Characteristics and driving mechanisms of evolution of groundwater chemistry in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain and its exploitation and utilization suggestions
-
摘要:
研究目的 地下水是保障黄淮海平原生产、生活所需的主要水资源之一。在人类活动的影响下,地下水环境恶化已成为制约社会经济发展和生态平衡的重要因素。深入探究地下水化学演化特征及其形成机制,可为地下水资源的合理开发利用提供重要参考依据。
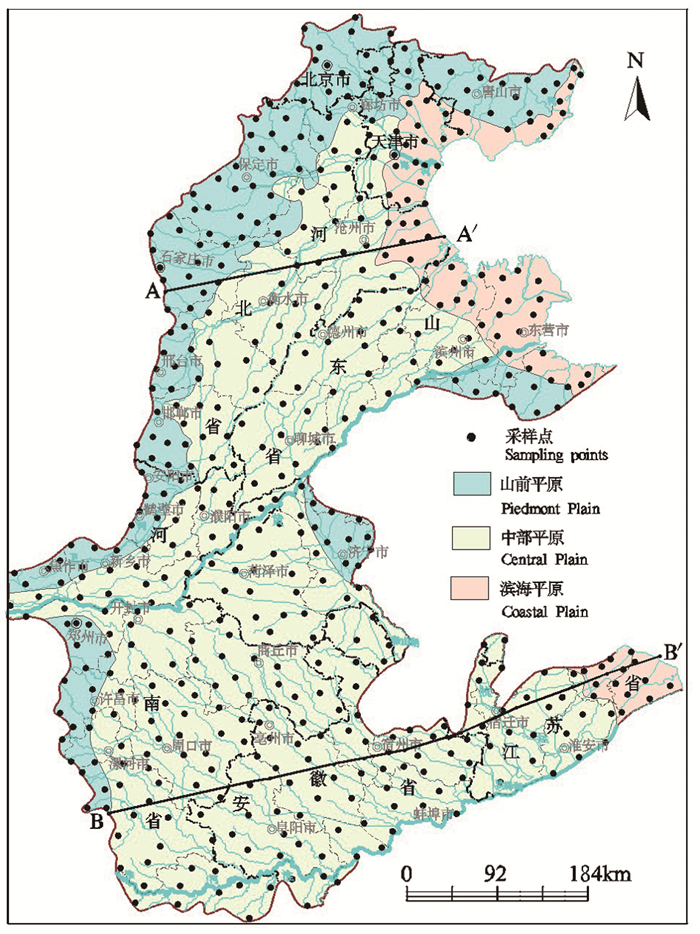
研究方法 本文将黄淮海平原分为山前平原、中部平原、滨海平原三个水文地质单元,综合运用Piper三线图、Gibbs图、主成分分析等方法,研究了中国黄淮海平原的地下水化学特征及其形成机制。
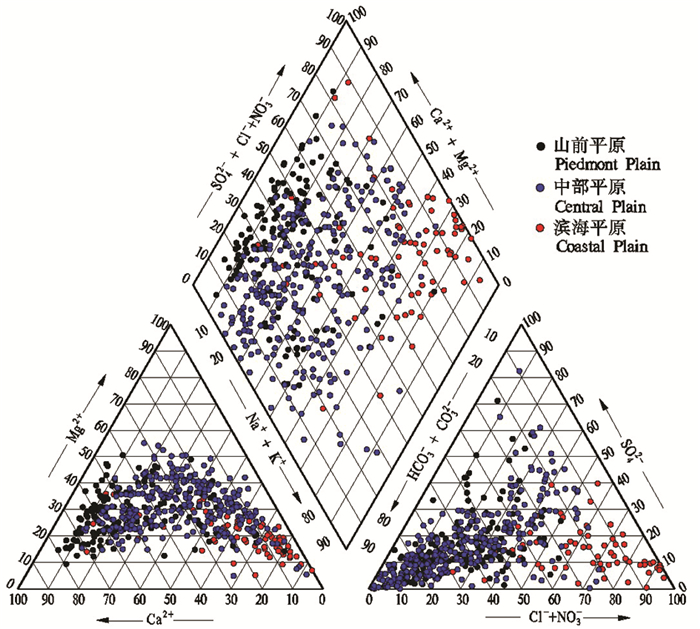
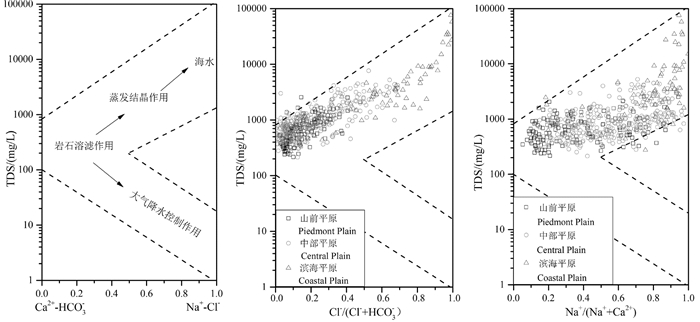
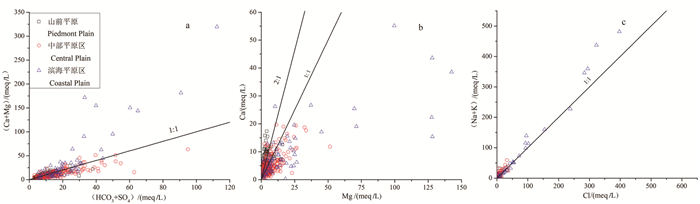
研究结果 结果显示,从山前平原到中部平原再到滨海平原地下水中TDS含量逐渐升高,由淡水逐渐演化为微咸水、咸水、盐水、卤水;研究区地下水化学类型从山前平原的44种增至中部平原的74种,而后下降至滨海平原的22种;其中,山前平原地下水化学类型以HCO3-Ca·Mg、CO3-Ca为主,主要受控于一个4因素模式,相比之下,中部平原和滨海平原地下水化学则分别受控于3因素模式。
结论 黄淮海平原地下水化学特征呈明显分带性,从山前平原到中部平原到滨海平原地下水化学类型由CO3型逐渐演化为CO3·SO4型、CO3·Cl型、SO4型、SO4·Cl型,最终演化为Cl型水。研究区地下水化学在空间尺度上主要受控于多种自然因素(岩石风化、蒸发浓缩和阳离子交替吸附、海水入侵),其在时间尺度上明显受多种人类活动(地下水超采、土地利用变化、生活污水、化肥、动物粪便)的影响。针对山前平原至滨海平原各区不同的地下水化学特征及其人类活动影响,有针对性地提出了黄淮海平原地下水资源开发利用方面的管控建议。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survy engineering.
Objective Groundwater is one of the major water resources to supply water for the production and daily life of human activities in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain (HP). The deterioration of groundwater environment has become an important factor restricting social and economic development and ecological balance at the conditions of human activities. Understanding the characteristics and driving mechanisms of evolution of groundwater chemistry can provide an important reference for the rational development and utilization of groundwater resources.
Methods In this paper, the HP is divided into three hydrogeological units including piedmont plain, central plain, and coastal plain. The characteristics and driving mechanisms of evolution of groundwater chemistry in HP in China are studied by using Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram, and principal component analysis.
Results Results showed that TDS concentrations in groundwater increased gradually from piedmont plain to coastal plain, and groundwater was evolved from freshwater to brine via brackish water and salt water. Groundwater in the study area was from 44 hydrochemical facies in the piedmont plain increased to 74 hydrochemical facies in the central plain, and then decreased to 22 hydrochemical facies in the coastal plain. Among them, the hydrochemical facies of groundwater in the piedmont plain were dominated by CO3-Ca · Mg and CO3-Ca, and was mainly controlled by a 4-factors model, by contrast, groundwater chemistry in the central and coastal plains was controlled by two 3-factors models, respectively.
Conclusions The chemical characteristics of groundwater in the HP are obviously zonal, and the hydrochemical facies of groundwater from the piedmont plain to the coastal plain was evolved gradually from CO3 facies to CO3 · SO4 facies, CO3 · Cl facies, SO4 facies, as well as SO4 · Cl facies, and finally convert to Cl facies. The groundwater chemistry in the study area is mainly controlled by a variety of natural factors such as rock weathering, evaporative concentration, cation alternate adsorption, and seawater intrusion on the spatial aspect, and is obviously affected by various human activities (e.g., groundwater overexploitation, land use change, domestic sewage, fertilizers, and animal manure) on the time aspect. According to the different chemical characteristics of groundwater and the impact of human activities in the areas from piedmont plain to coastal plain, the management and control suggestions on the development and utilization of groundwater resources in the HP are put forward.
-

-
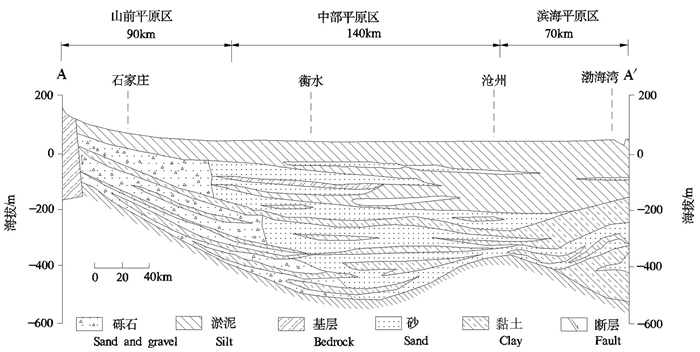
图 2 石家庄—渤海湾水文地质剖面图(A-A'剖面)(据张宗祜和李烈荣,2004)
Figure 2.
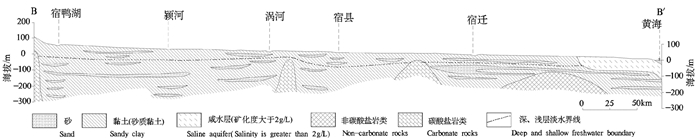
图 3 驻马店—黄海水文地质剖面图(B-B'剖面)(据国家地质总局水文地质工程地质研究所,1979)
Figure 3.
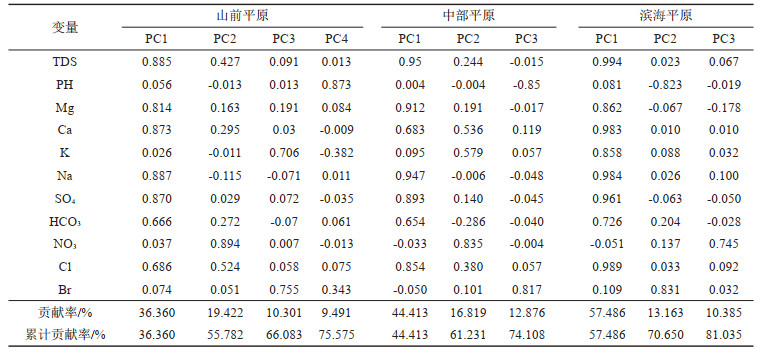
表 1 地下水主要离子含量及统计分析(单位:mg/L,pH除外)
Table 1. Statistics of chemical compositions in shallow groundwater of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain(unit: mg/L, except for pH)
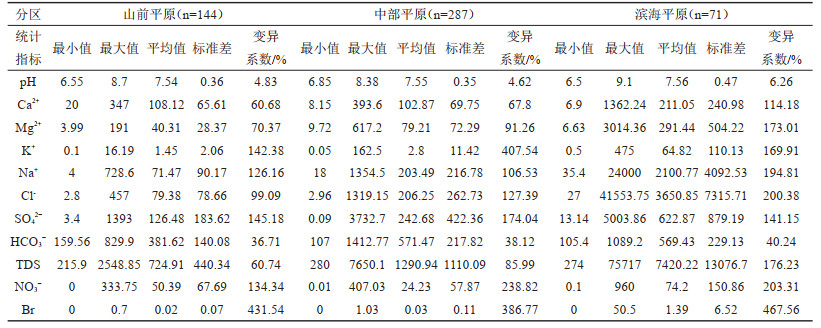
表 2 不同水文地质单元地下水化学的主成分(PC)载荷
Table 2. Principal component (PC) loadings of groundwater chemistry in different hydrogeological units
-
Abdelkader R, Larbri D, Rihab H, Fethi B, Chemseddine F, Azzedine H. 2012. Geochemical characterization of groundwater from shallow aquifer surrouding Fetzara Lake N.E. Algeria[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12517-010-0202-6
Abhijit M, Alan E F. 2008. Deeper groundwater chemistry and geochemical modeling of the arsenic affected western Bengal basin, West Bengal, India[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 23(4): 863-894. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.07.011
Borzi G, Tanjal C, Santucci L, Carol E. 2019. Geochemical mechanisms controlling the isotopic and chemical composition of groundwater and surface water in a sector of the Pampean plain (Argentina)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 683: 455-469. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.168
Carol E, Mas-Pla J, Kruse E. 2013. Interaction between continental and estuarine waters in the wetlands of the northern coastal plain of Samborombón Bay, Argentina[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 34(7): 152-163.
Chen Zhongyu, Wang Ying, Liu Jun, Wei Wen. 2010. Groundwater changes of selected groundwater systems in northern China in recent fifty years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 30(1): 115-126(in Chinese with English abstract).
China Geological Survey. 2012. Handbook of Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House(in Chinese).
Dalila Z, Abderrahmane B, Abderrahmane B, Lahcen B, Chemseddine F. 2016. Investigation of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics using the multivariate statistical analysis in Ain Djacer area, Eastern Algeria[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(56): 26993-27002. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2016.1180474
Fang H, Lin Z F, Fu X L. 2021. Spatial variation, water quality, and health risk assessment of trace elements in groundwater in Beijing and Shijiazhuang, North China Plain[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(40): 57046-57059. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14557-3
Fei Yuhong, Miao Jinxiang, Zhang Zhaoji, Chen Zongyu, Song Haibo, Yang Mei. 2009. Analysis on evolution of groundwaterdepression cones and its leading factors in North China Plain[J]. Resources Science, 31(3): 394-399(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gan L, Huang G X, Pei L X, Gan Y J, Liu C Y, Yang M N, Han D Y, Song J M. 2022. Distributions, origins, and health-risk assessment of nitrate in groundwater in typical alluvial-pluvial fans, North China Plain[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29: 17031-17048. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17067-4
Ge Dazhuan, Long Hualou, Li Yurui, Zhang Yingnan, Tu Shuangshuang. 2018. The Spatio-temporal pattern of multifunctional transformation of China's grain production system in the process of urbanization: The case of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Economic Geography, 38(4): 147-156, 182(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang G X, Liu C Y, Sun J C, Zhang M, Jing J H, Li L P. 2018. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 625: 510-518. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.322
Huang Jinou, Xian Yang, Li Wei, Zhang Dazheng, Zhuang Xiaoming. 2021. Hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater flow system in the typical coastal plain: A case study of Hangjiahu Plain[J]. Earth Science, 46(7): 2565-2582(in Chinese with English abstract).
Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, State General Administration of Geology. 1979. Hydrogeological Atlas of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: SinoMaps Press (in Chinese).
Jia Y F, Xi B D, Jiang Y H, Guo H M, Yang Y, Lian X Y, Han S B. 2018. Distribution, formation and human-induced evolution of geogenic contaminated groundwater in China: A Review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 643: 967-993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.201
Jiang Tisheng, Qu Cixiao, Wang Mingyu, Hu Bo. 2017. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater and the origin in the Pinggu plain, Beijing[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 31(11): 122-127(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Tisheng, Yang Zhongshan, Huang Zhenfang, Shi Junjie, Cai Le. 2010. Tendency and mechanism analysis of total hardness in shallow groundwater in the suburb of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 37(4): 33-37(in Chinese with English abstract).
Kortatsi B K. 2007. Hydrochemical framework of groundwater in the Ankobra Basin, Ghana[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 13(1): 41-74. doi: 10.1007/s10498-006-9006-4
Lei Ming, Kong Xiangbin, Zhang Xueliang, Wu Fangfang. 2017. Land use change and impact on groundwater storage in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Resources Science, 39(6): 1099-1116(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li C C, Gao X B, Wang Y X. 2015. Hydrogeochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater at Yuncheng Basin, northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 508: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.045
Li Shixiong, Li Duoding, Hao Hongqiang. 2006. The distribution characters and origin mechanics of ground fissures hazard in Hebei Plain[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 14(2): 178-183(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenpeng, Wang Longfeng, Yang Huifeng, Zheng Yuejun, Cao Wengeng, Liu Ke. 2020. The groundwater overexploitation status and countermeasure suggestions of the North China Plain[J]. China Water Resources, (13): 26-30(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li X H, Wang R, Li J F. 2018. Study on hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in eastern Songnen Plain[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 6(3): 161-170.
Li Zhenghong, Sun Jichao, Wang Shan, Guo Xiuhong. 2005. Assessment of the quality of groundwater in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (4): 51-55(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Yuanqing, Zhou Le, He Jin, An Yonghui, Fu Lei, Gong Lei, Yuan Liming. 2015. Research status and trend of shallow brackish exploitation in North China Plain[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 34(1): 137-141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zhongpei, Wang Fuqiang, Yu Furong. 2012. Variation of shallow groundwater level in Shijiazhuang Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 10(5): 124-127(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma J Z, Ding Z Y, Edmunds W M, Gates J B, Huang T M. 2009. Limits to recharge of groundwater from Xizang plateau to the Gobi desert, implications for water management in the mountain front[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 364: 128-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.10.010
Peña-Haro S, Llopis-Albert C, Pulido-Velazquez M, Pulido-Velazquez D. 2010. Fertilizer standards for controlling groundwater nitrate pollution from agriculture: El Salobral-Los Llanos case study, Spain[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 392: 174-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.08.006
Qiao Guangjian, Sun Meiying, Wang Bin. 2010. Analysis of cause of sharp decrease of wetlands in Hebei Plain[J]. Water Resources Protection, 26(3): 33-37(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qiao Xiaohui, Chen Jianping, Wang Mingyu, Sun Jialong, Jiang Tisheng. 2013. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in groundwater from the piedmont to coastal areas in the North China Plain [J]. Earth and Environment, 41(3): 209-215(in Chinese with English abstract).
Su Qiao, Yu Hongjun, Xu Xingyong, Yao Jing, Jiang Xingyu. 2011. Hydrochemical characteristics of underground brine in littoral Plain South of Laizhou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 29(2): 163-169(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Teng Yanguo, Zuo Rui, Wang Jinsheng, Lin Xueyu. 2010. Progress in geochemistry of regional groundwater evolution[J]. Advances in Water Science, 21(4): 127-136(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tian X, Fei Y H, Zhang Z J, Li Y S, Dun Y, Guo C Y. 2017. Analysis on hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in strongly exploited area in Hutuo River Plain[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 5(2): 130-139. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2017.9280013
Wan Changyuan, Wang Mingyu, Wang Huifang, Chen Jianping, Zhang Min, Chen Yawei. 2014. Temporal and spatial distributions of nitrogen contamination in groundwater along the typical cross-sections of the North China Plain[J]. Earth and Environment, 42(4): 472-479(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang J J, Liang X, Liu Y F, Jin M G, Knappett P S, Liu Y L. 2019. Hydrogeochemical evolution along groundwater flow paths in the Manas River Basin, Northwest China[J]. Ground Water, 57(4): 575-589. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12829
Wang Shiqin, Zhang Wenbo, Kong Xiaole. 2018. Spatial distribution characteristics of nitrate in shallow groundwater of the agricultural area of the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 26(10): 1476-1482(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiaoguang, Guo Changlai, He Haiyang, Liu Qiang. 2019. Study on the classification of groundewater depression cone[J]. Geology and Resources, 28(5): 487-492(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiaoxi, Wang Wenke, Wang Zhoufeng, Zhao Jiali, Xie Hailan, Wang Xiaodan. 2014. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of river water and groundwater along the downstream Luanhe River, northeastern China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 41(1): 25-33, 73(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Y S, Shen S L, Du Y J. 2018. Geological and hydrogeological environment with geohazards during underground construction in Hangzhou: A review[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11(18): 544 doi: 10.1007/s12517-018-3894-7
Yang Huifeng, Cao Wengeng, Zhi Chuanshun, Li Zeyan, Bao Xilin, Ren Yu, Liu Futian, Fan Cunliang, Wang Shufang, Wang Yabin. 2021. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on its overexploitation treatment[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1142-1155(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Guangxin, Deng Wei, He Yan, Ramsis Salama. 2006. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of groundwater in Songnen Plain, Northeast China[J]. Adwances in Water Science, 17(1): 20-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xiaolong, Sun Yongfu, Liu Dunwu. 2005. Analysis of groundwater in the Yellow River Delta Areas[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 21(6): 26-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xiyu, Zhang Guanghui, Yan Mingjiang. 2021. Evolution characteristics of total dissolved solids in the groundwater level funnel area in the Hufu piedmont plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(3): 72-81(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xueliang, Kong Xiangbin. 2014. Cropland sustainable use impacted by groundwater depletion in China's HHH Plains[J]. China Land Sciences, 28(5): 90-96(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zhaoji, Fei Yuhong, Chen Zongyu, Zhao Zongzhuang, Xie Zhenhua, Wang Yabin, Miao Puxiang, Yang Lizhi, Shao Jingli, Jin Menggui, Xu Guangming, Yang Qiqing. 2009. The Sustainable Utilization Evaluation Survey of Groundwater in North China Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House(in Chinese).
Zhang Zonghu, Li Lierong. 2004. Groundwater Resources in China (Comprehensive Volume)[M]. Beijing: SinoMaps Press (in Chinese).
Zhang Zonghu, Shi Dehong, Shen Zhaoli, Zhong Zuoshen, Xue Yuqun. 1997. Evolution and development of groundwater environment in North China Plain under human activities[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 18(4): 337-344(in Chinese with English abstract).
陈宗宇, 王莹, 刘君, 卫文. 2010. 近50年来我国北方典型区域地下水演化特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 30(1): 115-126.
费宇红, 苗晋祥, 张兆吉, 陈宗宇, 宋海波, 杨梅. 2009. 华北平原地下水降落漏斗演变及主导因素分析[J]. 资源科学, 31(3): 394-399.
戈大专, 龙花楼, 李裕瑞, 张英男, 屠爽爽. 2018. 城镇化进程中我国粮食生产系统多功能转型时空格局研究——以黄淮海地区为例[J]. 经济地理, 38(4): 147-156, 182.
国家地质总局水文地质工程地质研究所. 1979. 中华人民共和国水文地质图集[M]. 北京: 地图出版社.
黄金瓯, 鲜阳, 黎伟, 张达政, 庄晓明. 2021. 典型滨海平原区地下水流系统水化学场演化及成因: 以杭嘉湖平原为例[J]. 地球科学, 46(7): 2565-2582.
姜体胜, 曲辞晓, 王明玉, 胡波. 2017. 北京平谷平原区浅层地下水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 31(11): 122-127.
姜体胜, 杨忠山, 黄振芳, 史俊杰, 蔡乐. 2010. 北京郊区浅层地下水总硬度变化趋势及其机理浅析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 37(4): 33-37.
雷鸣, 孔祥斌, 张雪靓, 吴芳芳. 2017. 黄淮海平原区土地利用变化对地下水资源量变化的影响[J]. 资源科学, 39(6): 1099-1116.
李世雄, 李守定, 郜洪强. 2006. 河北平原地裂缝分布特征及成因机制研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 14(2): 178-183.
李文鹏, 王龙凤, 杨会峰, 郑跃军, 曹文庚, 刘可. 2020. 华北平原地下水超采状况与治理对策建议[J]. 中国水利, (13): 26-30.
李政红, 孙继朝, 汪珊, 郭秀红. 2005. 黄淮海平原地下水质量综合评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, (4): 51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.04.013
刘元晴, 周乐, 何锦, 何锦, 安永会, 付雷, 龚磊, 袁黎明. 2015. 华北平原浅层(微)咸水开发利用现状及趋势[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 34(1): 137-141.
刘中培, 王富强, 于福荣. 2012. 石家庄平原区浅层地下水位变化研究[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 10(5): 124-127.
乔光建, 孙梅英, 王斌. 2010. 河北省平原湿地减少原因分析[J]. 水资源保护, 26(3): 33-37.
乔晓辉, 陈建平, 王明玉, 孙嘉龙, 姜体胜. 2013. 华北平原地下水重金属山前至滨海空间分布特征与规律[J]. 地球与环境, 41(3): 209-215.
苏乔, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 姚菁, 姜兴钰. 2011. 莱州湾南岸滨海平原地下卤水水化学特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 29(2): 163-169.
孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽. 2018. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1128-1141 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12029/gc20180604
滕彦国, 左锐, 王金生, 林学钰. 2010. 区域地下水演化的地球化学研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 21(4): 127-136.
万长园, 王明玉, 王慧芳, 陈建平, 张敏, 陈亚伟. 2014. 华北平原典型剖面地下水三氮污染时空分布特征[J]. 地球与环境, 42(4): 472-479.
王仕琴, 郑文波, 孔晓乐. 2018. 华北农区浅层地下水硝酸盐分布特征及其空间差异性[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 26(10): 1476-1482.
王晓光, 郭常来, 何海洋, 刘强. 2019. 地下水降落漏斗分类研究[J]. 地质与资源, 28(5): 487-492.
王晓曦, 王文科, 王周锋, 赵佳莉, 谢海澜, 王小丹. 2014. 滦河下游河水及沿岸地下水水化学特征及其形成作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 41(1): 25-33, 73.
杨会峰, 曹文庚, 支传顺, 李泽岩, 包锡麟, 任宇, 柳富田, 范存良, 王树芳, 王亚斌. 2021. 近40年来华北平原地下水位演变研究及其超采治理建议[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1142-1155. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12029/gc20210411
章光新, 邓伟, 何岩, Ramsis Salama. 2006. 中国东北松嫩平原地下水水化学特征与演变规律[J]. 水科学进展, 17(1): 20-28.
张效龙, 孙永福, 刘敦武. 2005. 黄河三角洲地区地下水分析[J]. 海洋地质动态, 21(6): 26-28.
张希雨, 张光辉, 严明疆. 2021. 滹滏平原漏斗区地下水溶解性总固体演变特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(3): 72-81.
张雪靓, 孔祥斌. 2014. 黄淮海平原地下水危机下的耕地资源可持续利用[J]. 中国土地科学, 28(5): 90-96.
张兆吉, 费宇红, 陈宗宇, 赵宗壮, 谢振华, 王亚斌, 苗普祥, 杨丽芝, 邵景力, 靳孟贵, 许广明, 杨齐青. 2009. 华北平原地下水可持续利用调查评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
张宗祜, 李烈荣. 2004. 中国地下水资源(综合卷)[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社.
张宗祜, 施德鸿, 沈照理, 钟佐燊, 薛禹群. 1997. 人类活动影响下华北平原地下水环境的演化与发展[J]. 地球学报, 18(4): 337-344.
中国地质调查局. 2012. 水文地质手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
-



 下载:
下载: