Paleoproterozoic basement in eastern Central Asia Orogenic Belt:Evidence from granite and sedimentary strata in Sino-Mongolia border area
-
摘要:
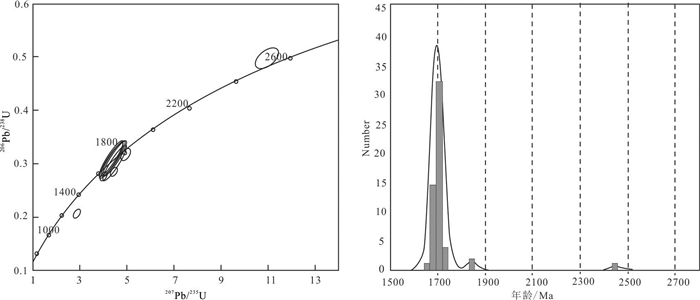
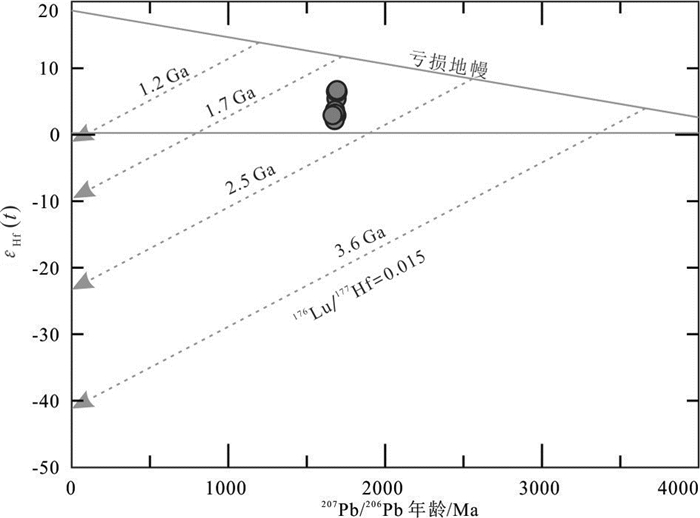
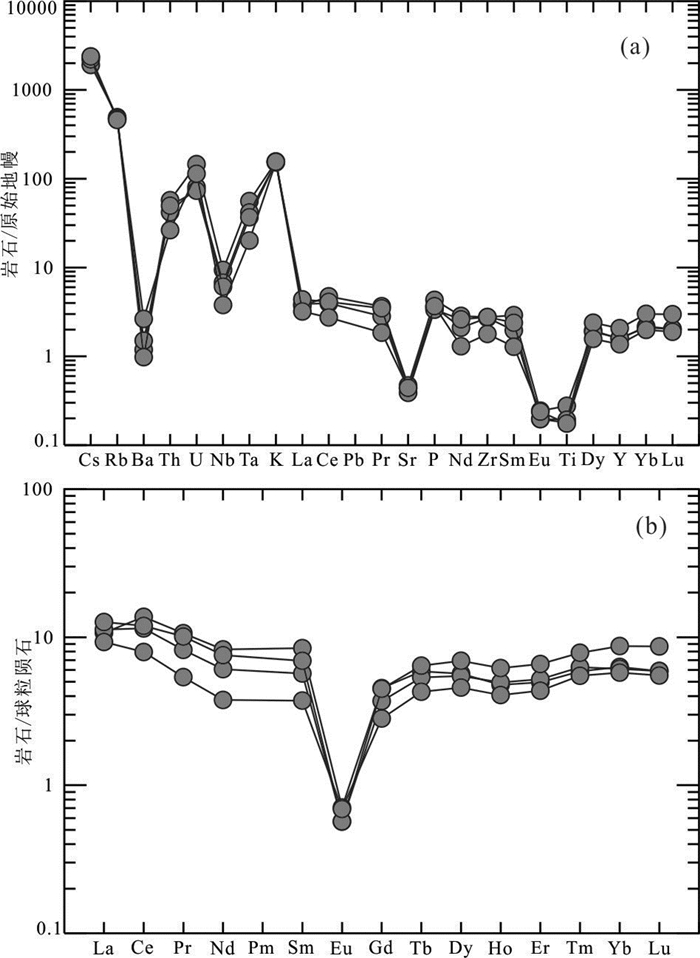
中亚造山带东段多个地块内鲜有古老结晶基底物质报道,严重制约了我们对其早期属性的认识。本研究在内蒙古北部与蒙古国接壤的乌力吉特敖包地区,发现了被中下泥盆统泥鳅河组不整合覆盖的古元古代细粒二长花岗岩和沉积地层(乌兰敖包组)。对二长花岗岩开展的LA-ICM-MS锆石U-Pb定年显示其结晶年龄为(1686±10)Ma,说明形成于古元古代。乌力吉特敖包二长花岗岩高钾钙碱性,过铝质(A/CNK=1.08~1.11),且含有大量白云母,属S-型花岗岩。不同于常见的显生宙以来的S-型花岗岩,乌力吉特敖包古元古代花岗岩具有正的εHf(t)值(+2.9~+6.7),但εHf(t)值远低于1.7 Ga地壳演化趋势线,且锆石原位Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄为2.0~2.3 Ga,因此其应该来源于古老变泥质岩部分熔融。乌力吉特敖包古元古代花岗岩形成于陆陆同碰撞的构造环境。在古元古代乌兰敖包组变质泥岩获得了一个显著的碎屑锆石峰值年龄(1698 Ma),且该地层被元古宙花岗岩侵入。本研究发现的乌力吉特敖包古元古代末期花岗岩和乌兰敖包组沉积地层说明:中亚造山带东缘各地块内存在古老的结晶基底物质。这为我们认识这些地块早期演化历史提供了重要地质证据。
Abstract:There are few reports of Archean crystalline basement in the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, which impedes researchers' understanding of ancient tectonic evolution of this area. In this study, the authors discovered Paleoproterozoic fine-grained adamellite and sedimentary rocks (Wulanaobao Formation) unconformably covered by the Niqiuhe Formation of Middle Lower Devonian in the Ulikit Obo area along central China-Mongolia border area. The zircon U-Pb dating results (LA-ICP-MS) show that the crystallization age of monzogranite is 1686 ±10 Ma, formed in Paleoproterozoic. The Ulikit Obo granites are high-K calc-alkaline, peraluminous (A/CNK=1.08-1.11). In combination with the existence of muscovite, the Ulikit Obo granites could be classified as S-type granites. They have positive εHf(t) value(+ 2.9-+ 6.7), which is located lower than the 1.7 Ga crustal evolution trend line; besides, the in-situ Hf isotope two-stage model age of zircon is 2.0-2.3 Ga, so the zircon should be derived from partial melting of pelites in syn-collisional tectonic settings. The Wulanaobao Formation was intruded by the Paleoproterozoic Ulikit Obo granites and their detrital zircons yielded a youngest age peak of ca. 1698 Ma. The discovery of Paleoproterozoic Ulikit Obo granites and Wulanaobao Formation indicates the existence of Paleoproterozoic crystalline basement for the microcontinental massifs in the eastern section of the Central Asian orogenic belt.
-

-
图 1 西伯利亚和华北板块及其间大地构造图(a,据Liu et al., 2018a修改)和研究区所处大地构造位置简图(b,据李英雷等, 2017;Liu et al., 2019修改)
Figure 1.
图 13 乌力吉特敖包古元古代花岗岩构造环境判别图(据Pearce et al., 1984;Pearce, 1996;)
Figure 13.
表 1 乌力吉特敖包古元古代花岗岩(TW4295)和乌兰敖包组泥岩(TW2320)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Ulikit Obo granites(TW4295) and mudstone(TW2320) from the Wulanaobao Formation

表 2 乌力吉特敖包早元古代花岗岩(TW4295)锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素数据
Table 2. In-situ zircon Lu-Hf isotope dating results of the Ulikit Obo granites(TW4295)
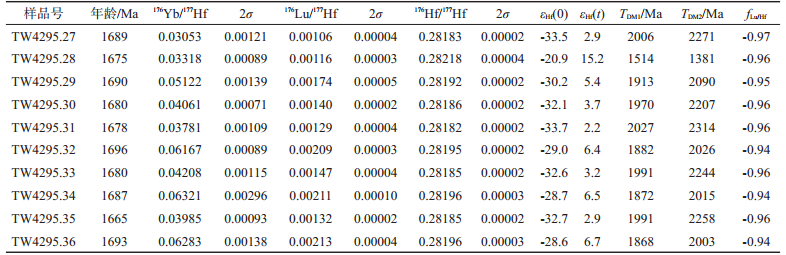
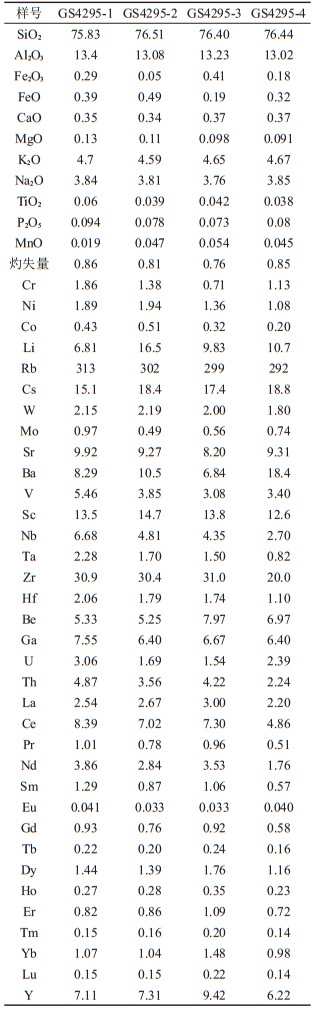
表 3 乌力吉特敖包古元古代花岗岩主量(%)和微量元素(10-6)含量
Table 3. Major(%) and trace element(10-6) concentrations of the Ulikit Obo granites
-
Chen Chenghong, Hsieh P S, Lee Chiyu, Zhou Hanwen. 2011. Two episodes of the Indosinian thermal event on the South China Block:Constraints from LA-ICPMS U-Pb zircon and electron microprobe monazite ages of the Darongshan S-type granitic suite[J]. Gondwana Research, 19(4):1008-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.10.009
Cui Yuliang, Qu Hongjie, Chen Yingfu, Wang Sen. 2019. First identification of~2.61Ga amphibolite in Jiefangyingzi area on the northern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Geology in China, 46(2):436-437 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dan Wei, Li Xianhua, Wang Qiang, Wang Xuance, Liu Yu, Wyman D A. 2014. Paleoproterozoic S-type granites in the Helanshan Complex, Khondalite Belt, North China Craton:Implications for rapid sediment recycling during slab break-off[J]. Precambrian Research, 254:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.07.024
Eizenhofer P R, Zhao Guochun, Zhang Jian, Sun Min. 2014. Final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean along the Solonker Suture Zone:Constraints from geochronological and geochemical data of Permian volcanic and sedimentary rocks[J]. Tectonics, 33(4):441-463. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2013TC003357
Fu Dong, Huang Bo, Kusky T M, Li Gangzhu, Wilde S A, Zhou Wenxiao, Yu Yang. 2018. A Middle Permian ophiolitic melange belt in the solonker Suture zone, Western Inner Mongolia, China:Implications for the Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Tectonics, 37(5):1292-1320. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2017TC004947
Gladkochub D P, Donskaya T V, Mazukabzov A M, Stanevich A M, Sklyarov E V, Ponomarchuk V A. 2007. Signature of Precambrian extension events in the southern Siberia[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 48(1):17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2006.12.001
Gladkochub, Dmitry P, Pisarevsky, Sergei A, Donskaya, Tatiana V, Ernst, Richard E, Wingate, Michael T D, Söderlund, Ulf, Mazukabzov, Anatoliy M, Sklyarov, Eugene V, Hamilton, Michael A, Hanes, John A. 2010. Proterozoic mafic magmatism in Siberian craton:An overview and implications for paleocontinental reconstruction[J]. Precambrian Research, 183:660-668. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.023
He Fubing, Wei Bo, Xu Jixiang, Sun Yonghua, Li Ruijie. 2017. Ages, origin and geological implications of the volcanic rocks in the Baoligaomiao Formation of East Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 44(6):1159-1174 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706011
He Zhenyu, Klemd R, Yan Lili, Zhang Zeming. 2018. The origin and crustal evolution of microcontinents in the Beishan orogen of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 185:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.012
He Zhengjun, Niu Baogui, Zhang Xinyuan, Zhao Lei, Liu Renyan. 2011a. Discovery of the paleo-weathered mantle of the rapakivi granite covered by the Proterozoic Changzhougou Formation in the Miyun area, Beijing and their detrital zircon dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(5):798-802 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201105020
He Zhengjun, Zhang Xinyuan, Niu Baogui, Liu Renyan, Zhao Lei. 2011b. The paleo-weathering mantle of the Proterozoic rapakivi granite in Miyun County, Beijing and the relationship with the Changzhougou Formation of Changchengian System[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(4):123-130 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201104010
Jung S, Mezger K, Hoernes S. 2001. Trace element and isotopic (Sr, Nd, Pb, O) arguments for a mid-crustal origin of Pan-African garnet-bearing S-type granites from the Damara orogen (Namibia)[J]. Precambrian Research, 110(1/4):325-355. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301926801001759
Li Huaikun, Li Huimin, Lu Songnian. 1995. Grain zircon U-Pb ages for volcanic rocks from Tuanshanzi formation of Changcheng system and their geological implications[J].Geochimica, 24(1):43-48 (in Chinese).
Li Huaikun, Lu Songnian, Li Huimin, Sun Lixin, Xiang Zhenqun, Geng Jianzhen, Zhou Hongying. 2009. Zircon and beddeleyite U-Pb precision dating of basic rock sills intruding Xiamaling Formation, North China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(10):1396-1404 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200910005
Li Huaikun, Su Wenbo, Zhou Hongying, Geng Jianzhen, Xiang Zhenqun, Cui Yurong, Liu Wencan, Lu Songnian. 2011. The base age of the Changchengian System at the northern North China Craton should be younger than 1670 Ma:Constraints from zircon U-Pb LA-MC-ICPMS dating of a granite-porphyry dike in Miyun County, Beijing[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3):108-120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Huaikun, Zhu Shixing, Xiang Zhenqun, Su Wenbo, Lu Songnian, Zhou Hongying, Geng Jianzhen, Li Sheng, Yang Fengjie. 2010. Zircon U-Pb dating on tuff bed from Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Yanqing, Beijing:Further constraints on the new subdivision of the Mesoproterozoic stratigraphy in the northern North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7):2131-2140 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jinyi. 2009a. Cycles and Stages of Geological History of China Mainland[J]. Geology in China, 36(3):504-527 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200903003
Li Jinyi, Zhang Jin, Yang Tiannan, Li Yaping, Sun Guihua, Zhu Zhixin, Wang Lijia. 2009b. Crustal tectonic division and evolution of the southern part of the North Asian orogenic region and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 39(4):584-605 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200904002
Li Shan, Wang Tao, Wilde S A, Tong Ying. 2013. Evolution, source and tectonic significance of Early Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (central segment)[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 126:206-234. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.06.001
Li Shan, Wilde S A, He Zhengjun, Jiang Xiaojun, Liu Renyan, Zhao Lei. 2014. Triassic sedimentation and postaccretionary crustal evolution along the Solonker suture zone in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Tectonics, 33(6):960-981. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1002/2013TC003444
Li Wenjing, Yin Changqing, Long Xiaoping, Zhang Jian, Xia Xiaoping, Wang Luojuan. 2017. Paleoproterozoic S-type granites from the Helanshan Complex in Inner Mongolia:Constraints on the provenance and the Paleoproterozoic evolution of the Khondalite Belt, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 299:195-209. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.07.009
Li Yinglei, Xu Guo, Liu Huichuan, Bai Lingqi, Su Yinchun, Liu Xiaonü. 2017. Petrogenesis and tectonic implication of volcanic rocks from Manitu Formation in the western Great Xing'an Range[J]. Geoscience, 31(4):683-696 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201704004
Liu Deliang, Shi Rendeng, Ding Lin, Huang Qishuai, Zhang Xiaoran, Yue Yahui, Zhang Liyun. 2017. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic granitoids in southern Qiangtang, Tibet:Implications for the subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean[J]. Gondwana Research, 41:157-172. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.04.007
Liu Huichuan, Li Yinglei, He Hongyun, Huangfu Pengpeng, Liu Yongzheng. 2018a. Two-phase southward subduction of the Mongol-Okhotsk oceanic plate constrained by Permian-Jurassic granitoids in the Erguna and Xing'an massifs (NE China)[J]. Lithos, 304:347-361. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9dcf91af9a836aa5218b8852fac61545
Liu Huichuan, Wang Yuejun, Li Zhonghai, Zi Jianwei, Huangfu Pengpeng. 2018b. Geodynamics of the Indosinian orogeny between the South China and Indochina blocks:Insights from latest Permian-Triassic granitoids and numerical modeling[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 130(7/8):1289-1306. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018GSAB..130.1289L/abstract
Liu Huichuan, Wang Yuejun, Cawood P A, Fan Weiming, Cai Yongfeng, Xing Xiaowan. 2015. Record of Tethyan ocean closure and Indosinian collision along the Ailaoshan suture zone (SW China)[J]. Gondwana Research, 27(3):1292-1306. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.12.013
Liu Huichuan, Li Yinglei, Wu Liwen, Huangfu Pengpeng, Zhang Ming. 2019. Geochemistry of high-Nb basalt-andesite in the Erguna Massif (NE China) and implications for the early Cretaceous back-arc extension[J]. Geological Journal, 54(1):291-307. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=195ac2e0eb9baaeb379d341b0a280dae
Liu Wei, Li Gangzhu, Bai Yuming, Zhang Siyuan, Li Chengyuan, Zhao Guangming. 2018. Discovery of the Mesoproterozoic quartz diorite in the Solonker Area, Urad Zhong Qi, Inner Mongolia, and its tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(10):2106-2119 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201810011
Luo Jun, Yun Jinbiao, He Zhiliang, Li Tianyi, Song Haiming. 2018. The discovery of Mesoproterozoic gneiss from Mao 11 well in Cha'gan Sag, Inner Mongolia:Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Geology in China, 45(3):632-633 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Niu Wenchao, Ren Bangfang, Ren Yunwei, Sun Lixin, Duan Xiaolong, Duan Lianfeng, Li Min, Zhang, Jiahun. 2017. Discovery of Neoproterozoic gneissic granite from the Beishan area, Inner Mongolia:Zircon U-Pb chronologic evidence[J]. Geology in China, 44(2):409-410 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Patiňo-Douce A E. 1999. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 168 (s1):55-75.
Patiňo-Douce A E, Harris Nigel. 1998. Experimental constraints on Himalayan anatexis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 39(4):689-710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
Pearce J. 1996. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 19(4):120-125. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace-element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic-rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Rämä Tapani O, Haapala I, Vaasjoki M, Yu Jianhua, Fu Huiqin. 1995.1700 Ma Shachang complex, northeast China:Proterozoic rapakivi granite not associated with Paleoproterozoic orogenic crust[J]. Geology, 23(9):815-818. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0815:MSCNCP>2.3.CO;2
Ren Jishu, Zhao Le, Li Chong, Zhu Junbin, Xiao Liwei. 2017. Thinking on Chinese tectonics-duty and responsibility of Chinese geologists[J]. Geology in China, 44(1):33-43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi Yuiruo, Anderson J L, Li Linlin, Ding Jing, Liu Cui, Zhang Wei, Shen Chonghui. 2016. Zircon ages and Hf isotopic compositions of Permian and Triassic A-type granites from central Inner Mongolia and their significance for Late Palaeozoic and Early Mesozoic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. International Geology Review, 58(8):967-982. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1138333
Song Shuguang, Wang Mingming, Xu Xin, Wang Chao, Niu Yaoling, Allen M B, Su Li. 2015. Ophiolites in the Xing'an-Inner Mongolia accretionary belt of the CAOB:Implications for two cycles of seafloor spreading and accretionary orogenic events[J]. Tectonics, 34(10):2221-2248. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003948
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implication for mantle composition and process[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(SI):313-345. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1989GSLSP..42..313S/abstract
Sun Lixin, Ren Bangfang, Wang Shuqing, Xu Xinying, Zhang Yun. 2018. Petrogenesis of the Mesoproterozoic gneissic granite in the Sonid Left Banner Area, Inner Mongolia, and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(11):2167-2189 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201811001
Wang Fei, Zhou Xinhua, Zhang Lianchang, Ying Jifeng, Zhang Yutao, Wu Fuyuan, Zhu Rixiang. 2006. Late mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an range (NE China):Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 251(1/2):179-198. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222410896_Late_Mesozoic_volcanism_in_the_Great_Xing'an_Range_NE_China_Timing_and_implications_for_the_dynamic_setting_of_NE_Asia
Wang Yuejun, Fan Weiming, Sun Min, Liang Xinquan, Zhang Yanhua, Peng Touping. 2007. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block:A case study in the Hunan Province[J]. Lithos, 96(3/4):475-502. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493706003033
Wang Yuejun, Zhang Aimei, Fan Weiming, Zhao Guochun, Zhang Guowei, Zhang Yuzhi, Zhang Feifei, Li Sanzhong. 2011. Kwangsian crustal anatexis within the eastern South China Block:Geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic fingerprints from the gneissoid granites of Wugong and Wuyi-Yunkai Domains[J]. Lithos, 127(1/2):239-260.
Wei Yunfeng. 2016. Age and geochemical characteristics of Paleoproterozoic granites in Lishi area, Shanxi Province[J]. Huabei land and resources, (3):93-95 (in Chinese).
Xiao Wenjiao, Windley B F, Hao Jie, Zhai Mingguo. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 22(6):1-20.doi:1029/2002TC001484. http://sourcedb.igg.cas.cn/cn/zjrck/200907/W020101130538854036897.pdf
Xu Hong, Peng Qiming, Palmer M R. 2004. Origin of tourmaline-rich rocks in a Paleoproterozoic Terrane (NE China):Evidence from Evaporite-Derived Boron[J]. Geology in China, 31(3):240-252 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jinhui, Wu Fuyuan, Liu Xiaoming, Xie Liewen. 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of the Miyun rapakivi granites from Beijing, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6):1633-1644 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200506011
Zhang Daohan, Wei Junhao, Fu Lebing, Schmitt A K, Wang Dahao, Tan Jun, Liu Jinke. 2017. Petrogenesis and thermal overprint of S-type granites in Helanshan region, North China Craton:Constraints on the 1.90 Ga khondalites decompression melting and 1.32 Ga tectono-thermal event[J]. Precambrian Research, 303:660-672. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.016
Zhang Kaijun. 2014. Genesis of the Late Mesozoic Great Xing'an Range Large igneous Province in eastern central Asia:A Mongol-Okhotsk slab window model[J]. International Geology Review, 56(13):1557-1583. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.946541
和政军, 牛宝贵, 张新元, 赵磊, 刘仁燕. 2011a.北京密云元古宙常州沟组之下环斑花岗岩古风化壳岩石的发现及其碎屑锆石年龄[J].地质通报, 30(5):798-802. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201105020
和政军, 张新元, 牛宝贵, 刘仁燕, 赵磊. 2011b.北京密云元古宙环斑花岗岩古风化壳及其与长城系常州沟组的关系[J].地学前缘, 18(4):123-130. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201104010
李怀坤, 李惠民, 陆松年. 1995.长城系团山子组火山岩颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地球化学, 24(1):43-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX501.003.htm
李怀坤, 陆松年, 李惠民, 孙立新, 相振群, 耿建珍, 周红英. 2009.侵入下马岭组的基性岩床的锆石和斜锆石U-Pb精确定年——对华北中元古界地层划分方案的制约[J].地质通报, 28(10):1396-1404. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD200910006.htm
李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 耿建珍, 相振群, 崔玉荣, 刘文灿, 陆松年. 2011.华北克拉通北部长城系底界年龄小于1670 Ma:来自北京密云花岗斑岩岩脉锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的约束[J].地学前缘, 18(3):108-120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201103013.htm
李怀坤, 朱士兴, 相振群, 苏文博, 陆松年, 周红英, 耿建珍, 李生, 杨锋杰. 2010.北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束[J].岩石学报, 26(7):2131-2140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201007015
李锦轶. 2009a.中国大陆地质历史的旋回与阶段[J].中国地质, 36(3):504-527. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090303&flag=1
李锦轶, 张进, 杨天南, 李亚萍, 孙桂华, 朱志新, 王励嘉. 2009b.北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 39(4):584-605. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200904002
刘伟, 李钢柱, 白宇明, 张思源, 李成元, 赵广明. 2018.内蒙古乌拉特中旗索伦山地区中元古代石英闪长岩的发现及其构造意义[J].地质学报, 92(10):2106-2119. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201810011
李英雷, 徐国, 刘汇川, 白灵麒, 苏银春, 刘小女. 2017.大兴安岭西缘玛尼吐组火山岩成因及构造指示[J].现代地质, 31(4):683-696. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201704004
罗军, 云金表, 何治亮, 李天义, 宋海明. 2018.内蒙古查干凹陷毛11井发现中元古代晚期变质岩:锆石U-Pb定年证据[J].中国地质, 45(3):632-633. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180317&flag=1
牛文超, 任邦方, 任云伟, 孙立新, 段霄龙, 段连峰, 李敏, 张家辉. 2017.内蒙古北山地区发现新元古代片麻状花岗岩:锆石U-Pb定年证据[J].中国地质, 44(2):409-410. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170219&flag=1
孙立新, 任邦方, 王树庆, 许新英, 张云. 2018.内蒙古苏尼特左旗中元古代片麻状花岗岩的成因及大地构造意义[J].地质学报, 92(11):2167-2189. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201811001
魏云峰. 2016.山西省离石一带古元古代花岗岩年代和地球化学特征[J].华北国土资源, (3):93-95. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbgtzy201603043
许虹, 彭齐鸣, Palmer Martin R. 2004.辽宁古元古代地体中富电气石岩石的成因:蒸发岩硼源的证据(英文)[J].中国地质, 31(3):240-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.03.002 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040302&flag=1
杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明, 谢烈文. 2005.北京密云环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 21(6):1633-1644. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200506011
崔玉良, 渠洪杰, 陈英富, 王森. 2019.华北板块北缘解放营子地区发现~2.61Ga斜长角闪岩[J].中国地质, 46(2):436-437. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190222&flag=1
任纪舜, 赵磊, 李崇, 朱俊宾, 肖黎微. 2017.中国大地构造研究之思考-中国地质学家的责任与担当[J].中国地质, 44(1):33-43. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170103&flag=1
何付兵, 魏波, 徐吉祥, 孙永华, 李瑞杰. 2017.内蒙古巴彦敖包地区宝力高庙组火山岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].中国地质, 44(6):1159-1174. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170610&flag=1
-




 下载:
下载: