Model and mechanism of "water exploration by cross layer" for high sulfate area in slope region of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau
-
摘要:
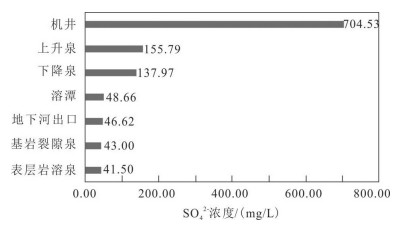
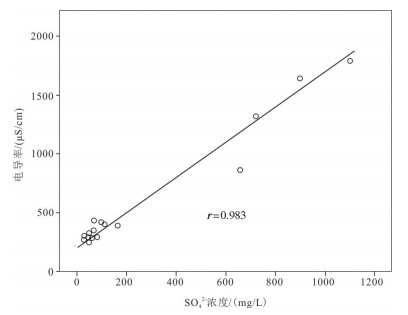
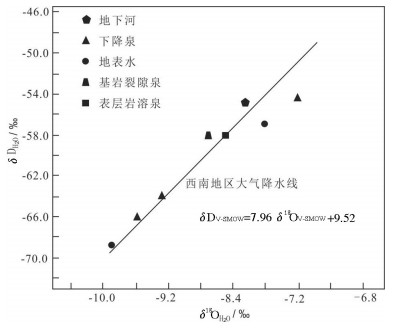
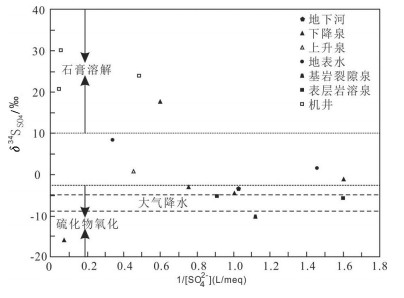
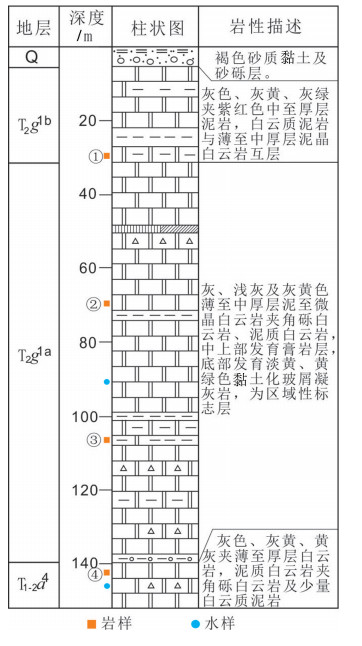
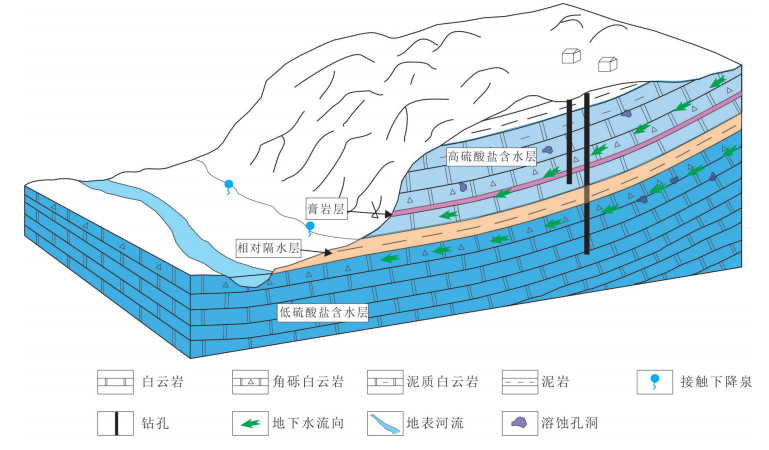
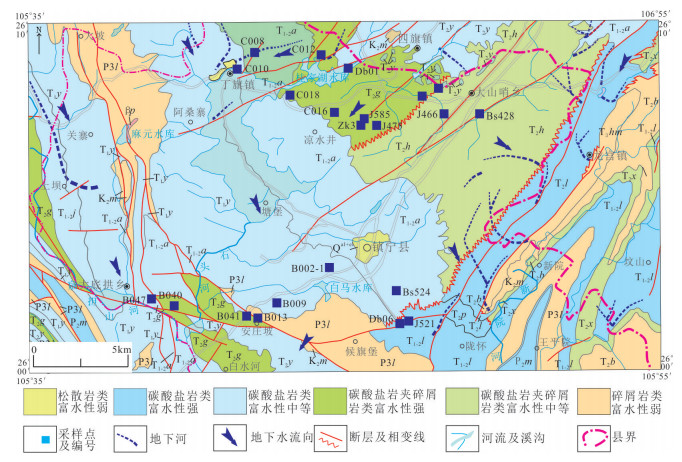
地下水是中国西南云贵高原斜坡地带重要的饮用水源,其中黔中镇宁县北部存在大面积地下水中硫酸盐超标地区,导致了当地出现水质性缺水问题。本次研究通过岩相古地理分析、水化学分析、D、18O、34S同位素测试、岩样测试、岩心观察等技术手段,查明了研究区内地下水的补给源主要为大气降水,地下水中硫酸盐(SO42-)浓度在30~1100 mg/L,平均值为221.78 mg/L,呈现高度富集SO42-的特点;在区域相对隔水层以上,不同类型地下水中SO42-浓度大体具有机井>上升泉>下降泉>溶潭>地下河出口>基岩裂隙泉>表层岩溶泉的规律;探讨了地表水、地下水中SO42-的来源,表层岩溶泉中硫酸根的来源主要为大气降水,高硫酸盐样品中硫酸根的来源主要为石膏溶解。在此基础上,结合钻井资料,掌握了研究区膏岩层分布及含水层结构特征,通过建立"越层找水"模式,采取下层低硫酸盐含水层,获取合格饮用水源,可有效解决当地水质性缺水问题。
Abstract:Groundwater is an important drinking water source in Southwest China. However, there exists a large area of sulfate exceeding standard in groundwater in the northern part of Zhenning County in Central Guizhou Province, which leads to the problem of water shortage in local area. The following conclusions were obtained by methods of lithofacies palaeogeographic analysis, hydrochemical analysis, D, 18O, 34S isotope test, rock sample test, core observation and other technical methods:The main source of water supply in the study area is meteoric water; the concentration of sulfate (SO42-) in groundwater is in the range of 30-1100 mg/L, with an average value of 221.78 mg/L, showing the characteristics of highly enriched S042-; the concentration of S042- in different types of groundwater exhibits the law of well > rising spring > falling spring > karst pool > underground river > bedrock fissure spring > epikarst spring; the source of sulfate root in epikarst spring is mainly meteoric water, and the source of sulfate root in high sulfate samples such as J469, J585, ZK3-2 and C010 is mainly dissolved in gypsum. On such a basis and in combination with drilling data, the authors detected the distribution of gypsum rock layer and the characteristics of aquifer structure, and adopted the lower sulfate aquifers to obtain qualified drinking water source by establishing the "cross layer water finding" model, which can effectively solve the problem of water shortage in the study area.
-

-
表 1 研究区样品水化学测试结果
Table 1. Hydrochemical test results of samples in the study area
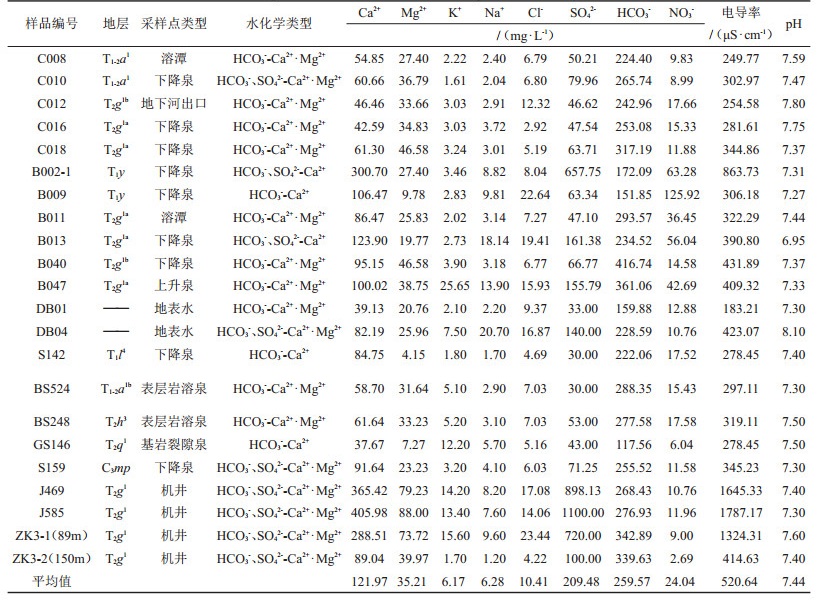
表 2 研究区样品δ34S(SO42-)测试结果
Table 2. δ34S(SO42-) test results of samples in the study area
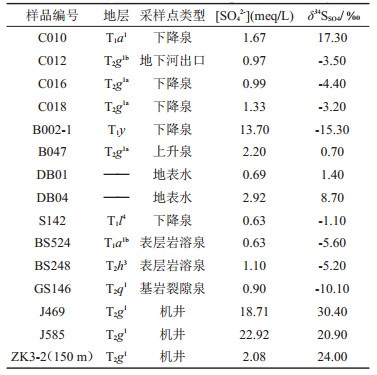
表 3 ZK3号钻井岩心样品测试结果
Table 3. Core sample of ZK3 borehole test results
-
Cao Jianhua, Jiang Zhongcheng, YuanDaoxian, Xia Riyuan, Zhang Cheng. 2017. The progress in the study of the karst dynamic system and global changes in the past 30 years[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):874-900(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201705005.htm
CLARKI, FRITZP. 1997. Environmental Isotopesin Hydrogeology[M]. NewYork:Lewis Publishers.
Dong Jianzhong, Liu Xingjuan. 2001. Study on the correlation between drinking water quality and causes of death in Shaxian County[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 18(6):375-376 (in Chinese).
Regional Geological Survey Brigade of Guizhou Geological and Mineral Bureau. 1992. Guizhou Atlas of the palaeogeography of Guiyang: Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House[M](in Chinese).
Guo Zhaobing, Dong Qiongyuan, Chen Tian, Chen Tianlei, Bao Chunxiao, Zhou Fei. 2010. Identification of environmental pollutants using sulfur stable isotope[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2(5):426-430 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njxxgcdxxb201005009
Han G L, Liu C Q.2004. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution:a study of the river waters draining karstdominatedterrain, Guizhou Province, China[J].Chemical Geology, 204(1/2):1-21.
Hanshaw B B, Back W. 1979. Major geochemical processes in the evolution of carbonate-quifer systems[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 43(1/4):287-312. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002216947990177X
Hosono T, Nakano T, Igeta A, Tayasu I, Tanaka T, Yachi S. 2007.Impact of fertilizer on a small watershed of Lake Biwa:Use of sulfur and strontium isotopes in environmental diagnosis[J]. Science of the Total Enviroment, 384(1/3):342-354. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969707005980
Hu Mingcheng. 2012. Environmental hazards by sulfate and treatment method of waste water containing sulfate[J]. Journal of Chengdu University(Natural Science Edition), 31(2):181-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201202024.htm
Jiang Yingkui, Liu Congqiang, Tao Faxiang. 2007. Sulfur isotope composition characters of Wujiang river water in Guizhou province[J]. Advances in Water Science, 18(4):558-565 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=skxjz200704013
Krouse H R, Crinenko V A. 1991. Stable Isotopic:Natural and Anthropogenic Sulphur in the Environment[M]. Chichester:John Wiley, 1-440.
Li Xiaodong, Liu Congqiang, Harue M, Li Siliang, Liu Xiaodong. 2010. The use of environmental isotopic (C, Sr, S) and hydrochemical tracers to characterize anthropogenic effects on karst groundwater quality:A case study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China[J]. Applited Geochemistry, 25(12):1924-1936. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.10.008
Li Xiaoqian, Liu Yunde, Zhou Aiguo, Zhang Bin. 2014. Sulfur and oxygen isotope compositions of dissolved sulfate in the Yangtze riverduring high water period and its sulfate source tracing[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(11):1547-1554 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201411009.htm
Li Yun, Jiang Yuehua, Zhou Xun, Jian Junyuan, Zhou Quanping, Li Yunfeng. 2014. Characteristics of Hydraulic Connection and Sulfate Contamination within the Groundwater System of Yangzhou-Taizhou-Jingjiang Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(2):183-190 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8307616
Liu Congqiang, Lang Yunchao, Satake H, Wu Jiahong, Li Siliang. 2008. Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate and chloride into the karstic ground eater of Guiyang, SW China:Combined δ37Cl and δ34S approach[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(15):5421-5427.
Macpherson G L. 1996. Hydrogeology of thin limestones:the Konza Prairie long-term ecological research site, Northeastern Kansas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 186(1-4):191-228. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(96)03029-6
Montoroi J P, Grünberger O, Nasri S. 2002. Groundwater geochemistry of a small reservoir catchment in Central Tunisia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 17(8):1047-1060. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00076-8
Niu Xinsheng, Liu Xifang, Chen Xiwen. 2014. Hydrochemical characteristics and origin for salt springs water in Dogai Coring area of north Qiangtang basin, Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(6):1003-1010. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201406004.htm
Ren Kun, Pan Xiaodong, Lan Ganjiang, Jiao Youjun, Zeng Jie, Meng Xiaojun, Pang Yuan. 2016. Sulfate concentrations and source identification in different water bodies of the Chadianqiao underground river basin in Central Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(8):1922-1932 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201608020
Wang Mingzhang. 2012. Considerations about the hydrogeology exploration works in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 29(2):81-85 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzdz201202003
Xiao Huanyun, Liu Congqiang. 2002. Sources of nitrogen and sulfur in wet deposition at Guiyang, southwest China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 36(33):5121-5130. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00649-0
Yang Pingheng, Lu Bingqing, He Qiufang, Chen Xuebin. 2014.Hydrogeochemical characteristics of typical karst groundwater system in Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 35(4):1290-1296 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201404012
Yang Yuncheng, Shen Zhaoli, Wen Dongguang, Hou Guangcai, Zhao Zhenhong, Wang Dong. 2008. Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of sulfatein groundwater of the Ordos Cretaceous Groundwater Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Snica, 29(5):553-562(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yongshuang, Sun Lu, Yin Xiulan, Meng Hui. 2017. Progress and prospect of research on environmental geology og China:A review[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):901-912 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201705006.htm
Zhao Jinfeng, Xia Keqin, Shi Yuchuan, Sun Jinyu.2004. Isotope component characteristics of Geleshan Tunnal'Chongqin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 15(2):94-97(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200402020.htm
曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 夏日元, 章程. 2017.岩溶动力系统与全球变化研究进展[J].中国地质, 44(5):874-900. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170504&flag=1
贵州省地矿局.贵州省地下水勘查规划[R]. 2009.
胡明成. 2012.硫酸盐的环境危害及含硫酸盐废水处理技术[J].成都大学学报(自然科学版), 31(2):181-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5422.2012.02.023
李小倩, 刘运德, 周爱国, 张彬. 2014.长江干流丰水期河水硫酸盐同位素组成特征及其来源解析[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 39 (11):1547-1554. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201411008
李云, 姜月华, 周迅, 贾军元, 周权平, 李云峰. 2014.扬-泰-靖地区地下水系统水力联系与硫酸盐污染特征[J].地球学报, 35(2):183-190. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8307616
董建忠, 刘杏娟. 2001.饮用水水质与居民死因的相关性研究[J].环境与健康杂志, 18(6):375 -376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2001.06.023
贵州省地质矿产局区域地质调查大队. 1992.贵州岩相古地理图集[M].贵阳:贵州科技出版社.
郭照冰, 董琼元, 陈天, 陈天蕾, 包春晓, 周飞. 2010.硫稳定同位素对环境污染物的示踪[J].南京工程信息大学学报(自然科学版), 2(5):426-430. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njxxgcdxxb201005009
蒋颖魁, 刘丛强, 陶发祥. 2007.贵州乌江水系河水硫同位素组成研究[J].水科学进展, 18(4):558-565. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2007.04.013
任坤, 潘晓东, 兰干江, 焦友军, 曾洁, 孟小军, 庞园. 2016.黔中茶店桥地下河流域不同水体硫酸盐浓度特征及来源识别[J].地质学报, 90(8):1922-1932. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.020
王明章. 2012.贵州省水文地质工作思考[J].贵州地质, 29(2):81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2012.02.003
杨平恒, 卢丙清, 贺秋芳, 陈雪彬. 2014.重庆典型岩溶地下水系统水文地球化学特征研究[J].环境科学, 35(4):1290-1296. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx201404012
杨郧城, 沈照理, 文冬光, 侯光才, 赵振宏, 王冬. 2008.鄂尔多斯白垩系地下水盆地硫酸盐的水文地球化学特征及来源[J].地球学报, 29(5):553-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.05.003
张永双, 孙璐, 殷秀兰, 孟晖. 2017.中国环境地质研究主要进展与展望[J].中国地质, 44(5):901-912. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170505&flag=1
赵金凤, 夏克勤, 石豫川, 孙晋玉. 2004.重庆歌乐山隧址区地下水同位素组成特征及意义[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 15(2):94-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.020
-



 下载:
下载: