-5 皮肤摄入 / / / / 7.57×10-7 / / 2.26×10-6 3.02×10-6 呼吸吸入 / 2.45×10-7 / / 3.79×10-8 / / 1.47×10-6 1.75×10-6 合计 / 2.45×10-7 / 7.40×10-7 6.71×10-6 / / 2.73×10-5 3.50×10-5 非致癌风险(HQ) 经口摄入 2.30×10-2 3.39×10-2 1.21×10-2 3.89×10-1 1.52×10-2 9.96×10-4 5.79×10-3 8.19×10-1 1.30 皮肤摄入 / / / / 1.73×10-3 / / 7.00×10-2 7.17×10-2 呼吸吸入 1.86×10-4 7.78×10-2 2.94×10-5 1.14×10-3 1.57×10-2 1.10×10-1 5.99×10-5 1.69×10-1 3.75×10-1 合计 2.32×10-2 1.12×10-1 1.21×10-2 3.90×10-1 3.26×10-2 1.11×10-1 5.85×10-3 1.06 1.74 致癌风险(CR) 水稻摄入 / / / 1.73×10-9 2.87×10-6 / / 1.05×10-6 3.92×10-6 非致癌风险(HQ) 水稻摄入 1.90×10-3 2.59×10-4 1.47×10-3 4.82×10-4 3.89×10-3 2.36×10-6 3.48×10-4 1.94×10-2 2.77×10-2 注:“/”表示无参考值及相应计算值。 -
[1] 张明超, 李景朝, 李鹏远, 等. 国内外铅锌矿资源及分布概述[J]. 中国矿业, 2016, 25(S1): 41-45, 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2016S1012.htm
Zhang M C, Li J C, Li P Y, et al. Summarize on the lead and zinc ore resources of the world and China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2016, 25(S1): 41-45, 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2016S1012.htm
[2] 郭尚其, 农泽喜, 周洁军. 铅锌矿开发对环境污染的调查分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(2): 336-341, 347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201902021.htm
Guo S Q, Nong Z X, Zhou J J. Investigation and analysis on environmental pollution caused by Pb-Zn deposit development[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2019, 33(2): 336-341, 347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201902021.htm
[3] Kan X, Dong Y, Feng L, et al. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China's lead-zinc mine tailings: A meta-analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 267: 128909. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33187663
[4] 王洋洋, 李方方, 王笑阳, 等. 铅锌冶炼厂周边农田土壤重金属污染空间分布特征及风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 437-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201901053.htm
Wang Y Y, Li F F, Wang X Y, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface farmland soil around a lead and zinc smelter[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 437-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201901053.htm
[5] 徐芹磊, 陈炎辉, 谢团辉, 等. 铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属污染现状与评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(2): 176-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201802027.htm
Xu Q L, Chen Y H, Xie T H, et al. Current situation and assessment of heavy metals pollution in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(2): 176-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201802027.htm
[6] 田美玲, 钟雪梅, 张云霞, 等. 矿业活动影响区稻田土壤和稻米中重金属含量及健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2919-2926. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806049.htm
Tian M L, Zhong X M, Zhang Y X, et al. Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metal contents in soil and rice of mine contaminated areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2919-2926. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806049.htm
[7] 冯宇佳, 赵全利, 孙洪欣, 等. 华北地区菜田土壤-蔬菜重金属污染状况和健康风险评价[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2017, 40(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT201701001.htm
Feng Y J, Zhao Q L, Sun H X, et al. Assessment of soil-vegetable contamination and health risk of heavy metals in vegetables around North China[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2017, 40(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT201701001.htm
[8] 毛香菊, 卞孝东, 肖芳, 等. 某铜矿区水土环境重金属污染及其农作物效应[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(5): 131-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH201805024.htm
Mao X J, Bian X D, Xiao F, et al. Heavy metal elements pollution and crop effect of a copper mine[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(5): 131-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH201805024.htm
[9] 高娟琴, 于扬, 王登红, 等. 川西甲基卡锂资源富集区根系土壤重金属含量水平及时空分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 681-692. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201812190137
Gao J Q, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. The content and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in root soils in the Jiajika Lithium Resource Area, western Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 681-692. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201812190137
[10] 杨维鸽, 赵培, 李美兰, 等. 秦岭山区尾矿库周边耕地土壤重金属污染特征研究[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 2021(3): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNNY202103004.htm
Yang W G, Zhao P, Li M L, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metal pollution in cultivated land around tailings reservoir in Shangzhou[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2021(3): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNNY202103004.htm
[11] 罗改, 谭晓莲. 金阳县丝窝土地开发区土壤重金属污染现状及生态风险评价[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2019, 39(10): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNCX201910013.htm
Luo G, Tan X L. Pollution situation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil in Siwo land development zone, Jinyang Country[J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2019, 39(10): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNCX201910013.htm
[12] 白婧, 张文, 张思思, 等. 锡矿山土壤重金属生态健康风险评价及重金属在优势植物的分布[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(3): 411-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ202103008.htm
Bai J, Zhang W, Zhang S S, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and their distribution in dominant plants in the Xikuangshan mining area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(3): 411-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ202103008.htm
[13] 王文华, 赵晨, 赵俊霞, 等. 包头某稀土尾矿库周边土壤重金属污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 金属矿山, 2017, 46(7): 168-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201707036.htm
Wang W H, Zhao C, Zhao J X, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around rare tailings in Baotou[J]. Metal Mine, 2017, 46(7): 168-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201707036.htm
[14] 于沨, 王伟, 于扬, 等. 川西九龙地区锂铍矿区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
Yu F, Wang W, Yu Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Jiulong Li-Be mining area, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 408-424. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
[15] 方传棣, 成金华, 赵鹏大, 等. 长江经济带矿区土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 230-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905025.htm
Fang C D, Cheng J H, Zhao P D, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soils of mining areas in the Yangtze River Economic Belt[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 230-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905025.htm
[16] 宋绵, 龚磊, 王艳, 等. 河北阜平县表层土壤重金属对人体健康的风险评估[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 133-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202109290135
Song M, Gong L, Wang Y, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil on human health in Fuping County, Hebei Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 133-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202109290135
[17] 梁雅雅, 易筱筠, 党志, 等. 某铅锌尾矿库周边农田土壤重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(1): 103-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201901015.htm
Liang Y Y, Yi X Y, Dang Z, et al. Pollution and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around a Pb-Zn tailing pond[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(1): 103-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201901015.htm
[18] 能子礼超, 勾琴, 刘盛余, 等. 模糊数学法综合评价土壤重金属污染程度研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2020, 42(7): 39-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT202007009.htm
Nengzi L C, Gou Q, Liu S Y, et al. Study on comprehensive evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution degree by fuzzy mathematics method[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2020, 42(7): 39-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT202007009.htm
[19] 刘晓媛, 刘品祯, 杜启露, 等. 地质高背景区铅锌矿废弃地土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019(2): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201902017.htm
Liu X Y, Liu P Z, Du Q L, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soil of lead-zinc mine wasteland with geological high background[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2019(2): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201902017.htm
[20] 郭绍英, 林皓, 谢妤, 等. 基于改进灰色聚类法的矿区土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(10): 146-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201710031.htm
Guo S Y, Lin H, Xie Y, et al. Evaluation on heavy metal pollution in soil of mining area based on improved grey clustering method[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(10): 146-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201710031.htm
[21] 包扬, 苏德, 杨巍, 等. 铜尾矿库土壤修复效应及周边植被恢复模式研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1): 86-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202201007.htm
Bao Y, Su D, Yang W, et al. Study on soil remediation effect of copper tailings pond and surrounding vegetation restoration model[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1): 86-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202201007.htm
[22] 彭丽梅, 赵理, 周悟, 等. 基于层次分析法的耕地土壤重金属污染风险区域划分[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(5): 61-67 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXB202005009.htm
Peng L M, Zhao L, Zhou W, et al. Regional classification of heavy metal pollution risk in cultivated soil based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2020, 39(5): 61-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXB202005009.htm
[23] 王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等. 一种农田土壤重金属影响评价的新方法: 土壤和农产品综合质量指数法[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7): 1225-1232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201607001.htm
Wang Y J, Liu C, Zhou D M, et al. A new approach for evaluating soil heavy metal impact: A comprehensive index combined soil environmental quality and agricultural products quality[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7): 1225-1232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201607001.htm
[24] 张耀, 孙刚, 王琪, 等. 湖北某铅锌矿区农用地重金属调查与类别划分[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(2): 139-145, 205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202202022.htm
Zhang Y, Sun G, Wang Q, et al. Investigation and classification of heavy metals in agricultural land in a lead-zinc mining area in Hubei Province[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(2): 139-145, 205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202202022.htm
[25] 蔡立梅, 王秋爽, 罗杰, 等. 湖北大冶铜绿山矿区蔬菜重金属污染特征及健康风险研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(4): 873-881. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201804020.htm
Cai L M, Wang Q S, Luo J, et al. Contamination characteristics and health risk for heavy metals via consumption of vegetables grown in regions affected by Tonglvshan mine in Hubei, China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(4): 873-881. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201804020.htm
[26] 陈家乐, 相满城, 唐林茜, 等. 运积型地质高背景稻田土壤重金属污染和人体健康风险评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2334-2340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ202108006.htm
Chen J L, Xiang M C, Tang L Q, et al. Assessing heavy metal pollution and human health risk of paddy soil with high geological background of transportation and deposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(8): 2334-2340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ202108006.htm
[27] 张浩, 王辉, 汤红妍, 等. 铅锌尾矿库土壤和蔬菜重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 1085-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202003035.htm
Zhang H, Wang H, Tang H Y, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risk evaluation of soil and vegetables in various functional areas of lead-zinc tailings pond[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 1085-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202003035.htm
[28] 陶美霞, 胡虎, 胡兰文, 等. 上饶市某铜矿废弃地土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(6): 1153-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201806021.htm
Tao M X, Hu H, Hu L W, el al. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in polluted abandon soil of Shangrao, Jiangxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(6): 1153-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201806021.htm
[29] 张云, 胡正生, 王一艳, 等. 某氧化铜矿尾矿区重金属污染特征及农作物健康风险评价[J]. 有色金属工程, 2021, 11(4): 125-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS202104018.htm
Zhang Y, Hu Z S, Wang Y Y, et al. Heavy metals pollution characteristics and crop health risk assessment around a copper oxide tailings pond[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2021, 11(4): 125-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS202104018.htm
[30] 张成丽, 张伟平, 程红丹, 等. 禹州市煤矿区周边土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 805-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201904012.htm
Zhang C L, Zhang W P, Cheng H L, et al. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment of farmland soil around coalmines in Yuzhou City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 805-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201904012.htm
[31] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.
[32] 国家环境保护局. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
State Environmental Protection Administration. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
[33] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS200802029.htm
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Jiang X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS200802029.htm
[34] Mao C P, Song Y X, Chen L X, et al. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice[J]. Catena, 2019, 175: 339-348.
[35] 周墨, 唐志敏, 张明, 等. 江西赣州地区土壤-水稻系统重金属含量特征及健康风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(12): 2149-2158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202112017.htm
Zhou M, Tang Z M, Zhang M, et al. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-rice system in the Ganzhou area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(12): 2149-2158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202112017.htm
[36] 宋波, 王佛鹏, 周浪, 等. 广西高镉异常区水田土壤Cd含量特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2443-2452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201905053.htm
Song B, Wang F P, Zhou L, et al. Cd content characteristics and ecological risk assessment of paddy soil in high cadmium anomaly area of Guangxi[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(5): 2443-2452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201905053.htm
[37] Zhao F J, Wang P. Arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice and mitigation strategies[J]. Plant and Soil, 2020, 446: 1-21.
[38] 孙慧, 毕如田, 郭颖, 等. 广东省土壤重金属溯源及污染源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2): 704-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201802033.htm
Sun H, Bi R T, Guo Y, et al. Source apportionment analysis of trace metal contamination in soils of Guangdong Province, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2): 704-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201802033.htm
[39] 毛竹, 张世熔, 李婷, 等. 铅锌矿区土壤重金属空间变异及其污染风险评价——以四川汉源富泉铅锌矿山为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(2): 617-621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200702040.htm
Mao Z, Zhang S R, Li T, et al. Spatial variability and environmental pollution assessment of soil heavy metal in the vicinity of a lead/zine mine—A case study from Fuquan lead/zine mine in Hanyuan County[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(2): 617-621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200702040.htm
[40] Sun Z, Xie X, Wang P, et al. Heavy metal pollution caused by small-scale metal ore mining activities: A case study from a polymetallic mine in South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 217-227.
[41] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1625-1636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006003.htm
Bao L R, Deng H, Jia Z M, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1625-1636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006003.htm
-




 下载:
下载: