The hydraulic connection between Jinci and Pingquan in Taiyuan' Shanxi and its contribution to the reflow of Jinci spring
-
摘要:
晋祠泉出露于山西太原西山悬瓮山下,由难老泉、圣母泉、善利泉组成。1954—1958年实测泉水平均流量为l.94 m3/s。与晋祠泉同处山前断裂带的平泉于1978年成为特大岩溶水自流井水源地,自流量最大达到1.56 m3/s。由于这些自流井的开采,使晋祠泉的流量急剧下降,1994年4月30日断流。研究山西太原晋祠泉—平泉水力联系对晋祠泉复流方案制定具有重要意义。本文以晋祠泉、平泉为研究对象,通过样品采集、水质监测,综合运用水化学(离子比例、硫同位素、氢氧同位素)方法。揭示晋祠泉—平泉水文地球化学特征和环境同位素特征,反映地下水流系统的特征、水力联系特征。得出1980—1992年,晋祠泉地下水水位的变化呈稳定下降趋势,主要原因是有太原化学工业公司、开化沟、淸徐县平泉村和梁泉村等水源地大量开采岩溶地下水,导致地下水水位下降。晋祠—平泉一带岩溶地下水氢氧同位素值较接近,说明这一带岩溶地下水补给来源与补给途径相近。水质监测分析得出晋祠泉与平泉各个离子变化趋势基本一致。说明晋祠与平泉存在紧密的水力联系,因此晋祠泉与平泉必然存在一个比较强的导水通道。可以通过在晋祠泉下游导水通道上帷幕灌浆,提高晋祠泉水水位,使晋祠泉出流。
Abstract:Jinci Spring,which is composed of Nanlao Spring,Shengmu Spring and Shanli Spring,is exposed at the foot of Xishan Mountain in Taiyuan. The average horizontal discharge of Jinci Spring was 1.94 m3/s from 1954 to 1958. Pingquan spring,located in the piedmont fault zone with Jinci spring,became the source of superlarge karst water self-flowing wells in 1978, with the maximum self-flowing rate reaching 1.56 m3/s. Because of the exploitation of these self-flowing wells,the flow of Jinci Spring dropped sharply and was cut off on April 30,1994. The study of the hydraulic connection between Jinci Spring and Pingquan Spring in Taiyuan,Shanxi Province,is of great significance for the formulation of Jinci Spring recharge plan. With Jinci spring and Pingquan spring as the research objects and through sample collection and water quality monitoring,hydrochemistry (ion ratio,sulfur isotope,hydrogen and oxygen isotope) methods were comprehensively applied. The result has revealed hydrogeochemical characteristics and environmental isotope characteristics of Jinci spring to Pingquan spring as well as the characteristics of groundwater flow system and hydraulic connection. From 1980 to 1992, the change of groundwater level in Jinci Spring showed a steady downward trend. The main reason was that a large number of karst groundwater was exploited in Taiyuan Chemical Industry Company,Kaihua Valley,Pingquan Village and Liangquan Village in Zhaoxu County,which resulted in the decline of groundwater level. The hydrogen and oxygen isotope values of karst groundwater in Jinci spring to Pingquan spring area were close to each other,indicating that the source of recharge and the way of recharge were quite similar. Water quality monitoring analysis shows that the change trend of each ion in Jinci spring and Pingquan spring is basically the same,suggesting that Jinci spring and Pingquan spring have close hydraulic connection,so Jinci spring and Pingquan spring must have a strong water channel. The water level of Jinci spring can be raised by curtain grouting on the downstream water channel of Jinci spring,so that Jinci spring can flow out.
-

-
表 1 取样点基本信息
Table 1. The information of sampling point

表 2 晋祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学类型
Table 2. Karst groundwater hydrochemical type of Jinci spring catchment

表 3 岩溶地下水中矿物饱和指数
Table 3. Mineral saturation index in karst groundwater
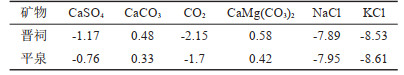
-
Cánovas C R, Olías M, Macias F, Torres E, San Miguel E G, Galván L, Ayora C, Nieto J M. 2016.Water acidification trends in a reservoir of the Iberian Pyrite Belt (SW Spain)[J].Science of The Total Environment, 541:400-411. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.070
Capaccioni B, Vaselli O, Tassi F, Santo A P, Huertas A D. 2011.Hydrogeochemistry of the thermal waters from the Sciacca Geothermal Field (Sicily, southern Italy)[J].Journal of Hydrology, 396(3):292-301. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169410007110
Fairchild I J, Tuckwell G W, Baker A, Tooth A F. 2006.Modelling of dripwater hydrology and hydrogeochemistry in a weakly karstified aquifer (Bath, UK):Implications for climate change studies[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 321 (1):213-231. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169405003884
Guo Xiaodong, Zhao Haiqing. 2014. Hydrochemical characteristics and correlation analysis of groundwater in Hunchun Basin[J]. Geology in China, 41(3):1010-1017(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/287536666_Hydrochemical_characteristics_and_correlation_analysis_of_groundwater_in_Hunchun_Basin
Han D M, Song X F, Currell M J, Yang J L, Xiao G Q. 2014. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 508:12-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.040
Han D, Kohfahl C, Song X, Xiao G, Yang J. 2011.Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 26(5):863-883. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.007
Jin Hua, Yang Cuolin, Zheng Xiuqing, Li Cijun.2005. Analysis of the Reduction in Flow from Jinci Springs[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, (4):488-490(in Chinese with English abstract).
Keul N, Langer G, Thoms S, de Nooijer L J, Reichart G J, Bijma J. 2017.Exploring foraminiferal Sr/Ca as a new carbonate system proxy[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 202:374-386. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.11.022
Li Xiangquan, Hou Xinwei, Zhou Zhichao, Liu Lingxia, Wang Zhenxing, Jiang Liangwen, Du Yuben, Deng Hongke. 2011.Isotopic characteristics of the main hot springs in southern Gaoligong Mountain[J]. Geology in China, 38(5):1347-1354(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Yongping, Zhang fawang, Shen haoyong, Zhao Chunhong, Wang Zhiheng, Hou Hongbing, Ren Jianhui, Guo Fangfang.2019.Recognition of the critical hydrogeological conditions of the Jinci Spring and Lancun Spring in Shanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 46(01):11-18, 34(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Wenbo, Gao Cunrong, Liu Bin, Chen Youjian. 2010. Hydrochemical constituents and correlation analysis of shallow groundwater in the Hetao Plain[J]. Geology in China, 37(3):816-823(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma R, Wang Y, Sun Z, Zheng C, Ma T, Prommer H. 2011.Geochemical evolution of groundwater in carbonate aquifers in Taiyuan, northern China[J].Applied Geochemistry, 26(5):884-897. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.008
Musgrove M, Stern L A, Banner J L. 2010. Springwater geochemistry at Honey Creek State Natural Area, central Texas:Implications for surface water and groundwater interaction in a karst aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 388 (1):144-156.
Pasvanoğlu S. 2013. Hydrogeochemistry of thermal and mineralized waters in the Diyadin (Ağri) area, Eastern Turkey[J].Applied Geochemistry, 38:70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.08.010
Petalas C, Lambrakis N. 2006.Simulation of intense salinization phenomena in coastal aquifers-the case of the coastal aquifers of Thrace[J].Journal of Hydrology, 324(1):51-64. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169405004762
Plummer L N, Busby J F, Lee R W, Hanshaw B B. 1990. Geochemical modeling of the Madison Aquifer in Parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota[J].Water Resources Research, 26(9):1981-2014. doi: 10.1029/WR026i009p01981
Pracný P, Faimon J, Všianský D, Přichystal A. 2019. Evolution of Mg/Ca and Sr/Ca ratios during the experimental dissolution of limestone[J].Chemical Geology, 523:107-120. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.05.040
Schiavo M A, Hauser S, Povinec P P. 2009.Stable isotopes of water as a tool to study groundwater-seawater interactions in coastal south-eastern Sicily[J].Journal of Hydrology, 364(1):40-49.
Shen Zhaoli, Wang Yanxin.2002.Review and Outlook of Water Rock Interaction Studies[J]. Earth Science, (2):127-133(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sim M S, Sessions A L, Orphan V J, Adkins J F. 2019.Precise determination of equilibrium sulfur isotope effects during volatilization and deprotonation of dissolved H2S[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 248:242-251. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.01.016
Smykatz-Kloss W, Kossl H, Hotzl H. 1990. The gypsum karst area of Foum Tatahouine, Southern Tunisia:Mineralogy and hydrogeochemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 84(1):206-207.
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang Chunlei, Zheng Xiuqing, Liang Yongping. 2020. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of karst groundwater in Longzici spring area[J]. Environmental Science, 41 (05):2087-2095(in Chinese with English abstract).
Temovski M, Futó I, Túri M, Palcsu L. 2018.Sulfur and oxygen isotopes in the gypsum deposits of the Provalata sulfuric acid cave(Macedonia)[J]. Geomorphology, 315:80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.05.010
Wang Yanxin, Ma Teng, Guo Haiqing. 2005. Groundwater and environmental change[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, (S1):14-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao Q, Jiang Y, Shen L, Yuan D. 2018.Origin of calcium sulfate-type water in the Triassic carbonate thermal water system in Chongqing, China:A chemical and isotopic reconnaissance[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 89:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.11.011
Yokota Y, Tanaka C, Kurosawa S, Yamaji A, Ohashi Y, Kamada K, Nikl M, Yoshikawa A. 2018. Effects of Ca/Sr ratio control on optical and scintillation properties of Eu-doped Li(Ca, Sr)AlF6 single crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 490:71-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2018.03.022
Yuan Daoxian. 1990. A review of karst geochemistry in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (05):41-42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan Jianfei, Deng Guoshi, Xu Fen, Tang Yeqi, Li Pengyue. 2016. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 43(4):1446-1456(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Haixiao, Shen Xiaoyu, Guo zhaobing, Guo Qingjun, Chen Shanli, Bai Yang, Wang Jinjin.2019, Investigations on sulfur isotopic compositions of day and night in atmospheric PM 2.5 in the Northern suburb of Nanjing City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32(3):440-446(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang J, Li T Y. 2019.Seasonal and interannual variations of hydrochemical characteristics and stable isotopic compositions of drip waters in Furong Cave, southwest China based on 12 years' monitoring[J].Journal of Hydrology, 572:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.052
Zhou J, Zhang Q, Kang F, Zhang Y, Yuan L, Wei D, Lin S. 2018.Using multi-isotopes (34S, 18O, 2H) to track local contamination of the groundwater from Hongshan-Zhaili abandoned coal mine, Zibo city, Shandong Province[J].International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 128:48-55.
郭晓东, 赵海卿. 2014.珲春盆地地下水水化学特征分析[J].中国地质, 41(3):1010-1017. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140326&flag=1
晋华, 杨锁林, 郑秀清, 李慈君. 2005.晋祠岩溶泉流量衰竭分析[J].太原理工大学学报, (4):488-490.
李向全, 侯新伟, 周志超, 刘玲霞, 王振兴, 蒋良文, 杜宇本, 邓宏科. 2011.高黎贡山南段主要热泉水化学同位素特征研究[J].中国地质, 38(5):1347-1354. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110521&flag=1
梁永平, 张发旺, 申豪勇, 唐春雷, 赵春红, 王志恒, 侯宏冰, 任建会, 郭芳芳. 2019.山西太原晋祠-兰村泉水复流的岩溶水文地质条件新认识[J].水文地质工程地质, 46(1):11-18, 34.
刘文波, 高存荣, 刘滨, 陈有鑑. 2010.河套平原浅层地下水水化学成分及其相关性分析[J].中国地质, 37(3):816-823. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100338&flag=1
沈照理, 王焰新. 2002.水-岩相互作用研究的回顾与展望[J].地球科学, (2):127-133.
唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平. 2020.龙子祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因[J].环境科学, 41(5):2087-2095.
袁道先.1990.中国岩溶地球化学研究的进展[J].水文地质工程地质, (5):41-42.
孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽.2018.哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J].中国地质, 45(6):1128-1141. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180604&flag=1
王焰新, 马腾, 郭清海, 马瑞. 2005.地下水与环境变化研究[J].地学前缘, (S1):14-21.
袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 唐业旗, 李鹏岳.2016.毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J].中国地质, 43(04):1446-1456. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160428&flag=1
张海潇, 沈潇雨, 郭照冰, 郭庆军, 陈善莉, 柏杨, 王瑾瑾. 2019.南京北郊地区昼夜大气PM (2.5)中硫同位素的组成及来源[J].环境科学研究, 32(3):440-446.
-




 下载:
下载:




