Study on Preparation and Au(Ⅲ) Adsorption Ability of Nitric Acid Modified Activated Carbon
-
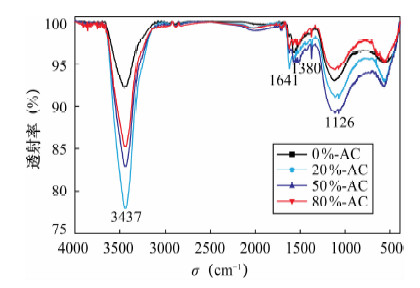
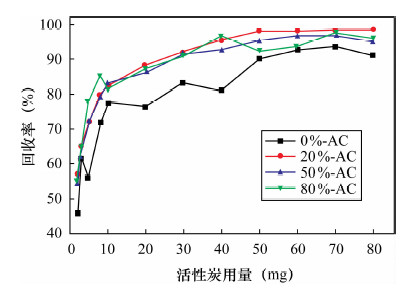
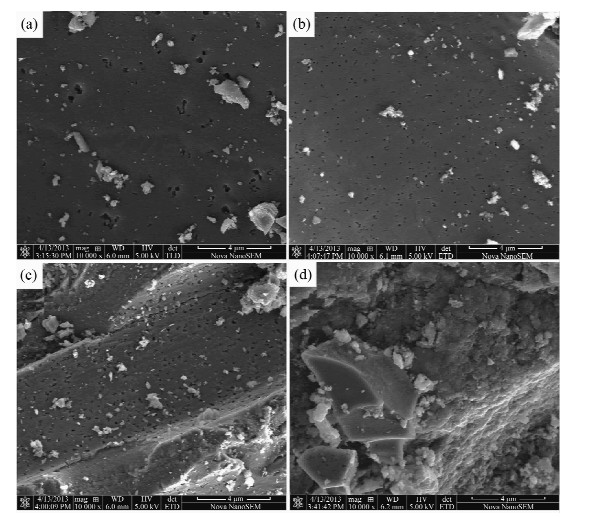
摘要: 活性炭因具有良好的吸附性能而得到广泛应用,但其吸附能力有限。本文采用氟化氢铵和不同浓度硝酸(0~80%硝酸)对活性炭进行表面改性处理,利用扫描电镜(SEM)、傅里叶变换红外光谱法(FT-IR)、BET氮吸附法、Boehm滴定法对改性前后活性炭进行了表征分析,并比较了改性前后的活性炭对Au(Ⅲ)的吸附效果。结果表明:随着硝酸浓度的增加,改性活性炭的灰分、平均比表面积、孔隙容量、吸附孔径均有不同程度的降低,发达的微孔结构受到影响,表面性能降低不利于增加其吸附容量;但表面含氧官能团羟基、羧基数量均明显增加,活性炭的极性、亲水性、催化性能、表面电荷和骨架电子密度发生改变,对金属离子的吸附选择性和吸附能力有所提高。20%硝酸改性活性炭的平均比表面积、孔径容量、吸附孔径减小程度较低,酚羟基含量和含氧官能团总量分别却增加了168.3%、109.1%;用于吸附Au(Ⅲ)的回收率可达99.1%,较未改性的活性炭提高最大,金测定值的精密度好(相对标准偏差为0.6%~1.4%),准确度高。表征分析表明,改性活性炭对金的吸附是表面物理吸附和官能团化学吸附并存的过程,而且官能团化学吸附起主要作用。Abstract: Activated carbon has been widely used due to its good adsorption performance; however, the adsorption capacity is limited. Activated carbon was modified by ammonium hydrogen fluoride and nitric acid with a series of different concentrations. The surface chemical characteristics of pre-modified and post-modified activated carbon were analyzed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrosocopy (FT-IR), Brunauer-emmett-teller (BET) Nitrogen Adsorption and Boehm Titration, and also their adsorption capability on Au(Ⅲ) was compared. The results showed that the ash, the specific surface area, pore volume and pore size of post-modified activated carbons decreased along with increasing concentration of nitric acid, which affected porous structure and reduced the absorption capacity. However, the quality of functional groups of hydroxyl and carboxyl dramatically increased. The polarity, hydrophilic, catalytic properties, surface charge and skeleton electron density of the activated carbon were improved, which increased adsorption selectivity and adsorption capacity for metal ions. The specific surface area, pore volume and pore size of activated carbon modified by 20% concentration of nitric acid had lower degree of reduction, but phenolic hydroxyl content and total oxygen functional groups were increased by 168.3% and 109.1%. Compared with pre-modified activated carbon, Au(Ⅲ) adsorption rates of activated carbon modified by 20% concentration of nitric acid had the largest increase of up to 99.1%. The precision range of Au determination was 0.6%-1.4% with high accuracy. Adsorption on Au(Ⅲ) of post-modified activated carbon was the coexistence of surface physical adsorption and chemical adsorption of functional groups, and chemical adsorption played a main role.
-
Key words:
- activated carbon /
- modification /
- Au /
- adsorption capability
-

-
表 1 活性炭改性前后灰分含量比较
Table 1. Comparison of ash content in unmodified and modified activated carbon
活性炭编号 灰分含量(%) 活性炭编号 灰分含量(%) 0%-AC 0.69 50%-AC 0.56 20%-AC 0.51 80%-AC 0.52 表 2 活性炭改性前后的表面积、孔径、孔容
Table 2. Specific surface area, pore size and pore volume of unmodified and modified activated carbons
物理性能 未改性活性炭0%-AC 改性活性炭 20%-AC 50%-AC 80%-AC BET比表面积(m2/g) 893.09 856.60 824.57 792.47 平均吸附孔径(nm) 2.543 2.536 2.518 2.507 平均孔隙容量(m3/g) 0.565 0.533 0.514 0.492 表 3 活性炭表面含氧官能团滴定结果
Table 3. Boehm titration results of oxygen groups on several GACS’ surface
活性炭 含氧官能团含量(mmol/g) 酸性官能团总量 (mmol/g) 羧基 内酯基 酚羟基 0%-AC 0.0919 0.0731 0.1324 0.2974 20%-AC 0.1729 0.0930 0.3552 0.6221 50%-AC 0.2611 0.1078 0.2941 0.6630 80%-AC 0.3264 0.1424 0.2254 0.6942 表 4 回收试验结果及精密度
Table 4. Recovery and precision tests for Au(Ⅲ)
活性炭 金加入量(μg) 金回收量(μg) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 0%-AC 50 48.1 41.6 45.5 46.5 42.3 89.6 6.2 20%-AC 49.2 48.2 47.8 47.6 48.8 96.6 1.4 50%-AC 47.8 48.3 45.6 43.6 46.4 92.7 4.0 80%-AC 49.5 45.8 46.1 44.2 45.1 92.3 4.4 0%-AC 400 381 365 355 370 347 90.9 3.6 20%-AC 399 398 398 396 386 98.9 1.4 50%-AC 396 384 389 390 378 96.9 1.8 80%-AC 391 369 372 383 371 94.3 2.5 0%-AC 1000 944 938 932 918 927 93.2 1.1 20%-AC 990 998 995 986 984 99.1 0.6 50%-AC 991 982 986 972 975 98.1 0.8 80%-AC 987 965 981 971 963 97.3 1.1 表 5 标准物质分析
Table 5. Analytical results of Au in standard materials
改性活性炭 标准物质编号 金含量(μg/g) 相对误差(%) 测定值 平均值 标准值 20%-AC GBW(E) 5.47 5.44 5.56 5.38 5.44 5.55±0.35 -1.98 070029 5.50 5.42 5.37 5.34 20%-AC GBW 18.5 17.8 18.1 17.9 18.0 18.3±0.40 -1.64 07297 17.8 17.6 18.0 18.1 -
[1] 孙兴家.活性炭吸附金的机理、应用及工艺管理[J].黄金科学技术,1994,2(5):34-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ405.005.htm
[2] 杨坤彬,彭金辉,郭胜惠,张利波,黄孟阳,夏洪应,张世敏.提金活性炭的研究现状及其展望[J].黄金,2007,28(1):46-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200701011.htm
[3] 薛光,姚万林,刘永生.地质样品中金富集分离方法的最新进展[J].黄金,2004,25(3):45-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200403016.htm
[4] 叶振华.化工吸附分离过程[M].北京:中国石化出版社,1992:2101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm
[5] Paul C J, Wu S N.Acid base-treated activated carbon: Characterization of functional groups and metal adsorptive properties[J].Langmuir,2004,20:2033-2242. doi: 10.1021/la0358015
[6] 杨金辉,王劲松,周书葵,邓钦文.活性炭改性方法的研究进展[J].湖南科技学院学报,2010,31(4):90-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JMLK201004027.htm
[7] 余梅芳,胡晓斌,倪生良.化学改性活性炭对Cu(Ⅱ)离子吸附性能的研究[J].湖州师范学院学报,2006,28(2):43-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZHX200602014.htm
[8] 陈仁辉.用煤质活性炭和合成活性炭吸附黄金[J].新型炭材料,1992(4):18-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTCL199204004.htm
[9] Yalcin M, Arol A I. Gold cyanide adsorption characteristics of activated carbon of non-coconut shell origin [J].Hydrom Etallurgy,2002,63:201-206. doi: 10.1016/S0304-386X(01)00203-1
[10] 魏留芳,周亚平,苏伟.氟化炭材料性能研究进展[J].炭素技术,2005,24(6):30-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TSJS200506012.htm
[11] 邱介山,王艳斌,邓贻钊.几种活性炭表面酸性基团的测定及其对吸附的影响[J].炭素技术,1996,3(4):11-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TSJS604.002.htm
[12] Boehm H P.Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon black and carbons[J].Carbon,1994,32 (5):759-769. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(94)90031-0
[13] 候方,陈明,佟朋友.硝酸处理对活性炭性能的影响[J].化学与生物工程,2011,28(5):70-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCHG200606004.htm
[14] 何玮,高琳,卢振伟,孙继红.煤质和木质吸金活性炭的结构与性能研究[J].化学试剂,2011,33(3):245-249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ201103018.htm
[15] 吴开金,官新宇,官九红,陈涵,林冠烽.硝酸改性对活性炭吸附性能的影响[J].福建林业科技,2009,36(4):35-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLK200904009.htm
[16] 冉龙国,黄 颖,张伟.硝酸处理对超级电容器用活性碳性能的影响[J].广州化工,2009,37(1):89-91. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA200901033.htm
[17] 张瑶,张克荣,罗永义,李崇福,蒋丽.活性炭对铅镉镍钴离子的吸附机理探讨[J].华西医科大学学报,1995,26(3):322-325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK503.026.htm
[18] Tolesc A, Marshall W E, Johns M.Surface functional groups on acid-actubated nut-shell carbons[J].Carbon,1999,37(7):1207-1214.
[19] 丁春生,彭芳,黄燕,曾海明,徐召燃.硝酸改性活性炭的制备及其对Cu2+的吸附性能[J].金属矿山,2011(10):135-138.
[20] 范延臻,王宝贞,王琳,余敏.改性活性炭对有机物的吸附性能[J].环境化学,2001,20(5):444-448. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX200105005.htm
[21] 孟冠华,李爱民,张全兴.活性炭的表面含氧官能团及其对吸附影响的研究进展[J].离子交换与吸附,2007,23(1):88-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJYX200701012.htm
[22] 彭芳.硝酸改性活性炭的制备及其吸附Cu2+、Cr6+的性能研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2012.
-



 下载:
下载: