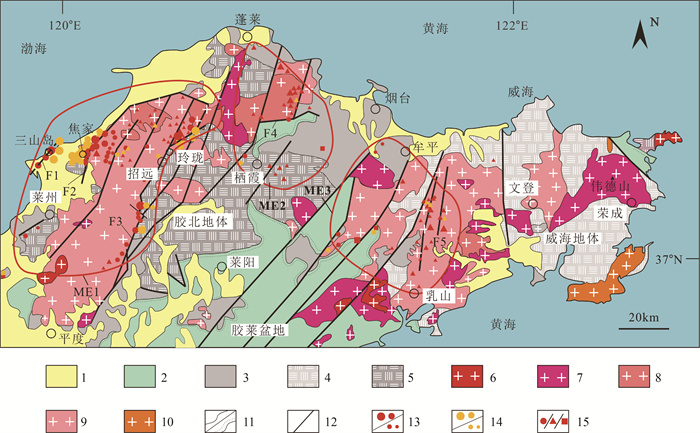
Current progress of metallogenic research and deep prospecting of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peniusula during 10 years for Exploration Breakthrough Strategic Action
-
摘要:
2011年原国土资源部组织实施找矿突破战略行动以来,胶东金矿深部找矿取得了重大成绩,新增金资源量约2958 t,勘查评价了12个大型及以上金矿床,发现了2个超巨型金矿床。胶东地区累计探明金资源量逾5000 t,占全国的1/3。这些成果的取得得益于对成矿构造背景、成矿规律、矿床成因等成矿理论认识的不断深化和勘查技术方法的不断进步。胶东金矿成矿作用及相关研究是国内地学研究的热点之一,总结了近10年胶东金矿成矿背景、矿床分布、成矿时代、矿床地球化学、成矿模式、矿床成因等方面的研究进展或突破,尤其是对深部成矿模式、大规模成矿机制等研究取得的原创性成果。研究表明,胶东金矿形成于埃达克性质花岗岩转化为弧花岗岩的岩浆活动背景,岩浆岩和岩石圈地幔地球化学性状转化为金成矿提供了物质来源,早白垩世热隆-伸展构造为大规模金成矿提供了有利条件,断裂倾角变化控制了流体聚集和富矿柱的形成,成矿物质和流体来源有幔源因素,胶东型金矿是与经典造山型金矿和其他已知金矿类型不同的新的金矿成因类型。胶东金矿勘查综合应用了成矿规律、大探测深度地球物理方法、构造叠加晕地球化学方法、三维地质建模、深孔钻探等技术方法,以赋矿构造位置为目标、以频率域电磁探测为主要技术手段的深部金矿阶梯找矿方法发挥了重要作用。深部勘查发现,新探明的金资源量集中于1000~2000 m深度,绝大部分为破碎带蚀变岩型矿化,三山岛地区和焦家地区的多个浅部矿体向深部连为一体,构成资源量大于1000 t的超巨型金矿床。探明了中国首个海域金矿床,在胶东东部发现黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型新的金矿化类型。综合分析指出,晚中生代构造体制转换对大规模成矿的影响、断裂控矿机理、成矿流体和物质来源、金矿资源潜力及精细高效的找矿技术等是今后的重点研究方向。
Abstract:Since the implementation of the Exploration Breakthrough Strategic Action organized by the former Ministry of Land and Resources in 2011, great achievements have been made in the deep prospecting of Jiaodong gold deposit, with the newly increased gold resources of about 2958 t.12 large gold deposits have been explored and evaluated, and 2 super-giant gold deposits have been found.The accumulated proven gold resources in Jiaodong Peninsula have reached more than 5000 tons, accounting for 1/3 of the whole country.These prospecting achievements are attributed to the deepening understanding of metallogenic theories such as metallogenic tectonic setting, metallogenic regularity and genesis of deposits and the continuous progress of exploration techniques and methods.The metallogenesis and related research of the Jiaodong gold deposit are the hotspots of domestic geological research.This article briefly summarizes the research progress in the recent 10 years in metallogenic background, deposit distribution, metallogenic epoch, geochemistry of ore deposit, metallogenic model and genesis, especially the original achievements in the research of deep metallogenic model and large-scale metallogenic mechanism.These results indicate that the Jiaodong gold deposit was formed in the magmatic activity background of adakite granite transformed into arc granite, the geochemical transformation of magmatic rocks and lithospheric mantle provides material sources for gold mineralization, the Early Cretaceous thermal doming-extension structures provided favorable conditions for large-scale gold mineralization, the change of fault dip angle controlled the fluid accumulation and the ore-rich pillars, the source of ore-forming materials and fluids have mantle-derived factors, and the Jiaodong type gold deposit is a new genetic type of gold deposit, which is different from the classical orogenic gold deposit and other known types.The exploration of the Jiaodong gold deposits comprehensively applied prospecting methods such as deep geophysical exploration, structural superimposed halo geochemical prospecting, three-dimensional geological modeling and deep drilling, etc., The ladder prospecting method for deep gold deposits, which takes the location of ore bearing structure as the target and frequency domain electromagnetic detection as the main technical means, plays an important role.This paper summarizes the important progress of deep exploration.The deep gold resources are concentrated in the depth of -1000 m to -2000 m, most of which are fracture zone altered rock type mineralization.Several shallow ore bodies in Sanshandao area and Jiaojia area are connected to the deep, forming a super-giant gold deposit with resources greater than 1000t.In recent years, the first offshore gold deposit in China has been discovered, and the pyrite carbonate vein type gold deposit has been defined as a new type in the east of Jiaodong.Finally, this paper briefly analyzes the unresolved problems in the deep exploration research of the Jiaodong gold deposit, and points out that the influence of Late Mesozoic structural system transformation on large-scale mineralization, the mechanism of fault-controlling ore, the source of ore-forming fluids and materials, the potential of gold resources and the fine and efficient prospecting techniques are the key research direction in the future.
-

-
表 1 胶东金矿稳定性与放射性同位素特征
Table 1. Stable and radioactive isotopes characteristics of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula
矿床 H-O和C-O同位素 S、Pb、Sr、Nd、He、Ar同位素 参考文献 石英流体包裹体的δDV-SMOW值为-81.3‰~-63.5‰,δ18OH2O V-SMOW值为-2.8‰~+5.9‰,指示成矿流体主要是岩浆源的,在成矿过程中或之后逐渐混入天水 不同阶段成矿流体黄铁矿的δ34S值为1.9‰~ 11.9‰,中阶段黄铁矿中流体包裹体3He/4He值为0.14~2.94 Ra,40Ar/ 36Ar值为675.10~5926.44 [110] 热液石英δ18O值为9.7‰~15.1‰,计算的流体δ18O值为0.97‰~10.79‰,δDH2O值为-100‰~-62‰ 主阶段热液硫化物δ34S值为7.8‰~12.6‰ [111] 三山岛 载金黄铁矿流体包裹体3He/4He=0.043~0.21 Ra,40Ar/36Ar=488~664 [112] 石英流体包裹体的δDV-SMOW值为-77‰~-53.6‰,δ18OH2O V-SMOW值为2.8‰~7.5‰,指示成矿流体源于初始岩浆水,后期有少量大气降水参与。铁白云石和方解石δ13CPDB值为-6.6‰~-5.9‰,落入典型的岩浆碳范围内,暗示金矿与深源流体有关 黄铁矿的δ34S值为8‰~9.3‰,与浅部δ34S值(8.4‰~10.5‰)基本一致,硫同位素体系在2000 m深度范围内达到平衡 [113] 新立 Ⅲ和Ⅲ阶段矿石中石英δ18OH2O V-SMO值为2.82‰~5.34‰, δDSMOW值为-88.3‰~-69.6‰,指示矿石流体主要为岩浆水。方解石δ13CPDB值为-6.4‰~-2.4‰,指示流体中有幔源的贡献 4个矿化阶段黄铁矿δ34SCDT值相似,变化于9.42‰~11.62‰,指示了壳源物质的参与。方解石的初始87Sr/86Sr值为0.710657 ~0.711542,指示了壳源贡献 [114] 焦家深部 黄铁矿的δ34S值为7.5‰~9.8‰,由浅到深δ34S值逐渐降低。3He/4He值为1.6±0.1~1.8±0.1 Ra,40Ar/36Ar值为750~3106,显示混合来源特征 [115] 新城 热液石英δ18O值为8.0‰~16.7‰,δDSMOW值为-96‰~-61‰,计算的δ18OH2O值为-6.4‰~8.9‰,成矿流体为变质来源 热液硫化物的δ34S值为4.3‰~10.6‰ [116] 望儿山 矿化流体δ18O值为2.13‰~7.5‰,δ18Dw值为-97.5‰~-61.4‰ 黄铁矿δ34S值为6‰~8.3‰,黄铁矿3He/4He值为1.58~2.71 Ra、40Ar/36Ar值为1220.3~1625.7 [8] 热液石英δ18O值为5.5‰~14.4‰,计算的δ18OH2O值为1.9‰~10.8‰,δD值为-77.3‰~-57.2‰; 碳酸盐的δ13CPDB值为-6.7‰~-6.3‰,δ18OSMOW值为10.6‰~11.1‰ 热液黄铁矿的δ34SCDT值为4.8‰~8.9‰,206Pb/204Pb值为17.158~17.511、207Pb/204Pb值为15.445~15.529、208Pb/204Pb值为37.709~38.000 [71] 谢家沟 石英流体包裹体的δ18O值为3.1‰~13.2‰,计算的δ18OH2O值为-9.7‰~5.7‰,δD值为-101.8‰~-83.1‰ 热液硫化物的δ34S值为4.7‰~7.8‰。206Pb/204Pb值为17.251~17.315,207Pb/204Pb值为15.486~15.519, 208Pb/204Pb值为37.904~38.029 [23] 大尹格庄 菱铁矿和碳酸盐C、O同位素值分别为-5.4‰~-2.2‰(δ13CV-PDB)和7.8‰~12.1‰(δ18OV-SMOW),计算的成矿流体分别是-7.1‰~-2.9‰和-4.1‰~5.7‰ δ34SCDT值为4.8‰~9.0‰,206Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb、208Pb/204Pb值分别为17.181~17.339、15.414~15.504、37.729~37.984及17.2157~17.3585、15.4595~15.6116、37.858~38.3328 [69, 117] 夏甸 石英流体包裹体的δ18O值为5.9‰~14.0‰,计算的δ18OH2O值为-8.1‰~7.5‰,δDv-smow值为-111.0‰~-78.0‰ [118] δD值为-72.1‰~-62.4‰, δ 18OH2O值为-1.4‰~9.7‰ δ34S值为6.95‰~8.1‰,指示了矿石中金属元素混合来源, 胶东岩群是S的主要来源 [111] 玲珑 成矿流体δD和δ18O值分别为-63‰~-57‰和6.0‰~9.3‰,在岩浆和变质水区域 热液黄铁矿δ34S值为5.6‰~7.9‰,在新太古代胶东岩群和中生代玲珑花岗岩、郭家岭花岗闪长岩和中基性脉岩范围内 [119] 台上 热液石英的δ18O值为10.9‰~12.5‰,计算的流体δ18O值为1.3‰~10.0‰,δ18DH2O值为-60‰~-45‰ 热液黄铁矿的δ34S值为4.5‰~8.0‰,在太古宙胶东岩群和中生代花岗岩类、中-基性脉岩范围内 [120] 黑岚沟 赋存于金-石英-黄铁矿脉中的黄铁矿δ34S值为6.6‰~7.9‰,赋存在金-多金属硫化物脉中的黄铁矿δ34S值为8.1‰~8.8‰ [121] 大柳行 成矿前和成矿后的黄铁矿具有较低的δ34S值(分别为3.7‰~5.6‰和5.3‰~6.4‰),而与成矿有关的黄铁矿具有较高的δ34S值(7.8‰~8.3‰)。黄铁矿的惰性气体同位素具有壳幔混合来源的3He/ 4He(1.13~1.50 Ra)和类似大气的40Ar/ 36 Ar(327~574)特征,独居石中Nd同位素值(εNd(t)=-13.7~-11.6)与赋矿的郭家岭花岗闪长岩一致 [38] 马家窑 热液石英流体包裹体的δ18OSMOW值为11‰~13.9‰,δ18OH2O值为-3.6‰~5.5‰,δDSMOW值为-95.97‰~-53.5‰ 黄铁矿δ34S值为5.4‰~11.7‰,206Pb/204Pb值为16.476~16.674、207Pb/204Pb值为15.2111~15.353、208Pb/ 204Pb值为36.979~37.803,初始87Sr/86Sr值为0.716136±0.000034 [78] 笏山 晚阶段黄铁矿的δ34S值5.69‰~6.98‰,早阶段为7.06‰~7.85‰。独居石原位εNd(t)值为-20.6~-18.4,与玲珑花岗岩的Nd同位素值吻合 [25] 辽上 δ18O值为相对窄的范围(8.2‰~8.3‰),δ13CV-PDB值为-6.0‰~-3.8‰,δ18OV-SMOW值为10‰~10.4‰,投点于岩浆岩区 206Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb和208Pb/204Pb值分别为17.125~17.248、15.455~15.467和37.786~37.904,黄铁矿3He/4He值为0.643~1.135 Ra、40Ar/ 36 Ar值为638.8~1169.1 [76] 载金矿物白云石δ13CV-PDB值为-4.6‰~-3.6‰,δ18OV-SMOW值为9.6‰~10.6‰,投点于岩浆岩区 黄铁矿δ34S值为7.2‰~9.4‰,206Pb/ 204Pb值为17.027~17.576,207Pb/204Pb值为15.435~15.503,208Pb/204Pb值为37.706~ 38.205 [122] 郭城 成矿相关石英δD值为-86‰~-69‰,δ18OH2O值为0.6‰~7.7‰ 矿石硫化物的δ34S值为8.5‰~12.7‰,206Pb/ 204Pb值为17.155~17.862,207Pb/204Pb值为15.410~15.454,208Pb/204Pb值为37.371~ 37.878,3He/4He值为0.41~2.39 Ra,40Ar/36Ar值为367~2112,40Ar-/4He值为0.40~3.78 [77, 123] 邓格庄 石英δD值为-99.8‰~-80.7‰,δ18OH2O值为7.9‰~15.9‰,成矿流体以岩浆水为主,成矿后期在地壳浅部遭受少量大气降水的混和 矿石硫化物的δ34S值为2.7‰~13‰,206Pb/ 204Pb值为17.007~17.304,207Pb/204Pb值为15.414~15.509,208Pb/204Pb值为37.374~37.708 [27] 金青顶 成矿阶段流体的δD和δ18O值分别为-87.1‰~-64.4‰和0.2‰~8.4‰,位于岩浆水和天水范围内。碳酸盐的δ13CPDB值为-5.4‰~-4.5‰,在岩浆有关的C范围内 黄铁矿δ34S值(5.5‰~6.1‰)与胶西北金矿相似 [124] 表 2 东金矿流体包裹体特征
Table 2. Fluid inclusion characteristics of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula
矿床 矿物组合或矿化阶段 流体包裹体类型 流体温度、盐度、密度 成因解释 参考文献 三山岛 4个矿化阶段:黄铁矿-石英阶段、石英-黄铁矿阶段、石英-黄铁矿-贱金属硫化物阶段、石英-碳酸盐阶段,金主要赋存在2和3阶段 3种类型流体包裹体:纯CO2、CO2-H2O和纯水 1、2~3和4阶段流体包裹体的温度(℃)分别是280~400、210 ~320和150~230,盐度(% NaCl equiv,后面简化为%)0.35~10.4、2.2~13.33、0.1~12.5,密度(g/cm3)0.61~1.07、0.82~1、0.7~0.98。早阶段压力165~200 MPa,主阶段压力90~175 MPa 金属和流体来源于俯冲的古太平洋板块脱水、脱硫和富集地幔楔脱气。水-岩硫化作用和压力波动,伴随流体不混溶和其他化学变化是金沉淀的主要机制 [111] 3个矿物共生组合阶段:石英±黄铁矿、金+石英+黄铁矿或金+石英+贱金属硫化物、石英+碳酸盐±黄铁矿 4种类型流体包裹体:纯CO2、H2O-CO2-NaCl、H2 O-NaCl包裹体、含子矿物或多相流体包裹体 3阶段流体包裹体温度(℃)分别是241~390、207~336和101~268,盐度(%)2.96~18.39、2.06~17.57、0.17~15.47,密度(g/cm3)0.74~1.10、0.73~1.10、0.63~1.11 成矿物质和流体来源于壳源和幔源成分的组合。CH4是控制金成矿的关键因素,CH4改变了成矿流体的物理化学条件,导致金沉淀 [110] 新立 4个矿化阶段:石英-钾长石-绢云母-黄铁矿阶段、石英-黄铁矿阶段、石英-多金属硫化物阶段、石英-碳酸盐-黄铁矿阶段 6种类型流体包裹体:单相气体、单相液体、CO2和H2O两相、富液相的两相、富气相的两相、三相流体包裹体。主成矿阶段为中—低温、低盐度、还原条件NaCl-H2O-CO2±CH4系统 4个矿化阶段流体包裹体温度(℃)分别为239~369、159~ 325、119~321和116~219,盐度(%)3.00~10.37、1.96~9.86、1.03~9.47和1.05~7.14 成矿流体和金属与俯冲的古太平洋板块脱水、脱硫和富集地幔楔脱挥发分有关,流体中的H2O可能是富集地幔楔脱挥发分释放出来的,CO2可能来源于地幔楔或俯冲大陆岩石圈地幔,S和Sr来源于俯冲的海底沉积物 [114] 寺庄 3个矿化阶段:早阶段、主阶段、晚阶段 3种类型流体包裹体: CO2-H2O、H2O、CO2 各阶段温度(℃): 303~390、279~298、195~289。属于CO2-H2O-NaCl流体系统,具中—低温度(160~360℃)、中—低盐度(3.00%~11.83%)、低密度(1.02~1.51 g/cm3)特征 变质水是成矿流体的主要来源,压力波动引起的流体不混溶是金成矿的关键机制 [128] 新城 4个矿化阶段:黄铁矿-石英-绢云母、石英-黄铁矿、石英-多金属硫化物、石英-碳酸盐,金赋存在2和3阶段 石英中3种类型流体包裹体:CO2-H2O、纯H2O、纯CO2气 温度221~304℃、盐度2.4%~13.3%,不同类型流体的共存是由于在221~304℃和78~208 MPa温压条件下单一均匀的H2O-CO2母流体分离所产生的流体不混溶所致 金以Au(HS)2-络合物形式运移,流体不混溶导致了H2S在热液中溶解减少,因此Au(HS)2-络合物分解与金的沉淀相伴 [139] 4个矿化阶段:黄铁矿-石英-绢云母阶段、石英-黄铁矿阶段、石英-多金属硫化物阶段、黄铁矿-碳酸盐阶段 3种类型流体包裹体:H2O-CO2、水(液相H2O+气相H2O)、CO2(液相CO2和气相CO2),为中温、富CO2、低盐度的变质流体 类型1和2包裹体均一温度(℃)分别是221~304、171~264,盐度(%)2.4~8.9、3.1~13.3,类型1和3包裹体密度(g/cm3)分别是0.858~1.022、0.681~0.751 由压力快速降低导致的流体不混溶产生了高品位金矿床。深源变质成矿流体与俯冲的古太平洋板块和上覆的含硫沉积物楔的俯冲脱水、脱碳有关 [116] 望儿山 4个矿化阶段:黄铁矿-石英-绢云母阶段、石英-黄铁矿阶段、石英-硫化物阶段、石英-碳酸盐阶段 3种类型流体包裹体: H2O-CO2-NaCl、纯H2O、纯CO2包裹体,以中高温度(285~350℃)、含CO2、少量CH4和低盐度为(3.38%~8.45%)特征,最终演化为中低温NaCl-H2O系统 阶段1的温压条件是85~190 MPa和334~300℃,阶段2和3的温压条件是40~200 MPa和288~230℃ 成矿流体为以变质流体为主的混合流体,与俯冲的古太平洋板块脱水和脱碳有关。Au(HS)2-是最可能的载金络合物,流体压力变化引起的流体不混溶,导致的Au(HS)2-分解是金的主要沉淀机制 [72] 谢家沟 3个矿化阶段:早阶段(钾长石)-绢云母-石英-黄铁矿、中阶段石英-金-多金属硫化物、晚阶段石英-碳酸盐,金主要赋存于中阶段 3种类型流体包裹体:CO2-H2O、纯CO2、纯H2O。初始流体为中温、富CO2低盐度H2O-CO2-NaCl液相系统,成矿流体由富CO2中温流体演化为贫CO2流体 3阶段均一温度(℃)分别为262~386、192~347和137~231,盐度(%)2.22~8.82、1.02~1.60和1.22~7.72,第1、2阶段流体捕获压力分别是224~302 MPa和191~258 MPa Au(HS)2-是最可能载金络合物,初始流体中CO2的逃逸导致了金的沉淀 [23] 大尹格庄 4个阶段:(钾长石)-黄铁矿-绢云母-石英、石英-金-黄铁矿、金-多金属硫化物、石英-碳酸盐 3种类型流体包裹体:NaCl-H2O,CO2-H2O-NaCl,纯CO2 第1阶段均一温度251~403℃,盐度2.2%~9.4%。第2和3阶段的温度、盐度分别是:216~339℃、1.8%~13.8%,195~321℃、1.4%~13.3%,第4阶段106~287℃、0.5%~7.7% 由早期酸性条件、相对高温和高fO2的Au(HS)O为主相转化为晚期中等pH、低温低fO2的Au(HS)-2相,金的沉淀与流体不混溶水岩相互作用有关 [140] 3个成矿作用阶段:金-石英-黄铁矿阶段、金(银)-石英-多金属硫化物阶段、石英-方解石-黄铁矿阶段 流体包裹体气相成分以H2O和CO2为主,少量C2H6、CH4、H2S、Ar和N2; 液相成分,阳离子主要为K+、Na+,少量Ca2+,阴离子主要为SO42-、Cl-及F-。属于中温、中低盐度流体 早、中、晚阶段流体包裹体的爆裂温度(℃)分别集中在325~385、240~330和165~195,金成矿温度为240~385℃。从早阶段到晚阶段,成矿流体温度和盐度降低 成矿流体主要来源于变质热液,晚阶段流体可能以大气降水为主 [141] 夏甸 3个矿化阶段:早阶段(钾长石)-绢云母-石英-黄铁矿、中阶段石英-金-多金属硫化物、晚阶段石英-碳酸盐 3种类型流体包裹体:NaCl-H2O、CO2-H2O-NaCl、纯CO2,成矿流体由富CO2中温流体演化为贫CO2流体 3个阶段均一温度(℃)分别为253~408、176~335和108~253,盐度(%)1.62~11.89、0.70~14.73和1.73~11.60。流体捕获压力88~339 MPa 成矿流体可能是变质水,有天水汇入 [118] 4个矿化阶段:石英-黄铁矿、含金细粒黄铁矿-石英、多金属硫化物-石英、石英-碳酸盐 3种石英流体包裹体类型:CO2-H2O、CO2-H2O±CH4、纯H2O。流体演化由中等温度和盐度的H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4系统到低温度和盐度的H2O-NaCl系统,由富CO2到贫CO2 第Ⅰ、Ⅱ-Ⅲ和Ⅳ阶段均一温度(℃)分别为282~368.6、210.3~298.9和110.6~216.9,盐度(%)分别为6.1~20.1、0.12~17.9和1.8~7.8 δ18O H2O值指示成矿流体为天水不断增加的岩浆水,流体不混溶造成了金的沉淀,是由挤压向伸展转换过程中的造山型金矿 [111] 玲珑 4个矿化阶段:乳白色石英-黄铁矿、灰白色石英-黄铁矿、石英-黄铁矿-贱金属硫化物、石英-碳酸盐,金主要赋存于2和3阶段 3种类型包裹体: H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4、H2O的H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4和富CO2的H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4包裹体。属于H2O-NaCl-CO2 ±CH4系统,中温(290~340℃)低盐度(4%~7%)富CO2,少量CH4 第2阶段281~359℃,第3阶段269~342℃。密度为0.517~0.933 g/cm3。金成矿的P-T范围是54~242 MPa,348~269℃,成矿深度5.4~9.0 km 成矿流体可能主要来自于变质流体,但是幔源或壳源的物质贡献不能忽略。流体不混溶是成矿的主要因素,水岩反应其次 [119] 台上 4个阶段:黄铁矿-石英-绢云母、石英-黄铁矿、石英-黄铁矿-贱金属硫化物、黄铁矿-碳酸盐,金主要赋存于2和3阶段 石英和方解石流体包裹体3种类型:富H2O的水-碳包裹体、富CO2的水-碳包裹体、碳包裹体。初始流体为中高温、富CO2、低盐度的H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4均一流体 4个阶段温度(℃)分别是285~336、215~317、212~315、158~236,盐度(%)1.4~7.1、0.2~9.1、3~7.8、1~7.3,密度(g/cm3)0.835~0.987、0.440~1.039、0.667~1.010、0.875~1.027 流体和金属来源可能是古太平洋板块和上覆的沉积物,以及胶东变质岩系。由于液压致裂压力由1700 bar快速变为580 bar,产生流体不混溶成矿。Au(HS)2-是最可能的载金络合物,硫化反应和流体不混溶是成矿的2个主要机制 [120] 马家窑 4个热液蚀变阶段 3种类型流体包裹体:纯液相或纯气相包裹体、气液两相包裹体、富CO2三相包裹体。为CO2-H2O-NaCl体系,成矿流体为中低温度、中低盐度、低密度、富CO2流体 阶段Ⅰ均一温度210~343℃,盐度1.57%~10.98%,密度0.65~1.02 g/cm3; 阶段Ⅱ、Ⅲ均一温度190~300℃,盐度峰值4%~10%;阶段Ⅳ均一温度120~200℃,盐度峰值4.2%~7.9%。由早至晚,温度、盐度、密度逐渐降低 氢-氧同位素指示成矿流体主要为岩浆流体,少量天水 [78] 辽上 白云石中包裹体有2种类型:气液包裹体,液相成分大于50%;富CO2气相包裹体。成矿流体富CO2含少量N2,为CO2-NaCl-H2O系统 包裹体具有中等—低的均一温度(280~320℃),中—低的盐度(6.29%~12.7%)和中—低的密度(0.83~0.97 g/cm3) [76] 金青顶 7个热液阶段:钾长石化、镜铁矿-石英脉、乳白色石英±硫化物脉、石英黄铁矿脉、石英-绢云母-黄铁矿蚀变和金矿化、石英-多金属硫化物脉、石英碳酸盐脉 4种类型流体包裹体:CO2 -H2O±CH4包裹体、纯CO2包裹体、含子矿物包裹体和水包裹体 初始流体为富CO2气体(357~420℃,7.2%~11.3%)和临界流体(368~400℃); 其后演化为H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4系统,温度300~364℃,盐度2.0%~9.7%;经相分离为H2O-CO2± CH4包裹体(温度265~309℃和265~287℃,盐度3.1%~7.1% 和4.3%~7.1%); 进一步演化为H2O-NaCl系统,温度163~258℃,盐度0.5%~9.0% 初始成矿流体可能是岩浆来源,在成矿后期有天水的加入。金的沉淀与流体冷却、流体不混溶和流体中硫含量的减少有关 [124] 表 3 找矿突破战略行动十年胶东金矿找矿及研究成果与以往对比
Table 3. Comparison of explopration and research of gold deposits between during 10 years for Exploration Breakthrough Strategic Action and the past in the Jiaodong Peninsula
对比内容 2011年以来 2011年以前 找矿成果 新增金资源量2958 t,新提交3个资源量在300 t以上的超大型金矿床,探明了海域金矿床 累计探明金资源量1932 t,单次提交的金矿床资源量均不超过100 t,探获的金矿床均在陆域 勘查深度 控制金矿床的钻孔深度主要为1000~2000 m,超过3000 m深度的探索钻孔3个,最大探索钻孔深度4006.17 m 20世纪探明的金矿床深度一般不超过500 m,最大钻孔深度不超过1000 m。21世纪前10年的找矿深度主要在1500 m以内 勘查技术方法 物探方法以大功率激电、可控源音频大地测深、大地电磁测深、频谱激电测量为主,高精度重力剖面、高精度磁法剖面辅助,探索应用广域电磁、反射地震等方法。化探方法主要为钻孔原生晕、构造叠加晕法,实验研究多维异常地球化学、穿透性地球化学等方法。三维建模方法在深部找矿中逐步应用 物探以重、磁、激电等方法为主,后期应用大功率激电、可控源音频大地测深法。化探方法主要为水系沉积物、土壤、原生晕测量等,后期使用构造叠加晕法 矿床成因 克拉通破坏型金矿、胶东型金矿、热隆-伸展成矿、造山型金矿、伸展型金矿,成矿物质和流体来源以壳源为主有幔源参与,幔源成因,俯冲洋壳成因 岩浆期后热液金矿、混合岩化岩浆热液金矿、绿岩带型金矿、造山型金矿,成矿物质和流体来源于壳源 赋矿规律 断裂产状阶梯变化赋矿,张性断裂控矿,挤压-伸展转换成矿,蚀变岩型金矿位于主断裂中、石英脉型金矿位于断裂下盘 大断裂赋矿,压扭性断裂控矿,石英脉型金矿在上、蚀变岩型金矿在下 成矿时代 120±2 Ma 多期成矿(中生代、太古宙、元古宙),早白垩世,120±5 Ma -
[1] 宋英昕, 宋明春, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿集区深部找矿重要进展及成矿特征[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : 4-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703003.htm
[2] 于学峰, 宋明春, 李大鹏, 等. 山东金矿找矿突破进展与前景[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(10) : 2847-2862. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201610022.htm
[3] 陈玉民, 范宏瑞, 崔仑, 等. 胶西北大规模金成矿作用与成因模型[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1-336.
[4] 宋明春, 张军进, 张丕建, 等. 胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造-岩浆背景[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(2) : 365-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502012.htm
[5] 刘殿浩, 吕古贤, 张丕建, 等. 胶东三山岛断裂构造蚀变岩三维控矿规律研究与海域超大型金矿的发现[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(4) : 162-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201504021.htm
[6] 张军进, 丁正江, 刘殿浩, 等. 山东莱州三山岛北部海域超大型金矿勘查实践与找矿成果[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2016, 24(1) : 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201601001.htm
[7] Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong Province, eastern China[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274.
[8] Li L, Santosh M, Li S R. The "Jiaodong type" gold deposits: Characteristics, origin and prospecting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 589-611.
[9] Song M C, Li S Z, Santosh M, et al. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 612-625.
[10] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm
[11] 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2015, 45: 1153-1168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htm
[12] 范宏瑞, 冯凯, 李兴辉, 等. 胶东-朝鲜半岛中生代金成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(10) : 3225-3238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201610021.htm
[13] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2) : 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm
[14] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿床: 基本特征和主要争议[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(4) : 406-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201804006.htm
[15] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 李杰, 等. 深部矿阶梯式找矿方法: 以胶东金矿集区深部找矿为例[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(1) : 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202201001.htm
[16] 林博磊, 李碧乐. 胶东玲珑花岗岩的地球化学、U-Pb年代学、Lu-Hf同位素及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(2) : 147-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201302005.htm
[17] Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic geochemistry of late mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146/147: 112-127.
[18] 黄涛, 杨立强, 刘向东, 等. 胶北地体地壳演化: 玲珑黑云母花岗岩继承锆石U-Pb年龄、微量元素和Hf同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2574-2594. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409010.htm
[19] Wu M, Zhao G, Sun M, et al. A synthesis of geochemistry and Sm-Nd isotopes of Archean granitoid gneisses in the Jiaodong Terrane: Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of the Eastern Block, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 255(1) : 885-899.
[20] 王斌, 宋明春, 霍光, 等. 胶东晚中生代花岗岩的源区性质与构造环境演化及其对金成矿的启示[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2) : 288-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202102009.htm
[21] Chai P, Zhang H R, Hou Z Q, et al. Geochronological framework of the Damoqujia gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for the timing and geologic setting of gold mineralization[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 596-613.
[22] Li Y J, Li S R, Santosh M, et al. Zircon geochronology, geochemistry and stable isotopes of the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 695-710.
[23] Chai P, Hou Z Q, Zhang H R, et al. Geology, Fluid inclusion, and H-O-S-Pb isotope constraints on the mineralization of the Xiejiagou gold deposit in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geofluids, 2019, (6) : 1-23.
[24] Ma W D, Fan, H R, Liu X, et al. Geochronological framework of the Xiadian gold deposit in the Jiaodong province, China: Implications for the timing of gold mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 86: 196-211.
[25] Yang K F, Jiang P, Fan H R, et al. Tectonic transition from a compressional to extensional metallogenic environment at-120 Ma revealed in the Hushan gold deposit, Jiaodong, North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 408-425.
[26] 唐文龙, 付超, 邹键, 等. 胶东唐家沟金矿床独居石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb同位素年代学及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(3) : 809-821. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202103014.htm
[27] 薛建玲, 庞振山, 李胜荣, 等. 胶东邓格庄金矿床成因: 地质年代学和同位素体系制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(5) : 1532-1550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201905015.htm
[28] Wang Z L, Yang L Q, Deng J, et al. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 95: 274-299.
[29] 刘跃, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶西北新城金矿床二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2559-2573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409009.htm
[30] 王中亮, 赵荣新, 张庆, 等. 胶西北高Ba-Sr郭家岭型花岗岩岩浆混合成因: 岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2595-2608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409011.htm
[31] 王立功, 祝德成, 郭瑞朋, 等. 胶西北仓上、三山岛岩体二长花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素研究[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(10) : 2081-2095. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201810009.htm
[32] 宋英昕, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 等. 胶东西北部北截岩体岩石成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5) : 1477-1500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005010.htm
[33] 罗贤冬, 杨晓勇, 段留安, 等. 胶北地块与金成矿有关的郭家岭岩体和上庄岩体年代学及地球化学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(10) : 1874-1888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201410008.htm
[34] Jiang P, Yang K F, Fan H R, et al. Titanite-scale insights into multi-stage magma mixing in Early Cretaceous of NW Jiaodong terrane, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2016, 258/259: 197-214.
[35] 耿科, 王瑞江, 李洪奎, 等. 胶西北地区北截金矿闪长玢岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(6) : 1099-1107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201506008.htm
[36] Deng J, Wang C M, Bagas L, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2015, 50: 987-1006.
[37] Cai Y C, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Decratonic gold mineralization: Evidence from the Shangzhuang gold deposit, eastern North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 54: 1-22.
[38] Feng K, Fan H R, Groves D I, et al. Geochronological and sulfur isotopic evidence for the genesis of the post-magmatic, deeply sourced, and anomalously gold-rich Daliuhang orogenic deposit, Jiaodong, China[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2020, 55: 293-308.
[39] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 等. 胶东伟德山地区铜钼多金属矿锆石U-Pb法测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2) : 607-618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302019.htm
[40] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 李杰, 等. 胶东与白垩纪花岗岩有关的金及有色金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(5) : 823-843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201505007.htm
[41] Song M C, Wang S S, Yang L X, et al. Metallogenic epoch and geological significance of nonferrous metallic and silver deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(4) : 1305-1325.
[42] Goss C S, Wilde S A, Wu F Y, et al. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrene, Shandong Province, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2010, 120(3/4) : 309-326.
[43] 宋明春, 李杰, 李世勇, 等. 鲁东晚中生代热隆伸展构造及其动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(4) : 941-964. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201804001.htm
[44] 李增达, 于晓飞, 王全明, 等. 胶东三佛山花岗岩的成因: 成岩物理化学条件、锆石U-Pb年代学及Sr-Nd同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2) : 447-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201802018.htm
[45] Huang X L, He P L, Wang X, et al. Lateral variation in oxygen fugacity and halogen contents in early Cretaceous magmas in Jiaodong area, East China: Implication for triggers of the destruction of the North ChinaCraton[J]. Lithos, 2016, 248/251: 478-492.
[46] Tang H Y, Zheng J P, Yu C M, et al. Multistage crust-mantle interactions during the destruction of the North China Craton: Age and composition of the Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Lithos, 2014, 190/191: 52-70.
[47] Cheng S B, Liu Z J, Wang Q F, et al. Mineralization age and geodynamic background for the Shangjiazhuang Mo deposit in the Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 80: 876-890.
[48] Song M C, Zhou J B, Song Y X, et al. Mesozoic Weideshan granitoid suite and its relationship to large-scale gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5703-5724.
[49] 杨宽, 王建平, 林进展, 等. 胶东半岛艾山岩体岩石地球化学特征及成因意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(4) : 693-703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201204005.htm
[50] 宋明春, 李杰, 周建波, 等. 胶东早白垩世高镁闪长岩类的发现及其构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1) : 279-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001022.htm
[51] 董学, 李大鹏, 赵睿, 等. 胶东泽头岩体锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石成因: 对区域早白垩世晚期成岩成矿作用的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5) : 1501-1514.
[52] 王瑞良, 张招崇, 曾庆栋, 等. 胶东栖霞金矿集区早白垩世花岗岩形成时代及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 43(1) : 186-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901014.htm
[53] Yan Q S, Metcalfe I, Shi X F, et al. Early Cretaceous granitic rocks from the southern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: implications for lithospheric extension[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(7) : 821-838.
[54] 王世进, 万渝生, 王伟, 等. 山东崂山花岗岩形成时代——锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 山东国土资源, 2010, 26(10) : 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201010003.htm
[55] Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hofmann A, et al. Rapid lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton: New evidence from Cretaceous mafic dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 432: 1-15.
[56] Liang, Y Y, Deng J, Liu X F, et al. Water contents of early Cretaceous mafic dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton: insights into an enriched lithospheric mantle source metasomatized by Paleo-Pacific Plate subduction-related fluids[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2019, 127(3) : 343-362.
[57] Liang Y Y, Deng J, Liu X F, et al. Major and trace element, and Sr isotope compositions of clinopyroxene phenocrysts in mafic dykes on Jiaodong Peninsula, southeastern North China Craton: Insights into magma mixing and source metasomatism[J]. Lithos, 2018, 302/303: 480-495.
[58] Liang Y Y, Liu X F, Wang Q F, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatism in the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Implications for crust-mantle interactions and lithospheric thinning of the eastern North China Craton[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(3) : 895-914.
[59] Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hou M L, et al. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous calc-alkaline lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Implication for lithospheric evolution of the eastern North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(2) : 859-872.
[60] Ding D S, Chen L, Gong E P, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-O isotopic constraints on the origin of the youngest Mesozoic adakitic dikes in Jiaodong peninsula, North China Craton: implications for Early Cretaceous crustal evolution[J]. International Geology Review, 2020, 62(4) : 446-464.
[61] Long Q, Hu R, Yang Y Z, et al. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous intermediate to mafic dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints on mantle source composition beneath eastern China[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2017, 125(6) : 713-732.
[62] Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hofmann A W, et al. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton?[J]. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 124: 250-271.
[63] Li L, Li S R, Santosh M, et al. Dyke swarms and their role in the genesis of world-class gold deposits: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 130: 2-22.
[64] Deng J, Yang L Q, Li H R, et al. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits: An overview from the Giant Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54: 378-391.
[65] Dai F Q, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, et al. The geochemical nature of mantle sources for two types of Cretaceous basaltic rocks from Luxi and Jiaodong in east-central China[J]. Lithos, 2019, 344/345: 409-424.
[66] LiangY Y, Liu X F, Qin C, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous mafic dikes in southeastern Jiaolai basin, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. International Geology Review, 2017, 59(2) : 131-150.
[67] Liu X F, Deng J, Liang Y Y, et al. Geochemical, mineralogical and chronological studies of mafic intermediate dykes in the Jiaodong Peninsula: implications for Late Mesozoic mantle source metasomatism and lithospheric thinning of the eastern North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2020, 62(18) : 2239-2260.
[68] Feng L Q, Gu X X, Zhang Y M, et al. Geology and geochronology of the Shijia gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103432.
[69] Yuan Z Z, Li Z K, Zhao X F, et al. New constraints on the genesis of the giant Dayingezhuang gold(silver) deposit in the Jiaodong district, north China craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 112: 103038.
[70] 宋英昕, 宋明春, 孙伟清, 等. 胶东金矿成矿时代及区域地壳演化——基性脉岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(5) : 908-919. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180513&flag=1
[71] Yang L Q, Deng J, Goldfarb R J, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold Province, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(4) : 1469-1483.
[72] Yang L Q, Guo L N, Wang Z L, et al. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 491-510.
[73] Sai S X, Deng J, Qiu K F, et al. Textures of auriferous quartz-sulfide veins and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Rushan gold deposit: Implications for processes of ore-fluid infiltration in the eastern Jiaodong gold Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 103254.
[74] Zhang L, Weinberg R F, Yang L Q, et al. Mesozoic orogenic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A focused event at 120±2 Ma during cooling of pregold granite intrusions[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(2) : 415-441.
[75] 薛建玲. 胶东牟乳成矿带金矿床成矿作用和深部远景研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2013.
[76] Li J J, Zhang P P, Li G H, et al. Formation of the Liaoshang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5903-5913.
[77] Tan J, Wei J H, Li Y J, et al. Origin and geodynamic significance of fault-hosted massive sulfide gold deposits from the Guocheng-Liaoshang metallogenic belt, eastern Jiaodong Peninsula: Rb-Sr dating, and H-O-S-Pb isotopic constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 687-700.
[78] Tian J P, Li J J, Zhang P P, et al. Formation of the Majiayao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and pyrite Rb-Srage[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5885-5902.
[79] 蔡亚春, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东胡八庄金矿成矿流体、稳定同位素及成矿时代研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5) : 1341-1351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105010.htm
[80] Deng J, Qiu K F, Wang Q F, et al. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold Province, easternChina[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(3) : 671-685.
[81] 李杰, 宋明春, 王美云, 等. 胶东尚家庄钼矿床Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(5) : 1612-1621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201305024.htm
[82] 李超, 裴浩翔, 王登红, 等. 山东孔辛头铜钼矿成矿时代及物质来源: 来自黄铜矿、辉钼矿Re-Os同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(2) : 240-249 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201602004.htm
[83] 柳振江, 王建平, 刘家军, 等. 胶东南宿花岗岩中辉钼矿的同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, S1: 483-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1246.htm
[84] 朱保霖, 柳振江, 成少博, 等. 胶东院格庄岩体中辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4) : 1353-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201604021.htm
[85] 刘善宝, 王登红, 陈毓川, 等. 胶东半岛烟台地区邢家山钨钼矿床地质特征及其辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(8) : 1294-1302. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110816&flag=1
[86] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘建辉, 等. 胶东邢家山钼钨矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(9) : 2721-2732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201209006.htm
[87] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 李国华, 等. 胶东邢家山地区燕山早期钼钨成矿母岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(2) : 556-569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201502015.htm
[88] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 等. 胶东中生代动力学演化及主要金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10) : 3045-3080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201510011.htm
[89] 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等. 中国东部岩石圈减薄研究中的几个问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3) : 51-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303005.htm
[90] Zhang J, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, et al. Postcollisional magmatism: Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(3/4) : 512-536.
[91] Deng J, Liu X F, Wang Q F, et al. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of early Cretaceous mafic diking—Lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia[J]. Geological Society America Bulletin, 2017, 129: 1379-1407.
[92] 孟繁聪, 李天福, 薛怀民, 等. 胶莱盆地晚白垩世不同地幔源区的两种基性岩浆——诸城玄武岩和胶州玄武岩的对比[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6) : 1644-1656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606021.htm
[93] 宋明春, 伊丕厚, 徐军祥, 等. 胶西北金矿阶梯式成矿模式[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(7) : 992-1000. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201207006.htm
[94] 王偲瑞, 杨立强, 成浩, 等. 基底构造对矿床定位的控制机制: 焦家金矿带构造应力转移模拟[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5) : 1529-1546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005013.htm
[95] Mao X C, Ren J, Liu Z K, et al. Three-dimensional prospectivity modeling of the Jiaojia-type gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China: A case study of the Dayingezhuang deposit[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 203: 27-44.
[96] Wang S R, Yang L Q, Wang J G, et al. Geostatistical determination of ore shoot plunge and structural control of the Sizhuang world-class epizonal orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(4) : 214.
[97] Yang L, Zhao R, Wang Q F, et al. Fault geometry and fluid-rock reaction: Combined controls on mineralization in the Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2018, 111: 14-26.
[98] Zhang L, Groves D I, Yang L Q, et al. Relative roles of formation and preservation on gold endowment along the Sanshandao gold belt in the Jiaodong gold province, China: importance for province-to district-scale gold exploration[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55: 325-344.
[99] Xia Z M, Liu J L, Ni J L, et al. Structure, evolution and regional tectonic implications of the Queshan metamorphic core complex in eastern Jiaodong Peninsula of China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(5) : 997-1013.
[100] Charles N, Augier R, Gumiaux C, et al. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula(China, East Asia)[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24: 412-428.
[101] 杨喜安, 赵国春, 宋玉波, 等. 胶东牟平-乳山成矿带拆离断层控矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(3) : 339-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201103002.htm
[102] Zhang L, Yang L Q, Wang Y, et al. Thermochronologic constrains on the processes of formation and exhumation of the Xinli orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 81: 140-153.
[103] 林少泽, 朱光, 严乐佳, 等. 胶东地区玲珑岩基隆升机制探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(5) : 832-844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201305004.htm
[104] 张丕建, 宋明春, 刘殿浩, 等. 胶东玲珑金矿田171号脉深部金矿床特征及构造控矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(5) : 855-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201505001.htm
[105] 宋明春, 崔书学, 姜洪利. 山东胶西北矿集区和焦家金矿田成矿构造系统[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(4) : 573-578. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110413&flag=1
[106] 杨立强, 邓军, 宋明春, 等. 巨型矿床形成与定位的构造控制: 胶东金矿集区剖析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(3) : 431-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201903005.htm
[107] Liu X, Fan H R, Evans N J, et al. Exhumation history of the Sanshandao Au deposit, Jiaodong: constraints from structural analysis and(U-Th) /He thermochronology[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1) : 7787.
[108] 李瑞红, 刘育, 李海林, 等. 胶东新城金矿床控矿构造变形环境: 显微构造和EBSD组构约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2546-2558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409008.htm
[109] 钱建平, 陈宏毅, 吴小雷, 等. 胶东望儿山金矿成矿构造分析和成矿预测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(2) : 221-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201102008.htm
[110] Wen B J, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold Province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 96-112.
[111] Liu J C, Wang J Y, Liu Y, et al. Ore genesis of the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Information from fluid inclusions and mineralization[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(S1) : 77-95.
[112] Han Z Y, Yu X W, Li S J, et al. He-Ar isotopic tracing of pyrite from ore-forming fluids of the Sanshandao Au deposit, Jiaodong area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 2019, 93(6) : 1797-1807.
[113] 姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5) : 1327-1340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htm
[114] Deng J, Liu X F, Wang Q F, et al. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 674-686.
[115] 李杰, 宋明春, 梁金龙, 等. 焦家深部金矿床成矿流体来源: 来自黄铁矿微量元素及S-He-Ar同位素的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1) : 297-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001023.htm
[116] Yang L Q, Deng J, Guo R P, et al. World-class Xincheng gold deposit: An example from the giant Jiaodong gold province[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7: 419-430.
[117] 张良, 刘跃, 李瑞红, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床铅同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2468-2480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409002.htm
[118] Chai P, Hou Z Q, Zhang Z Y. Geology, fluid inclusion and stable isotope constraints on the fluid evolution and resource potential of the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Resource Geology, 2017, 67(3) : 341-359.
[119] Guo L N, Deng J, Yang L Q, et al. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103434.
[120] Yang L Q, Deng J, Guo L N, et al. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 585-602.
[121] Feng K, Fan H, Hu F, et al. Involvement of anomalously As-Au-rich fluids in the mineralization of the Heilan'gou gold deposit, Jiaodong, China: Evidence from trace element mapping and in-situ, sulfur isotope composition[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 304-321.
[122] 薄军委, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床C、O、S、Pb同位素组成及矿床成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2) : 321-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202102010.htm
[123] Tan J, Wei J H, He H Y, et al. Noble gases in pyrites from the Guocheng-Liaoshang gold belt in the Jiaodong province: Evidence for a mantle source of gold[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 480: 105-115.
[124] Ma W D, Fan H R, Liu X, et al. Hydrothermal fluid evolution of the Jintingling gold deposit in the Jiaodong peninsula, China: Constraints from U-Pb age, CL imaging, fluid inclusion and stable isotope[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 287-303.
[125] 刘玄, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东大庄子金矿成矿流体及稳定同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30: 675-689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201104008.htm
[126] 郭林楠, 张潮, 宋宇宙, 等. 胶东望儿山金矿床氢-氧同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30: 2481-2494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409003.htm
[127] Wen B J, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Genesis of two different types of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold field, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and stable isotope[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 643-658.
[128] Wei Y J, Yang L Q, Feng J Q, et al. Ore-fluid evolution of the Sizhuang orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(3) : 190-209.
[129] Goldfarb R J, Groves D I. Orogenic gold: common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time[J]. Lithos, 2015, 233: 2-26.
[130] Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211: 47-69.
[131] Deng J, Wang Q F, Santosh M, et al. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere: a new model for the Jiaodong gold Province, eastern China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55: 257-274.
[132] Zhu Z Y, Jiang S Y, Mathur R, et al. Iron isotope behavior during fluid/rock interaction in K-feldspar alteration zone-a model for pyrite in gold deposits from the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China[J]. Geochimical et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 222: 94-116.
[133] Zhang Y W, Hu F F, Fan H R, et al. Fluid evolution and gold precipitation in the Muping gold deposit(Jiaodong, China) : Insights from in-situ trace elements and sulfur isotope of sulfides[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 218: 106617.
[134] Zartman R E, Doe B R. Plumbotectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(1/2) : 135-162.
[135] Faure G. Principles of isotope geology[C]//Friedman, O'Neil J R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest[M]. US Geological Survey Professional Paper(USGPO), 1977: 1-440.
[136] Mills S E, Tomkins A G, Weinberg R F, et al. Implications of pyrite geochemistry for gold mineralisation and remobilisation in the Jiaodong gold district, northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71: 150-168.
[137] Wang Z C, Cheng H, Zong K Q, et al. Metasomatized lithospheric mantle for Mesozoic giant gold deposits in the North China craton. Geology, 2020, 48(2) : 169-173.
[138] 李建威, 毕诗健, Vasconcelos P. 胶东苏鲁地体范家埠金矿成矿作用与矿床成因浅析: 兼与胶北地体金矿对比[J]. 高校地质学报, 2010, 16(2) : 125-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201002001.htm
[139] Wang Z L, Yang L Q, Guo L N, et al. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A fluid inclusion study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 701-717.
[140] Chai P, Zhang Z Y, Hou Z Q. Geological and Fluid Inclusion Constraints on Gold Deposition Processes of the Dayingezhuang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(4) : 955-971.
[141] 刘育, 杨立强, 郭林楠, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2507-2517. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409005.htm
[142] Hu F F, Fan H R, Jiang X H, et al. Fluid inclusions at different depths in the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geofluids, 2013, 13(4) : 528-541.
[143] Li X H, Fan H R, Yang K F, et al. Pyrite textures and compositions from the Zhuangzi Au deposit, southeastern North China Craton: implication for ore-forming processes[J]. Contrib. Miner. Petrol., 2018, 173: 73-93.
[144] 薛建玲, 李胜荣, 庞振山, 等. 胶东邓格庄金矿成矿流体、成矿物质来源与矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(5) : 1453-1468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201805017.htm
[145] 王中亮. 焦家金矿田成矿系统[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2012: 1-230.
[146] 胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨奎锋, 等. 胶东牟平邓格庄金矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 9: 2155-2164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200709014.htm
[147] Li X C, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Hydrothermal alteration associated with Mesozoic granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 53: 403-421.
[148] 陈炳翰, 王中亮, 李海林, 等. 胶东台上金矿床成矿流体演化: 载金黄铁矿稀土元素和微量元素组成约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2518-2532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409006.htm
[149] 郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 等. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源: 蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土与微量元素特征约束[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1) : 121-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901012.htm
[150] 张潮, 刘育, 刘向东, 等. 胶西北新城金矿床硫同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2495-2506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409004.htm
[151] Chai P, Zhang H R, Dong L L. Geology and ore-forming fluids of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Implications for mineral exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 204: 224-239.
[152] Zhao R, Wang Q F, Liu X F, et al. Uplift history of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton: implications for lithosphere thinning and gold mineralization[J]. Geological Magazine, 2017, 155(4) : 1-13.
[153] Hu H L, Fan H R, Liu X, et al. Two-stage gold deposition in response to H2S loss from a single fluid in the Sizhuang deposit(Jiaodong, China)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103450.
[154] Hu H L, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Ore-forming processes in the Wang'ershan gold deposit(Jiaodong, China) : Insight from microtexture, mineral chemistry and sulfur isotope compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 123(C) : 103600.
[155] 赛盛勋, 邱昆峰. 胶东乳山金矿床成矿过程: 周期性压力波动诱发的流体不混溶[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5) : 1547-1566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005014.htm
[156] Fan H, Zhai M, Xie Y, et al. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2003, 38: 739-750.
[157] Xu W G, Fan H R, Yang K F, et al. Exhaustive gold mineralizing processes of the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Displayed by hydrothermal alteration modeling[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 129: 152-169.
[158] 汪浩, 杨立强, 王偲瑞, 等. 胶西北寺庄金矿床红化蚀变过程及其对金成矿贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5) : 1515-1528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005012.htm
[159] Chen B H, Deng J, Wei H T, et al. Trace element geochemistry in quartz in the Jinqingding gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: implications for the gold precipitation mechanism[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(5) : 326.
[160] 沈保丰, 毛德宝, 李俊建. 中国绿岩带型金矿床类型和地质特征[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 1997, 20(4) : 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ199704000.htm
[161] 杨敏之, 吕古贤. 胶东绿岩带金矿地质地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-228.
[162] 李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 等. 胶东金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-423.
[163] 陈衍景, Franco P, 赖勇, 等. 胶东矿集区大规模成矿时间和构造环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(4) : 907-922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200404013.htm
[164] Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: A global synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18(1) : 1-75.
[165] Qiu Y M, Groves D I, McNaughton N G, et al. Nature, age and tectonic setting of granitoid-hosted, orogenic gold deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3/4) : 283-305.
[166] Zhou T H, Lu G. Tectonics, granitoids and mesozoic gold deposits in East Shandong, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2000, 16(1/2) : 71-90.
[167] 蒋少涌, 戴宝章, 姜耀辉, 等. 胶东和小秦岭: 两类不同构造环境中的造山型金矿省[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11) : 2727-2738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911004.htm
[168] 翟明国, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 非造山带型金矿——胶东型金矿的陆内成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1) : 85-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401006.htm
[169] Goldfarb R J, Santosh M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5(2) : 139-153.
[170] Zhu R X, Fan H R, Li J W, et al. Decratonic gold deposits[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(9) : 1523-1537.
[171] Groves D I, Santosh M. The giant Jiaodong gold province: the key to a unified model for orogenic gold deposits?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7: 409-417.
[172] Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment[J]. Economic Geology, 2016, 111: 105-126.
[173] Zhang L, Yang L Q, Weinberg R F, et al. Anatomy of a world-class epizonal orogenic-gold system: A holistic thermochronological analysis of the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 70: 50-70.
[174] Cheng N N, Hou Q L, Shi M Y. New Insight into the Genetic Mechanism of Shear Zone Type Gold Deposits from Muping-Rushan Metallogenic Belt(Jiaodong Peninsula of Eastern China)[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(12) : 775.
[175] 宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1) : 87-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201401008.htm
[176] 田杰鹏, 田京祥, 郭瑞朋, 等. 胶东型金矿: 与壳源重熔层状花岗岩和壳幔混合花岗闪长岩有关的金矿[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(5) : 987-996. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201605012.htm
[177] 李洪奎, 李逸凡, 梁太涛, 等. 山东胶东型金矿的概念及其特征[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(1) : 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201701001.htm
[178] 朱日祥, 孙卫东. 大地幔楔与克拉通破坏型金矿[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(9) : 1444-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202109003.htm
[179] Niu S, Cheng G S, Zhang J Z, et al. Study on the metallogenetism of sub-mantle plume and mantle branches in the gold mineralization concentration area of northwest Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Geologica Sinca, 2014, 5(88) : 1409-1420.
[180] Niu S Y, Chen C, Zhang J Z, et al. The thermal and dynamic process of core→mantle→crust and the metallogenesis of Guojiadian mantle branch in northwestern Jiaodong[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(4) : 249.
[181] De Boorder H. The Jiaodong gold district, northeastern China, in the context of the Late Paleozoic and Late Mesozoic large igneous provinces, orogeny and metallogeny in Eurasia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 574-588.
[182] Groves D I, Santosh M, Deng J, et al. A holistic model for the origin of orogenic gold deposits and its implications for exploration[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2020, 55: 275-292.
[183] Yang Q Y, Santosh M. Early Cretaceous magma flare-up and its implications on gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 626-642.
[184] Sun W D, Li S, Yang X Y, et al. Large-scale gold mineralization in eastern China induced by an Early Cretaceous clockwise change in Pacific plate motions[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(3) : 311-32.
[185] 朱照先, 赵新福, 林祖苇, 等. 胶东金翅岭金矿床黄铁矿原位微量元素和硫同位素特征及对矿床成因的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(3) : 945-959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202003019.htm
[186] Sun H S, Li H, Liu L, et al. Exhumation history of the Jiaodong and its adjacent areas since the Late Cretaceous: Constraints from low temperature thermochronology[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60: 531-545.
[187] Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization: A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 165-178.
[188] 豆敬兆, 付顺, 张华锋, 等. 胶东郭家岭岩体固结冷却轨迹与隆升剥蚀[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8) : 2325-2336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201508014.htm
[189] Wu L, Monié P, Wang F, et al. Multi-phase cooling of Early Cretaceous granites on the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Evidence from40Ar/39Ar and(U-Th) /He thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 334-347.
[190] 倪振平, 李秀章, 温桂军, 等. 山东胶西北地区金矿密集区资源潜力预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(4) : 1223-1234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201304021.htm
[191] 宋明春, 徐军祥. 大型-超大型矿床勘查方法与实践[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 1-397.
[192] 宋明春, 曹春国, 崔书学, 等. 一种深部金矿阶梯式找矿方法[P]. 2017, 中国专利: ZL 2015 1 0056575. X. 2017-11-10.
[193] Song M C, Wan G P, Cao C G, et al. Geophysical-geological interpretation and deep-seated gold deposit prospecting in Sanshandong-Jiaojia area, eastern Shandong Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(3) : 640-652.
[194] Yu X F, Shan W, Xiong Y X, et al. Structural framework and genetic analysis of gold concentration areas in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China: a new understanding based on high-resolution reflective seismic survey[J]. Acta Geologica Sinca, 2018, 92(5) : 1823-1840.
[195] 李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 山东三(山岛) -仓(上) 断裂带金矿床深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(S1) : 713-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1359.htm
[196] 马生明, 朱立新, 韩方法, 等. 胶西北焦家式金矿控矿构造蚀变带的地球化学标志[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(2) : 64-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201702012.htm
[197] Wang J, Zhu L X, Ma S M, et al. Application of the multi-attribute anomaly model for prospecting potential at depth: A case study of the Haiyu Au deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 207: 106359.
[198] 王学求, 张必敏, 于学峰, 等. 金矿立体地球化学探测模型与深部钻探验证[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6) : 869-885. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202006015.htm
[199] 宋明春, 张照录, 刘晓, 等. 矿床三维地质建模[S]. 山东省市场监督管理局, 2021: 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201605018.htm
[200] 王巧云, 刘汉栋, 陈建平, 等. 山东焦家金成矿带三维地质建模及成矿预测[J]. 地质学刊, 2014, 38(3) : 412-420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201403013.htm
[201] 陈进, 毛先成, 刘占坤, 等. 基于随机森林算法的大尹格庄金矿床三维成矿预测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(2) : 231-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202002008.htm
[202] 毛先成, 王迷军, 刘占坤, 等. 基于勘查数据的胶东大尹格庄金矿床控矿地质因素定量分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(4) : 84-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201904012.htm
[203] 于学峰, 杨德平, 李大鹏, 等. 胶东焦家金矿带3000m深部成矿特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(9) : 2893-2910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201909018.htm
[204] 宋明春, 丁正江, 张英传, 等. 一种海域金矿勘查钻探方法[P]. 2017, 中国专利: ZL 2015 1 0805542.0.
[205] 陈师逊, 杨芳, 张军进. 三山岛北部海域金矿海上钻探施工关键技术[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2016, 24(1) : 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201601004.htm
[206] 田振环. 海域金矿找矿方法研究——以山东省莱州市三山岛北部海域金矿为例[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(S1) : 19-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1003.htm
[207] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 等. 胶东焦家和三山岛巨型金矿床的发现及有关问题讨论[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(1) : 92-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901008.htm
[208] 刘殿浩, 张丕建, 丁正江, 等. 三山岛北部海域金矿勘查工作思路与实践[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015, 31(2) : 1-6, 11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201502002.htm
[209] 李国华, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东新类型金矿——辽上黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3) 423-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703012.htm
[210] 纪攀, 丁正江, 李国华, 等. 胶东辽上特大型金矿床地质特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2016, 32(6) : 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201606003.htm
-



 下载:
下载:
