Determination of Fifteen Rare-earth Elements in Iron Ores Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry with Microwave Digestion
-
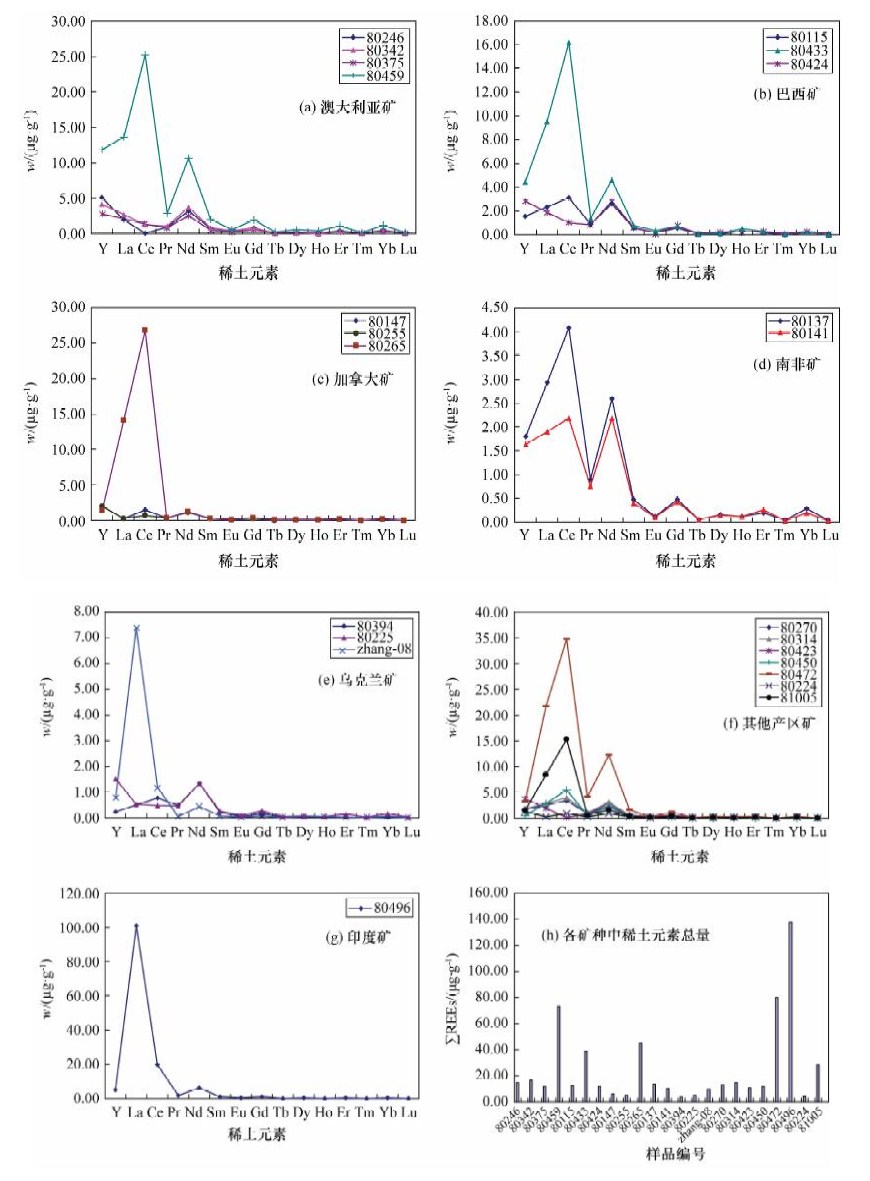
摘要: 分析地质样品中稀土元素的含量,现有的方法都受到基体干扰和共存元素干扰,电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)已在痕量元素分析中得到广泛应用,通过条件优化可准确测定稀土元素。本文建立了ICP-MS同时测定铁矿石中钇镧铈镨钕钐铕钆铽镝钬铒铥镱镥15个稀土元素的方法,样品用盐酸、硝酸和氢氟酸高温密闭消解,消解完全后转移定容,在线加入103Rh、115In、185Re内标液进行测定,方法回收率为95%~104%,精密度(RSD)≤3.5%。对12个国家24个代表性主产区进口的铁矿石样品进行检测,分析其稀土元素的配分模式特征为右倾型轻稀土富集,现阶段的进口铁矿粉多为多产区复合配矿。本方法较其他传统方法大幅降低能耗,提高了分析效率,初步探讨的稀土元素丰度特征可为研究主产区铁矿石的矿床成因、提高我国烧结球团矿的加工工艺提供依据。
-
关键词:
- 铁矿石 /
- 稀土元素 /
- 微波消解 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract: Matrix interference and co-existent elemental interference are the two key factors necessary to obtain accurate analysis results for Rare earth elements (REEs) in geological samples using the traditional methods. Since Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is widely conducted in the field of trace element analysis, accurate results of REEs are obtained under optimized conditions. This method was established using ICP-MS to determine 15 REEs and is detailed in this paper. The samples were digested in sealed containers with HCl, HNO3 and HF at high temperature. The solutions were set into a constant volume. Internal standard solutions of 103Rh, 115In and 185Re were on-line loaded into the sample solution during the measurement. The recovery rates are 95%-104% and the RSDs are less than 3.5%. REEs in 24 representative ore samples from 12 countries were analyzed and are reported in this paper. The results show that importing iron ores are LREEs enrichment type. Currently, imported fine ores are mostly combined with different iron ores from multi productive areas. This provides a technical reference for the comprehensive utilization of rare earth elements in iron ore and pollution control and also provides valuable information on the origin of the iron ore. -

-
表 1 试样消解程序设计
Table 1. Microwave acid digestion procedure
消解步骤 设定温度
θ/℃升温/降温时间
t/min温度保持时间
t/min1 150~160 1~5 1~5 2 180~200 1~5 10~20 3 100 1 10 4 100 1 0 表 2 ICP-MS工作参数
Table 2. Operating parameters of ICP-MS
工作参数 设定条件 RF功率 1150 W 采样深度 7.8 mm 载气流速 1.2 L/min 采样锥直径 1.0 mm 截取锥直径 0.4 mm 采样锥类型 镍锥 雾化泵转速 0.1 r/s 重复次数 3次 积分时间 1 s 灵敏度 7Li ≥ 8000 cps 89Y ≥ 20000 cps 205Tl ≥ 12000 cps 表 3 校准曲线及相关指标
Table 3. Calibration curve and relative index
稀土元素 质量数
m/z丰度/% 内标元素 回归方程 相关系数
r检出限/
(ng·mL-1)浓度范围
ρ/(ng·mL-1)Y 89 100 103Rh y=1.132x+0.1503 0.9999 0.0040 0~50 La 139 99.91 115In y=1.216x+0.3198 0.9999 0.0060 0~50 Ce 140 88.48 115In y=1.139x+0.5091 0.9999 0.0200 0~50 Pr 141 100 115In y=1.206x+0.4528 0.9998 0.0031 0~50 Nd 146 17.62 115In y=0.2275x+0.08503 0.9998 0.0073 0~50 Sm 147 14.97 115In y=1.921x+0.01943 1.0000 0.0077 0~50 Eu 151 47.82 185Re y=1.576x+0.0208 1.0000 0.0025 0~50 Gd 157 15.68 185Re y=0.5192x+0.03678 1.0000 0.0122 0~50 Tb 159 100 185Re y=3.229x+0.6124 0.9999 0.0014 0~50 Dy 163 24.97 185Re y=1.216x+0.3198 1.0000 0.0060 0~50 Ho 165 100 185Re y=1.139x+0.5091 0.9999 0.0200 0~50 Er 166 33.41 185Re y=1.081x+0.2177 0.9999 0.0035 0~50 Tm 169 100 185Re y=3.340x+0.1241 1.0000 0.0012 0~50 Yb 174 31.84 185Re y=1.114x+0.02557 1.0000 0.0086 0~50 Lu 175 97.41 185Re y=3.268x-0.3094 1.0000 0.00077 0~50 表 4 内标对基体效应的消除作用
Table 4. Elimination effect of internal standard for the matrix effect
待测元素 内标元素 加内标测定值
ρ/(ng·mL-1)RSD/% 无内标测定值
ρ/(ng·mL-1)RSD/% Y 103Rh 0.97 0.86 0.75 1.55 La 115In 1.03 1.03 0.74 2.03 Ce 115In 1.05 2.12 0.70 2.87 Pr 115In 1.02 2.35 0.69 3.05 Nd 115In 1.06 1.98 0.62 2.92 Sm 115In 1.01 1.60 0.67 1.47 Eu 185Re 1.00 1.10 0.71 1.23 Gd 185Re 1.01 0.95 0.67 1.09 Tb 185Re 0.98 2.45 0.70 2.13 Dy 185Re 1.00 0.55 0.63 1.34 Ho 185Re 0.99 1.73 0.66 0.96 Er 185Re 1.04 1.02 0.61 2.22 Tm 185Re 1.00 0.25 0.58 0.88 Yb 185Re 1.01 1.30 0.60 1.64 Lu 185Re 1.00 0.62 0.60 2.35 表 5 样品中15个元素的加标回收率
Table 5. Accuracy tests of the method
待测元素 ρ/(ng·mL-1) 回收率/% RSD/% 加标量 初始值 检测值 Y 10.0 11.84 21.78 99.5 1.8 La 10.0 13.68 23.71 100.2 2.0 Ce 25.0 25.25 50.53 101.1 1.9 Pr 3.0 2.91 5.79 95.8 2.9 Nd 10.0 10.66 20.47 98.2 3.5 Sm 2.0 2.03 4.08 102.7 2.2 Eu 0.5 0.58 1.10 103.6 1.6 Gd 2.0 1.98 3.97 99.4 1.4 Tb 0.5 0.26 0.76 100.7 2.6 Dy 0.5 0.61 1.12 101.0 3.2 Ho 0.5 0.45 0.95 100.2 3.3 Er 1.0 1.1 2.10 99.6 1.7 Tm 0.2 0.16 0.36 98.9 0.3 Yb 1.0 1.16 2.17 100.8 2.5 Lu 0.2 0.17 0.37 98.9 0.4 表 6 检测下限的确定
Table 6. Detection limits of the method
待测元素 样品空白分次测定值ρ/(μg·L-1)
标准偏差(δ空)3δ空 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Y 0.2100 0.2085 0.2138 0.2130 0.2078 0.2159 0.2170 0.2069 0.2849 0.2528 0.1758 0.2268 La 7.5696 7.9035 8.0951 7.7138 8.0517 8.0312 7.9104 7.8157 10.9233 8.0970 1.2882 3.2251 Ce 0.7863 0.7564 0.7491 0.7605 0.7609 0.7605 0.7574 0.7375 0.8611 0.7921 0.5442 0.6145 Pr 0.4766 0.4813 0.4758 0.4740 0.4775 0.4785 0.4725 0.4776 0.5001 0.4817 0.4605 0.4760 Nd 0.0874 0.0883 0.0880 0.0881 0.0878 0.0884 0.0879 0.0877 0.0906 0.0886 0.0859 0.0877 Sm 0.0255 0.0251 0.0265 0.0235 0.0266 0.0242 0.0246 0.0252 0.0277 0.0251 0.0207 0.0232 Eu 0.0289 0.0296 0.0327 0.0264 0.0313 0.0310 0.0314 0.0254 0.0353 0.0372 0.0245 0.0318 Gd 0.0401 0.0404 0.0404 0.0410 0.0407 0.0407 0.0401 0.0398 0.0422 0.0421 0.0376 0.0392 Tb 0.6861 0.6845 0.6796 0.6719 0.6639 0.6603 0.6797 0.6594 0.6757 0.6735 0.6220 0.6412 Dy 0.3319 0.3273 0.3268 0.3287 0.3235 0.3272 0.3272 0.3269 0.3280 0.3266 0.3219 0.3260 Ho 0.5127 0.5125 0.5133 0.5115 0.5134 0.5119 0.5122 0.5125 0.5140 0.5125 0.5098 0.5113 Er 0.2407 0.2298 0.2296 0.2358 0.2311 0.2328 0.2301 0.2283 0.2357 0.2313 0.2215 0.2291 Tm 0.1573 0.1446 0.1434 0.1486 0.1343 0.1445 0.1445 0.1436 0.1467 0.1428 0.1298 0.1412 Yb 0.0366 0.0355 0.0340 0.0307 0.0298 0.0314 0.0333 0.0323 0.0374 0.0394 0.0287 0.0349 Lu 0.3393 0.3349 0.3359 0.3335 0.3294 0.3323 0.3348 0.3198 0.3386 0.3308 0.3150 表 7 进口铁矿石样品稀土元素分析
Table 7. Analytical results of REEs in imported iron ore samples
样品编号 进口铁矿石矿种 ∑REEs/
(μg·g-1)中文名称 英文名称 80342 澳大利亚PORTMAN粉铁矿 Australia PORTMAN fines 16.40 80246 澳大利亚PORTMAN块铁矿 Australia PORTMAN lump 14.87 80375 澳大利亚哈默斯利块铁矿 Australia Hamsly lumps 12.08 80459 澳大利亚哈默斯利粉铁矿 Australia Hamsly fines 72.82 80115 巴西CVRD细精粉铁矿 Brazil CVRD concentrates 12.44 80433 巴西CVRD粉铁矿 Brazil CVRD fines 39.09 80424 巴西粉铁矿 Brazil fines 12.11 80147 加拿大球团矿 Canada pellets 6.39 80255 加拿大球团矿 Canada pellets 5.50 80265 加拿大细精粉铁矿 Canada concentrates 45.24 80423 毛里塔尼亚粉铁矿 Mauritania fines 11.22 80224 秘鲁球团矿 Beru pellets 21.77 80137 南非粉铁矿 South Africa fines 14.21 80141 南非块铁矿 South Africa lump ores 10.36 80314 委内瑞拉粉铁矿 Venezuela fines 15.03 80270 委内瑞拉块铁矿 Venezuela lump ores 13.48 80225 乌克兰粉铁矿 Ukraine fines 5.41 80394 乌克兰细精粉铁矿 Ukraine concentrates 3.85 Zhang-08 乌克兰球团矿 Ukraine pellets 10.18 80450 俄罗斯细精粉铁矿 Russia concentrates 12.08 80472 智利细精粉铁矿 Chile concentrates 80.22 80496 印度粉铁矿 India fines 137.28 80224 秘鲁球团矿 Peru pellets 4.31 81005 伊朗块铁矿 Iran lump ores 28.74 -
[1] Castor S B, Hedrick J B. Rare Earth Elements [M]//Industrial Minerals and Rocks. New York: Elsevier Press, 2006: 769-792.
[2] 闫升好,张招崇,王义天,陈柏林,周刚,何立新.新疆阿尔泰山南缘乔夏哈拉式铁铜矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].矿床地质,2005,24(1): 25-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200501003.htm
[3] 潘景瑜.铁矿中微量稀土元素总量的分离与测定[J].地球化学,1983(1): 98-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198301010.htm
[4] 何久康,苏淑琴,彭妹丽.DBC-CPA显色树脂相光度法测定铁矿中稀土总量方法研究[J].内蒙古大学学报: 自然科学版,1989,20(1): 87-90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMGX198901016.htm
[5] 武晓丽.三氯偶氮氯膦树脂相光度法测定铁矿中的稀土总量[J].分析化学,2002,30(4): 506. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX200204034.htm
[6] GBT 6730.24—2006,铁矿石 稀土总量的测定;萃取分离-偶氮氯膦mA分光光度法[S].
[7] 杨枝,李伯平,罗明标,宋金如,刘维.微色谱柱分离-光度法测定高稀土铁矿石中的微量钍[J].分析试验室,2008,27(3): 52-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY200803015.htm
[8] GB/T 6730.25—2006,铁矿石;稀土总量的测定;草酸盐重量法[S].
[9] 杨瑞瑛,贾秀琴,张海珠.中子活化法研究中祁连清水沟蛇绿岩中稀土元素的地球化学特征[J].同位素,2006,19(2): 65-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TWSZ200602000.htm
[10] Brunfelt A O, Roelandts I, Steinnes E. Determination of rubidium, caesium, barium and eight rare earth elements in ultramafic rocks by neutron-activation analysis[J].Analyst, 1974, 99: 277-284. doi: 10.1039/an9749900277
[11] 康惟道,孙素卿.原子吸收光谱法分析稀土元素的进展[J].光谱实验室,1991,8(4/5): 1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS1991Z2000.htm
[12] Djingova R, Ivanova J.Determination of rare earth elements in soils and sediments by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after cation-exchange separation [J].Talanta, 2002, 57: 821-829. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00126-1
[13] 田晓娅,张宏志.ICP-AES法同时测定岩石、矿物、土壤等样品中十五种稀土元素的方法研究[J].光谱实验室,1996,13(5): 57-63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS605.013.htm
[14] Robinson P, Higgins N C, Jenner G A. Determination of rare-earth elements, yttrium and scandium in rocks by anion exchange-X-ray fluorescence technique [J].Chemical Geology, 1986, 55(1-2): 121-137. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(86)90132-4
[15] Zhang J, Nozaki Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji basins of the western South Pacific Ocean [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23): 4631-4644. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00276-1
[16] 王初丹,侯明.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中的稀土、钍元素[J].桂林理工大学学报,2011,31(3): 454-456. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201103025.htm
[17] 常帼雄,李先锋,孙元方.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定15种稀土元素浅议[J].内蒙古水利,2011(3):176-178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSYJ200906032.htm
[18] 赵伟,张春法,郑建业.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].山东国土资源,2011,27(10): 49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2011.10.015
[19] GB/T 6682—2008,分析实验室用水规格和试验方法[S].
[20] 陈贺海,鲍惠君,付冉冉,应海松,芦春梅,金献忠,肖达辉.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定铁矿石中铬砷镉汞铅[J].岩矿测试,2012,31(2): 234-240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201202006.htm
[21] Houk R S.Mass spectrometry of inductively coupled plasma [J].Analytical Chemistry, 1986, 58(1): 97A-105A. doi: 10.1021/ac00292a003
[22] 李冰,尹明.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定生物样中的超痕量稀土时氧化物干扰的研究[J].岩矿测试,2000,19(2): 101-105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200002004.htm
[23] Longerich H P, Fryer B J, Strong D F, Kantipuly C J. Effects of operating conditions on the determination of the rare earth elements by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy,1987,42(1-2): 75-92. doi: 10.1016/0584-8547(87)80051-4
[24] 任春生,付冉冉,余清.铁矿石检验结果的数据处理[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2009: 98-104.
-



 下载:
下载: