Distribution characteristics and formation mechanism of high fluoride groundwater in Luan River Delta and suggestions for its utilization
-
摘要:
研究目的 滦河三角洲存在原生高氟地下水,查明地下水中氟的空间分布特征并分析其富集机理,有利于保障当地居民的用水安全。
研究方法 本研究在现场采集了96个浅层和190个深层地下水样品,系统分析了地下水的水化学特征和高氟地下水形成的水文地球化学过程。
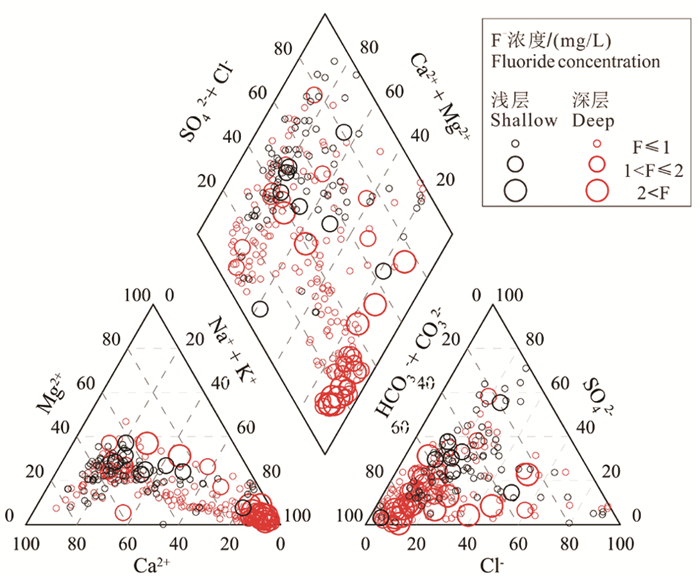
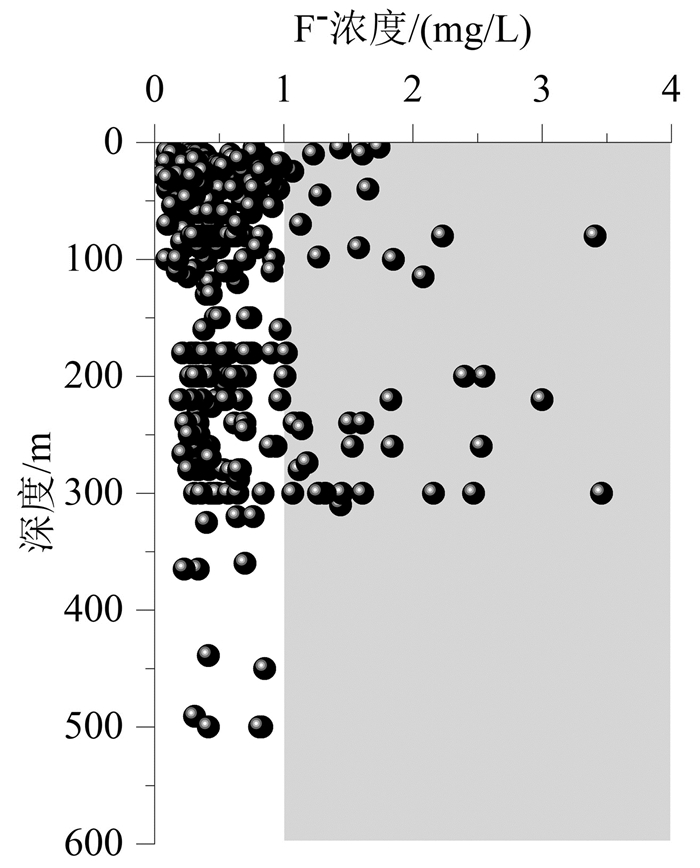
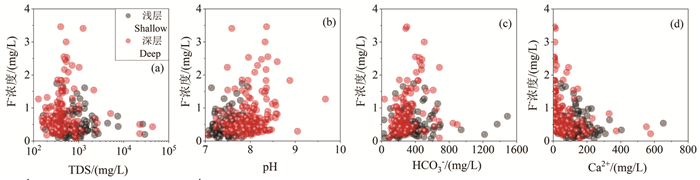
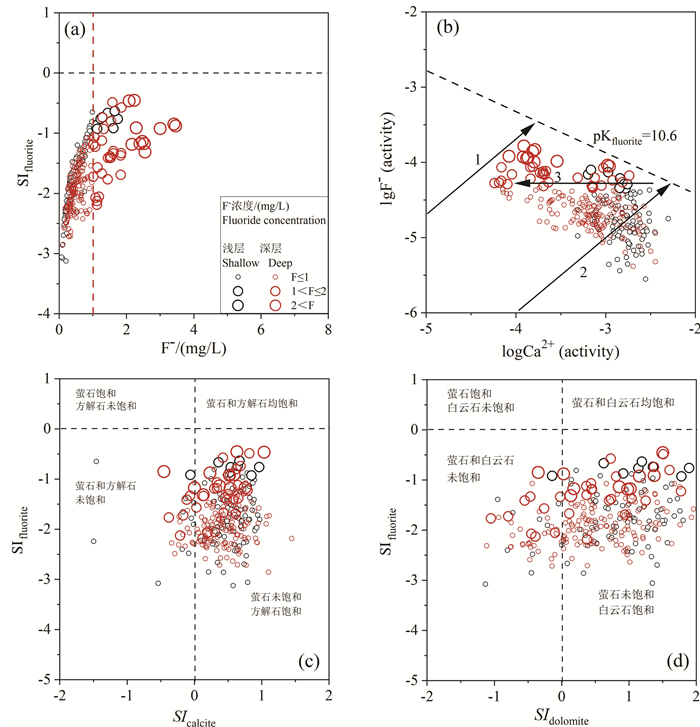
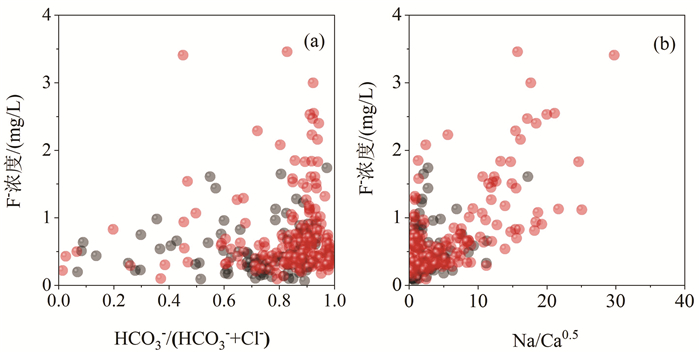
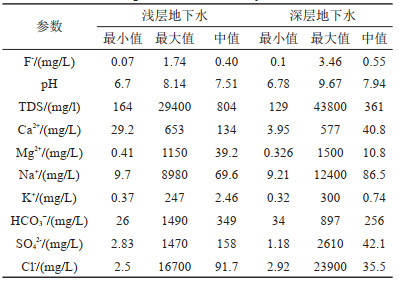
研究结果 结果表明,滦河三角洲有8%的浅层地下水样品和21%的深层地下水样品氟含量高于中国生活饮用水标准和地下水质量标准的1.0 mg/L。浅层高氟地下水呈局部小范围分布,而深层高氟水广泛分布在以HCO3-Na·Ca型水为主的含水层中。PHREEQC饱和指数计算结果表明,地下水中萤石为不饱和状态,萤石矿物溶解是地下水中F-的主要来源。
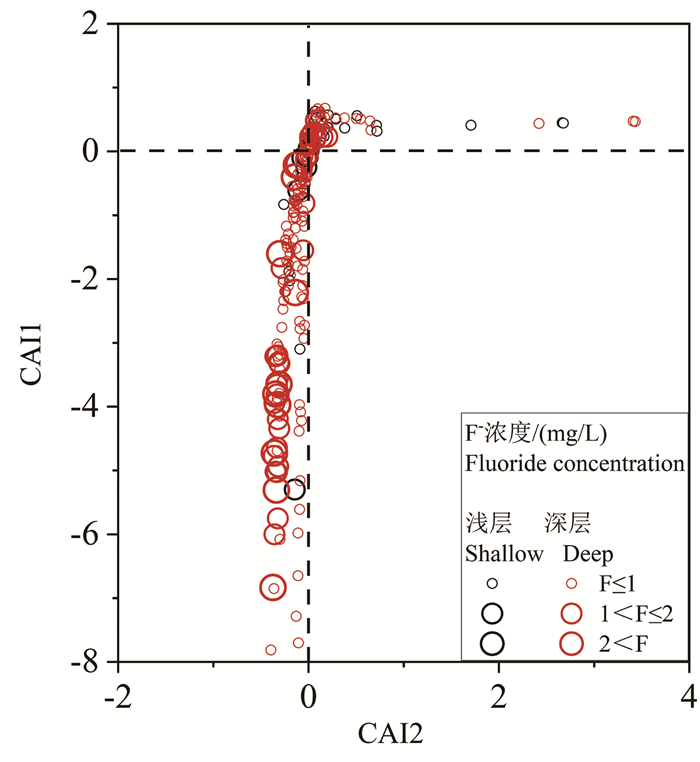
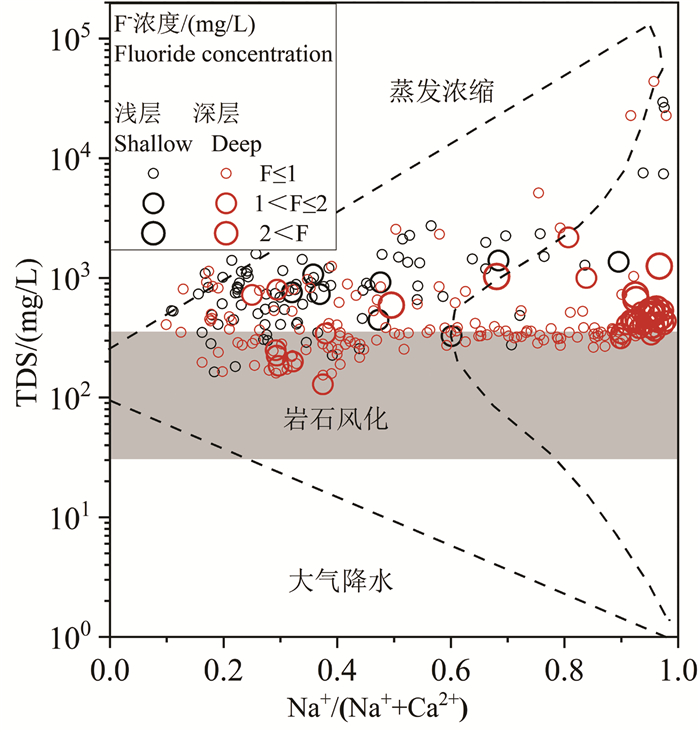
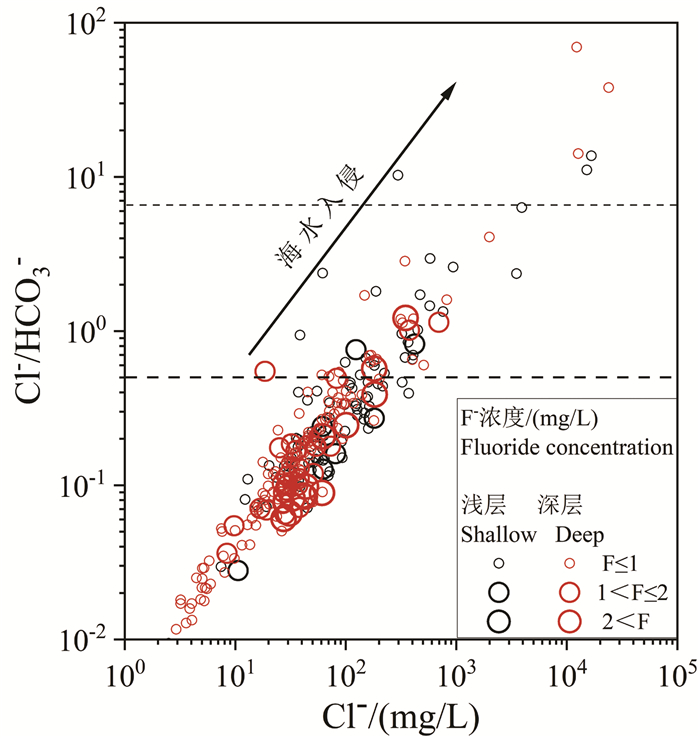
结论 对比分析浅层和深层高氟地下水的水化学特征发现,蒸发浓缩作用对浅层地下水中F-富集影响显著,而深层地下水氟富集主要受解吸与竞争吸附和阳离子交换控制。海水入侵对地下水中氟富集的影响较小。因此,本研究建议浅层和深层高氟水应分别通过电化学法和混凝沉淀法或吸附法降氟处理。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
Objective The Luanhe River Delta has naturally occurring high fluoride groundwater. Identifying the spatial distribution characteristics of fluoride in groundwater and analyzing its enrichment mechanism is beneficial for ensuring the safety of local residents' water supply.
Methods This study collected a total of 96 shallow and 190 deep groundwater samples on-site and conducted a systematic analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and the hydrogeochemical processes related to the formation of high fluoride groundwater.
Results Results show that 8% of the shallow groundwater samples and 21% of the deep groundwater samples in the Luan River Delta contain fluoride content higher than 1.0 mg/L of Chinese drinking water standards and groundwater quality standards. Shallow high fluoride groundwater is locally distributed in a small area, while deep high fluoride water is mainly concentrated in deep aquifers dominated by HCO3-Na·Ca type water. The calculation result of PHREEQC saturation index indicates that fluorite in groundwater is unsaturated, and fluorite mineral dissolution is the main source of groundwater F-.
Conlusions A comparative analysis of the water chemistry characteristics of shallow and deep groundwater with high F- suggested that evaporation and concentration have a significant impact on the enrichment of F- in shallow groundwater, while the enrichment of fluoride in deep groundwater is mainly controlled by desorption, competitive adsorption and cation exchange. In addition, seawater intrusion has little effect on F- enrichment in groundwater. Therefore, this study recommends that high fluoride groundwater in the shallow and deep aquifers should be treated separately using electrochemical methods and coagulation-precipitation or adsorption methods, respectively, to reduce fluoride levels.
-

-
表 1 研究区水化学组分特征值
Table 1. Characteristic values of groundwater chemical components in the study area
-
Cao Wengeng, Wang Yanyan, Ren Yu, Fei Yuhong, Li Jincheng, Li Zeyan, Zhang Dong, Shuai Guanyin. 2022. Status and progress of treatment technologies for arsenic-bearing groundwater[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1408-1426(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Q, Jia C P, Wei J C, Dong F Y, Yang W G, Hao D C, Jia Z W, Ji Y H. 2020. Geochemical process of groundwater fluoride evolution along global coastal plains: Evidence from the comparison in seawater intrusion area and Soil Salinization Area[J]. Chemical Geology, 552: 1-10.
Fang Cheng, Liu Futian, Meng Lishan, Liu Hongwei, Qin Yafei, Zheng Jinna. 2014. Application of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to study hydrologic cycle in the Caofeidian area[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 37(2): 102-107 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo H M, Zhang Y, Xing L N, Jia Y F. 2012. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao Basin, inner Mongolia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 27: 2187-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.01.016
Han Shuangbao, Li Fucheng, Wang Sai, Li Haixue, Yuan Lei, Liu Jingtao, Shen Haoyong, Zhang Xueqing, Li Changqing, Wu Xi, Ma Tao, Wei Shibo, Zhao Minmin. 2021. Groundwater resource and eco-environmental problem of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1001-1019(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao Qiyong, Xu Xiaotian, Zhang Xinbin, Zhou Lai. 2020. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine shallow groundwater in Yanggu area of the Northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 42(5): 668-677 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Karthikeyan M, Satheesh Kumar K K, Elango K P. 2009. Conducting polymer/alumina composites as viable adsorbents for the removal of fluoride ions from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 130(10): 894-901. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2009.06.024
Kim S H, Kim K J, Ko K S, Kim Y K, Lee K S. 2012. Co-contamination of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of unconsolidated aquifers under reducing environments[J]. Chemosphere, 87(8): 851-856. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.025
Li P Y, He X D, Li Y, Xiang G. 2019. Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifer in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A case study of Tongchuan, Northwest China[J]. Exposure & Health, 11: 95-107.
Li Zhiwei, Zhang Xiaoying, Zhang Mingzhu, Li Dan, Tan Guangxiong, Zhang Liang, Sun Liwei, Yang Fan, Hu Xiaonong. 2020. Comparison of indicators for the assessment of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers——Taking aquifers in Pearl River Estuary as an example[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 39(1): 16-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu H Y, Guo H M, Yang L J, Wu L H, Li F L, Li S Y, Ni P, Liang X. 2015. Occurrence and formation of high fluoride groundwater in the Hengshui Area of the North China Plain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(3): 2329-2340. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4225-x
Mcmahon P B, Brown C J, Johnson T D, Belitz K, Lindsey B. 2020. Fluoride occurrence in United States Groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 732: 1-15.
Miao Jinjie, Jin Jihong, Du Dong, Liu Hongwei, Bai Yaonan, Zhang Jing, Guo Xu. 2020. A study on compression and consolidation behaviors of soils in typical landsubsidence area in Cangzhou[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 43(3): 224-229 (in Chinese with English abstract).
National Health and Family Planning Commission. 2017. Bulletin on the development of health and family planning in China in 2016[J]. Health Management, 9: 22-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
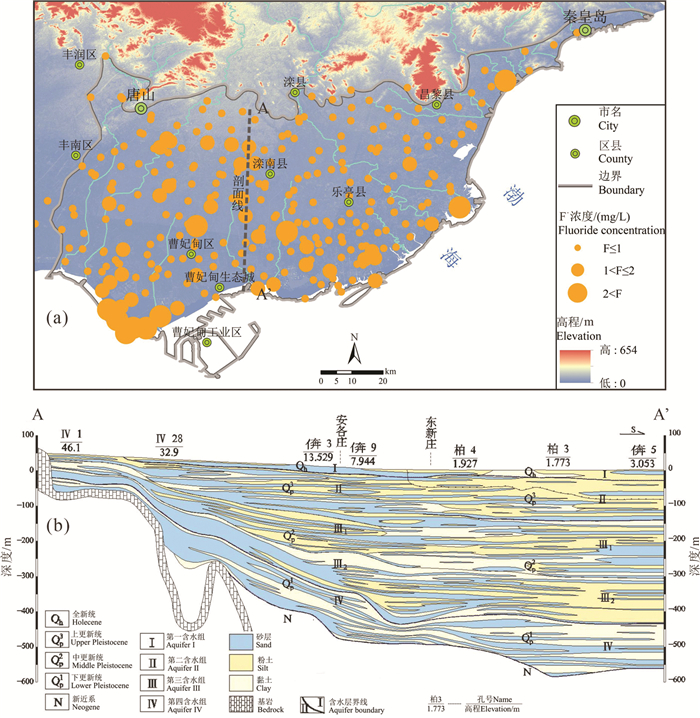
Niu Zhaoxuan, Jiang Xiaowei, Hu Yunzhuang. 2019. Characteristics and causes of hydrochemical evolution of deep groundwater in the Luanhe Delta[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 46(1): 27-34(in Chinese with English abstract).
Patel S C, Khalkho R, Patel S K, Sheikh J M, Behera D, Chaudhari S, Naraga P. 2014. Fluoride contamination of groundwater in parts of eastern India and a preliminary experimental study of fluoride adsorption by natural haematite iron ore and synthetic magnetite[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72: 2033-2049. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3112-1
Pei Shengliang, Bai Guangyu, Tian Lei, Zhang Jinde. 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics and origin of high fluorine groundwater in Xin Barag Youqi, Inner Mongolia [J]. Earth and Environment, 48(2): 203-209 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Saxena V K, Ahmed S. 2001. Dissolution of fluoride in groundwater: A water-rock interaction study[J]. Environmental Geology, 40(9): 1084-1087. doi: 10.1007/s002540100290
Schoeller H. 1967. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development [J]. Water Resources Series, 33: 44-52.
Su C M, Puls R. 2001. Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: Effects of phosphate, silicate, carbonate, borate, sulfate, chromate, molybdate, and nitrate, relative to chloride[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(22): 4522-4568.
Su C L, Wang Y X, Xie X J, Li J X. 2013. Aqueous geochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater on Datong Basin, northern China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 135(1): 79-92.
Tan Baoguo, Ma Lingling. 2018. Cause analysis of high fluorine groundwater in Datong Basin[J]. Shanxi Coal, 38(1): 49-52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang Minggao, Shen Zhaoli, Zhong Zuoshen. 1995. A geochemical study on fluorine in soil and groundwater of Quaternary System in Hebei Plain[J]. Earth Science, 20(4): 450-454 (in Chinese with English abstract).
World Health Organization. 2011. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality[S]. Genava: WHO.
Xing Lina, Guo Huaming, Weiliang, Zhan Yanhong, Hou Chuntang, Li Ruimin, Wang Yi. 2012. Evolution feature and gensis of fluoride groundwater in shallow aquifer from North China Plain[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 34(4): 57-67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yadav K K, Kumar S, Pham Q B, Gupta N, Rezania S, Kamyab H. 2019. Fluoride contamination, health problems and remediation methods in asian groundwater: A comprehensive review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 182: 1-23.
Yang Lei, Gong Xulong, Lu Xurong, Zhang Yan. 2015. Distribution and genesis of high-fluoride groundwater in northern Lianyungang area[J]. Geology in China, 42(4): 1161-1169 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ye Yonghong, Gong Jianshi, Wang Hesheng, Zhou Kaie, Li Liang. 2020. Relationship between high-fluoride groundwater and hydrochemical type in the plain[J]. Ground Water, 42(2): 1-3 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Hao, Wang Liming, Xu He, Kong Fanqing. 2017. Distribution and assessment of high fluorine groundwater in Haihe River Plain[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 28(3): 32-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
曹文庚, 王妍妍, 任宇, 费宇红, 李谨丞, 李泽岩, 张栋, 帅官印. 2022. 含砷地下水的治理技术现状与进展[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1408-1426. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220504?st=search
方成, 柳富田, 孟利山, 刘宏伟, 秦雅飞, 郑锦娜. 2014. 氢氧同位素在曹妃甸地区水循环研究中的应用[J]. 地质调查与研究, 37(2): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201402005.htm
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 2017. 2016年我国卫生和计划生育事业发展统计公报发布[J]. 健康管理, 9: 22-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKGL201709011.htm
韩双宝, 李甫成, 王赛, 李海学, 袁磊, 刘景涛, 申豪勇, 张学庆, 李长青, 吴玺, 马涛, 魏世博, 赵敏敏. 2021. 黄河流域地下水资源状况及其生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1001-1019. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210402?st=search
郝启勇, 徐晓天, 张心彬, 周来. 2020. 鲁西北阳谷地区浅层高氟地下水化学特征及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 42(5): 668-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202005008.htm
李志威, 张晓影, 张明珠, 李丹, 覃光雄, 张靓, 孙立伟, 杨帆, 胡晓农. 2020. 海水入侵指标对比分析与评价——以珠江口地下水含水层为例[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(1): 16-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ202001003.htm
苗晋杰, 靳继红, 杜东, 刘宏伟, 白耀楠, 张竞, 郭旭. 2020. 首都副中心及重点区域地下水环境质量评价与问题成因[J]. 地质调查与研究, 43(3): 224-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202003004.htm
牛兆轩, 蒋小伟, 胡云壮. 2019. 滦河三角洲地区深层地下水化学演化规律及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 46(1): 27-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201901004.htm
裴圣良, 白光宇, 田磊, 张进德. 2020. 内蒙古新巴尔虎右旗高氟水分布特征及成因分析[J]. 地球与环境, 48(2): 203-209. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202002006.htm
谭保国, 马玲玲. 2018. 大同盆地高氟地下水成因探讨[J]. 山西煤炭, 38(1): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXMT201801014.htm
汤鸣皋, 沈照理, 钟佐燊. 1995. 河北平原第四系水土中氟的地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学, 20(4): 450-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199504019.htm
邢丽娜, 郭华明, 魏亮, 詹燕红, 侯春堂, 李瑞敏, 王轶. 2012. 华北平原浅层含氟地下水演化特点及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 34(4): 57-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201204010.htm
杨磊, 龚绪龙, 陆徐荣, 张岩. 2015. 连云港北部地区高氟地下水分布特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 42(4): 1161-1169. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20150429?st=search
叶永红, 龚建师, 王赫生, 周锴锷, 李亮. 2020. 淮河流域平原区高氟地下水与水化学类型的关系研究[J]. 地下水, 42(2): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU202002001.htm
张浩, 王立明, 徐鹤, 孔凡青, 2017. 海河平原区高氟地下水分布与评估[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 28(3): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201703007.htm
-



 下载:
下载: