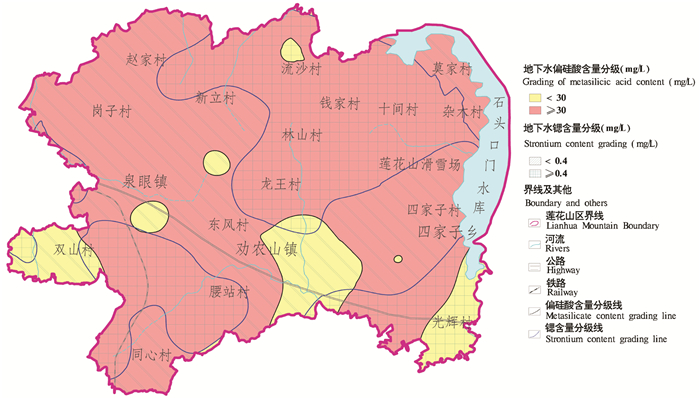
Formation mechanism of strontium and metasilicic acid groundwater in the Lianhuashan area, Changchun, Jilin Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 长春莲花山地区地下水中富含Sr和偏硅酸,查明地下水中锶及偏硅酸的形成机理具有重要意义。
研究方法 通过Piper三线图法及对研究区矿泉水形成的物质基础、水动力条件、水化学条件的深入研究。
研究结果 研究发现长春莲花山地区发育的松散岩、碎屑岩、火成岩是该地区地下水中锶及偏硅酸的富集的物质基础;大气降水与地表水入渗补给等为地下水长期与周围岩石(矿物)发生水解和溶滤作用、为地下水最终富锶及偏硅酸创造了条件。
结论 区域地层中存在16.3~80 m巨厚的基岩风化带,使富锶及富含偏硅酸的地下水呈面状分布,部分区域两种地下水同时存在,这一点不同与以往在基岩构造带上发现的线状分布的矿泉水源;前人在此区域上没有发现富含锶及偏硅酸的矿泉水,这一发现为地方经济发展提供了新的空间。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
Objective The groundwater in Lianhuashan area of Changchun is rich in strontium and metasilicic acid. It is important to understand the formation mechanism of strontium and metasilicic acid in groundwater.
Methods The material basis, hydrodynamic conditions and hydrochemical conditions of the formation of mineral water in the study area were studied in depth by using the Piper three-line diagram method.
Results It is found that the loose rock, clastic rock and igneous rock developed in Lianhuashan area of Changchun are the material basis for the enrichment of strontium and metasilicic acid in groundwater in this area; Atmospheric precipitation and infiltration recharge of surface water create conditions for the long-term hydrolysis and leaching of groundwater with surrounding rocks (minerals), and for the final enrichment of strontium and metasilicic acid in groundwater.
Conclusions There is a 16.3- 80 m thick bedrock weathering zone in the regional strata, which makes the groundwater rich in strontium and metasilicic acid distributed in a plane shape. In some areas, two kinds of groundwater exist at the same time, which is different from the linear distribution of mineral water resources found in the bedrock structural belt; No one in history has found mineral water rich in strontium and metasilicic acid in this area. This discovery provides imagination space for local economic development.
-

-
表 1 检测方法
Table 1. Test methods
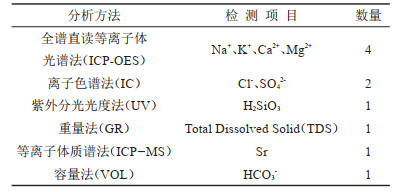
表 2 长春莲花山地区地下水化学分析结果(mg/L)
Table 2. Chemical analysis results(mg/L) of groundwater in Lianhuashan area, Changchun

表 3 舒卡列夫地下水类型分类统计
Table 3. Shukalev groundwater classification summary table
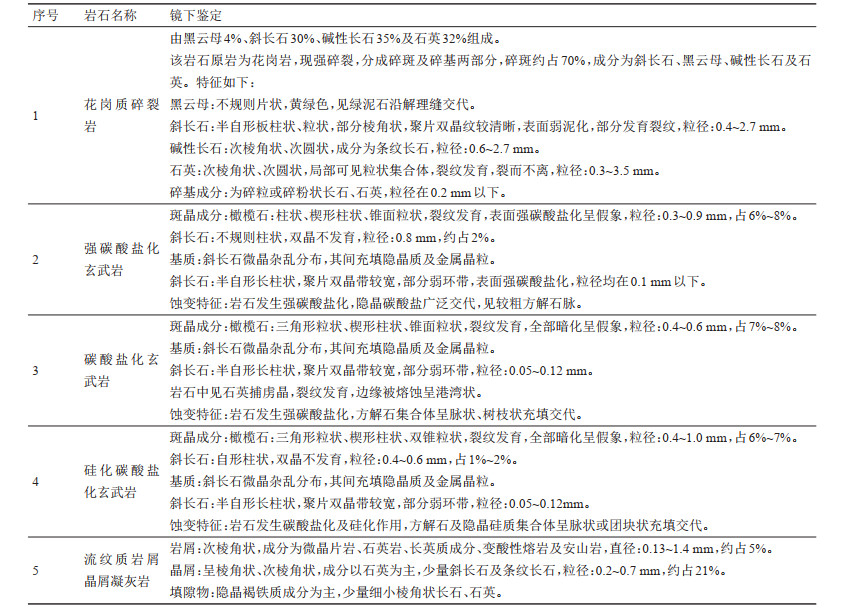
表 4 莲花山地区含水层代表性岩石鉴定结果
Table 4. Identification results of representative rocks of aquifer in Lianhuashan area
-
Audigane P, Gaus I, Czernichowski-Lauriol I, Karsten P, Tianfu X. 2007. Two-dimensional reactive transport modeling of CO2 injection in a saline aquifer at the Sleipner site, North Sea[J]. American Journal of Science, 307(7): 974-1008. doi: 10.2475/07.2007.02
Borgia A, Cattaneo L, Marconi D, Delcroix C, Rossi E, Clemente G, Amoroso C, Lo Re F, Tozzato E. 2011. Using a MODFLOW grid, generated with GMS, to solve a transport problem with TOUGH2 in complex geological environments: The intertidal deposits of the Venetian Lagoon[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 37(6): 783-790.
Dobson P, Salah S, Spycher N, Sonnenthal, E. 2004. Simulation of water-rock interaction in the Yellowstone geothermal system using TOUGHREACT[J]. Geothermics, 33(4): 493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2003.10.002
Guo Xiaodong, Zhao Haiqing. 2014. Hydrochemical characteristics and correlation analysis of groundwater in Hunchun Basin[J]. Geology in China, 41(3): 1010-1017(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hidalgo M C, Cruz-Sanjulián J. 2001. Groundwater composition, hydrochemical evolution and mass transfer in a regional detrital aquifer (Baza basin, southern Spain) [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 16(7): 745-758.
Indraratna B, Pathirage P U, Rowe R K, Banasiak L. 2014. Coupled hydro-geochemical modelling of a permeable reactive barrier for treating acidic groundwater[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 55: 429-439. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.09.025
Jin Yang, Jiang Yuehua, Dong Xianzhe, Yang Guoqiang, Liu Hongying, Lei Changzheng, Zhou Quanping, Zhang Hong, Mei Shijia, Yang Hui, Lü Jinsong, Li Yun. 2022. Chemical characteristics and eco-environmental effect of groundwater in Ningbo Plain, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1527-1542(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kenoyer G J, Bowser C J. 1992a. Groundwater chemical evolution in a sandy silicate aquifer in northern Wisconsin: 1. Patterns and rates of change[J]. Water Resources Research, 28(2): 579-589. doi: 10.1029/91WR02302
Kenoyer G J, Bowser C J. 1992b. Groundwater chemical evolution in a sandy silicate aquifer in northern Wisconsin: 2. Reaction modeling[J]. Water Resources Research, 28(2): 591-600. doi: 10.1029/91WR02303
Li Zhanmin. 1993. Formation of metasilicic acid components in drinking mineral water in China[J]. Survey Science and Technology, 11(1): 41-43(in Chinese).
Li Zhuang, Su Jingwen, Dong Changchun, Ye Yonghong, Yang Yang. 2022, Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution mechanisms of the groundwater in Dangtu area, Ma'anshan City, Anhui Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1509-1526(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Qingxuan, Wang Guiling, Zhang Fawang. 2004. Geochemical environment of strontium enrichment in mineral water[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 31(6): 19-23(in Chinese with English abstract).
Matthew M U, Sharp Jr J M. 2001. Tracing regional flow paths to major springs in Trans-Pecos Texas using geochemical data and geochemical models[J]. Chemical Geology, 179(1): 53-72.
Parisia S, Paternosterb M, Perrc F, Mongelli G. 2011. Source and mobility of minor and trace elements in a volcanic aquifer system: Mt. Vulture (southern Italy) [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 110(3): 233-244. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.06.010
Plummer L N, Prestenrnon E C, Parkhurst D L. 1991. An Interactive Code (NETPATH) for Modeling NET Geochemical Reactions along a Flow Path[R]. U.S.G.S. Water Resources Investigations.
Su Chuntian, Zhang Fawang, Xia Riyuan, Yao Xin, Zou Shengzhang, Luo Fei, Zhao Guangshuai, Yang Yang, Ba Junjie, Li Xiaopan. 2017. A study of the water-rock interaction of large rich Sr mineral spring in Xintian, Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 1029-1030(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Qifa, Guo Xiaodong, Tian Hui, Yu Huiming. 2019a. Comprehensive geological environment survey of Changji economic circle[R]. Shenyang: Shenyang Geological Survey Center, China Geological Survey(in Chinese).
Sun Qifa, Tian Hui, Guo Xiaodong, Yu Huiming, Ma Shimin, Li Lijun. 2017. The discovery of silicic acid and strontium enrichment areas in groundwater of Changchun area, Jilin Province[J]. Geology in China, 44(5): 1031-1032(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Qifa, Tian Hui, Guo Xiaodong, Yu Huiming. 2019b. Strontium-enriched areas discovered in Lianhuashan, Changchun[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 430-431(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Qifa, Yang Ke, Sun Zhuo'an, Jia Lin'gang, Tian Hui, Guo Xiaodong, Li Xuguang, Zhu Wei. 2022. Characteristics of groundwater quality in Changchun New Area and its evaluation on ecological health[J]. Geology in China, 49(3): 834-848(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Hongwei, Gong Qinghong, Zhao Xiangdong. 2004. Main groundwater storage structure in plain area of Jilin Province [J]. Jilin Geology, 23 (4): 64-68(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wicks C M, Herman J S. 1994. The effect of a confining unit on the geochemical evolution of ground water in the Upper Floridan aquifer system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 153(1): 139-155. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035316806810_55a0.html
Xu T, Pruess K. 2001. Modeling multiphase non-isothermal fluid flow and reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated fractured rocks: 1. Methodology[J]. American Journal of Science, 301(1): 16-33. doi: 10.2475/ajs.301.1.16
Xu T, Sonnenthal E, Spycher N, Pruess G, BrimhallJohn A. 2001. Modeling multiphase non-isothermal fluid flow and reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated fractured rocks: 2. Applications to supergene copper enrichment and hydrothermal flows[J]. American Journal of Science, 301(1): 34-59. doi: 10.2475/ajs.301.1.34
Xu T, Sonnenthal E, Spycher N, Pruess K. 2004. TOUGHREACT User's Guide: A Simulation Program for Non-isothermal Multiphase Reactive Geochemical Transport in Variably Saturated Geological Media[R]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Yan Jinxu. 1993. Analysis on the distribution and genesis of metasilicic acid type mineral water in Northern Zhejiang[J]. China Coalfield Geology, 5 (4): 47-57(in Chinese).
Yan Ruhui, Sun Tingfang, He Ping. 1996. Basic characteristics and formation rules of drinking natural mineral water resources in Anhui Province[J]. Anhui Geology, 6(3): 63-76(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Zhiwei, Wei Fucai. 2003. Summary on the genesis of CO2 in groundwater[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 22(2): 118-123(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Yanlin, Shao Changsheng, Jing Jing, Chen Lide, Wang Shichang, Lu Tao, Zhang Ao, Wang Cen, Liu Guangning. 2019. Exploration of mineral water resources in city clusters along the middle reaches of the Yangtze and discoveries-A case study of the dataset of the hydrogeological survey in the 1: 50000 Tingsiqiao Map-sheet, Xianning City[J]. Geology in China, 46(S2): 74-82(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Guosong. 2017. Occurrence characteristics and formation mechanism of drinking natural mineral water in Linqian mining area, Fujian Province[J]. Low Carbon World, 7(24): 78-79(in Chinese).
Zhao Li. 2005. Chemical characteristics and genetic analysis of natural mineral water in Eastern Yanshan[J]. Water Science and Engineering Technology, (1): 24-26(in Chinese).
郭晓东, 赵海卿. 2014. 珲春盆地地下水水化学特征分析[J]. 中国地质, 41(3): 1010-1017. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20140326?st=search
金阳, 姜月华, 董贤哲, 杨国强, 刘红樱, 雷长征, 周权平, 张鸿, 梅世嘉, 杨辉, 吕劲松, 李云. 2022. 浙江宁波平原地下水水化学特征及其生态环境效应[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1527-1542. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220511?st=search
李占敏. 1993. 我国饮用矿泉水中偏硅酸组分的形成[J]. 勘察科学技术, 11(1): 41-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCKX199301010.htm
李状, 苏晶文, 董长春, 叶永红, 杨洋. 2022. 安徽马鞍山市当涂地区地下水水化学特征及演化机制[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1509-1526. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220510?st=search
刘庆宣, 王贵玲, 张发旺. 2004. 矿泉水中微量元素锶富集的地球化学环境[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 31(6): 19-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200406004.htm
苏春田, 张发旺, 夏日元, 姚昕, 邹胜章, 罗飞, 赵光帅, 杨杨, 巴俊杰, 李小盼. 2017. 湖南新田发现大型富锶矿泉水及机理研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 1029-1030. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20170515?st=search
孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽. 2018. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1128-1141. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20180604?st=search
孙岐发, 郭晓东, 田辉, 于慧明. 2019a. 长吉经济圈地质环境综合调查[R]. 中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心.
孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 于慧明. 2019b. 长春莲花山发现锶富集区[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 430-431. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20190219?st=search
孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 于慧明, 马诗敏, 李丽君. 2017. 吉林长春地区地下水中发现偏硅酸和锶富集区[J]. 中国地质, 44(5): 1031-1032. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20170516?st=search
孙岐发, 杨柯, 孙茁桉, 贾林刚, 田辉, 郭晓东, 李旭光, 朱巍. 2022. 长春新区地下水水质特征及其对生态健康的评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(3): 834-848. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220311?st=search
王宏伟, 龚庆红, 赵向东. 2004. 吉林省平原区地下水主要蓄水构造[J]. 吉林地质, 23(4): 64-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ200404011.htm
严金叙. 1993. 浙北地区偏硅酸型矿泉水分布与成因分析[J]. 中国煤田地质, 5(4): 47-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT199304009.htm
阎如璲, 孙庭芳, 贺平. 1996. 安徽省饮用天然矿泉水资源的基本特征与形成规律[J]. 安徽地质, 6(3): 63-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHDZ603.008.htm
闫志为, 韦复才. 2003. 地下水中CO2的成因综述[J]. 中国岩溶, 22(2): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200302007.htm
杨艳林, 邵长生, 靖晶, 陈立德, 王世昌, 路韬, 张傲, 王岑, 刘广宁. 2019. 长江中游城市群矿泉水资源勘查与发现——以咸宁市汀泗桥幅1∶50 000水文地质调查数据集为例[J]. 中国地质, 46(S2): 74-82. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/2019S208?st=search
余国松. 2017. 福建林前矿区饮用天然矿泉水赋存特征与形成机理[J]. 低碳世界, 7(24): 78-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DTSJ201724050.htm
赵力. 2005. 燕山东部天然矿泉水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 水科学与工程技术, (1): 24-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBSD200501011.htm
-




 下载:
下载: