A study of enrichment environment and formation mechanism of strontium mineral water in Gansu Province
-
摘要:
甘肃省位于中国四大地理区(北方区、南方区、西北区和青藏高原区)的相接部位,气候类型多样、地质构造活动强烈、地形复杂、地貌形态多样,复杂的地质条件、多样的地理气候环境和水文地质条件,为锶矿泉水的形成提供了有利条件。通过对全省644个水点的样品检测分析,表明锶含量主要集中在0.09~1.00 mg/L,最高值达15.6 mg/L,锶含量≥0.40 mg/L、达到饮用天然矿泉水界限含量的水点共有411个,占全部水点的58.1%,锶是甘肃省地下水中普遍含有并且含量较丰的微量元素之一。经统计分析表明,在水文地质单元上,以山前盆地第四系地下水为主的河西走廊平原区和以白垩系碎屑岩孔隙裂隙水为主的陇东黄土丘陵区地下水中最有利于锶的富集;地下水类型上,以中新生界碎屑岩地下水锶最易富集,而以变质岩为主的基岩裂隙水不利于锶的富集;循环特征上,以具备深循环条件的盆地型地下水系统最有利于锶的富集,而循环路径短、交替条件较强烈的局部水流系统中地下水锶偏贫。围岩中的锶丰度,决定了地下水中锶的含量,白垩系和新近系碎屑岩、古生界碳酸盐岩中锶丰度高,决定了白垩系碎屑岩地下水、新近系碎屑岩地下水和碳酸盐岩岩溶水具备锶矿泉水富集的物质条件;同时锶在地下水中富集,还与地下水所处的构造环境和地下水循环运移特征有关,盆地型的地下水流系统和进行深循环的地下水从补给区到排泄区径流距离远,循环路径长,地下水在含水层的滞留时间长,有利于锶在地下水中的溶解和富集。
Abstract:Gansu Province is located at the juncture of the four major geographical areas of China, i.e., north area, south area, northwest area and the Tibetan Plateau, and is characterized by various climates, strong geo-tectonic activities, complex topography, diverse geomorphologic forms, and complex geological and hydrogeological conditions; all these factors provide favorable conditions for forming strontium mineral water. The test and analysis of the mineral water samples from 644 water spots in the whole province show the strontium content of these mineral water are mainly in the range of 0.09-1.00 mg/L, the highest value is 15.6 mg/L, and there are 411 water points where the strontium content is higher than or equal to 0.40 mg/L, and reaches the level content of drinking natural mineral water, accounting for 58.1% of all water points; therefore, strontium is one of the most common and abundant trace elements in groundwater of Gansu Province. The statistic analysis of these testing data shows the following phenomena:the hydrogeological units which are most favorable to strontium enrichment are the Quaternary groundwater in the piedmont basin of the Hexi Corridor plain area and the Cretaceous pore and gap groundwater of clastic rock in the Loess hilly area in east Gansu Province; the type of groundwater which is likely to enrich strontium element is the Mesozoic and Cenozoic detrital groundwater rather than the fractured groundwater of bedrock in metamorphic rock area. The circulation characteristics are that the basin-type groundwater system with deep circulation conditions is most favorable to strontium enrichment, while the groundwater strontium content of the local flowing system where the circulation path is short and the alternate conditions are stronger is poor. The content of strontium in groundwater depends on the strontium abundance in surrounding rocks. Strontium abundance is higher in Cretaceous and Neogene clastic rocks and Paleozoic carbonate rocks than in the other rocks, so the groundwater in the Cretaceous and Neogene clastic rocks and the carbonate karst groundwater has certain material conditions for enrichment of strontium mineral water. At the same time, strontium accumulation in groundwater is related to the geo-tectonic environment in which the groundwater is located and the characteristics of groundwater circulation and migration. The basin-type groundwater flowing system and the groundwater for deep circulation are far away from the recharge area to the discharge area, and the circulation path is long. The retention time of groundwater is long in aquifers, which is beneficial to the dissolution and enrichment of strontium in groundwater.
-

-
表 1 研究区样品测试(N=644)主要指标标准差统计
Table 1. Statistic table of standard deviation of main indicators of sample (N=644) test in the study area
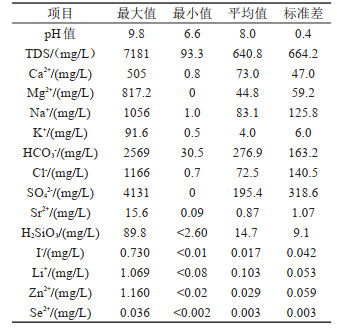
表 2 锶矿泉水点pH值和锶含量(mg/L)一览表
Table 2. pH and strontium content(mg/L)of the main strontium mineral water sites

表 3 研究区水文地质单元锶矿泉水点统计
Table 3. Statistical table of strontium mineral water sites in different hydrogeological units in the study area
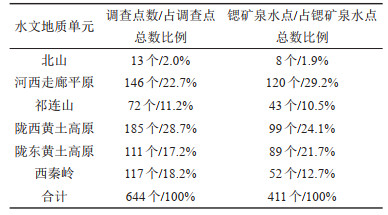
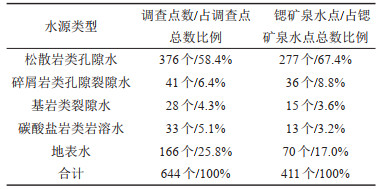
表 4 研究区不同水源锶矿泉水点统计
Table 4. Statistical table of strontium mineral water sites in different water sources in the study area
-
Ding Hongwei, Zhang Ju. 2005. Goechemical properties and evolution of groundwater beneath the Hexi corridor, Gansu Province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 22(1):24-28(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj200501005
Fan Youjun, Fan Shufang, Ren He. 2010.Genetic study of the rich strontium content in water quality of Heihe River Basin[J]. Popular Science & Technology, 12(10):132-133(in Chinese).
Hu Jinwu, Wang Zengyin, ZhouLian, Wang Yusong. 2004.Hyrogeochemical characteristics of the strontium in karst water.Carsologica Sinica, 23(1):37-42(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenpeng, Hao Aibing. 1999. Groundwater formation evolves mode and its meanings in the dry basin of the northwest in China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 26(4):28-32(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Qingxuan, Wang Guiling, Zhang Fawang.2004.Geochemical environment of trace element strontium (Sr) enriched in mineral waters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engimeering Geology, 31(6):19-23(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=11313528
Liu Xinbiao, Zhang Yanlin, Wang Yanjiang, Zhou Bin. 2007. Analysis of hydrochemistry characteristic in the Longdong basin[J].Geology of Chemical Minerals, 29(4):237-241(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC200704009.htm
Liu Xinbiao, Zhang Yanlin, Wang Yanjiang, Zhou Bin. 2009.Evaluation of the movement of cretaceous groundwater beneath the Longdong basin[J].Arid Zone Research, 26(2):176-180(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ200902004.htm
Su Chuntian, Zhang Fawang, Xia Riyuan, Yao Xin, Zou Shengzhang, Luo Fei, Zhao Guangshuai, Yang Yang, Ba Junjie, Li Xiaopan. 2017. A study of the water-rock interaction of large rich Sr mineral spring in Xintian, Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):1029-1030(in Chinese with English abstract).
Su Chuntian, Huang Chenhui, Zou Shengzhang, Xie Daixing, Zhao Guangshuai, Tang Jiansheng, Luo Fei, Yang Yang. 2017. Enrichm entenvironment and sources of strontium of groundwater in Xintian county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(5):678-683(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201705010.htm
Sun Qifa, Tian Hui, Guo Xiaodong, Yu Huiming, Ma Shimin, Li Lijun. 2017. The discovery of silicic acid and strontium enrichment areas in groundwater of Changchun area, Jilin Province[J].Geology in China, 44(5):1031-1032(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Qifa, Tian Hui, Guo Xiaodong, Yu Huiming. 2019. Strontiumenriched areas discovered in Lianhuashan, Changchun[J].Geology in China, 46(2):430-431(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-LVKJ201918014.htm
Wang Yugong, Chen Yueyuan, Wang Jianbo. 2009. Development of natural mineral water in Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Geology, 18 (1):60-65(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200901015.htm
Wang Zengyin, Liu Juan, Wang Tao, Wang Yusong, Hu Jinwu. 2003.Application advances of strontium geochemistry in hydrogeology research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 22(4):91-95 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298618782_Application_advances_of_strontium_geochemistry_in_hydrogeology_research
Wei Rongdao, Yao Baogui. 2005. Discussions of the Distrbution characteristics and genesis of the tertiary confined water and its strontium mineral waters in longquan of Yongdeng County, Gansu province[J].Acta Geologica Gansu, 14(1):86-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GSDZ200501017.htm
Wu Dongdong, Kang Weidong, Wang Wenxiang, An Yonghui, Shao Xinmin, Li Wenpeng. 2017. Study on Sr geochemistry characteristics of groundwater in Zhangye basin[J].Water Resources and Power, 35(4):41-45(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SDNY201704011.htm
Xu Peiyao, Ding Zhinong. 1997. Formation of potable natural mingeral spring water congtaining strontium[J].Site Investigation Science and Technology, 15(5):36-38(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCKX199705008.htm
Zhang Yanlin, Li Shengyong, Cui Xudong, Liu Xinbiao. 2005. The geological features analysis of karst in eastern foot of Liupan montain[J]. Acta Geologica Gansu, 14(1):71-75(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200501013.htm
Zhang Yanlin, Li Shengyong, Fu Donglin, Cui Xudong. 2006.Formation mechanism of karst groundwater Longdong basin, northwestern China[J]. Geology in China, 33(6):1393-1399(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281570773_Formation_mechanism_of_karst_groundwater_in_the_western_Longdong_basin_northwestern_China
丁宏伟, 张举.2005.河西走廊地下水水化学特征及其演化规律[J].干旱区研究, 22(1):24-28. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj200501005
樊有俊, 樊姝芳, 任河.2010.黑河流域水质锶含量丰富成因研究[J].大众科技, 12(10):132-133. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZJI201010067.htm
胡进武, 王增银, 周炼, 汪玉松.2004.岩溶水锶元素水文地球化学特征[J].中国岩溶, 23(1):37-42. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyr200401007
李文鹏, 郝爱兵.1999.中国西北干旱盆地地下水形成演化模式及其意义[J].水文地质工程地质, 26(4):28-32. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3581330
刘庆宣, 王贵玲, 张发旺.2004.矿泉水中微量元素锶富集的地球化学环境[J].水文地质工程地质, 31(6):19-23. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=11313528
刘心彪, 张彦林, 王延江, 周斌.2007.陇东盆地地下水水化学特征分析[J].化工矿产地质, 29(4):237-241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HGKC200704009.htm
刘心彪, 张彦林, 王延江, 周斌.2009.陇东盆地白垩系地下水运移研究[J].干旱区研究, 26(2):176-180. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj200902004
苏春田, 张发旺, 夏日元, 姚昕, 邹胜章, 罗飞, 赵光帅, 杨杨, 巴俊杰, 李小盼.2017.湖南新田发现大型富锶矿泉水及机理研究[J].中国地质, 44(5):1029-1030. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170515&flag=1
苏春田, 黄晨晖, 邹胜章, 谢代兴, 赵光帅, 唐建, 罗飞, 杨杨.2017.新田县地下水锶富集环境及来源分析[J].中国岩溶, 36(5):678-683. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95841X/201705/674200994.html
孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 于慧明, 马诗敏, 李丽君.2017.吉林长春地区地下水中发现偏硅酸和锶富集区[J].中国地质, 44(5):1031-1032. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170516&flag=1
孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 于慧明.2019.长春莲花山发现锶富集区[J].中国地质, 46(2):430-431. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190219&flag=1
王玉功, 陈月源, 王建波.2009.甘肃省天然矿泉水开发利用现状分析与可持续发展[J].甘肃地质, 18 (1):60-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSDZ200901015.htm
王增银, 刘娟, 王涛, 汪玉松, 胡进武.2003.锶元素地球化学在水文地质研究中的应用进展[J].地质科技情报, 22(4):91-95. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200304017
魏荣道, 姚宝贵.2005.甘肃永登龙泉第三系锶型承压矿泉水分布特征与成因探讨[J].甘肃地质学报, 14(1):86-89. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96503A/200501/15889903.html
武冬冬, 康卫东, 王文祥, 安永会, 邵新民, 李文鹏.2017.张掖盆地地下水锶元素地球化学特征研究[J].水电能源科学, 35(4):41-44. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95255X/20174/671759982.html
许佩瑶, 丁志农.1997.含锶饮用天然矿泉水的形成[J].勘察科学技术, 15(5):36-38. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2868176
张彦林, 李生永, 崔旭东, 刘心彪.2005.六盘山东麓地区岩溶地质特征分析[J].甘肃地质学报, 14(1):71-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-gsdz200501013.htm
张彦林, 李生永, 付东林, 崔旭东.2006.陇东盆地西部岩溶地下水形成机制研究[J].中国地质, 33(6):1393-1399. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060624&flag=1
-




 下载:
下载:








