New Analysis of the Ore-controlling Structure and Gold Mineralization Model in the Southwest Section of the Xuefeng Arcuate Structural Belt
-
摘要:
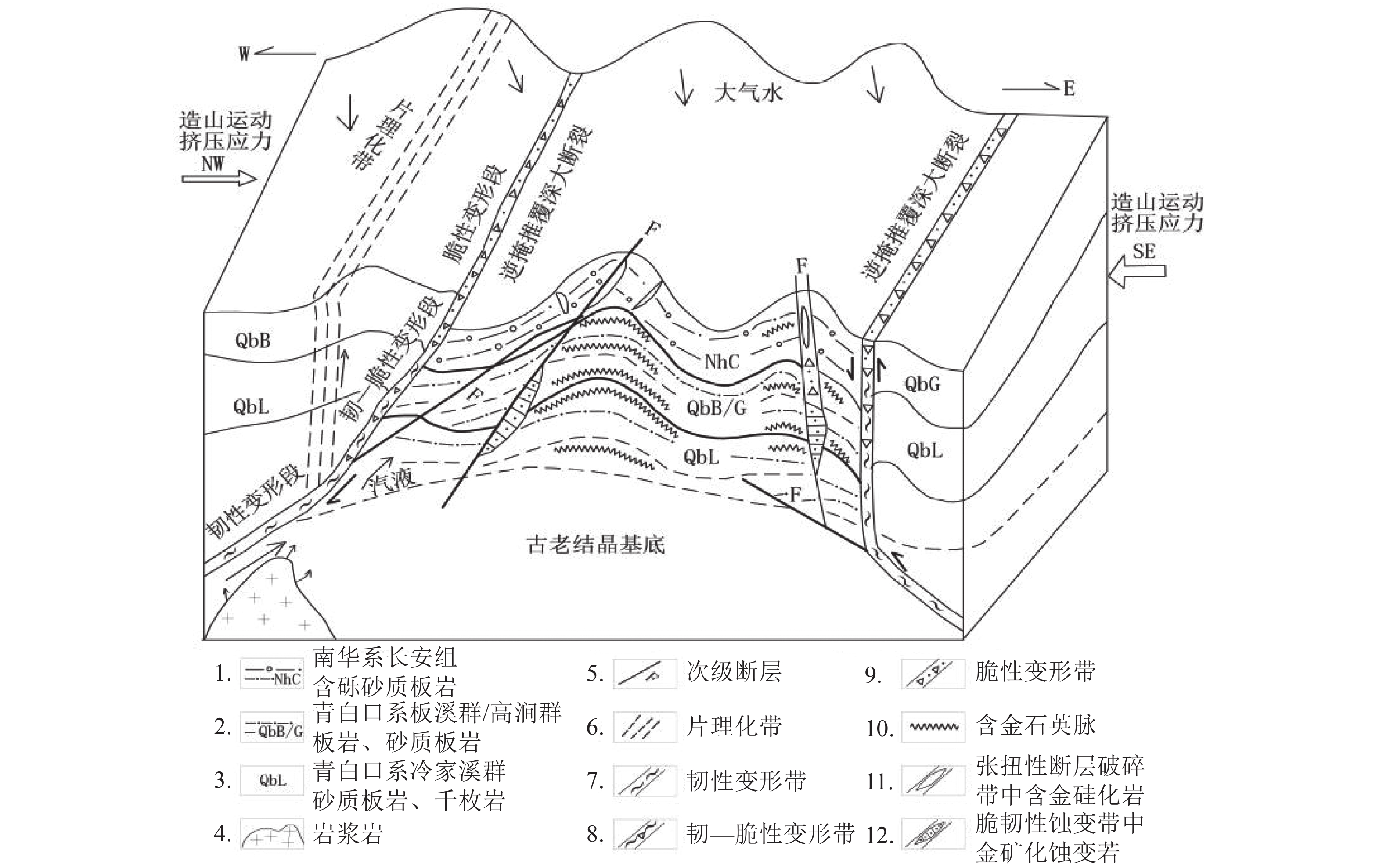
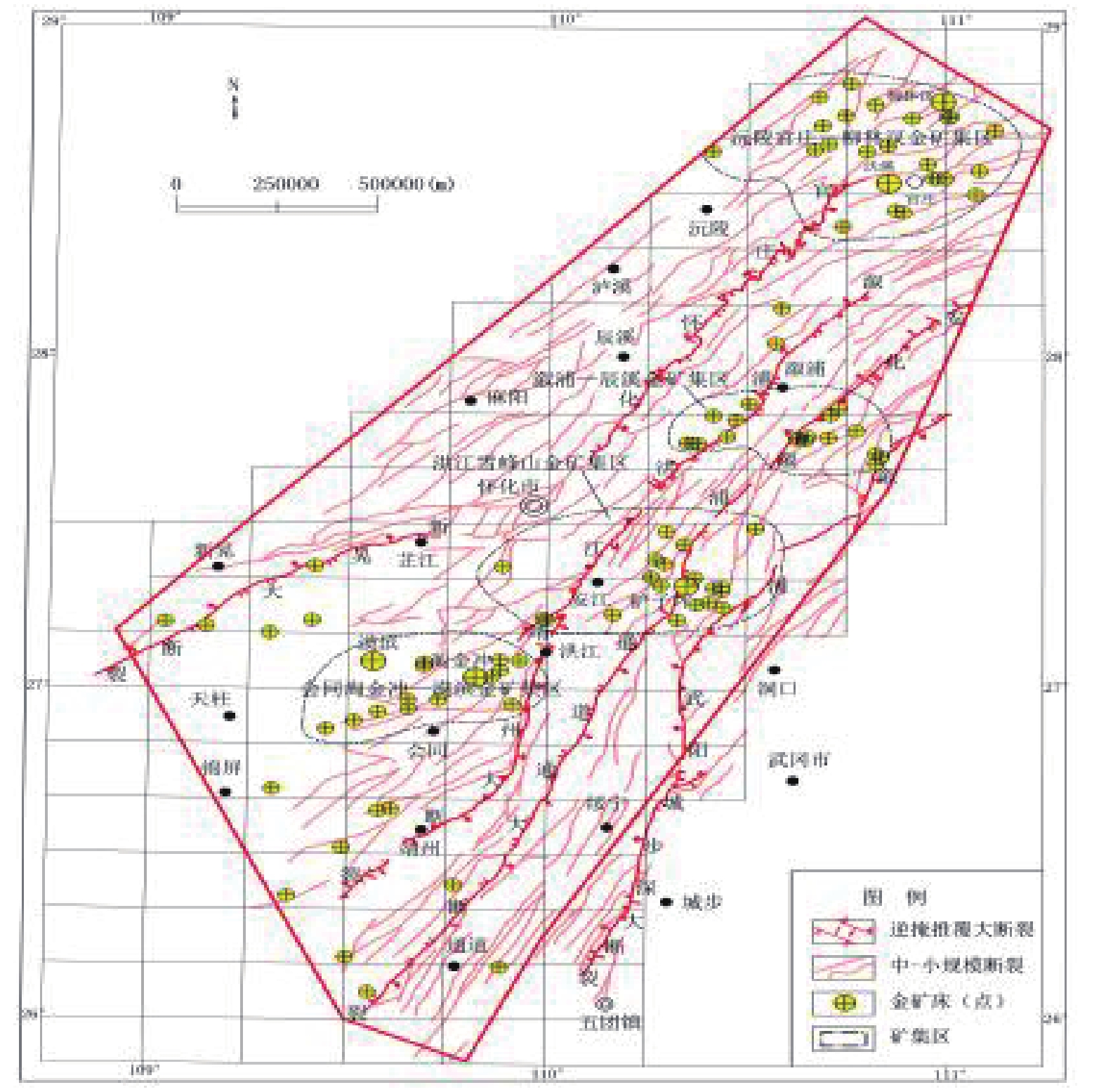
这是一篇地球科学领域的论文。雪峰弧形构造带西南段是湖南最重要的金矿成矿区带。该区新元古界青白口系冷家溪群、板溪群/高涧群和南华系是主要赋金层位。本文以研究区赋矿地层、容矿围岩、导矿构造、容矿构造为基础,从构造控矿规律及成矿模式方面进行综合研究。结果表明,该区构造控矿在金的成矿过程中起关键作用,沅陵—怀化—新晃、溆浦—洪江—靖州、安化—溆浦—通道、新化—武阳—城步四条推覆型深大断裂为主要导矿构造,控制着矿集区分布;NE向次级断裂及伴生的褶皱-冲断系统、NW向断裂、区域复背斜与轴部断层联合部位、脆-韧性剪切带和剪切裂隙及劈(片)理化带是主要容矿构造,控制着矿体最终空间定位。通过分析构造控矿规律,包括区域构造控制矿床成带成区分布、构造运动多旋迴迭加形成“三期二向”构造迭加部位富集成矿、脆-韧性构造系统控制矿体垂向分布以及特定构造部位富集成矿,建立了该区金矿复合成矿模式。
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of earth science. The southwest section of the Xuefeng arc structure is the most important gold ore mineralization zone in Hunan. The Lower Paleozoic Qingbaikou Formation, including the Coldjiaxi Group, Banxi Group, Gaojian Group, and Nanhua Formation, are the main gold-bearing strata in this area. Based on the study of ore-forming strata, ore-bearing surrounding rock, ore-bearing structure, and orebody structure, the paper forms a comprehensive analysis of tectonic ore-controlling rules and ore-forming models. The results suggest that structural control plays a crucial role in the process of gold mineralization. Guanzhuang-Huaihua-Xinhuang, Xupu-Hongjiang-Jingzhou, Anhua-Xupu-Tongdao, and Xupu-Wuyang-Chengbu are the four main ore-controlling thrust faults controlling the distribution of mineralized areas. The NE-trending secondary faults and associated fold-thrust systems, NW-trending faults, regional anticlines and synclines, brittle-ductile shear zones, and shear fractures and cleavage planes are the main ore-hosting structures that control the final spatial location of the ore bodies. By analyzing the rules of structural control on mineralization, including regional structural control on the distribution of ore deposits, the enrichment of mineralization in the overlapping parts of "three stages and two directions" structural superposition, the control of brittle-ductile structural systems on the vertical distribution of ore bodies, and the enrichment of mineralization in specific structural locations, a composite gold mineralization model has been established for this area.
-

-
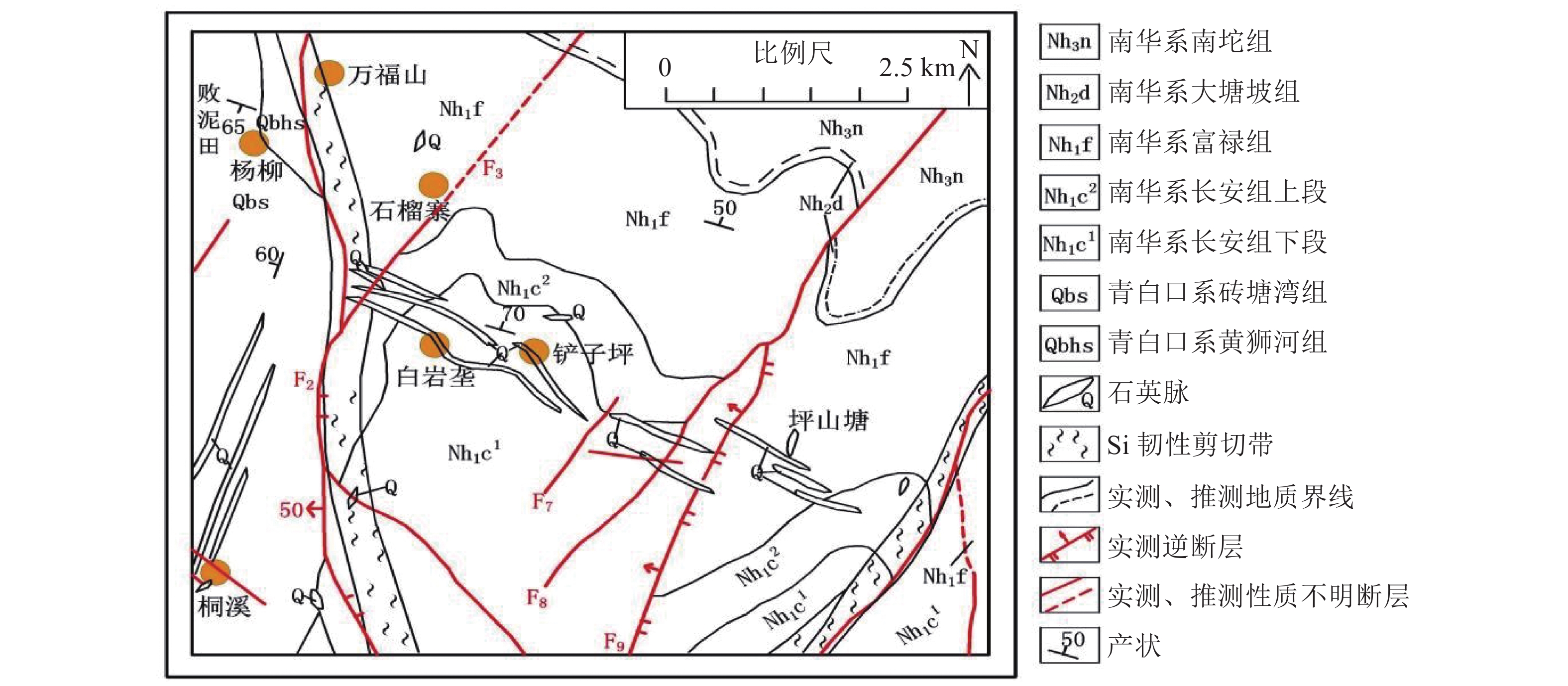
图 2 沃溪金锑钨矿床地质简图(据顾雪祥等[21]修改)
Figure 2.
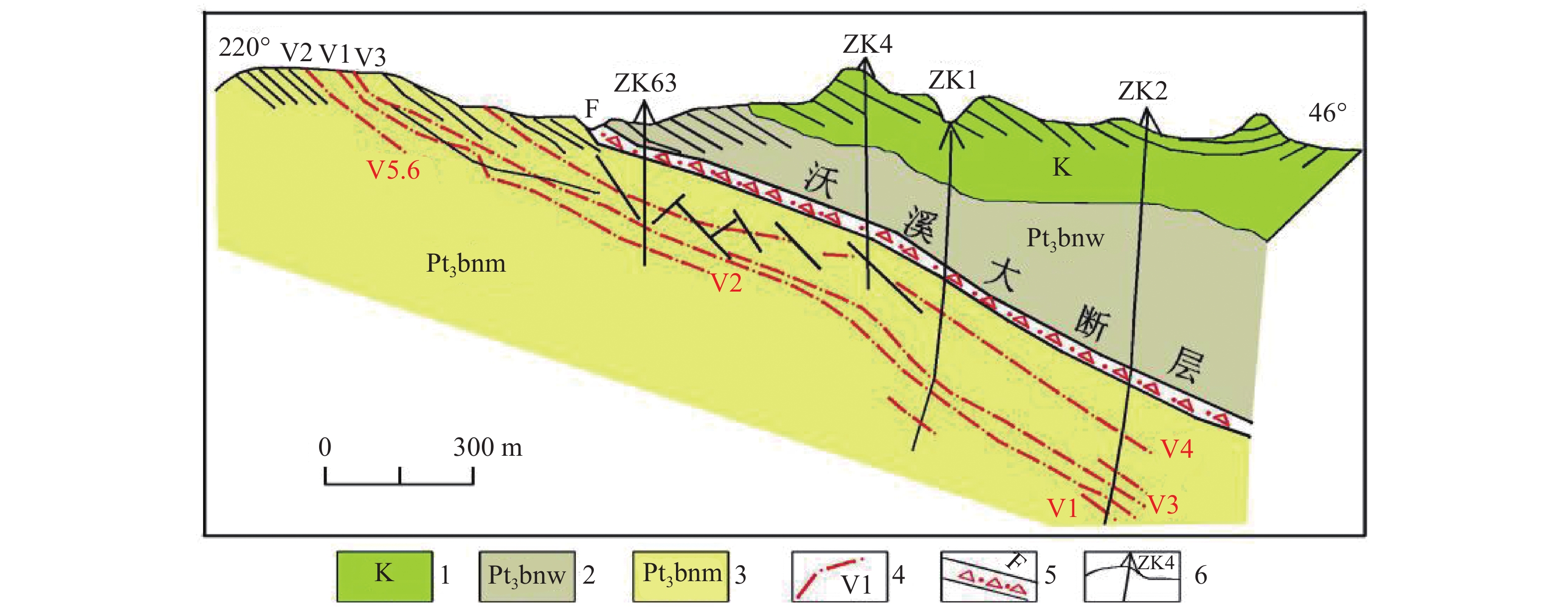
图 3 沃溪金锑钨矿4勘探线剖面(据刘升友等[2]修改)
Figure 3.
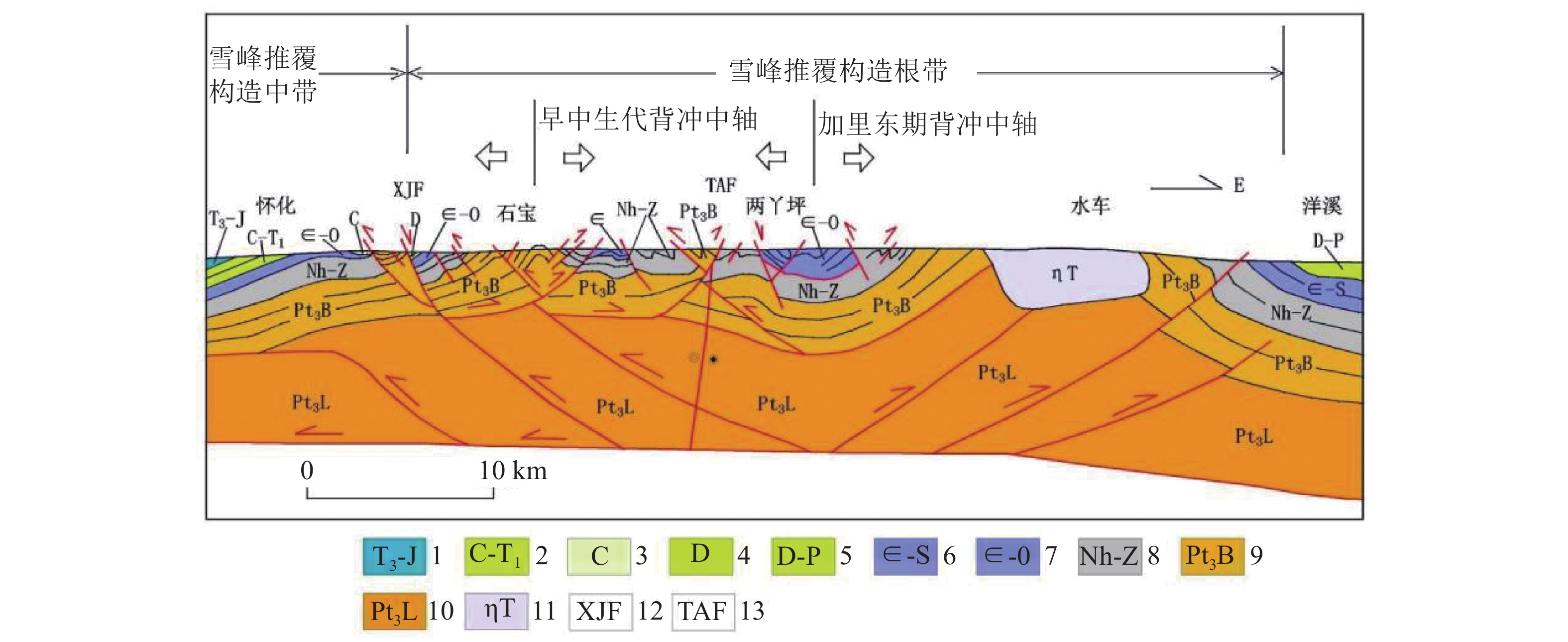
图 4 雪峰造山带中段怀化-洋溪构造剖面(据柏道远等[17]修改)
Figure 4.
表 1 研究区板溪群/高涧群地层对比
Table 1. Stratigraphic correspondence of Banxi Group/Gaojian Group in the study area
系 岩石地层 年龄值 北部地层区 南部地层区
青
白
口
系板溪群 牛牯坪组 高涧群 岩门寨组 800 Ma 百合垅组 多益塘组 五强溪组 架枧田组 通塔湾组 砖墙湾组 820 Ma 马底驿组 黄狮洞组 横路冲组 石桥铺组 宝林冲组 冷家溪群 表 2 雪峰弧形构造带西南段金矿床分类
Table 2. Classification of gold deposits in the southwest section of Xuefeng arcuate structural belt
类型 主要控矿因素 矿例 类 亚类 雪峰造山型 石英脉型 顺层脉 地层层位:青白口系板溪群或高涧群
容矿围岩:板岩、砂质板岩、凝灰质板岩
容矿构造:NE向断层裂隙或层间破碎带
矿体构造:主要由石英单脉组成
矿石类型:含金石英脉型沃溪、柳林汊、
官庄、龙王江、漠滨、
阳湾团、米贝等切层脉 地层层位:青白口系高涧群
容矿围岩:条带状凝灰质板岩、砂质板岩
容矿构造:NW向剪切裂隙带
矿体构造:主要由石英细脉、脉带组成
矿石类型:含金石英型淘金冲、喇叭堂、
青山坨、洞塘、
深溪剪切裂隙脉 地层层位:南华系长安组(富禄组)
容矿围岩:凝灰质长石石英砂岩、粉砂岩
容矿构造:NW向断裂隙
矿体构造:主要由石英细脉、脉带组成
矿石类型:含金石英型响溪、中山、
白岩云、
平茶、茶溪、蚀变岩型 破碎带蚀变岩型 地层层位:南华系长安组
容矿围岩:含砾砂质板岩、砂质板岩
容矿构造:NW向张扭剪切带
矿体构造:主要由强硅化蚀变岩、绢英岩、角砾状蚀变岩组成
矿石类型:含金石英岩、黄铁绢英岩型、蚀变板岩铲子坪、青山洞 韧性剪切带蚀变
岩型地层层位:青白口系高涧群和南华系长安组
容矿围岩:砂质板岩、长石石英砂岩、板岩
容矿构造:NE向韧脆性剪切带
矿体构造:由片理化石英团块和网脉蚀变板岩组成
矿石类型:含金弱硅化蚀变板岩大坪、桐溪、洪江垄 蚀变基性岩型 地层层位:青白口系高涧群
容矿岩性:闪长岩辉、绿岩岩墙
容矿构造:NE向断层破碎带
矿体构造:由石英细脉和网脉蚀变岩组成
矿石类型:含金蚀变闪长岩、辉绿岩型字溪、大洪山、于家湾 表 3 雪峰弧形构造带西南段金矿床(点)产出层位与容矿构造关系统计
Table 3. Statistical of the relationship between the occurrence horizon of gold deposits (points) and the ore-hosting structure in the southwest section of Xuefeng arcuate structural belt
赋矿层位 矿床
(点)数北东
走向北西
走向近东西
走向青白口系板溪群
(高涧群)
(75)马底驿组(24) 24 20 4 五强溪组(51) 51 42 9 南华系下统
(18)长安组(21) 14 3 11 湘锰组(1) 1 1 洪江组(3) 3 3 白垩系(1) 白垩系(1) 1 1 合计 94 70 20 4 -
[1] 罗献林. 湖南金矿床的成矿特征与成因类型[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1991(1):23-33. LUO X L. Main characteristics and genetic types of gold ore deposits in Hunan[J]. Journal of Gulin College of Geology, 1991(1):23-33.
LUO X L . Main characteristics and genetic types of gold ore deposits in Hunan[J]. Journal of Gulin College of Geology, 1991 (1): 23-33.
[2] 刘升友, 鲍振襄, 鲍珏敏. 湖南前寒武系金矿特征及成矿规律[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2013, 29(1):37-45. LIU S Y, BAO Z X, BAO Y M. Gold deposit features and metallogenic regularity of Precambrian in Hunan Province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2013, 29(1):37-45.
LIU S Y, BAO Z X, BAO Y M. Gold deposit features and metallogenic regularity of Precambrian in Hunan Province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2013, 29(1): 37-45.
[3] 李伟, 谢桂青, 张志远, 等. 流体包裹体和C-H-O同位素对湘中古台山金矿床成因制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(11):3489-3506. LI W, XIE G Q, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Constraint on the genesis of Gutaishan gold deposit in central Hunan Province: evidence from fluid inclusion and C–H–O isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(11):3489-3506.
LI W, XIE G Q, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Constraint on the genesis of Gutaishan gold deposit in central Hunan Province: Evidence from fluid inclusion and C–H–O isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(11): 3489-3506.
[4] 江福兵, 毛寅, 孙立吉, 等. 湖南洪江市石榴寨金矿流体包裹体特征及地质意义[J]. 矿产与地质. 2021, 35(3): 467-472.
JIANG F B, MAO Y, SUN L J, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and geological implication of Shiliuzhai gold deposit in Hongjiang City, Hunan[J]. Mineral Resources And Geology. 2021, 35(3): 467-472.
[5] 曹亮, 段其发, 彭三国, 等. 雪峰山铲子坪金矿床流体包裹体特征及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(2):212-224. CAO L, DUAN Q F, PENG S G, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Chanziping gold deposit in western Hunan Province and their geological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(2):212-224. doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2015.02.002
CAO L, DUAN Q F, PENG S G, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Chanziping gold deposit in western Hunan Province and their geological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(2): 212-224. doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2015.02.002
[6] ZHU Y N, PENG J T. Infrared microthermometric and noble gas isotope study of fluid inclusions in ore minerals at the Woxi orogenic Au–Sb–W deposit, western Hunan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65:55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.014
[7] WANG C, SHAO Y J, EVANS N J, et al. Genesis of Zixi gold deposit in Xuefengshan, Jiangnan Orogen (South China): Age, geology and isotopic constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117:103301. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103301
[8] LI W, XIE G Q, MAO J W, et al. Precise age constraints for the Woxi Au–Sb–W deposit, south China[J]. Economic Geology, 2023, 118(2):509-518. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4971
[9] 杨光治, 顾尚义. 江南造山带金矿成矿年龄的讨论[J]. 贵州科学, 2013, 31(3):73-79. YANG G Z, GU S Y. Discussion on mineralization age of gold deposits in Jiangnan orogen[J]. Guizhou Science, 2013, 31(3):73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2013.03.016
YANG G Z, GU S Y. Discussion on mineralization age of gold deposits in Jiangnan orogen[J]. Guizhou Science, 2013, 31(3): 73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2013.03.016
[10] 崔长征, 熊英, 雷引玲. 湖南某锑矿石工艺矿物学研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(3):76-78+82. CUI C Z, XIONG Y, LEI Y L. Research on process mineralogy of antimony ore in Hunan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3):76-78+82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.03.014
CUI C Z, XIONG Y , LEI Y L. Research on process mineralogy of antimony ore in Hunan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3): 76-78+82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.03.014
[11] 蔡光耀, 安芳. 造山型金矿床地质背景、地球化学特征和成矿模型研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6):163-172. CAI G Y, AN F. Review of geological background, geochemical characteristics and ore-forming model of orogenic gold deposits[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2018, 37(6):163-172.
CAI G Y, AN F. Review of geological background, geochemical characteristics and ore-forming model of orogenic gold deposits[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2018, 37(6): 163-172.
[12] CHEN S M, ZHOU Y X, LI B, et al. Genesis of Chaxi gold deposit in Southwestern Hunan Province, Jiangnan Orogen (South China): Constraints from fluid inclusions, H–O–S–Pb isotopes, and pyrite trace element Concentrations[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(7):867. doi: 10.3390/min12070867
[13] 金妮, 金小燕, 刘湘勤, 等. 雪峰弧形成矿带西南段金矿成矿规律及成矿模式研究[J]. 矿产与地质, 2022, 36(3):547-556. JIN N, JIN X Y, LIU X Q, et al. Metallogenic regularity and metallogenic model of gold depositsin the southwest of Xuefeng arc metallogenic belt[J]. Mineral Resources And Geology, 2022, 36(3):547-556.
JIN N, JIN X Y, LIU X Q, et al. Metallogenic regularity and metallogenic model of gold depositsin the southwest of Xuefeng arc metallogenic belt [J]. Mineral Resources And Geology, 2022, 36(3): 547-556.
[14] 邱曼, 黄学雄, 毛益林, 等. 我国金矿资源概况及选冶技术研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2023(2):106-115. QIU M, HUANG X X, MAO Y L, et al. General situation of gold resources and research progress of mineral processing and hydrometallurgy technology in China[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023(2):106-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.02.019
QIU M, HUANG X X, MAO Y L, et al. General situation of gold resources and research progress of mineral processing and hydrometallurgy technology in China[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023(2): 106-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.02.019
[15] 黄建中, 孙骥, 周超, 等. 江南造山带(湖南段)金矿成矿规律与资源潜力[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(2):230-252. HUANG J Z, SUN J, ZHOU C, et al. Metallogenic regularity and resource potential of gold deposits of Hunan area in the Jiangnan orogenic belt, South China[J]. Earth Sciences, 2020, 41(2):230-252. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.020801
HUANG J Z, SUN J, ZHOU C, et al. Metallogenic regularity and resource potential of gold deposits of Hunan area in the Jiangnan orogenic belt, South China[J]. Earth Sciences, 2020, 41(2): 230-252. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.020801
[16] 陈衍景. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1181-1196. CHEN Y J. Orogenic-type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6):1181-1196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.001
CHEN Y J. Orogenic-type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1181-1196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.001
[17] 柏道远, 熊雄, 杨俊, 等. 雪峰造山带中段地质构造特征[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(2):399-418. BO D Y, XIONG X, YANG J, et al. Geological structure characteristics of the middle segment of the Xuefeng Orogen[J]. Chinese Geological, 2014, 41(2):399-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.008
BO D Y, XIONG X , YANG J , et al. Geological structure characteristics of the middle segment of the Xuefeng Orogen[J]. Chinese Geological, 2014, 41(2): 399-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.008
[18] WANG Q F, YANG L, ZHAO H S, et al. Towards a universal model for orogenic gold systems: a perspective based on Chinese examples with geodynamic, temporal, and deposit-scale structural and geochemical diversity[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 103861.
[19] Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al. Orogenic glod deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other Au deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13:7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
[20] 孙玉珍. 湘西沃溪金锑钨矿床成因与沃溪断层的控矿作用分析[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2013, 29(6):1-3+43. SUN Y Z. Discussion on ore genesis of the Woxi Au–Sb–W deposit and ore-controlling role of the Woxi fault[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 29(6):1-3+43.
SUN Y Z. Discussion on ore genesis of the Woxi Au–Sb–W deposit and ore-controlling role of the Woxi fault[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 29(6): 1-3+43.
[21] 顾雪祥, 刘建明, Oskar S, 等. 湖南沃溪金-锑-钨矿床成因的稀土元素地球化学证据[J]. 地球化学, 2005(5):428-442. GU X X, LIU J M, OSKAR S, et al. REE Geochemical evidence for the genesis of Woxi Au–Sb–W deposit, Hunan Province[J]. Geochimica, 2005(5):428-442. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.002
GU X X, LIU J M, OSKAR S, et al. REE Geochemical evidence for the genesis of Woxi Au–Sb–W deposit, Hunan Province[J]. Geochimica, 2005(5): 428-442. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.002
[22] 饶家荣, 王纪恒, 曹一中. 湖南深部构造[J]. 湖南地质, 1993(S1):1-101. RAO J R, WANG J H, CAO Y Z. Hunan deep tectonic[J]. Hunan Geology, 1993(S1):1-101.
RAO J R, WANG J H, CAO Y Z. Hunan deep tectonic[J]. Hunan Geology, 1993(S1): 1-101.
[23] 王先辉, 何江南, 杨俊. 区域地质调查报告(怀化市幅1/25万)[R]. 内部资料, 2014.
WANG X H, HE J N, YANG J. Regional geological survey report (Huaihua City Area 1: 250000) [R]. Internal Information, 2014.
[24] 张俊岭. 湖南省沅陵县柳林汊金矿区矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019(21):60-61. ZHANG J L. Geological characteristics and prospecting criteria of Liulincha gold deposit in Yuanling county, Hunan province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019(21):60-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.21.037
ZHANG J L. Geological characteristics and prospecting criteria of Liulincha gold deposit in Yuanling county, Hunan province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, (21): 60-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.21.037
[25] GROVES D I, SANTOSH M, DENG J, et al. A holistic model for the origin of orogenic gold deposits and its implications for exploration[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55(2):275-92. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00877-5
[26] 彭建堂. 湖南雪峰地区金成矿演化机理探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学. 1999(2): 45-52.
PENG J T. Gold mineralization and its evolution in the Xuefeng district, Hunan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1999(2): 45-52.
[27] 李华芹, 王登红, 陈富文, 等. 湖南雪峰山地区铲子坪和大坪金矿成矿作用年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(7):900-905. LI H Q, WANG D H, CHEN F W, et al. Study on chronlogy of the Chanziping and Daping gold deposit in XueFeng mountains in Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(7):900-905. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.006
LI H Q, WANG D H, CHEN F W, et al. Study on chronlogy of the Chanziping and Daping gold deposit in XueFeng mountains in Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(7): 900-905. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.006
[28] 彭渤, 黄瑞华. 湖南前寒武系脉型金矿床构造成矿机理[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1996(3):201-211. PENG B, HUANG R H. Tectonic metallogenic mechanism of the pre-Cambrian vein type gold deposit in Hunan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1996(3):201-211. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.1996.03.002
PENG B, HUANG R H. Tectonic metallogenic mechanism of the pre-Cambrian vein type gold deposit in Hunan [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1996(3): 201-211. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.1996.03.002
[29] 吕书君, 刘树生, 李永德, 等. 湖南铲子坪金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2019, 35(3):325-336. LV S J, LIU S S, LI Y D, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Chanziping gold deposit in Xuefengshan Area, Hunan Province.[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2019, 35(3):325-336.
LV S J, LIU S S, LI Y D, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Chanziping gold deposit in Xuefengshan Area, Hunan Province. [J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2019, 35(3): 325-336.
[30] CHU Y, LIN W, FAURE M, et al. Phanerozoic tectonothermal events of the Xuefengshan Belt, central South China: Implications from U–Pb age and Lu–Hf determinations of granites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 150:243-55. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.005
[31] 王自强, 高林志, 丁孝忠, 等. “江南造山带”变质基底形成的构造环境及演化特征[J]. 地质论评. 2012. 58(3): 401-413.
WANG Z Q, GAO L Z, DING X Z, et al. Tectonic environment of the metamorphosed basement in the Jiangnan Orogen and its evolutional features[J]. Geological Review . 2012. 58(3): 401-413.
[32] 邱正杰, 范宏瑞, 丛培章, 等. 造山型金矿床成矿过程研究进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(1):21-28. QIU Z J, FAN H R, CHONG P Z, et al. Recent progress in the study of ore-forming processes of orogenic gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(1):21-28. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2015.01.002
QIU Z J, FAN H R, CHONG P Z, et al. Recent progress in the study of ore-forming processes of orogenic gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(1): 21-28. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2015.01.002
-



 下载:
下载: