Prediction model of potential debris flow hazard of rainfall type in Bailong River Basin, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 泥石流灾害是白龙江流域分布广泛并常引起群死群伤的重大地质灾害,准确评价泥石流活动规模及其危险度,是泥石流危险性预警预报的前提,合理构建危险性预报模型是泥石流防灾减灾的关键。
研究方法 本文以研究区历史泥石流案例和对应降雨资料为基础数据,采用统计分析方法,通过分析形成泥石流关键地质环境条件及其相互关系,构建了白龙江流域潜在泥石流危险度定量评价模型,提出了两类泥石流危险级别临界判别模式。
研究结果 结果表明:(1)以泥石流活动规模、沟床平均比降、流域切割密度、不稳定沟床比例为判断因子的泥石流危险度动态定量计算模型,能快速准确预测未来不同工程情景和降雨频率工况下泥石流危险度;(2)影响降雨型泥石流发生的地形条件由流域面积、10°~40°斜坡坡度面积比、沟床平均纵比降等组成,降雨条件主要由泥石流爆发前的24 h累积降雨量、触发泥石流1 h降雨量或10 min降雨量等组成;(3)依据30条典型泥石流沟危险度计算结果,获得泥石流危险性临界判别值,提出了降雨型潜在泥石流危险性1 h预报模型(Ⅰ类)和10 min预报模型(Ⅱ类),其中Ⅰ类模型高危险度以上泥石流预测精度大于87.5%,Ⅱ类模型中等危险度以上泥石流预测精度大于80%,而两类预报模型验证准确率为83.3%。
结论 研究成果为泥石流精准预警预报提供了技术支撑,对建立中小尺度泥石流实时化预警系统具有一定参考意义。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological hazard survey engineering.
Objective Debris flow is a major geological disaster widely distributed in Bailong River Basin and often causes mass casualties. Accurate evaluation of the scale and risk of debris flow is the premise of the early warning and prediction of debris flow. Reasonable construction of risk prediction model is the key to debris flow disaster prevention and reduction.
Method Based on the reported debris flow cases and corresponding rainfall data in the study area, the quantitative evaluation model of potential debris flow risk in Bailong River Basin is constructed by analyzing the key geological environmental conditions and their relationship, and two kinds of critical discrimination models of debris flow risk level are proposed.
Results The results show that: (1) The dynamic quantitative calculation model of debris flow risk degree with debris flow activity scale, average gradient of gully bed, watershed cutting density and unstable gully bed ratio can be used as judgment factors to quickly and accurately predict the risk degree of debris flow under different engineering scenarios and rainfall frequencies in the future; (2) The topographic conditions affecting the occurrence of rainfall type debris flow are composed of watershed area, slope area ratio of 10 °-40 °, average longitudinal ratio of gully bed, etc; the rainfall conditions are mainly composed of 24 h cumulative rainfall before the outbreak of debris flow, 1 h rainfall or 10min rainfall triggering debris flow, etc; (3) Based on the risk calculation results of 30 typical debris flow gullies, the critical discrimination value of debris flow risk is obtained, and the 1h prediction model and 10min prediction model of potential debris flow risk of rainfall type are proposed. Among them, the prediction accuracy of debris flow above high risk of class Ⅰ model is greater than 87.5%, the prediction accuracy of debris flow above medium risk of class Ⅱ model is greater than 80%, and the verification accuracy of the two prediction models is 83.3%.
Conclusions The research results provide technical support for the accurate early warning and prediction of debris flow, and have a certain reference significance for the establishment of small and medium-sized debris flow real-time early warning system.
-

-
表 1 数据类型及数据来源
Table 1. Sources and types of data
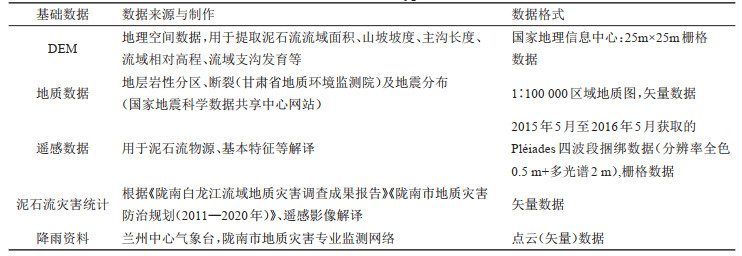
表 2 改进后单沟泥石流危险度评价因子的权重系数及转换函数
Table 2. Weight coefficient and conversion function of risk assessment factor for single gully debris flow after improvement
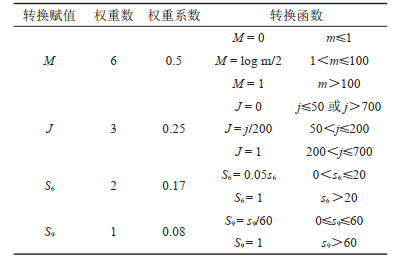
表 3 研究区30条泥石流沟不同降雨频率下泥石流规模及综合危险度
Table 3. Scale of debris flow and comprehensive risk under different rainfall frequency of 30 debris flow gullies in the study area

表 4 典型泥石流沟泥石流危险性预报综合因子参数统计
Table 4. Statistical table of comprehensive factors for debris flow risk prediction of typical debris flow gullies
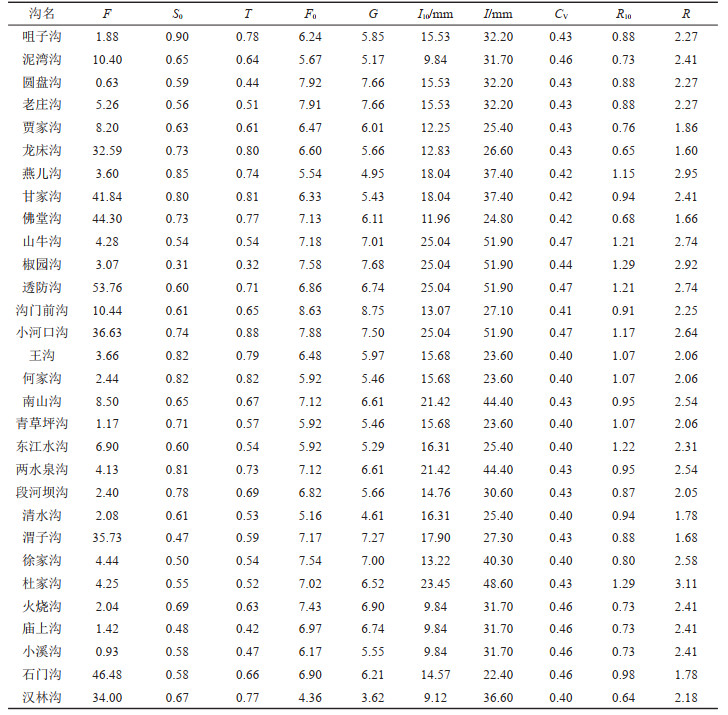
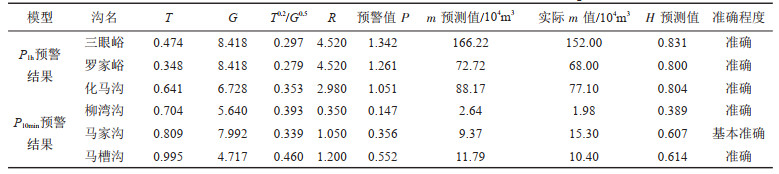
表 5 模型实例验证结果统计
Table 5. Statistical table of validation results of model examples
-
Bai Liping, Sun Jiali, Nan Yun. 2008. Analysis of the critical rainfall thresholds for mudflow in Beijing, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(5): 674-680(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cai Xiangxing, Li Honglian, Cui Bintian. 1989. Exploring and discussing of the debris flow control engineering in Macao gully[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 9(6): 50-59(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ding Guiling, Wang Yihong, Mao Jian, Yao Kang, Liu Huanhuan. 2017. A study of the rainfall threshold of debris flow forewarning in Beijing based on susceptibility analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 44(3): 136-142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao Bo, Zhang Maosheng, Zhang Chenghang, Yu Guoqiang. 2016. Rainfall threshold for debris flow in Sanyanyu valley, Zhouqu, China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 31(1): 25-28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Fuyun, Song Xiaoling, Xie Yu, Meng Xingmin. 2015. A discussion the geological hazards meteorological warning system in Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contral, 26(1): 127-133(in Chinese with English abstract).
He Chaoyang, Xu Qiang, Ju Nengpan, Huang Jian, Xiao Yang. 2018. Real-time early warning technology of debris flow based on automatic identification of rainfall process[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(3): 703-710(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lanzhou Institute of Glaciobgy and Cryopedology, Academia Science and Traffic Science Instilute of Gansu Province. 1982. China Bebris Flow in Gansu Province[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 156-181(in Chinese).
Li Shuzhen, Dai Shuang, Wang Huawei, Zhang Xiang. 2015. Fault features and their implication on distribution and formation of landslides in Bailongjiang Region[J]. Journal of Langzhou University, 51 (2): 145-152(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Xilin. 2010. Quantitative assessment on site-specific debris flow hazard and application[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 30(3): 241-245(in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo Hongdong, Li Ruidong, Zhang Bo, Cao Bo. 2019. An early waring model system for predicting meteorological risk associated with geological disasters in the Longnan area, Gansu Province based on the information value method[J]. Earth Science Fronties, 26(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract).
Meng Xingmin, Chen Guan, Guo Peng, Xiong Muqi, Janusz Wasowki. 2013. Research of landslides ans debris flow in Bailong river basin: Progrss and prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 33(4): 1-15(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qu Yongping, Tang Chuan. 2014. Preliminary study of prediction model for early waring of debris flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(1): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shang Hui, Wang Mingxuan, Luo Donghai, Feng Jiao, Wang Aijun. 2019. Single gully debris flow hazard assessment based on function assignment model and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contral, 30(1): 61-69(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tan Binyan. 1990. The study of prediction for debris flow caused by rainstorm[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 4(4): 14-20(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Gaofeng, Deng Bing, Mao Jiarui, Tian Yuntao, Ye Zhennan, Guo Ning, Gao Youlong. 2020. Prediction model of activity of rainfall-type debris flow in Bailongjiang River Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 51(5): 12-20(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Gaofeng, Ye Zhennan, Li Gang, Tian Yuntao, Deng Bing, Guo Ning, Chen Zongliang. 2019. Geological hazard risk assessment of Zhouqu county in Bailong river basin[J]. Journal of Catastrphology, 34(3): 128-133(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Gaofeng, Yang Qiang, Tian Yuntao, Ye Zhennan, Chen Zongliang, Gao Youlong, Guo Ning, Deng Bing. 2019. Establishment of assessment model for debris flow susceptibility: A case study from Shimen township to Yangtang river in the Bailong River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 36(3): 761-770(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Wei, Li Tianhong, Ni Jinren. 2012. Rapid assessment of debris flow gully hazards based on environmental factor codes[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 20(5): 874-885(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiwen, Zhang Tiejun, Feng Jun, Wang Suichan, Liu Zhiguo. 2004. Study of the geological calamity meteorogical grade prediction in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Meteorology, 22(1): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yiming, Yin Kunlong. 2018. A study of the typhoon-triggered debris flow hazard degree of a single gully[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 37(3): 124-130(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhihua, Guo Zhaocheng, Du Mingliang, Cheng Zunlan. 2011. Model study of monitoring and early warning of rainstorm induced landslide and debris flow based on digital landslide technology[J]. Earth Science Fronties, 18(5): 303-309(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhihua, Guo Zhaocheng, Du Mingliang, Cheng Zunlan. 2012. Model study of predicting rainstorm induced landslide and debris flow at Niumian gully, the focal area of 2008-05-12 Earthquake[J]. Earth Science Fronties, 19(1): 228-238(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhilu, Zhang Yan, Sun Chang. 2005. Study on geology disaster weather forecast and forewarning technique in Longnan area[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 16(1): 105-110(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Yongming, Xie Youyu. 1997. Study on prediction models of precipitation-typed debeis flow[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 6(4): 48-54(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wen Mingsheng, Liu Chuanzheng, Liu Yanhui, Fang Zhiwei. 2019. Regional warning of geological hazards in high seismic intensity area of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contral, 30(1): 10-19(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie Yongping, Zhang Xueyan, Li Yuan, Cao Hongyang. 2016. Forming conditions and quantitative assessment on Yan'er gully debrisflow hazard in Longnan of Gansu[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contral, 27(4): 50-55(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Jiwei, Yu Guoqiang, Zhang Maosheng, Cong Kai. 2017. Critical rainfall thresholds for debris flow in Zhouqu, China[J]. Mountain Research, 35(1): 39-47(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Weimin, Huang Xiao, Zhang Chunshan, Si Haibao. 2014. Deformation behavior of landslides and their foemation mechanism along Pingding-Huama active fault in Bailongjiang River Region[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 44 (2): 574-583.
Yang Xiaofeng, Zhu Jun, Cao Yungang, Gong Jing, Cao Zhenyu, Yin Lingzhi. 2017. Risk assessment of Qipangou debris flow based on determining weight method and effectiveness anslysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 28(1): 22-29(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Yan, Zhang Xujiao, Ye Peisheng, Hu Yue, Wu Zhonghai. 2012. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for risk assessment of the Malanghe debris flow gully in Baoshan area, Western Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(2/3): 351-355(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu B, Li L, Wu Y F. 2013. A formation model for debris flows in the Chenyulan river waterhed, Taiwan[J]. Natural Hazards, 68(2): 745-762. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0646-6
Yu Bin, Chu Shengming, Zhu Yuan, Xie Hong. 2013. Impacts of weathering on formation of gullied debris flow[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 33 (6): 51-56(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Bin, Wang Tao, Zhu Yuan. 2016. Research on the topographical and rainfall factors of debris flows caused by shallow landslides[J]. Advances in Water Science, 27(4): 542-550(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Bin, Yang Yonghong, Su Yongchao, Huang Wenjie, Wang Gaofeng. 2010. Research on the gisant debris flow hazards in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province on August 7, 2010[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(4): 437-444(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Bin, Zhu Yuan, Wang Tao, Chen Yuanjing, Zhu Yunbo. 2014. Prediction model for occurrence of debris flows in channels with runoff initiation mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(3): 450-455(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Bin, Zhu Yuan, Wang Tao, Zhu Yunbo. 2015. Research on the 10-minute rainfall perdiction model for debris flows[J]. Advances in Water Science, 26(3): 347-355(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Nan, Fang Zhiwei, Han Xiao, Chen Chunli, Qi Xiaobo. 2018. The study on temporal and spatial distribution law and cause of debris flow disaster in China in recent years[J]. Earth Science Fronties, 25(2): 299-308(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yongshuang, Yao Xin, Guo Changbao, Li Lingjing, Yang Zhihua, Du Guoliang. 2016. Regional warning of debris flow hazards after Wenchuan earthquake in Longmenshan region[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 51(5): 1014-1023(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Pingyi, Cheng Zhunlan, Wang Yangchun. 2000. Research of rainfall-debris flow and environment in upper reaches of Yangzi river[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 14(5): 35-62(in Chinese with English abstract).
白利平, 孙佳丽, 南赟. 2008. 北京地区泥石流灾害临界雨量阈值分析[J]. 地质通报, 27(5): 674-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.05.013
蔡祥兴, 李鸿琏, 崔炳田. 1989. 马槽沟泥石流防治工程初探[J]. 水土保持通报, 9(6): 50-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB198906007.htm
丁桂伶, 王翊虹, 冒建, 姚康, 刘欢欢. 2017. 北京市泥石流易发区降雨预警阈值研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 44(3): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201703022.htm
高波, 张茂省, 张成航, 于国强. 2016. 甘肃舟曲三眼峪泥石流降雨临界阈值[J]. 灾害学, 31(1): 25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.01.006
郭富赟, 宋晓玲, 谢煜, 孟兴民. 2015. 甘肃地质灾害气象预警技术方法探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 26(1): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201501027.htm
何朝阳, 许强, 巨能攀, 黄健, 肖洋. 2018. 基于降雨过程自动识别的泥石流实时预警技术[J]. 工程地质学报, 26(3): 703-710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201803017.htm
李淑贞, 戴霜, 王华伟, 张翔. 2015. 白龙江地区断裂构造与滑坡分布及发生关系[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 51 (2): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201502001.htm
刘希林. 2010. 沟谷泥石流危险度计算公式的由来及其应用实例[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 30(3): 241-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK201003003.htm
罗鸿东, 李瑞冬, 张勃, 曹博. 2019. 基于信息量法的地质灾害气象风险预警模型: 以甘肃省陇南地区为例[J]. 地学前缘(中国地质大学(北京); 北京大学), 26(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201906033.htm
孟兴民, 陈冠, 郭鹏, 熊木齐, Janusz Wasowki. 2013. 白龙江流域滑坡泥石流灾害研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 33(4): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201304004.htm
屈永平, 唐川. 2014. 暴雨型泥石流预警模型初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.001
尚慧, 王明轩, 罗东海, 冯皎, 王爱军. 2019. 基于函数赋值模型与模糊综合评判法单沟泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 30(1): 61-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201901007.htm
谭炳炎. 1990. 暴雨泥石流预报的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 4(4): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS199004002.htm
王高峰, 杨强, 田运涛, 叶振南, 陈宗良, 高幼龙, 郭宁, 邓兵. 2019. 泥石流易发性评价模型的构建——以白龙江流域石门乡羊汤河段为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(3): 761-770. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201903028.htm
王高峰, 邓兵, 毛佳睿, 田运涛, 叶振南, 郭宁, 高幼龙. 2020. 白龙江流域降雨型泥石流活动规模预测模型[J]. 科学技术与工程, 51(5): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202026013.htm
王高峰, 叶振南, 李刚, 田运涛, 邓兵, 郭宁, 陈宗良. 2019. 白龙江流域舟曲县城区地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 灾害学, 34(3): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2019.03.024
王伟, 李天宏, 倪晋仁. 2012. 基于环境要素编码的泥石流沟道危险度快速识别[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 20(5): 874-885. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0930.2012.05.013
王锡稳, 张铁军, 冯军, 王遂缠, 刘治国. 2004. 甘肃地质灾害气象等级预报研究[J]. 干旱研究, 22(1): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSQX200401002.htm
王一鸣, 殷坤龙. 2018. 台风暴雨型泥石流单沟危险度研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 37(3): 124-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201803018.htm
王志禄, 张燕, 孙畅. 2005. 陇南地质灾害气象预报及预警技术研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 16(1): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2005.01.025
王治华, 郭兆成, 杜明亮, 程尊兰. 2011. 基于数字滑坡技术的暴雨滑坡、泥石流预警、监测模型研究[J]. 地学前缘, 18(5): 303-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201105028.htm
王治华, 郭兆成, 杜明亮, 程尊兰. 2012. 5.12震源区牛眠沟暴雨滑坡泥石流预测模型[J]. 地学前缘, 19(1): 228-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201026.htm
魏永明, 谢又矛. 1997. 降雨型泥石流(水石流)预报模型研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 6(4): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH704.007.htm
温铭生, 刘传正, 刘艳辉, 方志伟. 2019. 汶川地震高烈度区崩滑流灾害区域预警[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 30(1): 10-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201901002.htm
解咏平, 张雪燕, 李源, 曹洪洋. 2016. 甘肃陇南燕儿沟泥石流条件及其危险度评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 27(4): 50-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201604009.htm
徐继维, 于国强, 张茂省, 丛凯. 2017. 舟曲地区泥石流降雨临界阈值[J]. 山地学报, 35(1): 39-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201701006.htm
杨艳, 张绪教, 叶培盛, 胡悦, 吴中海. 2012. 基于模糊数学法评价滇西保山地区麻榔河泥石流沟的危险性[J]. 地质通报, 31(2/3): 351-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2012Z1018.htm
杨为民, 黄晓, 张春山, 司海宝. 2014. 白龙江流域坪定-化马断裂带滑坡特征及其形成演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44 (2): 574-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201402017.htm
杨小凤, 朱军, 曹云刚, 龚竞, 曹振宇, 尹灵芝. 2017. 基于不同方法的泥石流危险性评价对比分析——以四川汶川七盘沟泥石流为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 28(1): 22-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201701004.htm
余斌, 杨永红, 苏永超, 黄文杰, 王高峰. 2010. 甘肃省舟曲8.7特点泥石流调查研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 18(4): 437-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.04.001
余斌, 褚胜名, 朱渊, 谢洪. 2013. 风化作用对沟谷型泥石流发育环境的影响研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 33 (6): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201306011.htm
余斌, 王涛, 朱渊, 等. 2016. 浅层滑坡诱发沟谷泥石流的地形和降雨条件[J]. 水科学进展, 27(4): 542-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201604010.htm
余斌, 朱渊, 王涛, 陈源井, 朱云波. 2014. 沟床启动型泥石流预报研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(3): 450-455.
余斌, 朱渊, 王涛, 朱云波. 2015. 沟床启动型泥石流的10min降雨预报研究[J]. 水科学进展, 26(3): 347-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201503007.htm
张楠, 方志伟, 韩笑, 陈春利, 祁小博. 2018. 近年来我国泥石流灾害时空分布规律及成因分析[J]. 地学前缘(中国地质大学(北京); 北京大学), 25(2): 299-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201802036.htm
张永双, 姚鑫, 郭长宝, 李凌婧, 杨志华, 杜国梁. 2016. 龙门山地区震后泥石流灾害区域预警研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 51(5): 1014-1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.026
中国科学院兰州冰川冻土研究所. 1982. 甘肃泥石流[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版, 156-181.
朱平一, 程尊兰, 汪阳春. 2000. 长江上游暴雨泥石流与环境研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 14(5): 35-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2000.05.006
-




 下载:
下载:



