Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Zhongshangou gold deposit, Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area, Hebei Province: Limitation on the intrusive rock related telluride-gold deposits
-
摘要:
研究目的 中山沟金矿位于华北克拉通北缘、尚义—崇礼—赤城深大断裂的南侧,是河北省张宣金矿集区典型金矿床之一。本文探讨了矿床成矿流体特征和演化,以期为该矿床找矿勘查提供理论依据。
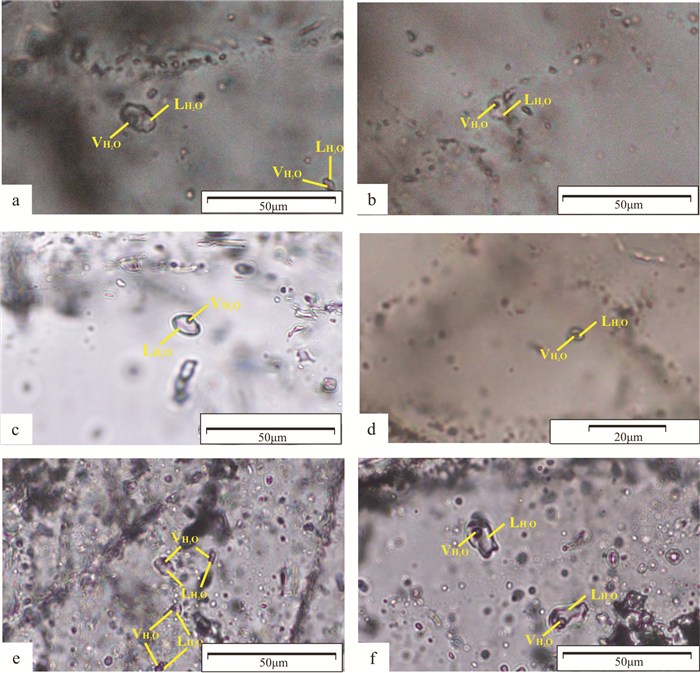
研究方法 本文总结了中山沟金矿的成矿背景、矿区地质特征、矿体及矿石特征,选取4个阶段的代表性样品,开展了流体包裹体岩相学和显微测温、氢氧同位素、氦氩同位素等研究。
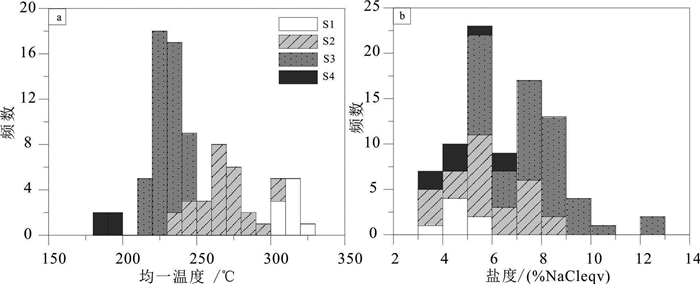
研究结果 研究发现中山沟金矿可划分为4个成矿阶段:钾长石-黄铁矿-石英阶段(Ⅰ)、乳白色石英-黄铁矿阶段(Ⅱ)、烟灰色石英-硫化物阶段(Ⅲ)和贫硫化物-碳酸盐阶段(Ⅳ)。各成矿阶段主要发育气液两相原生流体包裹体。流体包裹体测温数据表明,其主成矿阶段均一温度为210~250℃、盐度为6.01%~13.62% NaCleqv。氢、氧同位素研究表明,δ18O水和δDV-SMOW值分别为-2.97‰~6.96‰和-94.6‰~-80.2‰,具有明显向大气降水线发生漂移而呈线性变化的特征。黄铁矿氦、氩同位素研究表明,3He/4He值为1.82×10-7~9.24×10-7,40Ar/36Ar值为699.9~2200.4,R/Ra值为0.13~0.66,放射成因40Ar*为55.89%~86.57%,幔源He为2.00%~10.86%。
结论 中山沟金矿成矿流体经历了从中高温、中低盐度至低温、中低盐度的持续演化过程。其主成矿阶段发生了强烈的沸腾作用,成矿晚期有大量的大气降水的混入。随着成矿作用的进行,幔源物质参与成矿的比例逐渐升高。成矿流体具有壳幔混合的特点。综上所述,中山沟金矿的成矿流体具有侵入岩型碲金矿床的特点。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective The Zhongshangou gold deposit is located in the north margin of North China Craton and the south side of Shangyi-Chongli-Chicheng deep fault. It is one of the typical gold deposits in Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua gold concentration area, Hebei Province. This paper discusses the characteristics and evolution of ore-forming fluids, in order to provide a theoretical basis for the exploration of the deposit.
Methods This paper summarizes the regional mineralizing setting, geological characteristics of the mining area, ore body and ore characteristics. Representative samples from four metallogenic stages were selected to conduct research on fluid inclusion petrography and micro thermometry, hydrogen and oxygen isotopes, and helium and argon isotopes.
Results The results indicate that it can be divided into four metallogenic stages: K-feldspar-pyrite-quartz stage (Ⅰ), milky white quartz-pyrite stage (Ⅱ), smoky gray quartz-sulfide stage (Ⅲ) and sulfide-poor-carbonate stage (Ⅳ). Gas-liquid two-phase primary fluid inclusions are mainly developed in each mineralization stage. The temperature measurement data of fluid inclusions show that the homogenization temperature and salinity of main ore-forming stage are respectively 210-250℃ and 6.01%-13.62%NaCleqv. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope show that δ18OH2O and δDV-SMOW values are respectively -2.97‰-6.96‰ and -94.6‰--80.2‰, which show that the δ18OH2O values drift to the atmospheric water line and show a linear change. Helium and argon isotope of the pyrite show that 3He/4He values are 1.82×10-7-9.24×10-7, 40Ar/36Ar values are 699.9-2200.4, R/Ra values are 0.13-0.66, radiogenic 40Ar* values are 55.89%-86.57%, and mantle derived helium values are 2.00%-10.86%.
Conclusions The ore-forming fluid has experienced a continuous evolution process from medium-high temperature and medium-low salinity to low temperature and medium-low salinity. The main ore-forming stage experienced strong boiling. In the late stage of mineralization, there mixed in a large amount of meteoric water. With the development of mineralization, the proportion of mantle derived materials in mineralization increased gradually. The ore-forming fluid has the characteristics of magma fluid mixed with the crust and mantle. To sum up, the ore-forming fluid of Zhongshangou gold deposit is characterized by the intrusive rock related telluride-gold deposit.
-

-
图 1 大地构造位置(a)及区域地质简图(b)(据宋瑞先等, 2013; Bao et al., 2016修改)
Figure 1.
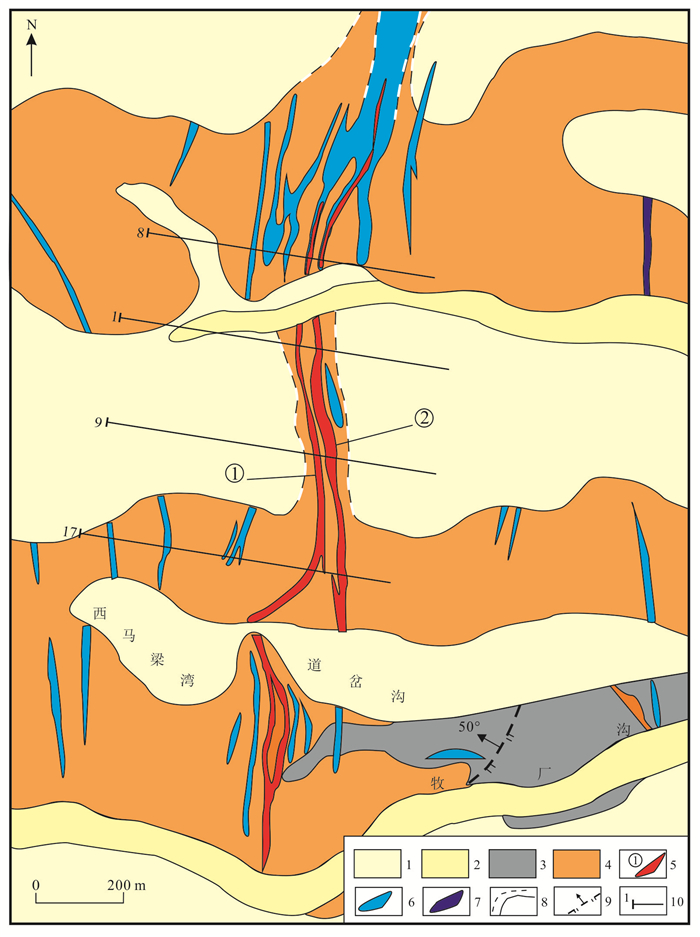
图 2 中山沟金矿矿区地质图(据刘辉峰和王吉玉, 1992修编)
Figure 2.
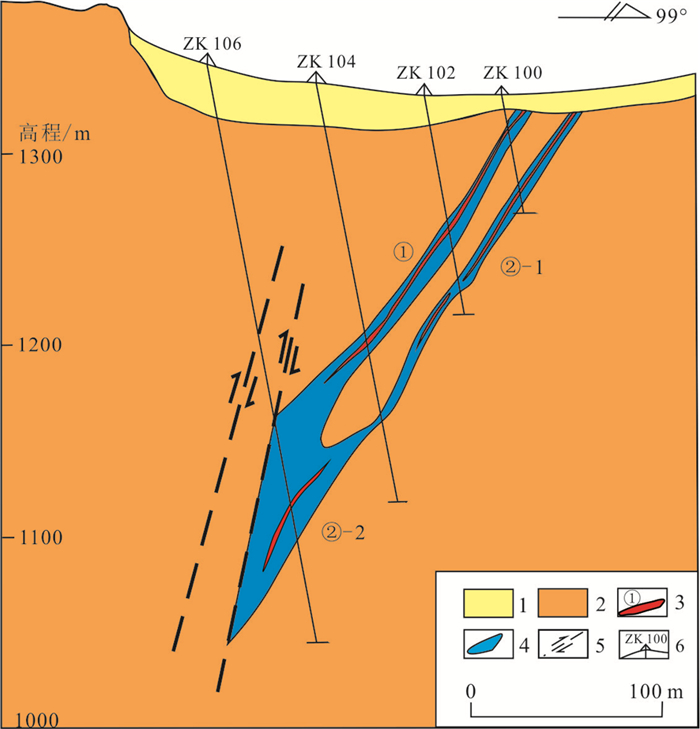
图 3 中山沟金矿1号勘探线剖面图(据刘辉峰和王吉玉, 1992修编)
Figure 3.
图 10 中山沟金矿氢氧同位素关系图(底图据Taylor, 1974)
Figure 10.
图 11 中山沟金矿成矿流体40Ar/36Ar−R/Ra(a)和4He−3He图解(b)(底图据Mamyrin and Tolstikhin, 1984修改)
Figure 11.
表 1 中山沟金矿氢、氧同位素分析结果
Table 1. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions in the Zhongshangou gold deposit

表 2 中山沟金矿黄铁矿氦、氩同位素组成
Table 2. Helium and argon isotopic compositions of pyrite in the Zhongshangou gold deposit

表 3 地球中He-Ar来源及特征值含量
Table 3. Sources and eigenvalue of He-Ar in the earth

-
Ballentine C J, Burgess R, Marty B. 2002. Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 47(1): 539-614. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.47.13
Bao Z W, Li C J, Zhao Z H. 2016. Metallogeny of the syenite-related Dongping gold deposit in the northern part of the North China Craton: A review and synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.002
Bao Z W, Sun W D, Li C J, Zhao Z H. 2014. U-Pb dating of hydrothermal zircon from the Dongping gold deposit in North China: Constraints on the mineralization processes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 61: 107-119. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.02.006
Bodnar R J, Sanchez P L, Moncada D, Steele-MacInnes M. 2014. Fluid inclusions in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 13: 119-142.
Burnard P G, Hu R Z, Turner G, Bi X W. 1999. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(10): 1595-1604. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00108-8
Chen Jun, Wang Henian. 2004. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 116-117 (in Chinese).
Chen Qian. Studies on Fluid Characteristics and Mineralization Mechanism of the Dabaiyang Gold Deposit, Northwest of Hebei[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yanjing, Ni Pei, Fan Hongrui, Pirajno F, Lai Yong, Sun Wenchao, Zhang Hui. 2007. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in different hydrothermal gold deposit systems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2085-2108 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.009
Clayton R N, O'Neil J R, Mayeda T K. 1972. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 77: 3057-3067. doi: 10.1029/JB077i017p03057
Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Mao J W. 2009. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 264(1/4): 101-121.
Deng Jinfu, Feng Yanfang, Liu Cui, Xiao Qinghui, Su Shangguo, Zhou Su, Gao Yanguang. 2009. Yanshanian (Jurassic-Cretaceous) orogenic processes, magma sources and metallogenesis as well as coal formation in the Taihangshan- Yanshan- West Liaoning region[J]. Geology in China, 36 (3): 623-633 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.009
Fan H R, Hu F F, Wilde S A, Yang K F, Jin C W. 2011. The Qiyugou gold-bearing breccia pipes, Xiong'ershan region, central China: Fluid-inclusion and stable-isotope evidence for an origin from magmatic fluids[J]. International Geology Review, 53(1): 25-45. doi: 10.1080/00206810902875370
Groves D I, Santosh M, Zhang L. 2020. A scale-integrated exploration model for orogenic gold deposits based on a mineral system approach[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 11(3): 719-738. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.12.007
Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. 1988. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solution[J]. Economic Geology, 83(1): 197-202. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197
Han Yinwen, Ma Zhendong. 2003. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 245-250 (in Chinese).
Hu Ruizhong, Bi Xianwu, Turner G, Burnard P. 1999. He and Ar isotopic geochemistry of gold ore-forming fluids in Ailaoshan gold deposit belt[J]. Science in China (series D), 29(4): 321-330 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu R Z, Burnard P G, Bi X W. 2004. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jinshajiang fault belt, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 203(3/4): 305-317.
Hu R Z, Burnard P G, Bi X W, Zhou M F, Peng J T, Su W C, Zhao J H. 2009. Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi Province, China: Evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes[J]. Chemical Geology, 266(1/2): 86-95.
Hu R Z, Burnard P G, Turner G, Bi X W. 1998. Helium and Argon isotope systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in West Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 146(1/2): 55-63.
Hu R Z, Zhou M F. 2012. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China: An introduction to the thematic issue[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 47(6): 579-588. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0431-6
Hu Xiaodie, Chen Zhihong, Zhao Yanming, Wang Kuiyua. 1997. The metallogenetic epoch of the Xiaoyingpan gold deposit——The new material of U-Pb isotopic age on single zircon[J]. Progress in Precambrian Research, 20(2): 22-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jean-Baptiste P, Fouquet Y. 1996. Abundance and isotopic composition of helium in hydrothermal sulfides from the East Pacific Rise at 13°N[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(1): 87-93. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00357-6
Jiang N, Liu Y S, Zhou W G, Yang J H, Zhang S Q. 2007. Derivation of Mesozoic adakitic magmas from ancient lower crust in the North China craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(10): 2591-2608. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.02.018
Jiang N, Zhang S Q, Zhou W G, Liu Y S. 2009. Origin of a Mesozoic granite with A-type characteristics from the North China craton: Highly fractionated from Ⅰ-type magmas[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 158: 113-130. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0373-2
Kendrick M A, Burgess R, Pattrick R A D. 2001. Fluid inclusion noble gas and halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-porphyry mineralizing fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65: 2651-2668. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00618-4
Li Changcun, Han Xiuli. 1998. Study on fluid inclusions in Zhongshan gold deposit[J]. Gold, 19(3): 7-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Changcun, Zhang Zeng. 1999. The geological characteristics of Zhongshangou gold deposit[J]. Journal of Hebei Institute of Technology, 21: 18-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Changmin, Deng Jinfu, Su Shangguo, Liu Cui, Liu Xinmiao. 2014. U-Pb chronology and Hf isotope study of zircon in the western section of Shuiquangou rock mass, Northern Hebei Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3301-3314(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Chuangju, Bao Zhiwei. 2012. Geochemical characteristics and geodynamic implications of the Early Cretaceous magmatisms in Zhangjiakou Region, northwest Hebei Province, China[J]. Geochimica, 41(4): 343-358 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.04.005
Liu Huifeng, Wang Jiyu. 1992. Geological Exploration Report of Zhongshangou Gold Deposit in Changdi Township, Chongli County, Hebei Province[R]. Shijiazhuang Comprehensive Geological Brigade of Hebei Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (in Chinese).
Liu Jia, Cai Pengjie, Zeng Xiahua, Du Wenyang, Liu Lei. 2021. Geology, ore-forming fluid and metallogenic age of orogenic gold deposits in the Northern Qaidam[J]. Geology in China, 48(2): 374-387 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jiajun, Zhai Degao, Wang Dazhao, Gao Shen, Yin Chao, Liu Zhenjiang, Wang Jianping, Wang Yinhong, Zhang Fangfang. 2020. Classification and mineralization of the Au- (Ag)- Te- Se deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(2): 79-98(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Wenjian. 2014. Study on Metallogenic Characteristics and Mineralization of Gold Deposits in Northern Hebei Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mamyrin B A, Tolstikhin I N. 1984. Helium isotopes in the earth's mantle[J]. Develop Geochemical, 3: 97-134.
Mao J W, Li Y Q, Goldfarb R, He Y, Zaw K. 2003. Fluid inclusion and noble gas studies of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China: A mantle connection for mineralization?[J]. Economic Geology, 98(3): 517-534.
Mao Jingwen, Li Yinqing. 2001. Fluid inclusions of the Dongping gold telluride deposit in Hebei Province, China: Involvement of mantle fluid in metallogenesis[J]. Mineral Deposits, 20(1): 23-36(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.01.004
Miao L C, Qiu Y M, Mcnaughton N, Luo Z K, Groves D, Zhai Y S, Fan W M, Zhai M G, Guan K. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of granitoids from Dongping area, Hebei Province, China: Constraints on tectonic evolution and geodynamic setting for gold metallogeny[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 19: 187-204. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00041-5
Podosek F A, Bernatowicz T J, Kramer F E. 1981. Adsorption of xenon and krypton on shales[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45(12): 2401-2415. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90094-6
Qiu H N. 1996. 40Ar-39Ar dating of the quartz samples from two mineral deposits in western Yunnan (SW China) by crushing in vacuum[J]. Chemical Geology, 127: 211-222. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00093-3
Shui Lansu. 2002. Geological structural characteristics and ore control of Zhongshangou gold deposit[J]. Journal of North China University of Technology, 24(2): 128-131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Simmons S F, Sawkins F J, Schlutter D J. 1987. Mantle- derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature, 329(6138): 429-432. doi: 10.1038/329429a0
Simmons S F, White N C, John D A. 2005. Geological characteristics of epithermal precious and base metal deposits[J]. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 485-522.
Song Ruixian, Wang Youzhi, Wang Zhenpeng. 2013. Geological and Mineral Resources in Zhangjiakou[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-188 (in Chinese).
Stuart F M, Burnard P G, Taylor R P, Turner G. 1995. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He, Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W- Mo mineralization, South Korea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(22): 4663-4673. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00300-2
Stuart F M, Turner G. 1992. The abundance and isotopic composition of the noble gases in ancient fluids[J]. Chemical Geology, 101(1/2): 97-109.
Stuart F M, Turner G, Duckworth R C, Fallick A E. 1994. Helium isotopes as tracers of trapped hydrothermal fluids in ocean-floor sulfides[J]. Geology, 22 (9): 823-826. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0823:HIATOT>2.3.CO;2
Taylor H P. 1974. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 69: 843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843
Tian Wei, Chen Bin, Liu Chaoqun, Zhang Huafeng. 2007. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope composition of Xiaozhangjiakou ultra-basic rock mass in Northern Hebei Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3): 583-590 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Trull T, Kurz M D, Jenkins W I. 1991. Diffusion of cosmogenic 3He in olivine and quartz: Implications for surface exposure dating[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 103(1/4): 241-256.
Turner G, Burnard P, Ford J L, Gilmour J D, Lyon I C, Stuart F M. 1993. Tracing fluid sources and interactions[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 344(1670): 127-140.
Turner G, Wang S S. 1992. Excess argon, crustal fluid and apparent isochrons from crushing K feldspar[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 110: 193-211. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(92)90048-Z
Wang D Z, Liu J J, Zhai D G, Carranza E J M, Wang Y H, Zhen S M, Wang J, Wang J P, Liu Z J, Zhang F F. 2019. Mineral paragenesis and ore-forming processes of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China[J]. Resource Geology, 69(3): 287-313. doi: 10.1111/rge.12202
Wu Shanshan. 2009. Metallogenic and Ore-controlling Structures of Zhongshan Gold Deposit in Chongli, Hebei Province[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Yongchang. 1996. Mantle source noble gas in natural gas[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 3(3): 63-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Yongchang. 1998. Rare Gas Geochemistry in Natural Gas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-104 (in Chinese).
Yin Jianzhao. 1994. Study on the types of gold deposits in the Northwestern Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 3(3): 176-185(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Yuxing, Xu Hong, Wu Xiangke, Yang Lijun, Tian Zhu, Gao Shen, Wang Qiushu. 2012. Characteristics of the Au-Ag-Te minerals and its ore-forming fluids in Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 345-356(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai D G, Williams-Jones A E, Liu J J, Tombros S F, Cook N J. 2018. Mineralogical, fluid inclusion, and multiple isotope (H-O-S-Pb) constraints on the genesis of the Sandaowanzi epithermal Au-Ag-Te deposit, NE China[J]. Economic Geology, 113(6): 1359-1382. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4595
Zhang P H, Zhu J C, Zhao Z H, Gu X P, Lin J F. 2004. Zincospiroffite, a new tellurite mineral species from the Zhongshangou gold deposit, Hebei Province, People's Republic of China[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 42: 763-768. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.42.3.763
Zhang Yunqiang, Li Shengrong, Chen Haiyan, Zhang Xiubao, Zhou Qifeng, Cui Juchao, Song Yubo, Guo Jie. 2012. Trace element and He-Ar isotopic evidence of pyrite for the source of ore-forming fluids in the Jinqingding gold deposit, eastern Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 39(1): 195-204 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zhaochong. 1995. Genesis Mechanism of Shuiquangou Complex and its Relationship with Gold Mineralization in Northern Hebei Province[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhen S M, Wang Q F, Wang D Z, Emmanuel J M C, Liu J J, Pang Z S, Cheng Z Z, Xue J L, Wang J, Zha Z J. 2020. Genesis of the Zhangquanzhuang gold deposit in the northern margin of North China Craton: Constraints from deposit geology and ore isotope geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 122: 103511.
Zheng Hongwei, Wang Fengxiang, Song Peng, Wang Guochen. 2013. Study on metallogenesis of Zhongshangou gold deposit[J]. Science and Technology Vision, 19: 177-177 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Hongwei. 2014. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Shuijingtun Gold Deposit and Zhongshangou Gold Deposit in Zhangxuan Area[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 1-66 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈骏, 王鹤年. 2004. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 116-117.
陈茜. 2013. 冀西北大白阳金矿成矿流体及成矿机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, Pirajno F, 赖勇, 苏文超, 张辉. 2007. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2085-2108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200709009.htm
邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 刘翠, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 周肃, 高延光. 2009. 太行-燕辽地区燕山期造山过程、岩浆源区与成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 36(3): 623-633. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20090309?st=search
韩吟文, 马振东. 2003. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 245-250.
胡瑞忠, 毕献武, Turner G, Burnard P. 1999. 哀牢山金矿带金成矿流体He和Ar同位素地球化学[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 29(4): 321-330.
胡小蝶, 陈志宏, 赵彦明, 王魁元. 1997. 河北小营盘金矿成矿时代——单颗粒锆石U-Pb同位素年龄新证据[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 20(2): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ199702001.htm
李昌存, 韩秀丽. 1998. 中山沟金矿流体包裹体研究[J]. 黄金, 19(3): 7-9.
李昌存, 张增. 1999. 中山沟金矿床地质特征[J]. 河北联合大学学报, 21: 18-21.
李长民, 邓晋福, 苏尚国, 刘翠, 刘新秒. 2014. 冀北水泉沟岩体西段锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3301-3314.
李创举, 包志伟. 2012. 冀西北早白垩世岩浆岩的地球化学特征及其地球动力学背景[J]. 地球化学, 41(4): 343-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201204004.htm
刘辉峰, 王吉玉. 1992. 河北省崇礼县场地乡中山沟金矿勘探地质报告[R]. 河北省地质矿产局石家庄综合地质大队.
刘嘉, 蔡鹏捷, 曾小华, 杜文洋, 刘雷. 2021. 柴达木盆地北缘造山型金矿地质、成矿流体及成矿时代特征[J]. 中国地质, 48(2): 374-387. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210203?st=search
刘家军, 翟德高, 王大钊, 高燊, 尹超, 柳振江, 王建平, 王银宏, 张方方. 2020. Au-(Ag)-Te-Se成矿系统与成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 27(2): 79-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202002007.htm
刘文建. 2014. 冀北金矿成矿特征及成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
毛景文, 李荫清. 2001. 河北省东坪碲化物金矿床流体包裹体研究: 地幔流体与成矿关系[J]. 矿床地质, 20(1): 23-36.
水兰素. 2002. 中山沟金矿地质构造特征及控矿[J]. 华北理工大学学报, 24(2): 128-131.
宋瑞先, 王有志, 王振彭. 2013. 张家口地质矿产[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-188.
田伟, 陈斌, 刘超群, 张华锋. 2007. 冀北小张家口超基性岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 23(3): 583-590. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703007.htm
吴姗姗. 2009. 河北崇礼中山沟金矿成矿控矿构造研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院.
徐永昌. 1996. 天然气中的幔源稀有气体[J]. 地学前缘, 3(3): 63-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY603.006.htm
徐永昌. 1998. 天然气中稀有气体地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-104.
银剑钊. 1994. 冀西北地区金矿类型研究[J]. 贵金属地质, 3(3): 176-185.
余宇星, 许虹, 吴祥珂, 杨利军, 田竹, 高燊, 王秋舒. 2012. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿Au-Ag-Te系列矿物特征及其成矿流体[J]. 岩石学报, 28(1): 345-356.
张运强, 李胜荣, 陈海燕, 张秀宝, 周起凤, 崔举超, 宋玉波, 郭杰. 2012. 胶东金青顶金矿床成矿流体来源的黄铁矿微量元素及He-Ar同位素证据[J]. 中国地质, 39(1): 195-204. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20120119?st=search
张招崇. 1995. 冀北水泉沟杂岩体的成因机制及其与金的成矿作用关系的研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院.
郑宏伟, 王丰翔, 宋鹏, 王国晨. 2013. 中山沟金矿成矿作用研究[J]. 科技视界, 19: 177-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201319136.htm
郑宏伟. 2014. 张宣地区水晶屯金矿和中山沟金矿地质特征对比及矿床成因探讨[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 1-66.
-




 下载:
下载: