Wind erosion, land desertification and ecogeological effects in the northern piedmont of Yinshan Mountain in Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
研究目的 阴山北麓作为我国土地沙化最严重的区域之一,受风蚀作用影响严重。本文通过研究该地区风蚀作用、土地荒漠化与植被类型分布三者之间的关系,阐明风蚀作用对基岩风化成土过程的影响,揭示风蚀对土地沙化的影响,诠释生态地质特征与生态系统的耦合关系,为干旱、半干旱地区生态系统保护修复提供科学依据。
研究方法 本文选择该地区缓坡丘陵、低山丘陵和中山三种地貌区的基岩风化剖面为研究对象,对比研究了不同风蚀强度下岩石风化过程中元素的迁移过程、土壤质地特征以及地表植被类型与覆盖度变化规律。
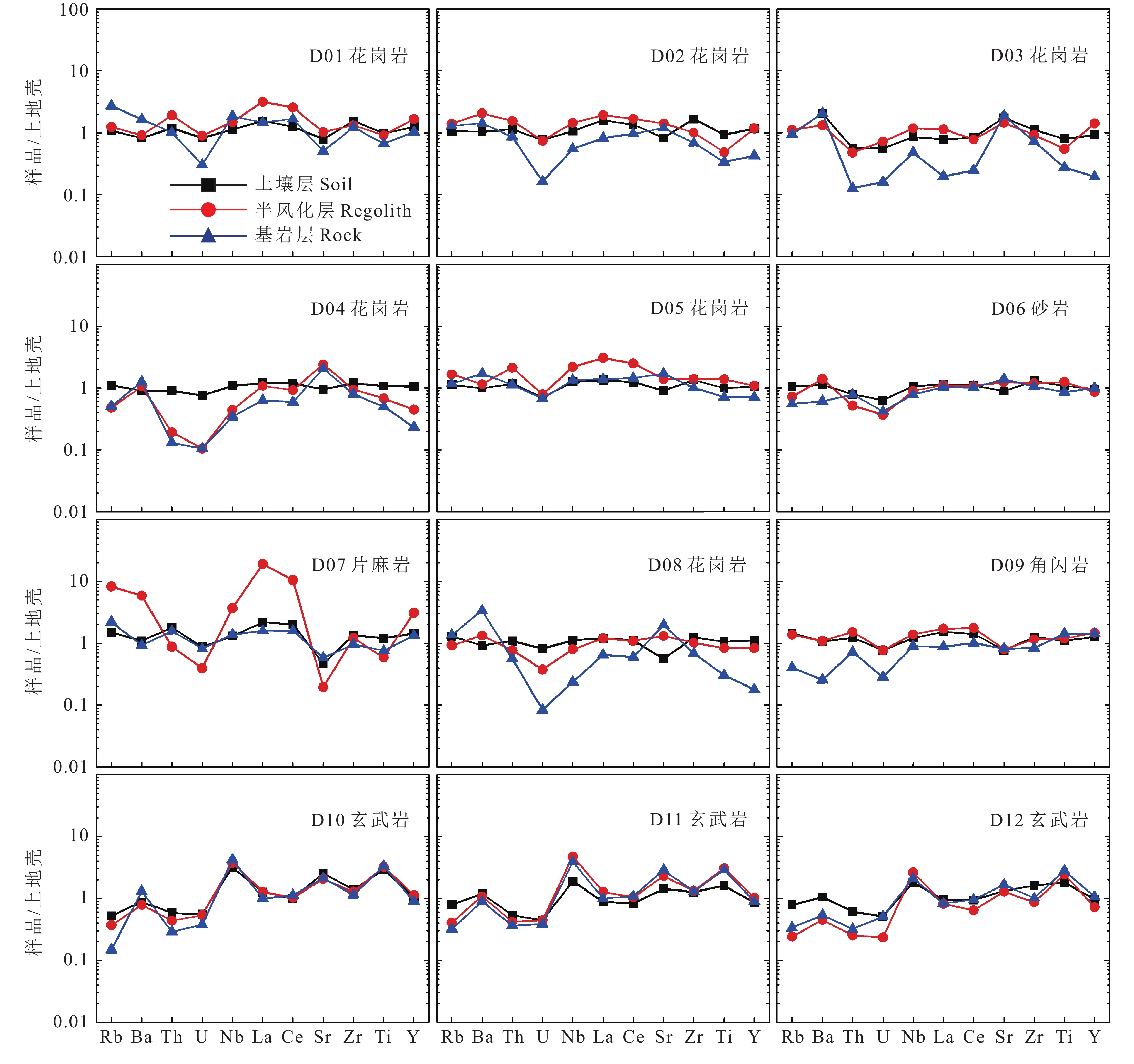
研究结果 缓坡丘陵区受风蚀作用影响较大,细粒风化产物大量迁出,表土Al2O3含量显著减少,土壤剖面CIA值变化异常、厚度变薄、养分流失、保水能力下降,植被类型以草为主,稀疏矮小,覆盖度较低;低山丘陵区受风蚀作用影响较小,黏粒、粉粒少量迁出,少量极细砂迁入,表土Al2O3含量减少,土壤CIA值变化正常、厚度变化不大、养分少量流失,植被类型以草为主,分布相对密集,且有低矮灌木生长;中山区受风蚀作用影响最小,以黏粒、粉粒物质迁入为主,风化产物迁出甚少,表土Al2O3含量增加,CIA值显著升高,植被类型以低矮灌木为主,山坡上有大片乔木生长,长势较好。
结论 强烈的风蚀作用使得阴山以北缓坡丘陵区土壤中的细粒物质被迁移至中山区,造成缓坡丘陵区土壤厚度与质量较中山区差,因此缓坡丘陵区植被稀疏,土地沙化较严重,山地区植被涨势较好。
Abstract:This paper is the result of ecological geological survey engineering.
Objective As one of severe desertification areas in China, the northern piedmont of Yin Mountain is seriously impacted by wind erosion. The relationship of wind erosion, land desertification and the distribution of vegetation types in this area was studied, to clarify the impact of wind erosion on the weathering process from the bedrock to the soil, to reveal the effect of wind erosion on land desertification, to interpret the coupling relationship between eco-geological characteristics and ecosystems, and to provide a scientific basis for the protection and restoration of ecosystem at arid and semi-arid regions.
Methods Weathering profiles was selectively collected from rocks to soils, which distributed in the gentle slope hills, low mountain hills and mid-mountain. To compare the influence of different wind erosion intensities, some works were performed to analyze the migration processes of elements during rock weathering, characteristics of soil texture, and change patterns of surface vegetation types and its coverage.
Results The gentle slope hilly area was greatly influenced by wind erosion. Many fine particles of weathering products were moved out, which appeared as the content of Al2O3 in surface soil decreasing significantly and values of CIA in soil profile changing abnormally. Thus, the soil thickness became thinner with the soil nutrients being lost and the water retention ability be weakened. As the result, the grass is the main vegetation type with sparse distribution. The low hilly area was less affected by wind erosion. A small amount of clay and silt grains were emigrated, and some fine sands were immigrated, which appeared as the content of Al2O3 in surface soil decreasing and values of CIA in soil profile changing normally. Thus, the soil thickness was almost unchanged with the soil nutrients being lost slightly. As the result, the vegetation type was dominated by the grass with low shrubs growing, and their distribution was relatively denser. The middle-mountain area was impacted by the wind erosion at the least degree. A certain amount of clay and silt was immigrated almost without emigration of weathering products, which appeared as the content of Al2O3 in surface soil increased with a great increase of CIA values. As the result, the vegetation types were mainly short shrubs, and a large number of trees were densely grown on the hillside.
Conclusions Intense wind erosion caused the migration of fine-grained materials in the soil from the gentle slope hills north of Yin Mountain to the mid-mountain area, which resulted in worse soil thickness and quality at the gentle slope hills while comparing to those at the mid-mountain area. Consequently, vegetation is sparse and land desertification is more severe in the gentle slope hills, while vegetation shows better growth in the mountain areas.
-

-
表 1 阴山北麓岩石风化剖面中常量元素含量及化学蚀变指数(%)
Table 1. Major element content and chemical alteration index in rock weathering profile in the northern piedmont of Yin Mountain (%)
地貌区 点号 岩性 层位 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O CIA 低山丘陵 D01 花岗岩 土壤层 60.01 10.96 5.13 2.23 4.65 2.20 2.16 53.34 风化层 55.64 11.00 4.41 1.92 8.37 2.24 2.58 51.97 基岩层 67.56 13.59 2.12 0.74 0.61 3.46 5.95 50.66 D02 花岗岩 土壤层 61.12 11.54 4.30 1.78 3.27 2.25 2.48 53.37 风化层 62.04 12.50 2.43 0.88 6.07 2.74 3.78 48.84 基岩层 70.43 13.18 1.50 0.75 1.58 3.90 4.00 49.19 D03 花岗岩 土壤层 60.26 13.16 4.36 2.69 2.86 3.38 3.07 48.31 风化层 69.92 10.04 3.99 3.41 4.62 2.72 5.16 40.86 基岩层 67.28 14.40 1.58 0.33 0.73 5.14 5.47 47.83 D04 花岗岩 土壤层 57.36 13.10 5.62 2.17 2.60 2.25 2.13 57.45 风化层 58.87 14.72 4.46 1.93 3.89 3.78 1.88 50.44 基岩层 64.27 15.01 2.87 1.62 2.87 4.95 2.11 48.98 D05 花岗岩 土壤层 59.86 13.35 4.98 1.84 2.09 2.62 2.63 54.92 风化层 55.25 14.13 7.27 2.03 2.96 3.77 3.07 48.66 基岩层 63.50 13.67 3.82 1.72 3.00 4.25 4.04 44.83 中山 D06 砂岩 土壤层 60.83 12.80 5.50 2.34 1.71 2.70 2.41 55.76 风化层 55.83 12.89 6.31 2.79 1.72 3.12 2.17 54.82 基岩层 50.88 11.16 3.69 2.42 11.82 3.43 1.71 45.92 D07 片麻岩 土壤层 57.36 13.47 6.73 2.57 1.73 1.47 2.61 63.71 风化层 47.87 9.36 3.66 6.10 2.58 0.21 6.62 54.36 基岩层 63.37 14.30 4.00 2.15 1.67 4.69 2.95 50.65 D08 花岗岩 土壤层 60.89 13.30 5.49 2.16 1.51 1.97 2.50 60.49 风化层 63.80 13.88 5.02 1.84 1.91 3.41 2.47 54.14 基岩层 72.99 13.35 1.57 0.77 1.51 3.57 4.89 48.99 D09 角闪岩 土壤层 58.24 13.56 6.67 2.25 2.38 2.53 2.68 54.68 风化层 56.27 14.48 7.00 2.23 2.24 2.71 2.66 55.93 基岩层 54.14 12.61 9.35 2.89 5.54 3.80 1.23 47.70 缓坡丘陵 D10 玄武岩 土壤层 49.15 14.69 9.05 2.94 5.39 1.95 1.70 64.00 风化层 47.99 15.59 9.43 3.07 6.75 1.78 1.55 67.43 基岩层 43.15 14.91 9.98 3.21 13.62 2.26 1.14 63.22 D11 玄武岩 土壤层 57.02 12.31 5.96 2.34 4.54 2.18 2.40 55.78 风化层 45.63 15.09 10.53 2.64 8.80 2.14 2.09 61.90 基岩层 47.41 14.09 9.99 4.07 9.50 3.51 2.25 50.21 D12 玄武岩 土壤层 56.38 13.00 7.23 2.66 3.55 2.20 1.97 58.13 风化层 43.91 12.96 9.11 3.24 11.38 1.86 1.39 62.99 基岩层 49.11 14.91 9.64 3.82 8.94 3.65 1.46 52.33 表 2 阴山北麓岩石风化剖面表层土壤粒度统计(%)
Table 2. Surface soil grain size statistics of rock weathering profile in the northern piedmont of Yinshan Mountain (%)
地貌区 粒度名称 黏粒 粉粒 极细砂 细砂 中砂 粗砂 极粗砂 粒径/mm <0.002 0.002~0.05 0.05~0.1 0.1~0.25 0.25~0.5 0.5~1 1~2 低山丘陵 D01花岗岩 4.45 48.39 34.54 12.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 D02花岗岩 4.52 47.59 32.80 11.80 2.16 1.13 0.00 D03花岗岩 3.93 62.20 17.80 8.97 6.00 1.10 0.00 D04花岗岩 3.66 71.67 19.98 3.39 1.29 0.01 0.00 D05花岗岩 5.27 58.45 20.78 6.81 2.93 5.33 0.43 中山 D06砂岩 5.13 60.54 13.96 9.99 8.21 2.17 0.00 D07片麻岩 4.11 64.69 18.42 5.72 3.58 3.12 0.36 D08花岗岩 6.97 70.96 18.17 3.90 0.00 0.00 0.00 D09角闪岩 4.39 64.51 16.30 6.43 5.56 2.78 0.03 缓坡丘陵 D10玄武岩 5.70 68.57 18.75 6.40 0.58 0.00 0.00 D11玄武岩 5.67 62.39 16.38 12.14 3.42 0.00 0.00 D12玄武岩 4.82 63.32 16.87 7.40 6.85 0.74 0.00 -
[1] Carni A, Matevski V, Juvan N, Kostadinovski M. 2016. Transition along gradient from warm to mesic temperate forests evaluated by GAMM[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 9(4): 421−433. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtv069
[2] Chen Ruzhang, Zhang Liping, Wu Yanhong, Qiu Luyang. 2016. Soil profile weathering feature of eroded weathering granite slope at different sections[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(6): 1380−1388 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Xingren, Zhou Jun. 2012. Features of distribution of trace elements in soils in the Jianghuai Area, Anhui and analysis of the cause of formation[J]. Geology of Anhui, 22(2): 123−129 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Zhengxin, Wei Enfeng. 2002. Strategies for rejuvenation of degenerated natural grassland within northern agro−grazing ecotone of Yinshan Mountains, Inner Mongolia[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 9(1): 41−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chepil W S. 1953. Factors that influence clod structure and erodibility of soil by wind[J]. Soil Science, 75(6): 473−484.
[6] Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M. 1995. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary−rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 23(10): 921−924. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2
[7] Huang Chengmin, Gong Zitong. 2000. Quantitative study on the development of soils derived from basalts in northern Hainan island[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 20(4): 337−342 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Huang Chengmin, Gong Zitong. 2002. Study on genesis of soils derived from basal in northern Hainan island Ⅲ. element geochemistry[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 39(5): 643−652 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Huang Zhenguo. 1966. Red Weathering Crust in South China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese).
[10] Jian Zhonghua, Xu Mingxing, Song Mingyi, Huang Chunlei, Zheng Wen, Chen Zaihong. 2013. Impacts of different soil parent material on quality of Pujiang peach−shaped plum[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 41(10): 4356−4361 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Kanhaiya S, Singh B P, Singh S. 2018. Mineralogical and geochemical behavior of sediments solely derived from Bundelkhand granitic complex, Central India: Implications to provenance and source rock weathering[J]. Geochemistry International, 56(12): 1245−1262. doi: 10.1134/S0016702918120054
[12] Li Dajing, Xu Ruiyang, Ding Xue, Wang Ziyu, Song Alin. 2018. Changes of wind erosion climatic erosivity and vegetation dynamics response in northern China from 1981 to 2020[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(2): 15−20.
[13] Li Xiaoli, Shen Xiangdong, Zhang Yajing. 2006. Experimental analysis on soil wind−erosion amount in Siziwang Banner North Yinshan Mountain, Inner Mongolia[J]. Arid Land Geography, 29(2): 292−296 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Xiaoli. 2007. Experimental Study on Influencing Factors of Soil Wind Erosion and Its Movement Characteristics in Northern Foot of Yinshan Mountain[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 1−131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Xusheng, Han Zhiyong, Yang Shouye, Chen Yingyong, Wang Yongbo, Yang Dayuan. 2007. Chemical weathering intensity and element migration features of the Xiashu loess profile in zhenjiang[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 62(11): 1174−1184 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Li Zhengji. 1996. Large scale system of rock−soil−plant[J]. Geological Review, 42(4): 369−372 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Liu Wenjing, Tu Chenglong, Lang Yunchao, Feng Jiayi, Li Longbo, Wang Qilian, Liu Congqiang. 2010. Major and trace element compositions of yellow and limestone soils in the karst area of southwest China: Implications for weathering and soil−formation processes[J]. Earth and Environment, 38(3): 271−279 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Liu Zhengguang. 2021. Advances in soil erosion research[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 41(4): 92−96 (in Chinese).
[19] Luo Li. 2018. Analysis of factors affecting the degree of rock weathering[J]. Chemical Enterprise Management, 28: 19−20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] McLennan S M. 1993. Weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 101(2): 295−303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[21] Mu Xingmin, Li Pengfei, Ggao Peng, Zhao Guangju, Sun Wenyi. 2016. Review and evaluation of soil erosion models applied to China loess plateau[J]. Yellow River, 38(10): 100−110,114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. 1982. Early proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 299(5885): 715−717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[23] Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. 1995. Nature and composition of the continental crust: A lower crustal perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(3): 267−309.
[24] Song Zhaoliang, Hang Hao, Luo Weijun, Liu Taoze. 2020. Soil evolution and its controlling mechanisms in a critical zone[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 39(1): 24−29.
[25] Sun Houyun, Sun Xiaoming, Jia Fengchao, Wang Yanli, Li Duojie, Li Jian. 2020. The eco−geochemical characteristics of germanium and its relationship with the genuine medicinal material scutellaria baicalensis in Chengde, Hebei province[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1646−1667 (inChinese with English abstract).
[26] Sun Yuechao, Chen Zhi, Zhao Yonglai, Su Jie, Pan Kun, Dongmei. 2013. Test of grassland soil erosion of farming−pastoral zone in northern foot of Yinshan Mountains[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 44(6): 143−147 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Tang Keli. 2004. Soil and Water Conservation in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[28] Tao Shu, Cao Jun, Li Bengang, Xu Fuliu, Chen Weiyuan. 2001. Distribution pattern of trace elements in soil from Shenzhen area[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 38(2): 248−255 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Trofimov V T. 2013. Current state, tasks, and problems of the further development of ecological geology[J]. Moscow University Geology Bulletin, 68(3): 155−164. doi: 10.3103/S0145875213030083
[30] Wang X M, Yi Y, Dong Z B, Zhang C X. 2009. Responses of dune activity and desertification in china to global warming in the twenty−first century[J]. Global & Planetary Change, 67(3/4): 167−185.
[31] Wang Yange, Hu Xiaohai, Sun Hailian, Zhai Xiu, Liang Jiye. 2019. Soil erosion and conservation at agro−pastoral ecotone of north piedmont in Yinshan Mountain during 2000 to 2015[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 39(2): 127−135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wei Jie, Cao Jianjun, Li Xifei. 2003. Forestry ecological construction and sustainable management countermeasures in hilly wind−erosion desertization area in north of Yinshan Mountains in Inner Mongolia[J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design, 26(2): 14−16, 42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wu Xiaoguang. 2019. The Soil Wing Erosion Influence and Effect of Ecological De−farming on the North Foot of Yinshan Mountain in Inner Mongolia[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 1−213 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Xiao L G, Li G Q, Zhao R Q, Zhang L. 2021. Effects of soil conservation measures on wind erosion control in China: A synthesis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 778: 146308. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146308
[35] Xu Jiapan, Li Jihong, Wei Yujie. 2020. Fractal characteristics of particle composition for soils developed from different parent materials[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(5): 1197−1205 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Yan D T, Chen D Z, Wang Q C, Wang J G. 2010. Large−scale climatic fluctuations in the latest ordovician on the Yangtze block, South China[J]. Geology, 38(7): 599−602. doi: 10.1130/G30961.1
[37] Yan Yuchun. 2008. Degradation, Restoration and Carbon Sequestration Dynamics of Typical Steppe in Inner Mongolia Under Grazing, Reclamation and Enclosure[D]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 1−213 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yang Junxiong, Liu Congqiang, Zhao Zhiqi, Ding Hu, Liu Taoze, Tu Chenglong, Fan Bailing, Huang Lu. 2016. Geochemical behavior of rare−earth element during the weathering of granite under different climatic conditions[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 36(1): 128−140 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Yue Y J, Shi P J, Zou X Y, Ye X Y, Zhu A X, Wang J A. 2015. The measurement of wind erosion through field survey and remote sensing: A case study of the Mu Us Desert, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 76(3): 1497−1514. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1516-6
[40] Zhang Chunlai, Song Changqing, Wang Zhenting, Zhou Xueyong, Wang Xuesong. 2018. Review and prospect of the study on soil wind erosion process[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 33(1): 27−41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Zhang Jiaqiong, Liu Zhang, Yang Mingyi, Zhang Fengbao, Wang Yongji, Deng Xinxin. 2018. Soil erosion and its influence factors on a slope in the wind−water erosion crisscross region on the loess plateau[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(1): 1−6,22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zhang Kun, Ji Hongbing, Chu Huashuo, Song Changshun, Wu Yanfei. 2018. Material sources and element migration characteristics of red weathering crusts in southwestern Guizhou[J]. Earth and Environment, 46(3): 257−266.
[43] Zhang Tengfei. 2020. Effect of wind erosion on soil grain size characteristics of newly cultivated land[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 40(18): 121−123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhao Haipeng, Song Hongquan, Liu Pengfei, Li Xiaoyang, Wang Tuanhui. 2019. Spatio−temporal variations of soil organic matter and nutrient losses resulted from wind erosion in northern China from 1980 to 2015[J]. Geographical Research, 38(11): 2778−2789 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhou Yong, Wang Deshui. 1999. Analysis on the present situation of farming−pastoral ecotone in China[J]. Management for Economy in Agricultural Scientific, (1): 18−20 (in Chinese).
[46] 陈儒章, 张丽萍, 邬燕虹, 邱陆旸. 2016. 侵蚀性花岗岩坡地不同地貌部位土壤剖面风化特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 53(6): 1380−1388. doi: 10.11766/trxb201603240644
[47] 陈兴仁, 周俊. 2012. 安徽江淮地区土壤微量元素分布特征及成因分析[J]. 安徽地质, 22(2): 123−129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2012.02.013
[48] 陈正新, 尉恩凤. 2002. 内蒙古阴山北麓农牧交错带退化草地复壮对策[J]. 水土保持研究, 9(1): 41−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2002.01.011
[49] 黄成敏, 龚子同. 2000. 海南岛北部玄武岩上土壤发育过程的定量研究[J]. 地理科学, 20(4): 337−342.
[50] 黄成敏, 龚子同. 2002. 海南岛北部玄武岩上土壤发生研究Ⅲ. 元素地球化学特征[J]. 土壤学报, 39(5): 643−652. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2002.05.005
[51] 黄镇国. 1996. 中国南方红色风化壳[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
[52] 简中华, 徐明星, 宋明义, 黄春雷, 郑文, 陈再宏. 2013. 不同成土母质对浦江桃形李品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 41(10): 4356−4361. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.10.045
[53] 李达净, 许端阳, 丁雪, 王子玉, 宋阿琳. 2018. 1981—2010年中国北方风蚀气候侵蚀力演变与植被动态响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(2): 15−20.
[54] 李晓丽, 申向东, 张雅静. 2006. 内蒙古阴山北部四子王旗土壤风蚀量的测试分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 29(2): 292−296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2006.02.021
[55] 李晓丽. 2007. 阴山北麓土壤风蚀的影响因素及运动特性的试验研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学,1−131.
[56] 李徐生, 韩志勇, 杨守业, 陈英勇, 王永波, 杨达源. 2007. 镇江下蜀土剖面的化学风化强度与元素迁移特征[J]. 地理学报, 62(11): 1174−1184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.11.006
[57] 李正积. 1996. 时代前缘的全息探索—岩土植物大系统研究[J]. 地质论评, 42(4): 369−372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1996.04.015
[58] 刘文景, 涂成龙, 郎赟超, 冯家毅, 李龙波, 汪齐连, 刘丛强. 2010. 喀斯特地区黄壤和石灰土剖面化学组成变化与风化成土过程[J]. 地球与环境, 38(3): 271−279.
[59] 刘争光. 2021. 土壤侵蚀研究进展[J]. 农业与技术, 41(4): 92−96.
[60] 罗莉. 2018. 岩石风化程度影响因素浅析[J]. 化工管理, (28): 19−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2018.28.015
[61] 穆兴民, 李朋飞, 高鹏, 赵广举, 孙文义. 2016. 土壤侵蚀模型在黄土高原的应用述评[J]. 人民黄河, 38(10): 100−110,114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2016.10.021
[62] 宋照亮, 张浩, 罗维均, 刘涛泽. 2020. 关键带土壤演化及其控制机制研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 39(1): 24−29.
[63] 孙厚云, 孙晓明, 贾凤超, 王艳丽, 李多杰, 李健. 2020. 河北承德锗元素生态地球化学特征及其与道地药材黄芩适生关系[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1646−1667
[64] 孙悦超, 陈智, 赵永来, 苏洁, 潘坤, 冬梅. 2013. 阴山北麓农牧交错区草地土壤风蚀测试[J]. 农业机械学报, 44(6): 143−147. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.06.025
[65] 唐克丽. 2004. 中国水土保持[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[66] 陶澍, 曹军, 李本纲, 徐福留, 陈伟元. 2001. 深圳市土壤微量元素含量成因分析[J]. 土壤学报, 38(2): 248−255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2001.02.014
[67] 王彦阁, 胡晓海, 孙海莲, 翟琇, 梁继业. 2019. 阴山北麓农牧交错区2000—2015年土壤流失及保持量变化研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 39(2): 127−135.
[68] 魏洁, 曹建军, 李希飞. 2003. 内蒙古阴山北部丘陵风蚀沙化区林业生态建设与可持续经营对策[J]. 内蒙古林业调查设计, 26(2): 14−16,42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6993.2003.02.005
[69] 吴晓光. 2019. 内蒙古阴山北麓生态退耕对土壤风蚀的影响及效应研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学,1−213.
[70] 徐加盼, 李继洪, 魏玉杰, 张光辉, 阳邦戈, 蔡崇法. 2020. 不同母质类型发育土壤颗粒组成分形特征[J]. 土壤学报, 57(5): 1197−1205. doi: 10.11766/trxb201904280012
[71] 闫玉春. 2008. 放牧、开垦与围封下内蒙古典型草原的退化与恢复及碳截存动态[D]. 北京: 北京师范大学, 1−213.
[72] 杨骏雄, 刘丛强, 赵志琦, 丁虎, 刘涛泽, 涂成龙, 范百龄, 黄露. 2016. 不同气候带花岗岩风化过程中稀土元素的地球化学行为[J]. 矿物学报, 36(1): 128−140.
[73] 张春来, 宋长青, 王振亭, 邹学勇, 王雪松. 2018. 土壤风蚀过程研究回顾与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 33(1): 27−41. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.01.0027
[74] 张加琼, 刘章, 杨明义, 张风宝, 王永吉, 邓鑫欣. 2018. 黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错带坡面土壤侵蚀特征及其影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(1): 1−6, 22.
[75] 张坤, 季宏兵, 褚华硕, 宋长顺, 吴燕飞. 2018. 黔西南喀斯特地区红色风化壳的物源及元素迁移特征[J]. 地球与环境, 46(3): 257−266.
[76] 张腾飞. 2020. 风力侵蚀作用对新增耕地土壤粒度特征的影响[J]. 农业与技术, 40(18): 121−123.
[77] 赵海鹏, 宋宏权, 刘鹏飞, 李霄阳, 王团徽. 2019. 1980—2015年风蚀影响下中国北方土壤有机质与养分流失时空特征[J]. 地理研究, 38(11): 2778−2789. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020181424
[78] 周涌, 汪德水. 1999. 中国农牧交错带现状分析[J]. 农业科研经济管理, (1): 18−20.
-




 下载:
下载: