The Application of Electron Microprobe Dating Method on a Genetic Type of Uraninite
-
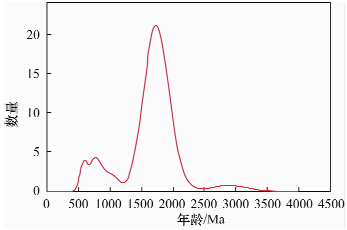
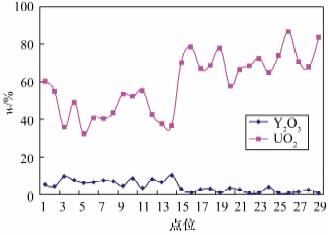
摘要: 电子探针Th-U-Pb测年因其高分辨率与高精度的优势,在独居石、锆石等定年矿物中得到了推广,但在Th、U、Pb含量高的晶质铀矿、沥青铀矿等矿物中则应用较少。本文在铁矿床变质岩绿泥石、阳起石黑云母蚀变岩首次发现U含量高的晶质铀矿,基于此,结合该铁矿床地区的地质背景,利用偏光显微镜与电子探针等分析测试手段,将镜下蚀变现象、年龄计算与其他相关元素分析相结合,重点对晶质铀矿的成矿年龄及成矿规律进行探讨。研究发现:通过镜下观察判断,晶质铀矿的成因类型与澳大利亚著名的变质型铀矿相似,均为古老的变质型,且周围的脉石矿物均为绿泥石,绿泥石皆由黑云母退变质而成,铀矿的赋存位置显示其与黑云母、绿泥石之间有紧密联系,其成矿年龄与黑云母、绿泥石形成年龄息息相关。继而根据电子探针数据计算成矿年龄,判断成矿期次,得出主要成矿期在(1654±17) Ma~(1805±17) Ma,为中元古代中期,且主要成矿期与热液蚀变作用黑云母化有关,后期活化富集时期在(657±17) Ma~(807±17) Ma,为新元古代南华纪时期,此阶段是热液侵入、绿泥石化广泛发育的时期;选取较大颗粒对晶质铀矿的环带年龄进行计算,从年龄分布上证实后期有强烈的流体活动的发生,且主要与绿泥石化相关。另外,对比变质型与沉积型铀矿中Y2O3与UO2含量发现,两者之间存在负相关关系,此关系对判断铀矿成因即是否为变质型或沉积型可能有指示意义,但缺乏大量的数据佐证,需进一步研究。Abstract: Based on the advantages of high resolution and accuracy, Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA) method for Th-U-Pb is conducted to date monazite and zircon, is not typically applied in uraninite, pitchblende and other minerals which contain high contents of Th, U and Pb. Uraninite with a high content of U was first found in the iron deposit, whose rock type was chlorite and actinolite biotite altered rock. Based on the region′s geological background, the microscopic alteration, age calculation and other related elements analysis, the uraninite mineralization age and metallogenic regularity have been studied intensely by Microscope and EPMA. The research results indicate that the genetic type of uraninite is similar to the famous metamorphic uraninite in Australia, belonging to the old metamorphic type. The gangue minerals are all chlorite altered by biotite. Occurrence characteristics of the uraninite reveal the close relationship between uraninote and biotite-chlorite. The mineralization age is also intimately related to the formation age of biotite and chlorite. According to the oxide content data of elements (U, Th and Pb) by EPMA, mineralized periods were obtained as the main mineralization stage is (1654±17) Ma-(1805±17) Ma, which is the mid Proterozoic and relate to the hydrothermal alteration of biotite. The later activation and enrichment period is (657±17) Ma-(807±17) Ma, which is the Neoproterozoic Nanhua period when hydrotherm invaded and chloritization was widely developed. Large-sized uraninite grains were selected to calculate their zoning ages. The age distribution shows that the strong fluid activity occurs at the late stage, and is mainly related to the chloritization. In addition, comparing the elements′ content (Y2O3 and UO2) between metamorphic uranium and sedimentary uranium, a negative correlation relationship was found between the two types. This relationship may have significance in determining whether it is metamorphic or sedimentary type, but this conclusion needs further study due to the lack of convincing evidence.
-
Key words:
- uraninite /
- Electron Probe Microanalysis /
- age /
- zone age /
- mineralized periods
-

-
表 1 研究区晶质铀矿与我国其他地区变质型铀矿成分对比
Table 1. Comparison of the uraninite′s component in the study area and other metamorphic regions
研究地区 项目 w/% UO2 PbO ThO2 本研究区变质型晶质铀矿 变化范围 49.44~83.79 6.57~29.37 0.55~14.99 平均值 66.56 17.78 6.90 我国其他地区
变质型铀矿[11]变化范围 UO2 27.16~67.51 6.60~11.24 0.014~0.24 UO36.74~48.98 平均值 UO2 54.49 8.54 0.061 UO320.97 表 2 晶质铀矿电子探针元素U、Pb、Th含量与年龄计算结果
Table 2. The contents of U,Pb,Th in the uraninite and their ages
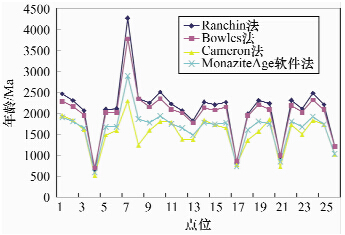
编号 w/% 年龄/Ma 编号 w/% 年龄/Ma UO2 PbO ThO2 Age1 Age2 Age3 Age4 UO2 PbO ThO2 Age1 Age2 Age3 Age4 U1 70.541 22.373 5.147 2457 2278 1938 1894 U14 73.1 21.244 4.465 2261 2115 1831 1770 U2 72.244 21.413 5.044 2299 2151 1825 1796 U15 70.772 20.066 5.378 2194 2071 1719 1730 U3 70.09 18.554 5.333 2049 1952 1604 1635 U16 67.755 19.98 7.553 2254 2142 1640 1772 U4 78.5 6.571 6.008 647 683 506 583 U17 83.797 8.78 0.552 831 844 771 733 U5 66.989 18.436 8.682 2091 2019 1469 1669 U18 67.416 17.615 9.659 1976 1931 1353 1593 U6 68.949 18.864 6.617 2103 2009 1579 1673 U19 66.649 20.231 9.827 2292 2195 1558 1801 U7 49.44 29.367 14.999 4259 3767 2284 2881 U20 70.142 19.972 3.518 2224 2079 1847 1745 U8 57.645 18.909 18.145 2343 2343 1238 1853 U21 74.311 9.239 7.139 955 991 717 838 U9 66.676 19.643 8.328 2242 2140 1589 1766 U22 67.642 20.288 6.678 2303 2173 1719 1802 U10 68.501 22.408 7.874 2498 2338 1805 1925 U23 66.601 18.37 8.182 2100 2023 1495 1674 U11 72.371 20.602 4.637 2213 2078 1779 1740 U24 66.017 21.29 6.952 2471 2311 1820 1907 U12 65.263 17.751 10.103 2049 1999 1374 1643 U25 67.883 19.254 5.131 2196 2072 1721 1730 U13 73.873 17.347 6.815 1807 1759 1367 1473 U26 74.295 11.477 3.46 1208 1210 1012 1034 表 3 U9晶质铀矿环带数据
Table 3. The band data of uraninite U9
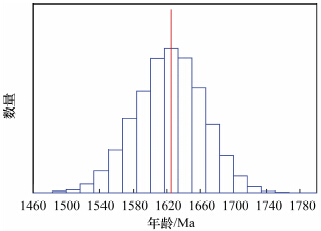
氧化物 w/% U9-1 U9-2 U9-3 U9-4 U9-5 U9-6 U9-7 U9-8 U9-9 U9-10 U9-11 U9-12 U9-13 U9-14 U9-15 U9-16 U9-17 U9-18 U9-19 U9-20 UO2 59.284 58.777 60.091 60.889 60.201 61.366 61.734 61.141 60.315 61.487 61.88 61.13 61.282 60.199 62.323 61.828 67.684 68.821 63.683 61.426 PbO 18.353 17.312 17.458 17.595 18.069 18.686 15.946 17.709 18.078 17.528 16.873 17.759 18.011 17.833 17.331 17.612 20.294 20.416 19.129 17.744 ThO2 18.006 20.121 16.939 15.492 16.447 15.213 15.794 15.052 14.766 15.042 14.651 15.111 15.297 16.015 16.3 17.007 8.295 7.928 13.376 16.434 年龄/Ma
(Ag4)1772 1687 1689 1691 1738 1768 1540 1698 1747 1676 1618 1701 1717 1722 1636 1664 1792 1780 1762 1686 表 4 U18晶质铀矿环带数据
Table 4. The band data of uraninite U18
氧化物 w/% U18-1 U18-2 U18-3 U18-4 U18-5 U18-6 U18-7 U18-8 U18-9 U18-10 U18-11 U18-12 U18-13 U18-14 U18-15 U18-16 U18-17 U18-18 U18-19 U18-20 UO2 70.475 73.426 74.663 76.972 77.4 79.229 82.957 81.783 82.812 81.881 78.799 77.186 76.769 75.22 75.491 74.086 73.241 73.832 69.946 69.565 PbO 19.763 18.192 18.443 16.443 16.819 9.315 5.54 6.81 5.495 7.355 10.926 10.261 13.434 11.274 12.875 17.164 14.102 13.9 19.197 21.006 ThO2 2.851 2.095 0.937 2.078 0.962 4.486 4.77 4.378 4.802 3.179 4.591 4.788 3.005 4.861 4.066 2.957 4.71 5.137 3.299 4.938 年龄/Ma
(Ag4)1728 1564 1566 1380 1405 804 473 584 470 629 935 899 1157 1001 1127 1474 1250 1225 1695 1822 表 5 研究区变质型铀矿与其他地区沉积型铀矿的Y2O3与UO2含量
Table 5. The content of Y2O3 and UO2 in the study area and other sedimentary uranium deposits
氧化物 研究区变质型铀矿 w/% 其他地区沉积型铀矿w/% 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Y2O3 2.68 0.79 2.39 2.69 0.87 3.11 2.27 0.35 0.96 3.58 0.43 0.34 1.30 2.20 0.26 4.97 4.23 9.51 7.57 6.14 6.38 7.45 6.87 4.48 8.44 3.13 7.82 6.29 9.93 UO2 70.09 78.5 66.99 68.95 77.93 57.65 66.68 68.50 72.37 65.26 73.87 86.77 70.77 67.75 83.8 60.43 54.97 35.62 48.94 32.35 40.89 40.43 43.61 53.42 52.16 55.25 42.48 37.69 36.84 -
[1] 张照志,赵磊,孟庆祝,陈卉泉.电子探针化学测年技术及其在地学中的应用[J].现代地质,2001,15(1): 69-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200101012.htm
[2] 周剑雄,陈振宇,芮宗瑶.独居石的电子探针钍-铀-铅化学测年[J].岩矿测试,2002,21(4): 241-246. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020467&flag=1
[3] 李学军,郭涛,王庆飞.电子探针化学测年方法[J].地学前缘,2003,10(2): 411-413. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200302026.htm
[4] 张文兰,王汝成,华仁民.副矿物的电子探针化学定年方法原理及应用[J].地质论评,2003,49(5): 253-260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200303005.htm
[5] 彭松柏,朱家平,李志昌.电子探针铀-钍-铅定年方法及其在构造分析中的应用前景[J].岩矿测试,2004,23(1): 44-45. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040113&flag=1
[6] 张昭明.电子探针在测定晶质铀矿年龄中的应用[J].放射性地质,1982(5): 408-411. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD198205004.htm
[7] Bowles J F W.Age dating of individual grains of uraninite in rocks from electron microprobe analyses [J]. Chemical Geology,1990,83(1-2): 47-53. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419090139X
[8] Kempe U. Precise electron microprobe age determination in altered uraninite: Consequences on the intrusion age and the metallogenic significance of the Kirchberg granite Erzgebirge, Germany [J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology ,2003,145(1): 107-118. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00410-002-0439-5
[9] Votyakov S L, Ivanov K S, Khiller V, Bochkarev V,Erokhin Y.Chemical microprobe Th-U-Pb age dating of monazite and uraninite grans from granites of the Yamal crystalline basement [J].Doklady Earth Sciences, 2011, 439(1): 994-997. http://www.springerlink.com/index/F678271577677854.pdf
[10] 葛祥坤.电子探针Th-U-Pb微区测年方法及其在铀矿地质研究中的应用前景[J].铀矿地质,2008,4(3): 175-179. http://epub.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=0&CurRec=1&recid=&FileName=YKDZ200803008&DbName=CJFD2008&DbCode=CJFQ&pr=
[11] 徐国庆,王爱珍,顾绮芳,张静宜,张昭明,黄裕柱.我国晶质铀矿和沥青铀矿的某些矿物学特征[J].矿物学报,1982(3): 193-199. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB198203004.htm
[12] [13] 孙玉宝.安徽霍邱李老庄铁矿-菱镁矿矿床地质特征及矿床成因类型[J].矿产与地质,2007,21(5): 535-536. http://epub.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=4&CurRec=1&recid=&FileName=KCYD200705009&DbName=CJFD2007&DbCode=CJFQ&pr=
[14] Muto T, Hirono S, Kurata H.Some aspects of fixation of uranium from natural waters [J].Mining Geology, 1965,15(74): 287- 298. http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/4543656
[15] Nutt C J.Description of drill-hole ⅧV core from the Jabiluka unconformity-type deposit, Northern Territory, Australia [R].U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report,1984, 2(1): 84-299.
[16] Ludwig K R, Grauch R I, Nutt C J, Nash J T, Frishman D, Simmons K R. Age of uranium mineralization at the Jabiluka and Ranger deposits, Northern Territory, Australia: New U-Pb isotope evidence [J].Economic Geology, 1987, 82(4): 857-874. http://economicgeology.org/content/82/4/857.short
[17] Gustafson L B, Curtis L W. Post-Kombolgie metasomatism at Jabiluka, Northern Territory, Australia, and its significance in the formation of high-grade uranium mineralization in lower proterozoic rocks [J].Economic Geology, 1983, 78(1): 26-56. http://economicgeology.org/content/78/1/26.short
[18] Ewers G R, Ferguson J.The Nabarlek uranium deposits, Northern Territory, Australia; Some petrologic and geochemical constraints on genesis [J].Economic Geology,1983,78(5): 823-837. http://economicgeology.org/content/78/5/823.short
[19] Hegge M R, Rowntree J C.Geologic setting and concepts on the origin of uranium deposits in the East Allgator River region, N.T., Australia [J].Economic Geology, 1978, 73(8): 1420-1429. http://economicgeology.org/content/73/8/1420.short
-




 下载:
下载: