Characteristics and origin of the Denggeng and Mabu hot spring in Lushui County, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
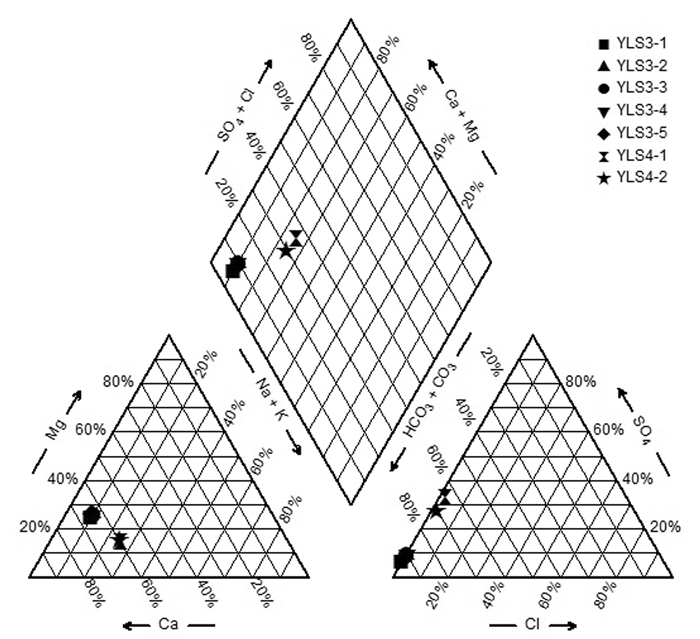
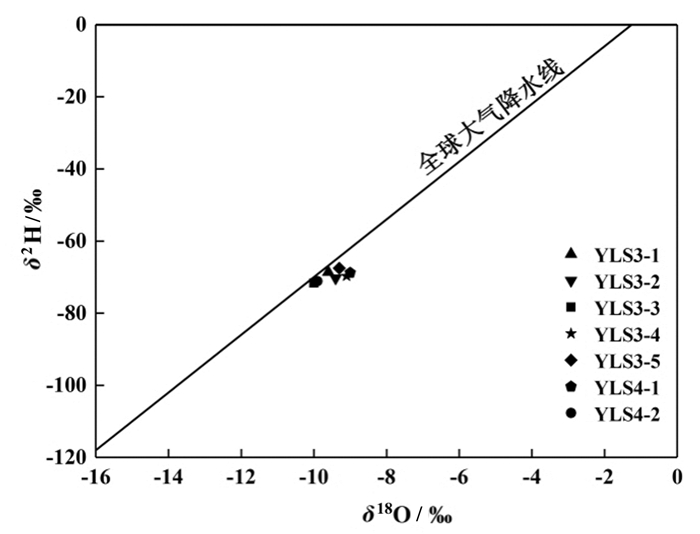
登埂温泉与玛布温泉位于云南泸水市,出露于怒江深切峡谷西岸。研究区分布的主要地层为第四系(Q42)砂土、砾土,石炭系上统卧牛寺组(C3w)玄武岩和三叠系河湾街组下段(T2h1)灰岩。温泉水温为48.9~69.6℃,矿化度为0.493~0.782 g/L,水化学类型分别为HCO3·Ca-Mg型和HCO3·Ca-Na型,为中低温、弱酸性温泉。热水中F-含量为0.78~2.13 mg/L,H2SO3为41.0~70.2 mg/L,含有锂、锶、铷、铯、钡等微量元素。氢氧稳定同位素组成表明研究区温泉补给来源为大气降水,用同位素方法估算温泉的补给区高程为1260~1435 m,补给区温度为6.18~9.02℃,计算的热储温度为100~127.5℃。研究区温泉Ca2+与HCO3-含量较高,占阴、阳离子的毫克当量浓度百分比分别达到60%、82%以上,水中方解石、文石矿物都处于饱和状态,水中CO2含量较高且pCO2远高于大气中pCO2,具有有利于CaCO3沉积的水化学和水动力条件,导致登埂温泉YLS3-1、YLS3-3及YLS3-4和玛布温泉YLS4-1的沉积钙华。登埂温泉与玛布温泉是地下水在怒江西部山区补给区获得大气降水入渗补给,在经历深循环过程中获得深部热流加热后上升在怒江河谷西岸流出地面形成的温泉,是渗入深循环型上升的的中低温温泉。热水在上升过程中与浅部冷水相遇,冷水混入比例为60%~73%,热水循环深度为2375.2~3161.7 m。
Abstract:Located in the Lushui County of Yunnan Province,the Denggeng hot spring and the Mabu hot spring emerge on the western bank of the Nujiang River valley. Sand of the Quaternary (Q42),basalt of the Upper Carboniferous Woniusi Group (C3w) and limestone of the Lower Formation of Triassic Hewan Group (T2h1) underlie the study area. The temperature of hot springs range from 48.9 to 69.6℃,and TDS from 0.493 to 0.782 g/L. The hydrochemical types of hot water are of HCO3·Ca-Mg type and HCO3·Ca-Na type. The hot springs are of low to moderate temperature and weak acid. The F- concentrations of the hot springs range from 0.78 to 2.13 mg/L,and the H2SiO3 concentrations from 41.0 to 70.2 mg/L. Li,Sr,Rb,Cs and Ba are relatively abundant in the hot water. The values of δ2H and δ18O of the spring water indicate that the hot springs in the study area are meteoric in origin. The elevation of the hot spring's recharge area is estimated to be from 1260 to 1435 m,the temperature of the recharge area varies in the range of 6.18-9.02℃,and the temperature of the geothermal reservoirs varies in the range of 100 -127.5℃. The content of Ca2+ and HCO3- in hot water is rich,and the percentages of milliequivalent concentrations of anions and cations are high,accounting for more than 60% and 82% respectively. Calcite and aragonite in the hot water are in the saturated state,the content of CO2 in water is high and the pCO2 in the hot water is much higher than atmospheric pCO2. The hydrochemical and hydrodynamic conditions are favorable to CaCO3 deposition. Travertines are precipitating near YLS3-1,YLS3-3 and YLS3-4 of the Denggeng hot spring and YLS4-1 of the Mabu hot spring. Thermal groundwater rises up to the land surface on the western bank of the Nujiang River valley after groundwater receives recharge from infiltration of precipitation in the recharge areas of the mountainous areas to the west of the Nujiang River,undergoes deep circulation and obtains heat from heat flow. The hot springs are of the deep infiltration-cycle type and are of low to moderate temperature. The hot water mixes with the shallow cold water when it rises to the land surface. The proportion of mixing cold water is about 60%-73%,and the circulation depth of the hot water ranges from 2375.2 to 3161.7 m.
-
Key words:
- hot spring /
- hydrochemistry /
- isotope /
- travertine /
- genesis /
- hydrogeological survey engineering /
- Lushui /
- Yunnan
-

-
表 1 温泉水样的水化学测试数据(mg/L)
Table 1. Chemical analyses of the hot water samples (mg/L)

表 2 研究区温泉的补给高程和补给区温度
Table 2. Estimated recharge altitude and temperature of the recharge area of the hot springs in the study area

表 3 研究区温泉初始参数
Table 3. Initial values of parameters of the hot spring in the study area
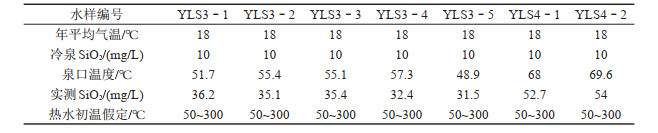
表 4 研究区温泉的冷热水混合比例及对应热储温度
Table 4. Mixing ratio of hot and cold water and temperature of the geothermal reservoirs of the hot springs in the study area
表 5 研究区地下热水循环深度
Table 5. Estimated circulation depth of the thermal groundwater in the study area
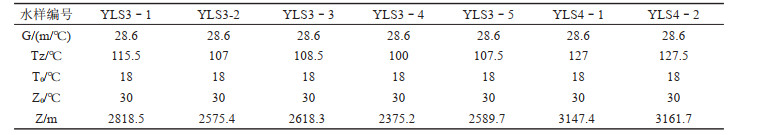
表 6 研究区温泉矿物饱和指数
Table 6. Mineral saturation index of the hot springs in the study area

-
Acikel S, Ekmekci M.2016.Hydrochemical characterization of Pamukkale travertines, Denizli, Turkey, for remediative measures[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(22):1456. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6258-1
Cheng Xing. 1994. Discussion on thin-water effect[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 13(3):207-213(in Chinese with English abstract).
Craig H. 1961. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science, 133:1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Craig H. 1961. Standard for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural water[J]. Science, 133:1833-1834. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3467.1833
Dai Yanan, Liu Zaihua. 2003. Hydrochemical features and carbon isotopes in a calcite-precipitating river in Xiaoqikong, Guizhou[J]. Tropical Geography, 23(4):324-328(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dreybrodt W, Buhmann D. 1991. A mass transfer model for dissolution and precipitation of calcite from solutions in turbulent motion[J]. Chemical Geology, 90(1/2):107-122. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419190037R
Dilsiz C. 2006. Conceptual hydrodynamic model of the Pamukkale hydrothermal field, southwestern Turkey, based on hydrochemical and isotopic data[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 14(4):562-572. doi: 10.1007/s10040-005-0001-4
Fouke B W, Farmer J D, Des Marais D J, Lisa Pratt, Neil C Sturchio, Peter C Burns, Mykell K Discipulo. 2000. Depositional facies and aqueous-solid geochemistry of travertine-depositing hot springs(Angel Terrace, Mammoth hot springs, Yellowstone National Park, U.S.A.)[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 70(3):565-585. doi: 10.1306/2DC40929-0E47-11D7-8643000102C1865D
Fournieer R O. 1977. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics, 5(1/4):41-50. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375650577900074
Giggenbach W F. 1988. Geothermal solute equilibrium, derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12):2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
Guo Xiaojuan. 2011. Hydrochemical Control Factors of Travertine Precipitation and Simulation of Travertine Formation of the Wang 4 Well in Tianjin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Zhongjie, Wang Jinguo, Chen Zhou, Shi Jiahui, Zhang Wenzhang. 2015. Discussion on the formation mechanism of Wenshui Longtan hot spring in Xishan, Heqing, Yunnan Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 43(5):43-48(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201505010.htm
Guo Yun, Zhi Chongyuan, Zhao Yuzhong, Ding Lei. 2007. Biological functions of the travertine sedimentation by diatoms and significance[J]. Shanghai Geology, 28(1):21-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_shanghai-land-resources_thesis/0201252216414.html
Gu Jirong, Fan Xiao, Fan Lixue. 2007. Analysis on influencing factors of travertine landscape in Huanglong[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 35(32):10319-10322(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY200732066.htm
Huo Dongxue, Zhou Xun, Liu Haisheng, Yu Mingxiao, Zhang Yuqi. 2019, Characteristics and Formation of the Wangjiazhuang Alkaline Hot Spring in Xiangyun County of Yunnan[J]. Geoscience, 33(6):680-690(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201903010.htm
He Jing, Li Bo. 2005. Major causes of landslides in Lushui County Nujiang autonomous perfecture[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Science and Technology), 30(4):1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KMLG200504000.htm
Kele S, Demény A, Siklósy Z, Tibor Németh, Magdolna B Kovács. 2008. Chemical and stable isotope composition of recent hotwater travertines and associated thermal waters, from Egerszalók, Hungary:Depositional facies and non-equilibrium fractionation[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 211(3):53-72. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-foreign_other_thesis/0204112229043.html
Li Tiesong. 2005. Sedimentary process and water chemistry property of contemporaneity sinter in Baishuitai[J]. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 26(4):350-353(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-igne200504002.htm
Liu Haisheng, Zhou Xun, Zhang Yuqi, Hai Kuo, Yu Mingxiao, Tan Mengru, Shang Ziqi. 2020. A brief review of the factors affecting deposition of travertines from hot springs[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 39(1):11-16.
Long Mi, Zhou Xun, Li Ting, Wang Xiaocui, Tang Liwei, Chen Ting, Guo Shuai. 2014. Characteristics and formation of the Songshan hot spring in Yanqing County of Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 28(5):1053-1060(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDDZ201405023.htm
Liu Chengzhi. 1966. The distribution of hot springs in Yunnan and their relationship with structural geology[J]. Geological Review, 24(3):211-220(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zaihua, Yuan Daoxian, He Shiyi, Cao Jianhua, You Shengyi. 2003.Origin and forming mechanisms of travertine at Huanglong Ravine of Sichuan[J]. Geochemica, 32(1):1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/qk/92960X/200301/7634284.html
Liu Zaihua, Zhang Meiliang, You Shengyi, Li Qiang, Sun Hailong, Wang Jinlaing, Wu Kongyun. 2004. Spatial and diurnal variations of geochemical indicators in a calcite-precipitating stream-Case study of Baishuitai, Yunnan[J]. Geochimica, 33(3):269-278(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX200403005.htm
Liu Yaping. 2009. A Preliminary of Analysis of the Formation of the Jifei Thermal Spring and Travertine, Yunan, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing)(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Juan, Zhou Xun, Fang Bin, Yang Yanxiong. 2007. Formation of hot springs at Wenquanpu, Qinhuangdao City, Hebei, China, and suggestions of their exploitation and utilization[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(3):344-349(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289638848_Formation_of_hot_springs_at_Wenquanpu_Qinhuangdao_City_Hebei_China_and_suggestions_of_their_exploitation_and_utilization
Mohammadi Z, Bagheri R, Jahanshahi R. 2010. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of Changal thermal springs, Zagros region, Iran[J]. Geothermics, 39(3):242-249. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.06.007
Pentecost A. 1994, The quaternary travertine deposits of Europe and Asia Minor[J]. Quaternary Scinence Reviews, 14:1005-1028. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0277379195001018
Pedley M, Andrews J, Ordonez S, Maria Angela Garcia del Cura, JuanAntonio Gonzales Martin, David Taylor. 1996. Does climate control the morphological fabric of freshwater carbonates? A comparative study of Holocene barrage tufas from Spain and Britain[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 121(3/4):239-257. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0031018295000801
Pentecost A, Zhang Z H. 2000. New and noteworthy list of bryophytes from active travertine sites of Guizhou and Sichuan, S.W. China[J]. Journal of Bryology, 22(1):66-68. doi: 10.1179/jbr.2000.22.1.66
Primc-Habdija B, Habdija I, An P M. 2001. Tufa deposition and periphyton overgrowth as factors affecting the ciliate community on travertine barriers in different current velocity conditions[J]. Hydrobiologia, 457(1/3):87-96. doi: 10.1023/A:1012265206470
Qu Lili, Xu Shiguang, Yang Xiumei, Xi Chuanyuan. 2011. Chemistry characteristics and formation analysis of hot spring on Yuejinggiao of Lu River[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 11(20):4723-4729(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201120014.htm
Tan Mengru, Zhou Xun, Zhang Yuqi.2019. Hydrochemical and isotopic and formation of the Menggajie hot spring Menghai County in Yunnan[J]. Science, 46(3):170-181(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201903010.htm
Tan Mengru. 2018. A Study of the Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characteristics and Geneses of Some of the Hot Springs in the Xishuangbanna Arae of Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of geosciences(Beijing)(in Chinese with English abstract).
Veysey J, Fouke B W, Kandianis M T, Thomas J Schickel, Roy W Johnson, Nigel Goldenfeld. 2008. Reconstruction of water temperature, pH, and flux of ancient hot springs from travertine depositional facies[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 78(1-2):69-76. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2008JSedR..78...69V
Wang Mengmeng. 2017. Characteristics of Some Hot Springs and Salt Springs and Formation of Travertines in Northwestern Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing)(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Ying, Zhou Xun, Yu Yuan, Liu Chunhui, Zhou Haiyan. 2007.Application of geothermometers to calculation of temperature of geothermal reservoirs[J]. Geoscience, 21(4):605-612(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200704003.htm
Wang Jieqing, Zhou Xun, Li Xiaolu, Wang Mengmeng, Shen Ye, Fang Bin. 2017. Hydrochemistry and formation of the Yangchimi hot spring in the lanping Basin of Yunnan[J]. Geoscience, 31(4):174-183(in Chinese with English abstract).
White Paul A, Hunt Trevor M. 2005. Simple modeling of the effects of exploitation on hot springs, Geyser Valley, Wairakei, New Zealand[J]. Geothermics, 34(2):187-207. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140670106801931
Wang Jiyang, Xiong Liangping, Pang Zhonghe. 1993. Low Medium Temperature Geothermal System of Convective Type[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 55-56(in Chinese).
Yu Jinsheng, Zhang Hongbin, Yu Fuji, Liu Deping.1984. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic compositions of meteoric waters in the eastern part of Xizang[J]. Geochemistry, 3(2):93-101.
Yu Lan. 2007. A Study of the Occurrence and Origin of Fluoride in Thermal Groundwater in Some Areas of China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Yanyan. 2006. A Study of the Formation and Evolution of the Wenluo Hot Spring and Precipitation Mechanism for the Nearby Tufa in Bobai, Guangxi[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Yulong. 2018. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, (5):57-58(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Yongtin, Li Xia, Guo Shuan. 2008. Geo-chemical characteristic and reasoning analysis of hot spring water in Longling area in Yunnan Province[J]. Guangdong Trace Elements Science, 15(2):39-46(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS200802009.htm
Zhang Dian. 1983. Conditions of groundwater movement for calcium carbonate deposition in cave system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2(1):33-41(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198301004.htm
Zheng Yuhui. 2015. Characteristics of the Tianshengqiao and Xiagei Hot Springs in Shangrila County of Yunan and Analysis of the Formation of the Travertine[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Xun, Li Juan, Zhou Haiyan, Fang Bin, Yu LanLi, Shi jun. 2008.Increase in thermal groundwater due to a flowing well near the Songshan hot spring in Beijing, China[J]. Environmental Geology, 53:1405-1411. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0749-z
Zhuo Chuanyuan.2009. An Analysis of the Origin Mechanism of Hot Spring on Yuejinqiao of Lu River and a Study on the Alternative Scheme of Its Restoration[D]. Beijing: Kunming University of Science and Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yuqi, Zhou Xun, Liu Haisheng, Tan Mengru, Hai Kuo, Yu Mingxiao, Huo Dongxue. 2018. Hydrogeological characteristics of the hot springs and salty springs occurring in the redbeds in the Lanping-Simao Basin of Yunnan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 45(3):40-48(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201803005.htm
Zou Pengfei, Qiu Yang, Wang Caihui. 2015. Analyses of the genesis of Tangshan Hot Spring Area in Nanjing[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 21(1):155-162(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201501016.htm
戴亚南, 刘再华. 2003.响水河钙华形成的水化学特征与碳稳定同位素研究[J].热带地理, 23(4):324-328. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RDDD200304006.htm
屈丽丽, 徐世光, 杨秀梅, 禚传源. 2011.怒江跃进桥温泉水化学特征及成因分析[J].科学技术与工程, 11(20):4723-4729.
郭忠杰, 王锦国, 陈舟, 施佳会, 张文章. 2015.云南省鹤庆西山温水龙潭温泉成因机制探讨[J], 工程勘察, 43(5):43-48.
郭云, 支崇远, 赵宇中, 丁蕾. 2007.硅藻对地表石灰华沉积的生物作用及其意义[J].上海地质, 28(1):21-24.
郭小娟. 2011.钙华沉积的水化学控制因素分析及天津王四井钙华形成的模拟研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
贺敬, 李波. 2005.怒江州泸水县滑坡的主要诱发因素分析[J].昆明理工大学学报(理工版), 30(4):1-4.
霍冬雪, 周训, 刘海生, 余鸣潇, 张彧齐. 2019.云南祥云县王家庄碱性温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J].现代地质, 33(6):680-690.
刘再华, 张美良, 游省易, 李强, 孙海龙, 汪进良, 吴孔运. 2004.碳酸钙沉积溪流中地球化学指标的空间分布和日变化特征:以云南白水台为例[J].地球化学, 33(3):269-278.
刘再华, 袁道先, 何师意, 曹建华, 游省易, W Dreybrodt, U Svensson, K Yo. 2003.四川黄龙沟景区钙华的起源和形成机理研究[J].地球化学, 32(1):1-10.
李娟, 周训, 方斌, 杨燕雄. 2007.河北秦皇岛市温泉堡温泉的形成与开发利用建议[J].地质通报, 26(3):344-349.
刘亚平. 2009.云南省昌宁县鸡飞温泉成因及钙华形成浅析[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
李铁松. 2005.白水台钙华区水化学特征及泉华沉积过程研究[J].西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 26(4):350-353.
龙汨, 周训, 李婷, 王晓翠, 唐丽伟, 陈婷, 郭帅.2014.北京延庆县松山温泉的特征与成因[J].现代地质, 28(5):1053-1060.
刘海生, 周训, 张彧齐, 海阔, 余鸣潇, 谭梦如, 尚子琦. 2020.温泉钙华沉积的影响因素[J].中国岩溶, 39(1):11-16.
刘承志. 1966.云南温泉之分布规律及其与构造地质关系[J].地质评论, 24(3):211-220.
谭梦茹. 2018.云南西双版纳地区部分温泉水化学和同位素特征及成因研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
谭梦茹, 周训, 张彧齐. 2019.云南勐海县勐阿街温泉水化学和同位素特征及成因研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 46(3):170-181.
王洁青, 周训, 李晓露, 王蒙蒙, 沈晔, 方斌. 2017.云南兰坪盆地羊吃蜜温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J].现代地质, 31(4):174-183.
汪集暘, 熊亮萍, 庞忠和. 1993.中低温对流型地热系统[M].北京:科学出版社, 55-56.
王莹, 周训, 于湲, 柳春晖, 周海燕. 2007.应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J].现代地质, 21(4):605-612.
王蒙蒙. 2017.云南西北地区部分温泉和盐泉特征及成因分析[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
辜寄蓉, 范晓, 范立学. 2007.黄龙钙华景观影响因素分析[J].安徽农业科学, 35(32):10319-10322.
尹玉龙. 2018.中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J].科技与创新, (5):57-58.
于永亭, 李晓, 郭爽. 2008.云南省龙陵地区温泉水化学特征及其成因分析[J].广东微量元素科学, 15(2):39-46.
杨妍妍. 2006.广西博白温罗温泉形成演化与钙华沉积机制研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
虞岚. 2007.我国部分地下热水中氟的分布与成因探讨[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
郑玉慧. 2015.云南省香格里拉县天生桥温泉和下给温泉特征及钙华形成分析[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
程星. 1994.薄水效应初论[J].中国岩溶, 13(3):207-213.
章典. 1983.洞穴碳酸钙沉积的水运动条件[J].中国岩溶, 2(1):33-41.
邹鹏飞, 邱杨, 王彩会. 2015.南京汤山温泉区地热水成因模式分析[J].高校地质学报, 21(1):155-162.
张彧齐, 周训, 刘海生, 谭梦如, 海阔, 余鸣潇, 霍冬雪. 2018.云南兰坪-思茅盆地红层中温泉和盐泉的水文地质特征[J].水文地质工程地质, 45(3):40-48.
禚传源.2009.怒江跃进桥地区温泉成因机制分析与跃进桥温泉恢复替代方案研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学.
-




 下载:
下载: