Investigation on the Coloring Mechanism of Freshwater Cultured Pearls with Different Color
-
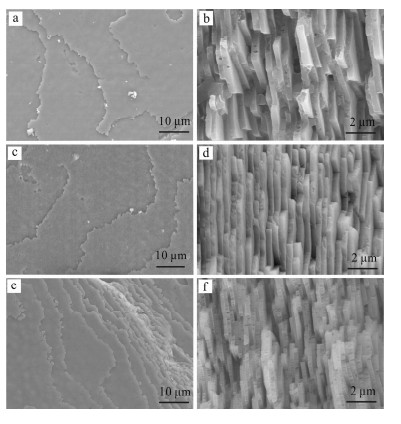
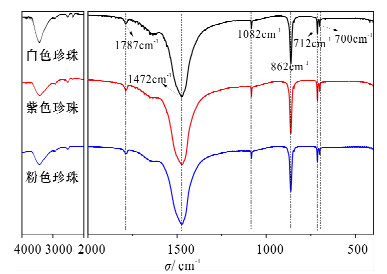
摘要: 珍珠的呈色机理一直存在有机物致色学说与微量金属离子致色学说,鉴于有机物致色机理与物体本身结构无关及珍珠中微量金属元素的测定,这些理论用于解释珍珠时呈色存在明显的局限,直至目前珍珠的呈色机理尚无定论。本文采用傅立叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)、X射线荧光光谱(XRF)、场发射扫描电镜(FE-SEM)等技术,对白、紫、粉红三种颜色的淡水养殖珍珠的呈色机理进行较为系统的研究。结果表明:不同颜色珍珠的红外光谱无明显差异;粉色珍珠中Ti、Fe、Mg与Cu的含量较白色与紫色珍珠高,白色珍珠中Mn的含量较粉色珍珠高;粉色与白色珍珠中Ti、Fe、Cu的含量差异较大,但紫色与白色珍珠中Ti、Fe、Cu的含量几乎接近;不同颜色珍珠的研磨粉体的颜色基本一致,反射主波长为(582±1) nm,说明珍珠内有机质与致色金属元素不应是珍珠呈色差异的主要原因。在同一直径不同颜色的珍珠中,其近外表面区域内珍珠层文石板片的厚度大小不一,其中粉色珍珠中文石板片的厚度相对较薄;珍珠表面的“叠瓦状”结构疏密也并不一致,粉色珍珠表面的文石片层更为紧密。研究认为,珍珠中内部文石板片厚度及其外表面形貌的差异应是珍珠呈现不同颜色的直接原因。Abstract: The coloring mechanism of pearls was debated on organic pigment or trace metal ions. In view of the theory of the coloring mechanism from organic pigment, which had no relationship with the structure of the object combined with the results of the trace metal elements determined by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry or the other instruments, the above two theories can not explain the coloring of pearls. The coloring mechanism of freshwater cultured pearls was investigated by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry and Field Emission-Scanning Electronic Microscope. The results indicate that, in terms of pearls with different color, the characteristic peaks were almost the same in the middle IR spectra of freshwater cultured pearls, which is due to the chemical bonds of organics in pearls. The contents of Ti, Fe, Mg and Cu elements in pink pearls were higher than those in white and purple pearls. Additionally, the content of Mn in white pearl was higher than that in pink ones. The contents of Ti, Fe and Cu elements were different between white and pink pearls, but they were the same between white and purple pearls. The color of ground powders of white, violet and pink pearls was almost the same yellow and the domain reflection wavelength was (582±1) nm. The above results showed that the coloring mechanism is from organic pigment or those trace metal elements directly. Although the diameters of pearls were the same, it was firstly discovered that the thickness of aragonite sheets were obviously different in the nacreous layer near the surface region of pearls for different colored pearls. The aragonite sheets hosted in pink pearls were the thinnest. Furthermore, the imbricate structure and morphology were also different on the surface of pearls, and that on the surface of pink pearls was the most inseparable when comparing with white and purple pearls. Hereby, the coloring mechanism of freshwater cultured pearl was attributed to the differences in the thickness of aragonite sheets and surface morphology.
-

-
表 1 不同颜色珍珠粉体的颜色测量结果
Table 1. The testing results of different color for pearl powder
样品名称 (RGB) (Lab) 反射主波长
λ/nmR G B L a b 白色珍珠 87 84 82 108.5 -7.9 -3.5 581 紫色珍珠 88 84 81 113.8 -7.7 -2.8 582 粉色珍珠 89 84 81 113.0 -7.5 -2.8 583 表 2 不同颜色的淡水养殖珍珠化学组成
Table 2. Chemical composition of freshwater cultured pearl with different color
样品
名称wB/% CaO Na2O MnO2 TiO2 MgO SrO P2O5 SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 CuO 白色 55.3300 0.5560 0.1790 0.1100 0.0766 0.0602 0.0566 0.0338 0.0230 0.0099 0.0051 紫色 55.3500 0.5740 0.0897 0.1400 0.0732 0.0657 0.0605 0.0342 0.0195 0.0201 0.0059 粉色 54.7800 0.6340 0.0710 0.4870 0.1100 0.0555 0.0770 0.0963 0.0411 0.0274 0.0092 表 3 不同颜色珍珠模拟反射峰位
Table 3. Simulated reflection peak wavelength of pearls with different color
样品名称 厚度/nm ne 反射峰位/nm 文石板片L1 有机质层L2 N=2 N=3 N=4 白色珍珠 403.30 38.60 1.58 696.43 464.28 348.21 紫色珍珠 351.23 33.62 606.52 404.35 303.26 粉色珍珠 253.33 24.25 437.47 291.64 218.74 -
[1] Ma H Y, Li R K, Yang L X, Zhang B L, Shen M D, Mu S C, Wei Q G. A modified integrated model of the internal structure of Chinese cultured pearls [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology—Materials Science Edition, 2011, 26(3): 510-513. doi: 10.1007/s11595-011-0258-5
[2] 张妮,郭继春,张学云,李加贵.淡水珍珠中文石球粒的发现与成珠机制探讨[J].矿物学报,2005, 25(3): 307-311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200503017.htm
[3] 张恩,彭明生,梁超伦,邹永廖,邢铭.珍珠显微结构及纳米矿物的电镜分析[J].矿物学报,2008, 28(2): 112-116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200802002.htm
[4] 黄青萍,盘红梅.珍珠的药理作用及临床应用[J].时珍国医国药, 2000, 11(6): 564-565.
[5] Hoskins C L, Alexander V. Determination of carotenoid concentrations in marine phytoplankt on by resonance Raman spectrometry [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1977, 49(6): 695-697. doi: 10.1021/ac50014a008
[6] Vukusic P, Sambles J R, Lawrence C R. Color mixing in wing scales of a butterfly [J]. Nature, 2000, 404: 457. doi: 10.1038/35006561
[7] Vukusic P, Sambles J R, Lawrence C R. Photonic structure in biology [J]. Nature, 2003, 424: 852-855. doi: 10.1038/nature01941
[8] 李勃,李琦,周济,李龙土.庄周之梦蝶的光子带隙结构[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(22): 2367-2368. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.22.019
[9] Zi J, Yu X, Li Y, Xu C, Wang X. Coloration strategies in peacock feather[J]. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences, 2003, 100(22): 12576-12578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2133313100
[10] Paker A R, Welch V L, Driver D, Matini N. Structure color-opal analogue discovered in a weevil [J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 786-787. doi: 10.1038/426786a
[11] 李耿,林瓴,沙拿利,赵海云.淡水养殖珍珠的光泽颜色与有机质的关系初探[J].桂林工学院学报,2007, 27(4): 569-571. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX200704024.htm
[12] 张刚生,谢先德,王英.三角帆蚌贝壳珍珠层中类胡萝卜素的激光拉曼光谱研究[J].矿物学报,2001, 21(3): 389-392. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200103024.htm
[13] 杨明月,郭守国,史凌云,王伟忠.淡水养殖珍珠的化学成分与呈色机理研究[J].宝石与宝石学杂志,2004, 6(2): 10-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB200402004.htm
[14] 李雪英,王海增,孙省利,张际标.不同颜色珍珠的傅里叶变换红外光谱和石墨炉原子吸收光谱分析[J].宝石与宝石学杂志, 2007, 9(1): 15-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB200701006.htm
[15] Yablonovitch E. Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1987, 58(20): 2059-2062. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.2059
[16] John S. Strong localization of photonics in certain disordered dielectric super lattices [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1987, 58(20): 2486-2489.
[17] Ho K M, Chan C T, Soukoulis C M. Existence of a photonic gap in periodic dielectric crystals by multibeam laser interference into a photopolymerizable resin[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1990, 65(25): 3152-3155. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.3152
[18] Li Z Y, Wang J. Creation of partial band gaps in anisotropic photonic-band-gap structure[J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(7): 3721-3729. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.58.3721
[19] Yablonovitch E. Photonic band gap structures [J]. Journal of Optical Society of American B, 1993, 10(2): 283-294. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.10.000283
[20] Fink Y, Winn J N, Fan S, Chen C. A dielectric omnidirectional reflector [J]. Science, 1998, 282(5394): 1679-1682. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5394.1679
[21] 木士春,马红艳.养殖珍珠微量元素特征及其对珍珠生长环境的指示意义[J].矿物学报, 2001, 21(3): 551-553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200103068.htm
[22] 张妮,郭继春,张学云,李加贵.珍珠表面形貌的AFM和SEM研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2004, 24(4): 370-374.
[23] 李勃,周济,李龙土,李琦,韩朔,郝智彪.鲍鱼壳中的一维光子带隙结构[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(13): 1422-1424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.13.022
[24] 严俊,张刚生.褶纹冠蚌贝壳结构特征及其彩虹色呈色机制[J].安庆师范学院学报:自然科学版, 2011, 17(3): 83-85.
[25] 张伟钢,严俊,汪港,李浩璇,张刚生.一种天然湿敏性二维可调光子带隙材料及其光学性能研究[J].无机材料学报, 2009, 24(1): 57-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WGCL200901011.htm
[26] Tan T L, Wong D, Lee P. Iridescence of a shell of mollusk Haliotis Glabra [J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(20): 4847-4854. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.004847
-



 下载:
下载: