Source teacing and He-Ar-S isotopic compositions of ore-forming fluid in the Zhengguang large gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 黑龙江争光金矿床位于兴安地块东缘嫩江—黑河北东向断裂带西北侧的奥陶纪多宝山岛弧带上。本文通过对主成矿期的矿石样品研究,探讨了成矿流体的来源。
研究方法 选择9件主成矿期的黄铁矿和方铅矿进行了系统研究,测定了He、Ar和S同位素组成。
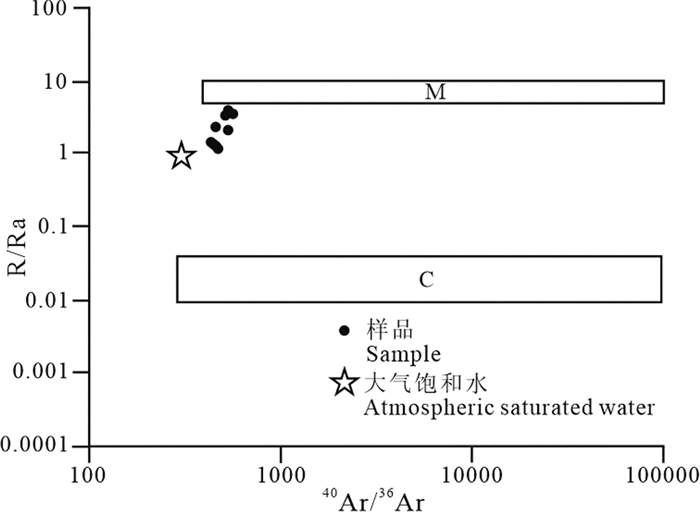
研究结果 其含金石英脉中黄铁矿和方铅矿的流体包裹体3He/4He=1.95×10-6~5.03×10-6,40Ar/36Ar=349.1~453.9。幔源He占13.17%~44.67%,平均27.58%,显示了成矿流体以大气降水为主,但同时有地幔流体成分,表明金矿床成矿作用与地幔活动有着密切的关系。矿物δ34S=-1.2‰~-3.9‰,平均-2.33‰,可能来自深源地幔流体,但其中有地壳流体的加入。
结论 洋壳向兴安地块俯冲,俯冲流体交代地幔楔发生部分熔融,流体上升至地表浅部与下渗的大气降水混合形成成矿流体,由于温度和压力的下降和流体沸腾作用导致成矿流体物理化学条件的改变,从而使成矿物质沉淀。
-
关键词:
- He-Ar-S同位素 /
- 壳幔相互作用 /
- 争光大型金矿 /
- 地质调查工程 /
- 大兴安岭
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
Objective Zhengguang gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province is located in the Ordovician Duobaoshan island arc belt on the northwest side of Nenjiang—Heihe NE trending fault zone in the eastern margin of Xing'an block. By study of the ore samples in the main metallogenic period, we aim to explore the source of ore-forming fluids.
Methods Nine ore samples from the main metallogenic stage were selected for systematic study of the He, Ar and S isotopic compositions.
Results The results show that the 3He/4He and 40Ar/36Ar ratios for fluid inclusions of pyrite and galena in the gold-bearing quartz veins are 1.95×10-6-5.03×10-6 and 349.1-453.9, respectively. The mantle-derived He accounting for 13.17%-44.67%, averagely 27.58%, indicating that the metallogenic fluid is mainly atmospheric precipitation, with the composition of mantle fluid as well, reflecting that the mineralization of gold deposit is closely related to mantle activity. The δ34S of minerals is-1.2‰ --3.9‰, averagely -2.33‰, probably from deep mantle fluid, also with the addition of crustal fluid.
Conclusions The oceanic crust subducted toward Xing'an block, with mantle wedge metasomatized by the subducted fluid, and resulted in partial melting and fluid rising to the shallow surface mixed with the downward precipitation to form the metallogenic fluids. The decrease of temperature and pressure and fluid boiling lead to the change of physical and chemical conditions of the metallogenic fluids and precipitate metallogenic materials.
-

-
图 1 黑龙江争光矿区地质图(据黑龙江齐齐哈尔矿产勘查开发总院, 2009修改)
Figure 1.
图 4 黄铁矿流体包裹体40Ar/36Ar-R/Ra图(据Mamyrin and Tolstihkin, 1984修改)
Figure 4.
图 5 黄铁矿流体包裹体4He-3He图(底图据Burnard et al., 1999修改)
Figure 5.
表 1 争光金矿黄铁矿和方铅矿流体包裹体He-Ar-S同位素组成
Table 1. Isotopic composition of He-Ar-S in fluid inclusions of pyrite and galena in Zhengguang gold deposit

-
Ballentine C J, Burgess R, Marty B. 2002. Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 47: 539-614. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.47.13
Burnard P G, Hu R Z, Turner G, Bi X W. 1999. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63: 1595-1604. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00108-8
Chao Wenxin. 2018. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Zhengguang Gold Deposit in Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chaussidon M, Lorand J P. 1990. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): An ion microprobe study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54(10): 2835-2846. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90018-G
Che Hewei, Zhou Zhenhua, Ma Xinghua, Ouyang Hegen, Liu Jun. 2016. Tentative discussion on genesis of Zhengguang Au deposit in northern Da Hinggan Mountains: Constrained by fluid inclusions and stable isotope composition[J]. Mineral Deposits, 35(3): 539-558 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng Ke, Li Nuo, Yang Yongfei, Zhang Cheng, Yu Yuanbang, Zhang Dongcai. 2013. Fluid inclusion constraints on the origin of the Zhengguang gold deposit, Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(1): 231-240 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fu Yanli, Yang Yanchen. 2010. Deposit genesis and prospecting criteria of Zhengguang gold deposit, Heilongjiang[J]. Gold, 31(6): 13-18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gammons C H, Williams Jones A E. 1997. Chemical mobility of gold in the porphyry-epithermal environment[J]. Economic Geology, 92 (1): 45-59. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.92.1.45
Gao Rongzhen, Lü Xinbiao, Yang Yongsheng, Li Chuncheng. 2015. Characteristics of cryptoexplosive breccias in the Zhengguang gold deposit of Heilongjiang Province and theirgeological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 50(5): 874-883 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao Yujie. 2015. Mineralization and Metallogenic Regularity of Duobaoshan Ore Concentration Area in Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-199 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Heald P, Foley N K, Hayba D O. 1987. Comparative anatomy of volcanic-hosted epithermal deposits acid-sulfate and adularia-sericite types[J]. Economic Geology, 80: 1-26.
Heilongjiang Qiqihar Mineral and Development Institute. 2009. Prospecting Report of Zhengguang Gold Deposit in Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province[R]. Heilongjiang Qiqihar Mineral and Development Institute, 82-116 (in Chinese).
Heinrich C A, Driesner T, Stefánsson A, Seward T M. 2004. Magmatic vapor contraction and the transport of gold from the porphyry environment to epithermal ore deposits[J]. Geology, 32(9): 761-764. doi: 10.1130/G20629.1
Heinrich C A. 2005. The physical and chemical evolution of low-salinity magmatic fluids at the porphyry to epithermal transition: A thermodynamic study[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 39: 864-889. doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0461-9
John D A, Hofstra A H, Fleck R J, Brummer J E, Saderholm E C. 2003. Geologic setting and genesis of the Mule Canyon low-sulfidation epithermal gold-silver deposit, North-Central Nevada[J]. Economic Geology, 98(2): 425-463. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.2.425
Kendrick M A, Burgess R, Pattrick R A D, Turner G. 2001. Fluid inclusion noble gas and Halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-porphyry mineralizing fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(16): 2651-2668. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00618-4
Li Junjie, Li Jian, Liu Hanbin, Zhang Jia, Jin Guishan, Zhang Jianfeng, Han Juan. 2015. Helium isotope composition of inclusions in mineral grains using Helix SFT Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(10): 1826-1831 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Yun, Fu Jiajun, Zhao Yuanyi, Zeng Hui. 2016. Chronological characteristics and metallogenic significance of Zhengguang gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(1): 151-162 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.01.010
Mamyrin B A, Tolstihkin I N. 1984. Helium Isotopes in Natures[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 273.
Mao J W, Kerrich R, Li H Y. 2002. High 3He/4He ratios in the Wangu gold deposit, Hunan Province, China: Implications for mantle fluids along the Tanlu deep fault zone[J]. Geochemical Journal, 36: 197-208. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.36.197
Mao J W, Li Y Q, Goldfarb R. 2003. Fluid inclusion and nobel gas studies of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province: A mantle connection for mineralization[J]. Economic Geology, 98(3): 517-534.
Moreir M, Blusztajn J, Curtice J. 2003. He and Ne isotopes in oceanic crust: Implications for noble gas recycling in the mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 216: 635-643. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00554-5
Ohmoto H. 1972. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotope in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 67: 551-579. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551
Rollinson H R. 1993. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M]. London: Longman Scientific and Technical Press, 306-308.
Song Guoxue, Qin Kezhang, Wang Le, Gou Jihai, Li Zhenzhen, Tong Kuangyin, Zou Xinyu, Li Guangming. 2015. Type, zircon U-Pb age and Paleo volcano edifice of Zhengguang gold deposit in Duobaoshan ore field Heilongjiang Province, NE-China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(8): 2402-2146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Stuart F M, Burnard P, Taylor R P. 1995. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluid: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralization, South Korea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59: 4663-4673. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00300-2
Sun Xiaoming, Xiong Dexin, Wang Shengwei, Shi Guiyong, Zhai Yong. 2006. Noble gases isotopic composition of fluid inclusions in scheelites collected from Daping gold mine, Yunnan Province, China, and its application for ore genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 725-732 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tong Kuangyin, Yang Yanchen, Song Gguoxue, Liang Haijun, Ma Longfei. 2015. Discussion on geological characteristics, ore genesis and prospecting of the Zhengguang Au-Zn deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 51(3): 507-518 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Winckler G, Aeschbach-Hertig W, Kipfer. 2001. Constraints on origin and evolution of red brines from helium and argon isotopes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 184: 671-683. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00345-9
Wu G, Chen Y C, Sun F Y. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the Early Paleozoic igneous rocks in the Duobaoshan area, NE China, and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 229-250. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.031
Wu Ziyu, Sun Youcai, Wang Baoquan. 2006. Geology and geochemistry of Zhengguang gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 42(1): 38-842 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Yongchang, Shen Ping, Tao Mingxin. 1996. Geochemistry of mantle-derived volatiles from natural gas in the eastern oil-gas Region. New types of helium Resources: Industrial reservoirs of mantle-derived helium in sedimentary crusts[J]. Science China (Series D), 26(1): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xue Chunji, Chen Yuchuan, Wang Denghong, Yang Jianmin, Yang Weiguang, Guan Ru. 2003. The Jinding and Baiyangping deposits, northwestern Yunnan: Geological feature, He, Ne and Xe isotope compositions, and metallogenic epoch[J]. Science in China, 33(4): 315-322 (in Chinese).
Yang Fuquan, Mao Jingwen, Wang Yitian, Zhao Caisgheng, Ye Hhuishou, Chen Wen. 2006. Chronology and geochemical characteristics of helium, argon, carbon and oxygen isotope in fluid inclusion of the Sawayaerdun gold deposit, Xinjiang, northwestern China and their significance[J]. Geological Review, 52(3): 341-351 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Yongsheng, Lü Xinbiao, Gao Rongzhen, Li Chuncheng, Sun Xixin, Li Jie, Gun Minshan, Wu Jianliang, Xing Weiwei. 2016. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological significance of the tonalite porphyry in Zhengguang gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(4): 674-700 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Zhigang, Qin Yunshan, Zhai Shikui. 2001. He, Ne and Ar isotope compositions of nuid inclusions in hvdmthe Ⅱ llal sum des flrom the TAG hydmthe Ⅱ llal 6eld, Mid-Atlantic Ridge [J]. Science in China (series D), 30(6): 628-633 (in Chinese).
Zhao Guangjiagn, Hou Yushu, Cheng Fuqiang. 2007. Geological characteristics and genesis of Zhengguang gold deposit in Heihe City of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 59(3): 91-94 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Guangjiang, Hou Yushu, Wang Baoquan. 2006. Geological characteristics and genesis of Zhengguang gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 22 (3): 3-6 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2006.03.002
晁温馨. 2018. 黑龙江省黑河市争光金矿矿床地质特征及成因研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-54.
车合伟, 周振华, 马星华, 欧阳荷根, 刘军. 2016. 大兴安岭北段争光金矿床成因探讨: 来自流体包裹体及稳定同位素的制约[J]. 矿床地质, 35(3): 539-558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201603007.htm
邓轲, 李诺, 杨永飞, 张成, 于援帮, 张东财. 2013. 黑龙江省黑河市争光金矿流体包裹体研究及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 29(1): 231-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201301019.htm
付艳丽, 杨言辰. 2010. 黑龙江省争光金矿床成因及找矿标志[J]. 黄金, 31(6): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201006008.htm
高荣臻, 吕新彪, 杨永胜, 李春诚. 2015. 黑龙江争光金矿床隐爆角砾岩特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 50(5): 874-883. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201405007.htm
郝宇杰. 2015. 黑龙江多宝山矿集区成矿作用与成矿规律研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-199.
黑龙江省齐齐哈尔矿产勘察开发总院. 2009. 黑龙江省黑河市争光岩金矿勘探报告[R]. 黑龙江省齐齐哈尔矿产勘察开发总院, 82-116.
李军杰, 李剑, 刘汉彬, 张佳, 金贵善, 张建锋, 韩娟. 2015. Helix SFT惰性气体质谱仪分析矿物包裹体中氦同位素组成[J]. 地质学报, 89(10): 1826-1831. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201510010.htm
李运, 符家骏, 赵元艺, 曾辉. 2016. 黑龙江争光金矿床年代学特征及成矿意义[J]. 地质学报, 90(1): 151-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201601010.htm
宋国学, 秦克章, 王乐, 郭继海, 李真真, 佟匡胤, 邹心宇, 李光明. 2015. 黑龙江多宝山矿田争光金矿床类型、U-Pb年代学及古火山机构[J]. 岩石学报, 31(8): 2402-2416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201508019.htm
孙晓明, 熊德信, 王生伟, 石贵勇, 翟勇. 2006. 云南大坪金矿白钨矿惰性气体同位素组成及其成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 725-732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603022.htm
佟匡胤, 杨言辰, 宋国学, 梁海军, 马龙飞. 2015. 黑龙江争光金锌矿地质特征、矿床成因及找矿潜力探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 51(3): 507-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201503011.htm
武子玉, 孙有才, 王保全. 2006. 黑龙江争光金矿地质地球化学研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 42(1): 38-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200601009.htm
徐永昌, 沈平, 陶明信. 1996. 东部油气区天然气中幔源挥发份的地球化学—Ⅰ. 氦资源的新类型: 沉积壳层幔源氦的工业储集[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 26(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199602014.htm
薛春纪, 陈毓川, 王登红, 杨建民, 杨伟光, 管荣. 2003. 滇西北金顶和白秧坪矿床地质和He, Ne, Xe同位素组成及成矿时代[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4): 315-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYJ202304009.htm
杨富全, 毛景文, 王义天, 赵财胜, 叶会寿, 陈文. 2006. 新疆萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床年代学、氦氩碳氧同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 52(3): 341-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200603008.htm
杨永胜, 吕新彪, 高荣臻, 李春诚, 孙喜新, 李杰, 衮民汕, 吴建亮, 邢伟伟. 2016. 黑龙江争光金矿床英云闪长斑岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(4): 674-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201604005.htm
曾志刚, 秦蕴珊, 翟世奎. 2000. 大西洋中脊TAG热液区硫化物中流体包裹体的He-Ne-Ar同位素组成[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 30(6): 628-633. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200006008.htm
赵广江, 候玉树, 程富强. 2007. 黑龙江黑河市争光岩金矿床地质特征及成因浅析[J]. 有色金属, 59(3): 91-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS200703022.htm
赵广江, 侯玉树, 王宝权. 2006. 黑龙江省争光金矿地质特征及成因初探[J]. 有色矿冶, 22(3): 3-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKY200603001.htm
-




 下载:
下载: