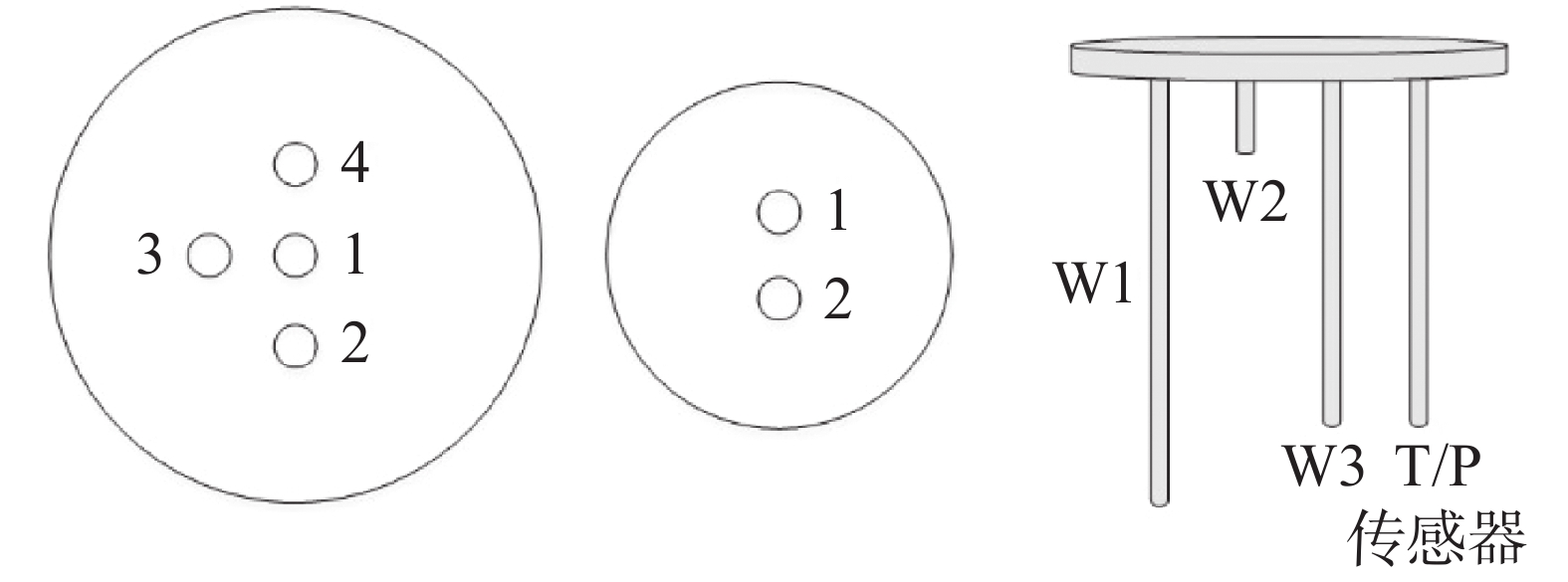Study on test method of karstification process: Take the development of karstification instrument as an example
-
摘要:
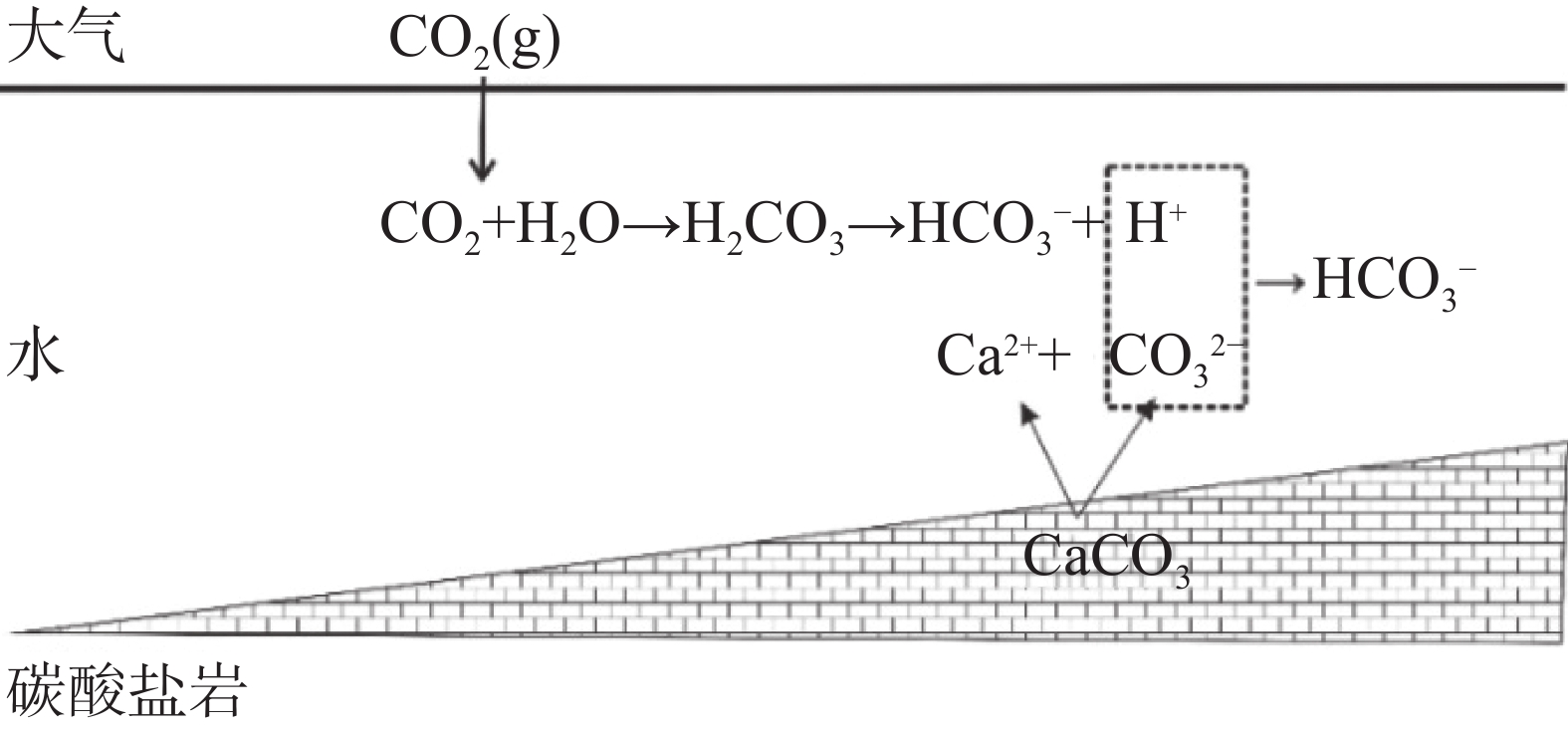
通过对前人试验装置的分析,以岩溶作用原理及其影响因素为基础,结合仪器使用单位的试验需求,研制岩溶作用仪。通过分析不同的CO2起源、岩溶发育深度、不同pH条件以及地下水循环深度的地质环境条件,提出了仪器的基本功能和适用条件,进行岩溶作用仪功能模块的论证设计和研制,并进行了验证性试验,且达到预期目标。得到如下成果:提出了四种岩溶作用模式,研制了五个岩溶作用功能模块,总结分析了功能模块与岩溶作用内在关系以及功能模块组合原则,提供不同地质环境条件下的岩溶作用试验。仪器可以实现:模拟地下水循环深度0~200 m,环境温度0~70 ℃,CO2起源:表生、内生起源Pco2=0.0~2.0 MPa,不同酸度背景条件:pH可控,不同水流速度条件下的沉积作用可控,岩溶裂隙张开度的沉积作用(可组合)。
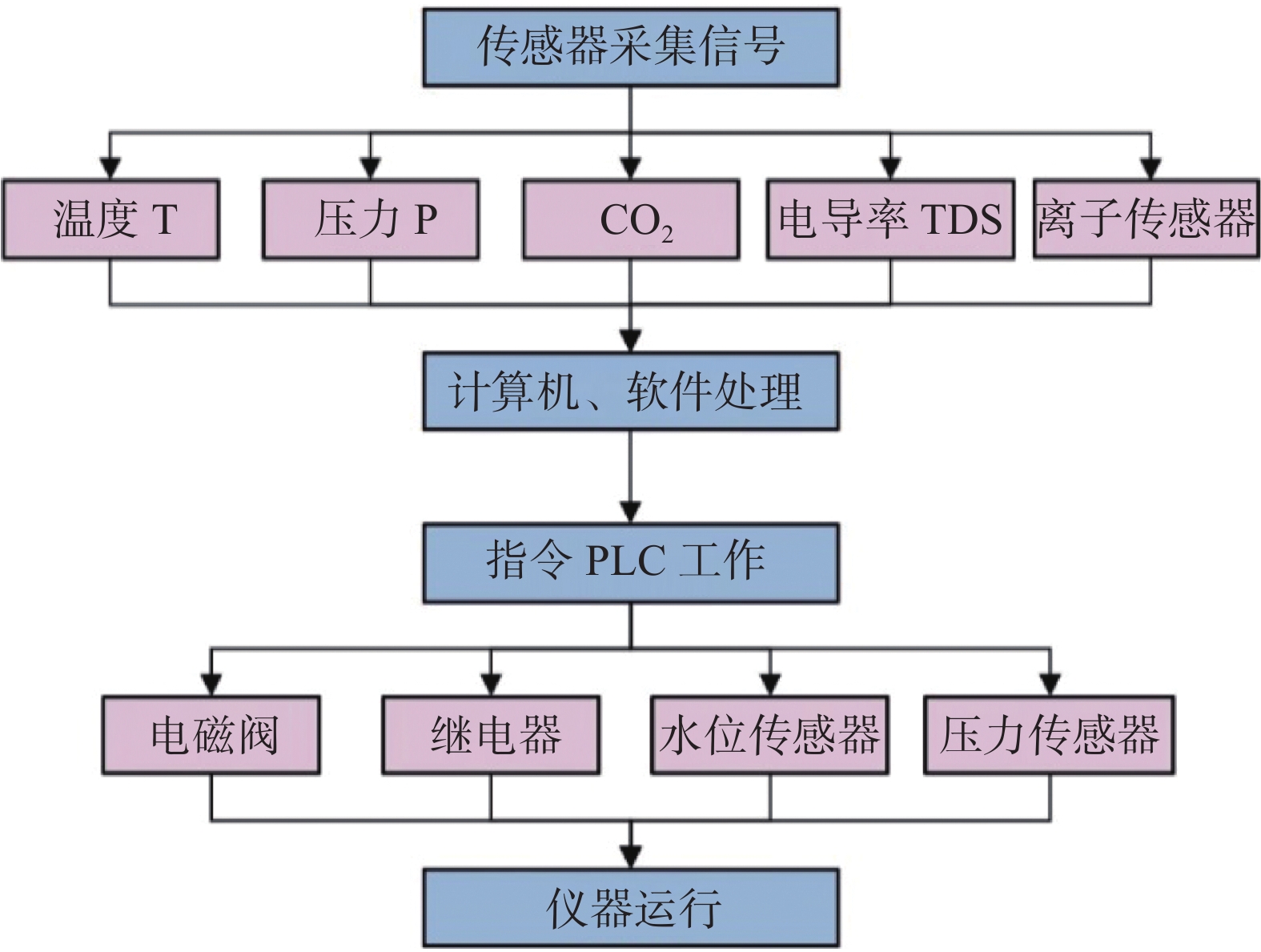
Abstract:In recent years, with the construction of national economy and the need to achieve the "double carbon goal", a large number of increasingly complex problems on karst science have been encountered, which need to be solved by simulating the process of karst action in different geological environment conditions. In the past, karst simulation was mainly carried out under normal temperature, normal pressure and certain pH conditions to determine the basic characteristics of karst and parameters such as the rate of karst, which could not effectively simulate karst under different geological conditions. Therefore, a comprehensive set of instruments for simulating karst action under different geological environmental conditions (e.g., ambient temperature of 0-70 ℃, subsurface depth of 200 m, different CO2 origins and different saturation levels, etc.) is needed to solve a series of scientific problems such as karst dissolution and sedimentation in different geological environmental contexts. Based on the principle of karstification, this paper defines the functions and parameters of the instrument by analyzing the geological environment conditions of different CO2 origins, karst development depths, different pH conditions and groundwater circulation depths. Based on the requirement of the karstification instrument, the parameters and modules of karstification instrument have been designed according to the instrument functions, karstification control factors and karstification principle. After the design of each part and the overall development of the instrument were completed, a verification test was carried out to illustrate the feasibility of the instrument. Finally, the following results are obtained. (1) Four karstification models are proposed, i.e., the origin of CO2 in the supergene zone—the shallow circulation karstification model of groundwater; CO2 origin of supergene zone—cyclic karstification model of groundwater depth; the origin of CO2 in the deep—the model of karst process of groundwater depth circulation; and the mode of groundwater circulation karstification under the biological action of supergene zone (such as the change of pH value of humic acid). (2) According to the basic principle of karstification and the four models of karstification, five karstification function modules are developed, CO2 (pH) solution function module of different geological environment origins, water circulation depth module, environmental background temperature module, dissolution module and sedimentation module. (3) The internal relationship between functional modules and karstification together with the combination principle of functional modules has been summarized and analyzed to provide karstification tests under different geological environment conditions. Finally, according to the principle of karstification, taking the computer as the basic control unit, the test parameters of different functional modules have been monitored by sensors and controlled by PLC, and the functional modules have been organically connected and controlled to meet the requirement of fully automatic karstification tests under different geological environment conditions.
Basic parameters of karstification instrument are listed as follows: (1) simulated groundwater circulation depth of 0-200 m; (2) ambient background temperature of 0-70 ℃; (3) CO2 origins—supergene origin Pco2=0.0 MPa and endogenous origin Pco2=0.0-2.0 MPa; (4) different acidity background conditions—pH value is controllable; (5) sedimentation that can be controlled under different flow velocities; (6) sedimentation of the opening degree of karst fissures (can be combined).
However, due to the limitations of time and cost, the instrument can be further improved. For example, in order to improve the preparation efficiency of saturated CO2 solution, the contact area between CO2 and water can be increased. A dual solution preparation system can be designed to prepare the solution so that the efficiency of the test can be increased. The maximum safe pressure of this instrument is 2 MPa (water circulation depth of 200 m). If a simulation of a greater water circulation depth is needed, the thickness of stainless-steel materials for solution preparation, dissolution reaction kettle and deposition reactor (meeting the requirements of high-pressure vessel specifications) can be increased, and a pressure pump with a larger pressure rise will be used.
-

-
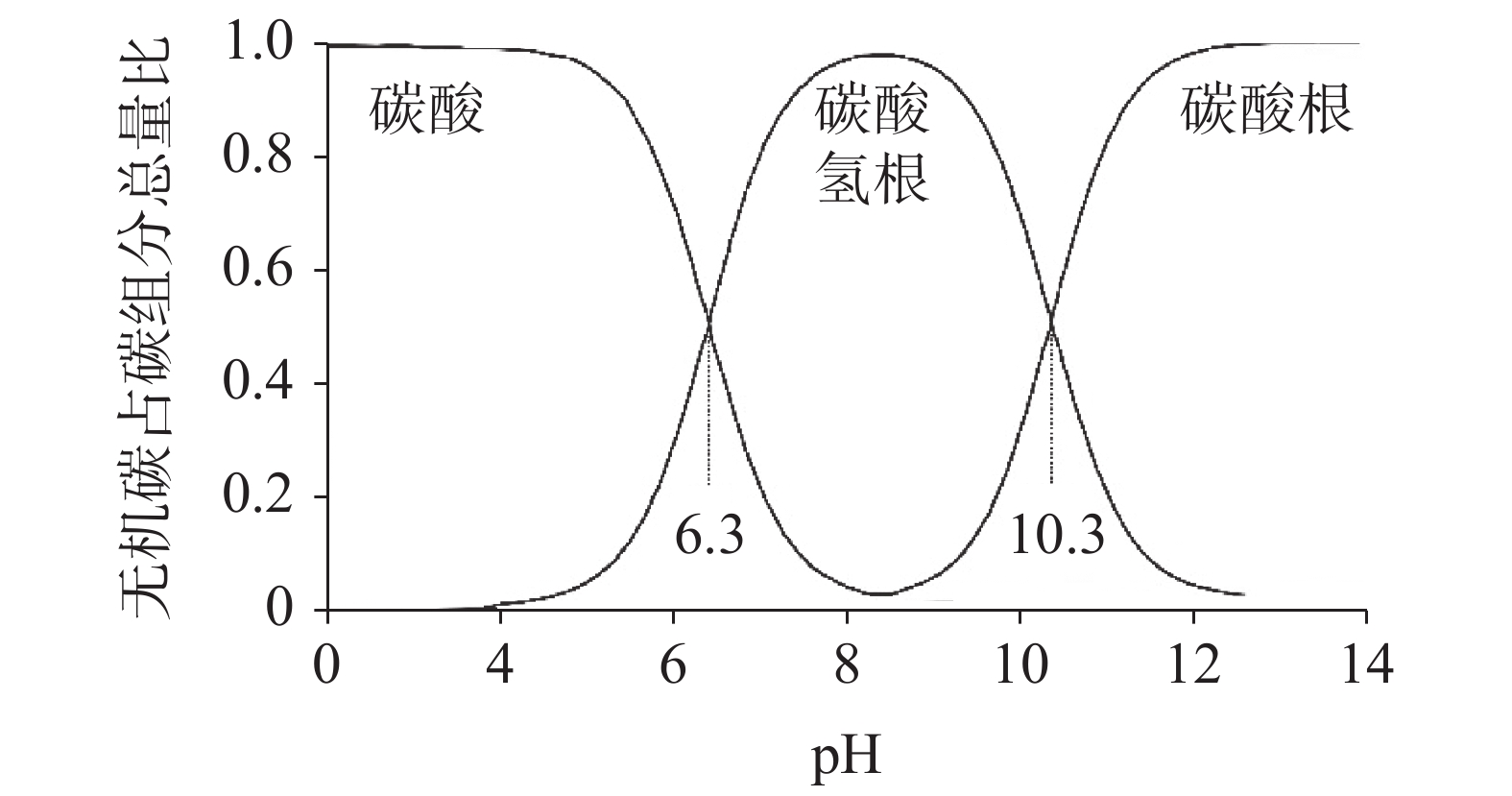
图 3 pH与溶解无机碳组分的关系[33]
Figure 3.
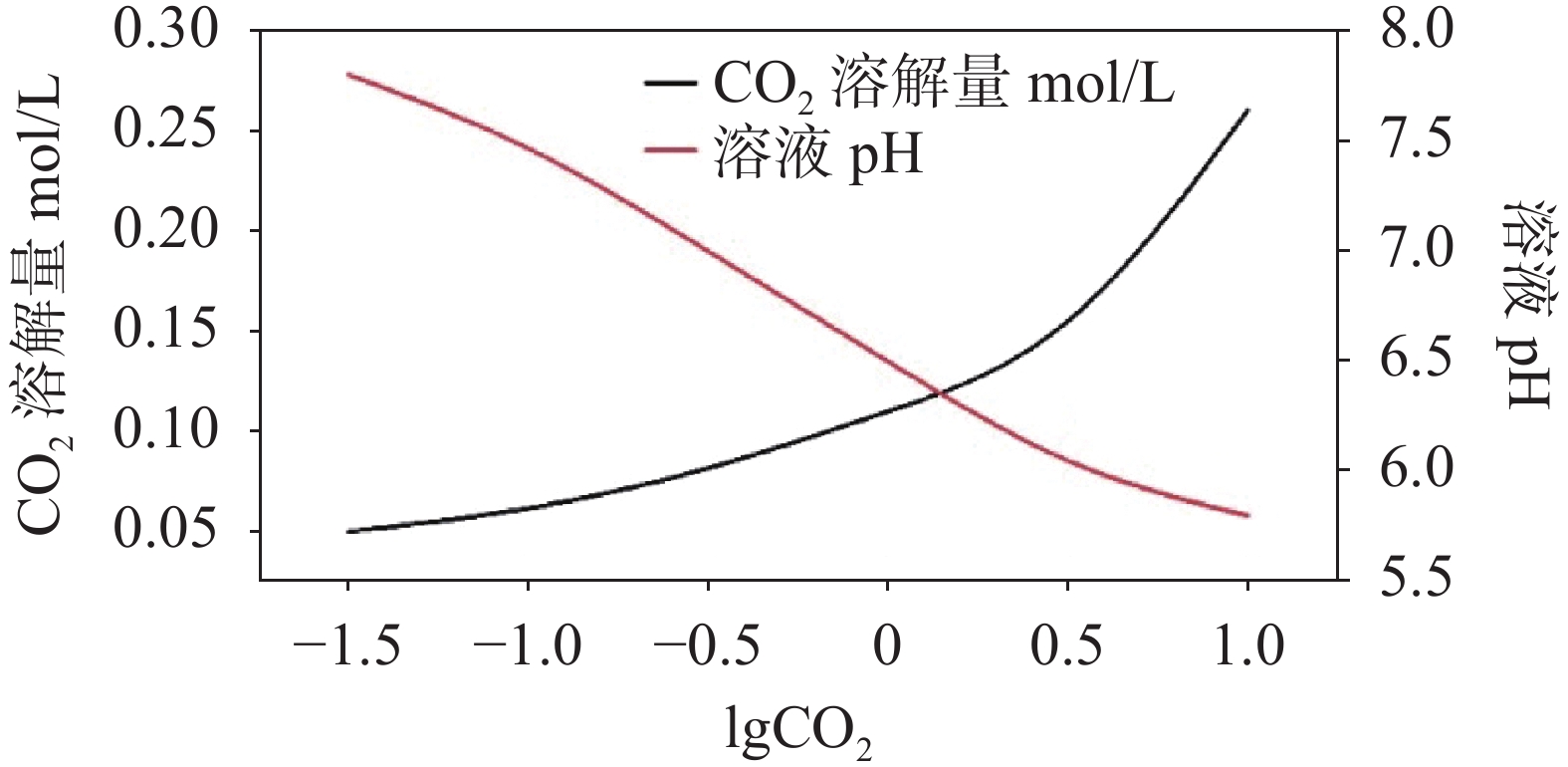
图 4 CO2溶解量、溶液pH与温度变化关系[34]
Figure 4.
图 5 CO2溶解量、溶液pH与Pco2变化关系图[34]
Figure 5.
表 1 仪器模块组成分析
Table 1. Apparatus development theory and process analysis
参与反应的物质 反应场所/实现方法 碳酸盐岩 溶蚀场所 不同地质环境背景岩溶溶蚀作用模拟系统 溶蚀反应釜 沉积场所 不同地质环境背景岩溶沉积模拟系统 岩溶沉积器 CO2 饱和CO2溶液制备场所 不同成因CO2或pH水溶液制备系统 溶液反应釜 水 酸(H+) 不同pH值溶液制备场所 压力 加压装置 温度 温度控制装置 表 2 传感器设置
Table 2. Sensor settings
监测目标 监测设备 温度 温度传感器 压力 压力传感器 水位 水位传感器(最高水位W1、
最低水位W2、水位监测W3) -
[1] 袁道先. 现代岩溶学和全球变化研究[J]. 地学前缘, 1997(Z1):21-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1997.01.003
YUAN Daoxian. Modern karstology and global change study[J]. Geoscience Frontier, 1997(Z1):21-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1997.01.003
[2] 卢耀如, 杰显义, 张上林, 赵成樑, 刘福灿. 中国岩溶(喀斯特)发育规律及其若干水文地质工程地质条件[J]. 地质学报, 1973(1): 121-136.
LU Yaoru, JIE Xianyi, ZHANG Shanglin, ZHAO Chengliang, LIU Fucan. The development law of karst and some hydrogeological and engineering geological conditions in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1973(1): 121-136.
[3] 卢耀如. 岩溶地区主要水利工程地质问题与水库类型及其防渗处理途径[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1982(4): 15-22.
LU Yaoru. Main hydraulic engineering geological problems and reservoir types in karst areas and their anti-seepage treatment methods[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1982(4): 15-22.
[4] Dreybrodt W. Mixing Corrosion in CaCO3-CO2-H2O systems and its role in the karstification of limestone areas[J]. Chemical Geology, 1981(32):221-236.
[5] Dreybrodt W, Buhmann D. A mass transfer model for dissolution and precipitation of calcite from solutions in turbulent motion[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991(90):107-122.
[6] 刘再华, Dreybrodt W, 李华举. 灰岩和白云岩溶解速率控制机理的比较[J]. 地球科学, 2006(3):411-416.
LIU Zaihua, Dreybrodt W, LI Huaju. Comparison of dissolution rate-determining mechanisms between limestone and dolomite[J]. Earth Science, 2006(3):411-416.
[7] Plummer L N, Wigley T M L. The dissolution of calcite in CO2-saturated solutions at 25 ℃ and 1 atmosphere total pressure[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1976, 40(2):191-202. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(76)90176-9
[8] Pokrovsky, Oleg S, Golubev, Sergey V, Schott, Jacques, Castillo, Alain. Calcite, dolomite and magnesite dissolution kinetics in aqueous solutions at acid to circumneutral pH, 25 to 150 C and 1 to 55 atm Pco2: New constraints on CO2 sequestration in sedimentary basins[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 265(1-2):20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.01.013
[9] 黄尚瑜, 宋焕荣. 碳酸盐岩的溶蚀与环境温度[J]. 中国岩溶, 1987, 6(4):27-36.
HUANG Shangyu, SONG Huanrong. The corrosion of carbonates and environment temperature[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1987, 6(4):27-36.
[10] 邵东梅. 不同水流速度下温度对奥陶系碳酸盐岩溶蚀速度的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2012, 40(3):62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2012.03.015
SHAO Dongmei. Influence of temperature on dissolution rate in Ordovician carbonate rock in different water flow rate[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2012, 40(3):62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2012.03.015
[11] 刘再华, 袁道先, 何师意, 曹建华, 游省易. 四川黄龙沟景区钙华的起源和形成机理研究[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(1): 1-10.
LIU Zaihua, YUAN Daoxian, HE Shiyi, CAO Jianhua, YOU Shengyi. Origin and forming mechanisms of travertine at Huanglong Ravine of Sichuan[J]. Geochemistry, 2003, 32(1): 1-10.
[12] 刘再华. 表生和内生钙华的气候环境指代意义研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(23):2229-2239.
LIU Zaihua. Research progress in paleoclimatic interpretations of tufa and travertine[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(23):2229-2239.
[13] 张英骏, 莫仲达. 黄果树瀑布成因初探[J]. 地理学报, 1982, 37(3):303-316. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1982.03.010
ZHANG Yingjun, MO Zhongda. The orgin and evolution of orange fall[J]. Acta Geographic Sinica, 1982, 37(3):303-316. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1982.03.010
[14] 程星. 薄水效应初论[J]. 中国岩溶, 1994, 13(3):207-212.
CHENG Xing. Discussion on thin-water effect[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1994, 13(3):207-212.
[15] 范明, 蒋小琼, 刘伟新, 张建勇, 陈红宇. 不同温度条件下CO2水溶液对碳酸盐岩的溶蚀作用[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(6): 825-830.
FAN Ming, JIANG Xiaoqiong, LIU Weixin, ZHANG Jianyong, CHEN Hongyu. Dissolution of carbonate rocks in CO2 solution under different temperatures[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(6): 825-830.
[16] 刘琦, 卢耀如, 张凤娥. 岩石高压溶蚀试验设备设计与实验分析[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2013, 32(9): 34-37.
LIU Qi, LU Yaoru, ZHANG Feng'e. Design and experimental analysis of pressure dissolution test equipment of rocks[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2013, 32(9): 34-37.
[17] 杨云坤, 刘波, 秦善, 罗平, 张单明, 周明辉, 石开波, 田永净. 基于模拟实验的原位观察对碳酸盐岩深部溶蚀的再认识[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(2): 316-322.
YANG Yunkun, LIU Bo, QIN Shan, LUO Ping, ZHANG Shanming, ZHOU Minghui, SHI Kaibo, TIAN Yongjing. Re-recognition of deep carbonate dissolution based on observation of in-situ simulation experiment[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2014, 50(2): 316-322.
[18] 张文博, 操应长, 远光辉. 不同升温速率下方解石与二氧化碳水溶液作用实验[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2017, 24(3): 57-65.
ZHANG Wenbo, CAO Yingchang, YUAN Guanghui. Experiment of interaction between calcite and fluid saturated with CO2 under different heating rates[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017, 24(3): 57-65.
[19] Alkattan, Marwan, Oelkers, Eric H, Dandurand, Jean-Louis, Schott, Jacques. An experimental study of calcite and limestone dissolution rates as a function of pH from -1 to 3 and temperature from 25 to 80 ℃[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 151(1):199-214. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00080-1
[20] Eisenlohr, Laurent, Meteva, Krassimira, Gabrovšek, Franci, Dreybrodt, Wolfgang. The inhibiting action of intrinsic impurities in natural calcium carbonate minerals to their dissolution kinetics in aqueous H2O-CO2 solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(7-8):989-1001. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00301-9
[21] 刘再华, W.Dreybrodt. 不同CO2分压条件下的白云岩溶解动力学机理[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 2001, 31(4): 377-384.
LIU Zaihua, W.Dreybrodt. Kinetic mechanism of dolomite dissolution under different partial pressure of CO2[J]. Science in China (Series B), 2001, 31(4): 377-384.
[22] 袁道先. 中国岩溶学[M].北京: 地质出版社, 1994.
YUAN Daoxian. China Karstology[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, Beijing, 1994.
[23] 袁道先, 蒋忠诚. IGCP 379“岩溶作用与碳循环”在中国的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000(1): 49-51.
YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Zhongcheng. Research progress of IGCP 379 "karstification and carbon cycle" in China [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2000 (1): 49-51.
[24] 刘再华, 袁道先, 何师意. 不同岩溶动力系统的碳稳定同位素和地球化学特征及其意义: 以我国几个典型岩溶地区为例[J]. 地质学报, 1997, 71(3): 281-288.
LIU Zaihua, YUAN Daoxian, HE Shiyi. Stable carbon isotope geochemical and hydrochemical features in the system of carbonate-H2O-CO2 and their implications: Evidence from several typical karst areas of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1997, 71(3): 281-289.
[25] 张远瞩. 外源酸(硫酸、硝酸)对岩溶碳循环的影响[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2017.
ZHANG Yuanzhu. Effect of allogenic acids (sulfuric acid, nitric acid) on karst carbon cycle[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017.
[26] 李瑞. 里湖地下河N、S来源及其水-岩作用过程[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016.
LI Rui. Sources of sulfate, nitrate and its water-rock interation process in Lihu underground water[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016.
[27] 钱海涛, 谭朝爽, 王思敬. 岩溶发育深度问题研究现状与展望[J]. 人民黄河, 2014, 36(11): 114-116.
QIAN Haitao, TAN Zhaoshuang, WANG Sijing. Progress and expectation of research on the depth of karsts in water resources and hydropower engineering[J].Yellow River, 2014, 36(11): 114-116.
[28] 邹成杰. 深岩溶发育的基本规律与水库岩溶渗漏的研究. 第四届全国工程地质大会论文选集(三)[C].第四届全国工程地质大会(中国北京), 1992: 179-195.
ZOU Chengjie. Study on the basic law of deep karst development and reservoir karst leakage. Selected papers of the Fourth National Engineering Geology Conference(3)[C]. The Fourth National Engineering Geology Conference, Beijing, China, 1992: 179-195.
[29] 莫阳春. 高水压充填型岩溶隧道稳定性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2009.
MO Yangchun. Stability research on high water pressure filled karst caves tunnel[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009.
[30] 谭周地, 李广杰, 何满朝. 河谷深岩溶的发育分布规律[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1984(1): 63-73.
TAN Zhoudi, LI Guangjie, HE Manchao. Developing features of deep karsts under a valley[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 1984(1): 63-73.
[31] 光耀华. 岩溶地区工程地质研究的若干新进展概述[J]. 中国岩溶, 1998, 17(4): 70-75.
GUANG Yaohua. An introduction to the progress of the geologic engineering researches in karst regions[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1998, 17(4): 70-75.
[32] 武鑫, 王艺霖, 黄敬军, 潘欢迎, 万军伟. 徐州地区碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 120-126.
WU Xin, WANG Yilin, HUANG Jingjun, PAN Huanying, WAN Junwei. Dissolution characteristics of carbonate and analysis of the key influence factors in Xuzhou region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 120-126.
[33] 钱会. 水文地球化学 (第2版)[M].北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
QIAN Hui. Hydrogeochemistry(2nd Edition) [M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2012.
[34] 贾祎轲. 二氧化碳地质封存过程中水-气-岩反应实验及模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
JIA Yike. Simulation of brine-gas sandstone interactions during carbon dioxide geological storage[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013.
[35] 房明. 塔河油田碳酸盐岩裂缝启动条件研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
FANG Ming. Study on opening conditions of fracture of carbonate rock in Tahe oilfield[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.
[36] 刘再华, Dreybrodt W. DBL理论模型及方解石溶解、沉积速率预报[J]. 中国岩溶, 1998, 17(1): 3-9.
LIU Zaihua, Dreybrodt W. The DBL model and prediction of calcite dissolution/precipitation rate[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1998, 17(1): 3-9.
-



 下载:
下载: