Meso−Cenozoic tectono−thermal evolution and prospect analysis of oil and gas exploration of the eastern Kuqa Depression in the Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
研究目的 库车坳陷油气资源丰富,但与油气生成与保存相关的构造−热演化研究很薄弱。
研究方法 本研究通过对库车坳陷东部典型钻孔样品开展磷灰石裂变径迹测试分析与热史模拟,精确重建了库车坳陷东部自中生代以来的构造−热演化史,并评价了烃源岩成熟演化期次。
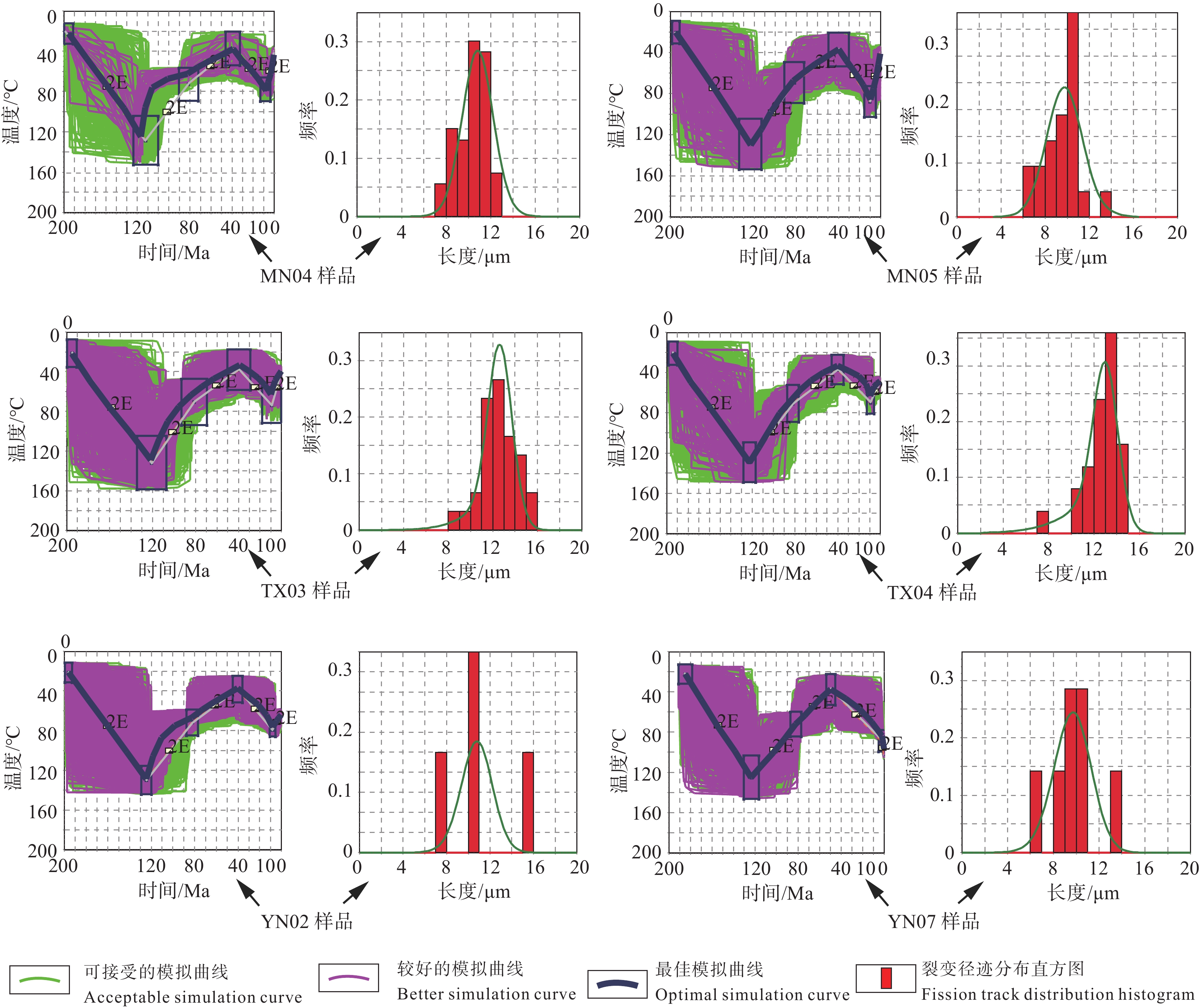
研究结果 本文基于原位LA–ICP–MS法测试的磷灰石裂变径迹年龄介于77.7~104.5 Ma,远小于地层年龄,有效地记录了晚白垩世的快速隆升事件。通过热史模拟揭示出库车坳陷东部地区自侏罗纪以来经历了早白垩世—晚始新世(120~40 Ma)和晚中新世至今(10~0 Ma)两期快速隆升事件,分别是由拉萨地块、印度板块与欧亚板块南缘碰撞的远程效应造成的。
研究结论 库车坳陷东部地区的差异性构造隆升是由南天山由北向南逐渐推进的俯冲挤压造成的。库车坳陷东部地区侏罗系烃源岩在多期沉降作用影响下表现为多阶段成熟演化模式,但受构造隆升事件的影响,曾在早白垩世—晚始新世和晚中新世至今处于停滞阶段。本研究厘定了库车坳陷东部自中生代以来的构造−热演化史,明确了主要烃源岩成熟演化过程,对区域构造演化和下一步油气勘探具有重要的指导意义。
Abstract:This paper is the result of oil and gas geological exploration engineering.
Objective Kuqa Depression is rich in oil and gas resources, but the study of tectonic–thermal evolution related to oil and gas generation and preservation is very weak.
Methods In this study, the apatite fission track test analysis and thermal history simulation were carried out on typical drilling samples in the eastern part of Kuqa Depression. The tectonic–thermal evolution history of the eastern part of Kuqa Depression since Mesozoic was accurately reconstructed, and the maturity evolution period of source rocks was evaluated.
Results The apatite fission track ages measured by in–situ LA–ICP–MS are between 77.7 Ma and 104.5 Ma, which are much smaller than the stratigraphic age, and the rapid uplift events of Late Cretaceous are effectively recorded. The thermal history simulation reveals that Kuqa Depression has experienced two periods of rapid uplift since Jurassic (Early Cretaceous–Late Eocene (120–40 Ma) and Late Miocene–present (10–0 Ma)), which are caused by the remote effect of the collision between Lhasa plate, Indian plate and the southern margin of Eurasia plate.
Conclusions The differential tectonic uplift in Kuqa Depression is caused by the subduction and compression of the southern Tianshan Mountains gradually advancing from north to south. The Jurassic source rocks in Kuqa Depression show a multi–stage mature evolution model under the influence of multi–stage subsidence. Affected by tectonic uplift events, the Jurassic source rocks mature evolution was at a stagnation stage from early Cretaceous to late Eocene and late Miocene. This study determines the tectonic–thermal evolution history of eastern Kuqa Depression since Mesozoic, and clarifies the mature evolution process of main source rocks, which have important guiding significance for regional tectonic evolution and next oil and gas exploration.
-

-
表 1 库车坳陷东部地区样品基本地质信息
Table 1. Geological information of the samples in the eastern Kubian Depression
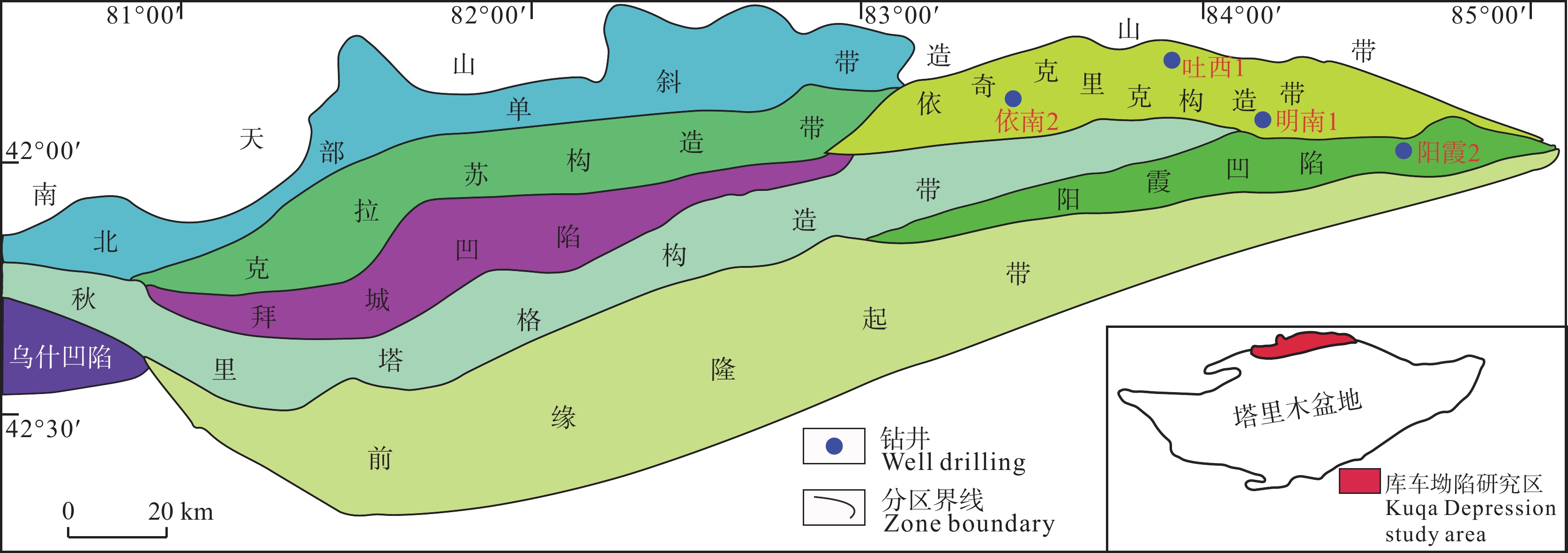
样品号 井号 深度/m 岩性 层位 TX1-03 吐西1井 1075.5 浅灰色中砂岩 下侏罗统(J1) TX1-04 吐西1井 1309.0 浅灰色中砂岩 下侏罗统(J1) YN2-02 依南2井 3407.9 红色泥质细砂岩 侏罗系(J) YN2-07 依南2井 4071.0 灰白色细砂岩 侏罗系(J) MN1-04 明南1井 964.0 灰白色中细砂岩 下侏罗统(J1) MN1-05 明南1井 1151.7 灰白色中砂岩 侏罗系(J) YX2-04 阳霞2井 5285.3 灰白色中细砂岩 侏罗系(J) 表 2 库车坳陷东部地区磷灰石裂变径迹测试结果
Table 2. Fission track results of apatites in the eastern Kuqa Depression
样品号 颗粒数(n)/个 ΣpiΩi 2σΣpiΩi ζICP 2σζICP P(χ2)/% 中值年龄/Ma 封闭径迹长度/μm Dpar/μm TX1-03 25 7.58×10−6 2.31×10−7 0.55 0.07 7.1 104.5±14.7 12.47±1.63(30) 2.65±0.32 TX1-04 30 4.91×10−6 1.28×10−7 0.55 0.07 32.2 100.6±14.6 12.63±1.55(25) 2.62±0.31 YN2-02 31 3.08×10−6 1.16×10−7 0.55 0.07 17.3 93.3±14.8 10.95±3.36(4) 2.59±0.20 YN2-07 43 5.89×10−6 1.39×10−7 0.55 0.07 20.1 91.1±13.1 13.14±1.52(22) 2.53±0.32 MN1-04 41 5.14×10−6 1.46×10−7 0.55 0.07 8.6 81.0±24.2 9.42±1.53(54) 2.51±0.20 MN1-05 27 5.35×10−6 1.80×10−7 0.55 0.07 12.3 79.1±27.6 11.66±1.36(39) 2.48±0.32 YX2-04 37 1.44×10−5 2.71×10−7 0.73 0.07 25.3 77.7±8.7 — — 注:ΣpiΩi、2σΣpiΩi分别表示某分组测试区域及区域误差值;ζICP、2σζICP分别表示基于LA–ICP–MS年龄标准的Zeta校准因子及其调整误差;P(χ2)表示卡方检验的结果,当该数值小于5%时,表示测试样品在沉积后没有经历过高温重置,记录的是仍是物源区信息,当该数值大于5%时,表示测试样品在接受沉积后经历过高温重置,此时样品的中值年龄记录的是沉积地区热历史信息;Dpar表示自发径迹蚀刻象的长轴长度。 -
[1] Allen M B, Windley B F, Chi Z, Chi Z, Zhongyan Z, Guang W. 1991. Basin evolution within and adjacent to the Tien Shan Range, NW China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 148(2): 369−378. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.148.2.0369
[2] Bullen M E, Burbank D W, Garver J I, Ye G, Abdrakhmatov. 2001. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the northwestern Tien Shan: New age estimates for the initiation of mountain building[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 113(12): 1544−1559. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1544:LCTEOT>2.0.CO;2
[3] Chang J, Qiu N S, Li J W. 2012. Tectono–thermal evolution of the northwestern edge of the Tarim Basin in China: Constraints from apatite (U–Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 61: 187−198. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.09.020
[4] Chang J, Tian Y T, Qiu N S. 2017. Mid–Late Miocene deformation of the northern Kuqa fold–and–thrust belt (southern Chinese Tian Shan): An apatite (U–Th–Sm)/He study[J]. Tectonophysics, 694: 101−113. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.12.003
[5] Cao Yuanzhi. 2009. Structural Characteristics of Piedmont Belt in Eastern Part of Kuqa Depression[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 1−74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Charreau J, Gilder S, Yan C, Dominguez S, Avouac J, Sen S, Jolivet M, Li Y, Wang W. 2006. Magneto stratigraphy of the Yaha section, Tarim Basin (China): 11 Ma acceleration in erosion and uplift of the Tian Shan Mountains[J]. Geology, 34(3): 181−184. doi: 10.1130/G22106.1
[7] Cheng Ya. 2020. Structural Analysis of Rastern Kuqa Depression: Influence of Preexisting Faults and Salt–rock Development on Tectonic Deformation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 1−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Donahue N D, Francek E R, Kiyotake E, Thomas E E, Wilhelm S. 2020. Assessing nanoparticle colloidal stability with single–particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SP–ICP–MS)[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 412(22): 1−12.
[9] Donelick R. 2005. Apatite fission–track analysis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 58(1): 49−94. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2005.58.3
[10] Du Jinhu, Tian Jun, Li Guoxin, Yang Haijun, Zang Yijie, Li Yong, Xu Zhenping, Luo Haoyu. 2019. Strategic breakthrough and prospect of Qiuritag structural belt in Kuqa Depression[J]. China Petroleum Exploration. 24(1): 16–23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Du Z L, Wang Q C, Zhou X H. 2007. Mesozoic and Cenozoic uplifting history of the Kuqa–South Tianshan Basin–Mountain system from the evidence of apatite fission track analysis[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 26(5): 399−408.
[12] Ehlers T A, Farley K A. 2003. Apatite (U–Th)/He thermochronometry: Methods and applications to problems in tectonic and surface processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 206(1/2): 1−14.
[13] Gavillot Y, Axen G J, Stockli D F, Horton B K, Fakhari M D. 2010. Timing of thrust activity in the High Zagros fold–thrust belt, Iran, from (U–Th)/He thermos chronometry[J]. Tectonics, 29(4): C4025.
[14] Jia Chengzao, Gu Jiayu, Zhang Guangya. 2002. Geological conditions of large and medium–sized gas fields in Kuqa Depression[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, (S1): 49−55 (in Chinese).
[15] Jia Chengzao, Chen Hanlin, Yang Shufeng, Lu Huafu, Zhou Yuzhang. 2003. Late Cretaceous uplift process of Kuqa Depression and its geological response[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, (3): 1−5, 15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Ketcham R A, Carter A, Donelick R A, Barbarand J, Hurford A J. 2007. Improved modeling of fission–track annealing in apatite[J]. American Mineralogist, 92(5/6): 799−810.
[17] Li Feng, Jiang Zhenxue, Li Zhuo, Xiao Zhongyao, Yuan Wenfang, Cao Shaofang. 2015. Characteristics of condensate oil in eastern Kuqa Depression and its accumulation significance[J]. Geoscience, 29(6): 1425−1434 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Li Shuangjian, Wang Qingchen, Li Zhong, Wang Daoxuan. 2006. Detrital modes of sandstones and their implications for basin–mountain evolution between the Kuqa Depression and South Tianshan Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 41(3): 465−478 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Li Yuejun, Wu Genyao, Lei Ganglin, Zhang Jingzhou, Wang Yueran, Liu Yalei. 2008. Deformation characteristics, age and mechanism of the Cenozoic foreland fold thrust belt in Kuqa, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, (3): 488−506 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Liu Z, Lu H, Jia C. 2000. Orogeny timing and fault–slip rate and their significance to the rejuvenated foreland thrusts belt of Kuche[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 27(1): 12−15.
[21] Luo Meng, Zhu Wenbin, Zheng Bihai, Zhu Xiaoqing. 2012. Mesocenozoic tectonic evolution in the Kuqa Basin: Evidence from apatite fission tracks[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 37(5): 893−902 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Ma Qian, Shu Liangshu, Zhu Wenbin. 2006. Study on the history of Mesozoic and Cenozoic burial, uplift and exhumation of Wu–Ku Highway section in Tianshan Mountains[J]. Xinjiang Geology, (2): 99−104 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Neng Yuan, Qi Jiafu, Xie Huiwen, Li Yong, Lei Ganglin, Wu Chao. 2012. Structural characteristics of northern margin of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(9): 1510−1519 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Pang Jianzhang. 2019. Apatite Fission Track Age Measurement Method Based on LA–ICP–MS and Cenozoic Extension in Qilian Mountains[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 1−122 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Qin X, Chen X H, Shao Z G, Zhang Y P, Wang Y C. 2022. New timing of the Indosinian intracontinental deformation from the Triassic growth strata in the Kuqa Depression, Southern Tianshan, China[J]. China Geology, 5(4): 771–773.
[26] Shi Gang. 2010. Influence of Structural Evolution on Oil and Gas Accumulation in Kuqa Depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1−58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Shu Liangshu, Guo Zhaojie, Zhu Wenbin, Lu Huafu, Wang Bo. 2004. Post–collision structure and basin–mountain evolution in the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, (3): 393−404 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Sobel E R, Chen J, Heermance R V. 2006a. Late Oligocene–Early Miocene initiation of shortening in the Southwestern Chinese Tian Shan: Implications for Neogene shortening rate variations[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 247(1/2): 70−81.
[29] Sobel E R, Dumitru T A. 1997. Thrusting and exhumation around the margins of the western Tarim basin during the India–Asia collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B3): 5043−5063. doi: 10.1029/96JB03267
[30] Sobel E R, Oskin M, Burbank D, Mikolaichuk A. 2006b. Exhumation of basement–cored uplifts: Example of the Kyrgyz Range quantified with Apatite Fission–track Thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 25(2): TC2008.1−TC2008.17.
[31] Stockli D F, Farley K A, Dumitru T A. 2000. Calibration of the apatite (U–Th)/He thermos chronometer on an exhumed fault block, White Mountains, California[J]. Geology, 28(11): 983−986. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<983:COTAHT>2.0.CO;2
[32] Sun Longde, Li Yuejun, Song Wenjie, Tian Zuoji, Wang Guolin, Wu Guanghui. 2002. Structure and hydrocarbon distribution in northern Tarim Basin[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, (S1): 1−13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Tang Liangjie, Yu Yixin, Yang Wenjing, Peng Gengxin, Lei Ganglin, Jin Wenzheng, Wan Guimei. 2006. Internal deformation characteristics of decollement in the front of Kuqa foreland fold thrust belt[J]. Geology in China, 33(5): 944−951 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wang Chao, Luo Jinhai, Che Zicheng, Liu Liang, Zhang Jingyi. 2009. Geochemical characteristics and LA–ICP–MS dating of zircon LA–ICP–MS in the Daban granitic pluton of Ouxidaban, Xinjiang: Implications from Paleozoic ocean basin subduction in the Tianshan Mountains, Southwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(2): 272−283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Wang Feiyu, Zhang Shuichang, Zhang Baomin, Zhao Mengjun. 1999. Organic matter maturity of Mesozoic source rocks in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, (3): 47−50, 97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Wang Weifeng, Wang Qian, Shan Xinjian. 2018. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of transverse faults in Kuqa foreland thrust belt[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 493−510 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Wilke F D, Sobel E R, Stockli D F. 2012. Apatite fission track and (U–Th)/He ages from the Higher Himalayan Crystallines, Kaghan Valley, Pakistan: Implications for an Eocene Plateau and Oligocene to Pliocene exhumation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 59: 14−23. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.06.014
[38] Wu Limin, Min Kang, Gao Jianfeng, Peng Touping. 2019. Principle experimental flow and application of LA–ICP–MS/FT fission track method[J]. Geology and Resources, 30(1): 75−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Yin A, Nie S, Craig P, Harrison T, Yang G. 1998. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan[J]. Tectonics, 17(1): 1−27. doi: 10.1029/97TC03140
[40] Yu S, Chen W, Evans N J, McInnes B I A, Yin J Y, Sun J B, Li J, Zhang B. 2014. Cenozoic uplift, exhumation and deformation in the north Kuqa Depression, China as constrained by (U–Th)/He thermos chronometry[J]. Tectonophysics, 630: 166−182. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.05.021
[41] Yu Shun, Chen Wen, Lü Xiuxiang, Noreen Evans, Brent McInnes, Yin Jiyuan, Sun Jingbo, Li Jie. 2014. Tectonic thermal evolution in the northern margin of Kucha Basin under the constraint of (U–Th)/He technology: A case study of Well Tuzi 2[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(1): 62−74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zeng Lianbo, Zhou Tianwei. 2004. Reservoir fracture distribution in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, (9): 23–25, 172, 4 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang S H, Liu C Y, Yang M H, Bai J K, Wang J Q. 2018. Latest Triassic to Early Jurassic thrusting and exhumation in the southern Ordos Basin, North China: Evidence from LA–ICP–MS–based apatite fission track thermochronology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 92(4): 1334−1348. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13630
[44] Zhang Wei, Xu Zhenping, Zhao Fengquan, Wu Shaojun, Huang Cheng, Zhang Xueqi. 2019. Tectonic deformation patterns and evolution characteristics of eastern Kuqa Depression[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(1): 48−53 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zheng Min, Meng Zifang. 2006. Division of Paleogene magnetic stratigraphy in Baicheng, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, (5): 650−656 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] 曹远志. 2009. 库车坳陷东段山前带构造特征[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 1−74.
[47] 成亚. 2020. 库车坳陷东部构造分析: 先存断裂与膏盐岩发育对构造变形的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 1−84.
[48] 杜金虎, 田军, 李国欣, 杨海军, 张义杰, 李勇, 徐振平, 罗浩渝. 2019. 库车坳陷秋里塔格构造带的战略突破与前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 24(1): 16−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.003
[49] 贾承造, 顾家裕, 张光亚. 2002. 库车拗陷大中型气田形成的地质条件[J]. 科学通报, (S1): 49−55.
[50] 贾承造, 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 卢华复, 周宇章. 2003. 库车坳陷晚白垩世隆升过程及其地质响应[J]. 石油学报, (3): 1−5, 15.
[51] 李峰, 姜振学, 李卓, 肖中尧, 袁文芳, 曹少芳. 2015. 库车坳陷东部凝析油特征及其成藏意义[J]. 现代地质, 29(6): 1425−1434.
[52] 李双建, 王清晨, 李忠, 王道轩. 2006. 砂岩碎屑组份变化对库车坳陷和南天山盆山演化的指示[J]. 地质科学, 41(3): 465−478.
[53] 李曰俊, 吴根耀, 雷刚林, 张敬洲, 王月然, 刘亚雷. 2008. 新疆库车新生代前陆褶皱冲断带的变形特征、时代和机制[J]. 地质科学, (3): 488−506.
[54] 罗梦, 朱文斌, 郑碧海, 朱晓青. 2012. 库车盆地中新生代构造演化: 磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 37(5): 893−902.
[55] 马前, 舒良树, 朱文斌. 2006. 天山乌—库公路剖面中、新生代埋藏、隆升及剥露史研究[J]. 新疆地质, (2): 99−104.
[56] 能源, 漆家福, 谢会文, 李勇, 雷刚林, 吴超. 2012. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部边缘构造特征[J]. 地质通报, 31(9): 1510−1519.
[57] 庞建章. 2019. 基于LA–ICP–MS的磷灰石裂变径迹年龄测试方法及祁连山新生代扩展研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 1−122.
[58] 石刚. 2010. 库车坳陷构造演化对油气成藏的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1−58.
[59] 舒良树, 郭召杰, 朱文斌, 卢华复, 王博. 2004. 天山地区碰撞后构造与盆山演化[J]. 高校地质学报, (3): 393−404.
[60] 孙龙德, 李曰俊, 宋文杰, 田作基, 王国林, 邬光辉. 2002. 塔里木盆地北部构造与油气分布规律[J]. 地质科学, (S1): 1−13.
[61] 汤良杰, 余一欣, 杨文静, 彭更新, 雷刚林, 金文正, 万桂梅. 2006. 库车前陆褶皱冲断带前缘滑脱层内部变形特征[J]. 中国地质, 33(5): 944−951.
[62] 王超, 罗金海, 车自成, 刘良, 张敬艺. 2009. 新疆欧西达坂花岗质岩体地球化学特征和锆石LA–ICP–MS定年: 西南天山古生代洋盆俯冲作用过程的启示[J]. 地质学报, 83(2): 272−283. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.02.012
[63] 王飞宇, 张水昌, 张宝民, 赵孟军. 1999. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷中生界烃源岩有机质成熟度[J]. 新疆石油地质, (3): 47−50, 97.
[64] 王伟锋, 王乾, 单新建. 2018. 库车前陆冲断带横断层发育特征及其形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 493−510.
[65] 武利民, 闵康, 高剑峰, 彭头平. 2021. 裂变径迹LA–ICP–MS/FT法原理、实验流程和应用[J]. 地质与资源, 30(1): 75−84.
[66] 喻顺, 陈文, 吕修祥, Noreen Evans, Brent McInnes, 尹继元, 孙敬博, 李洁. 2014. (U–Th)/He技术约束下库车盆地北缘构造热演化—以吐孜2井为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(1): 62−74.
[67] 曾联波, 周天伟. 2004. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷储层裂缝分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, (9): 23–25, 172, 4.
[68] 张玮, 徐振平, 赵凤全, 吴少军, 黄诚, 章学岐. 2019. 库车坳陷东部构造变形样式及演化特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 40(1): 48−53. doi: 10.7657/XJPG20190107
[69] 郑民, 孟自芳. 2006. 新疆拜城古近系磁性地层划分[J]. 沉积学报, (5): 650−656. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.05.005
-



 下载:
下载: