Evolution of karst geothermal system and its geothermal resource potential in Taiyuan Basin
-
摘要:
研究目的 太原盆地作为优质岩溶热储分布与城市供暖需求匹配良好的地区之一,其岩溶地热系统的形成演化与成因要素的研究对本区地热资源的整体开发以及断陷盆地型地热资源展布规律的认识均具有重要的指导意义。
研究方法 本文在综合前人研究成果与最新54口地热井资料的基础上,分析了太原盆地岩溶地热系统的热源、热储展布和水热动力学特征,并分8个单元评价了地热资源量。
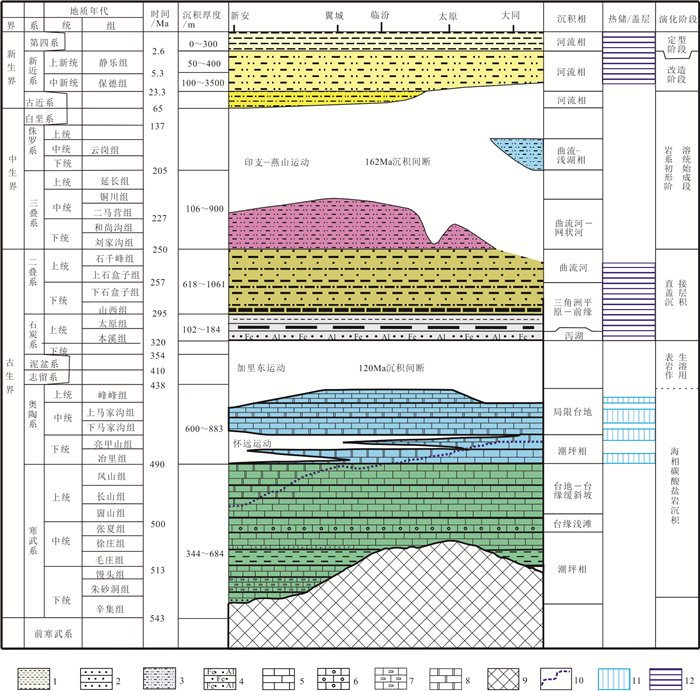
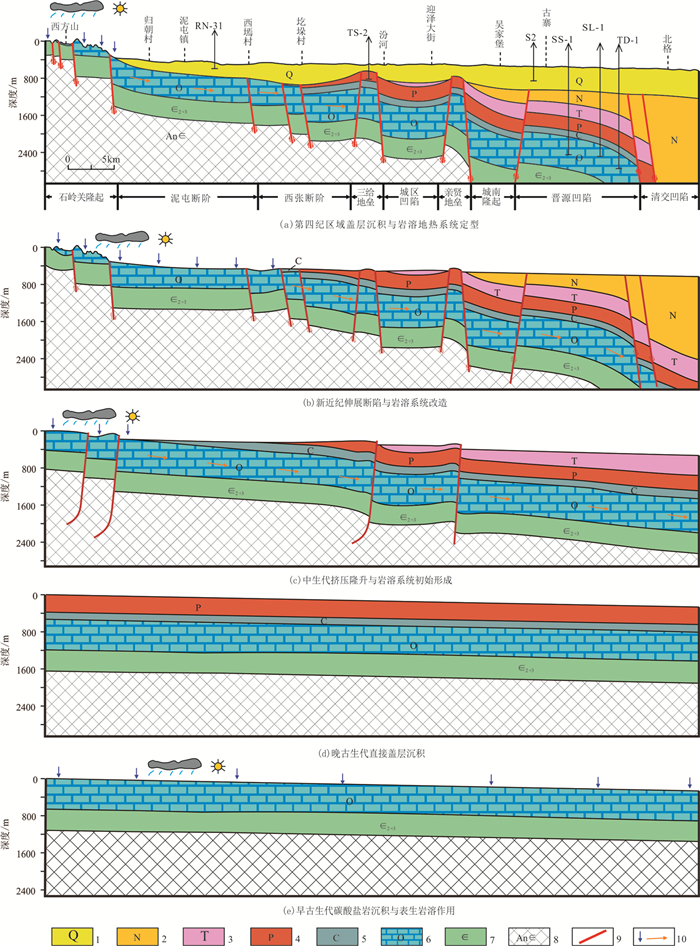
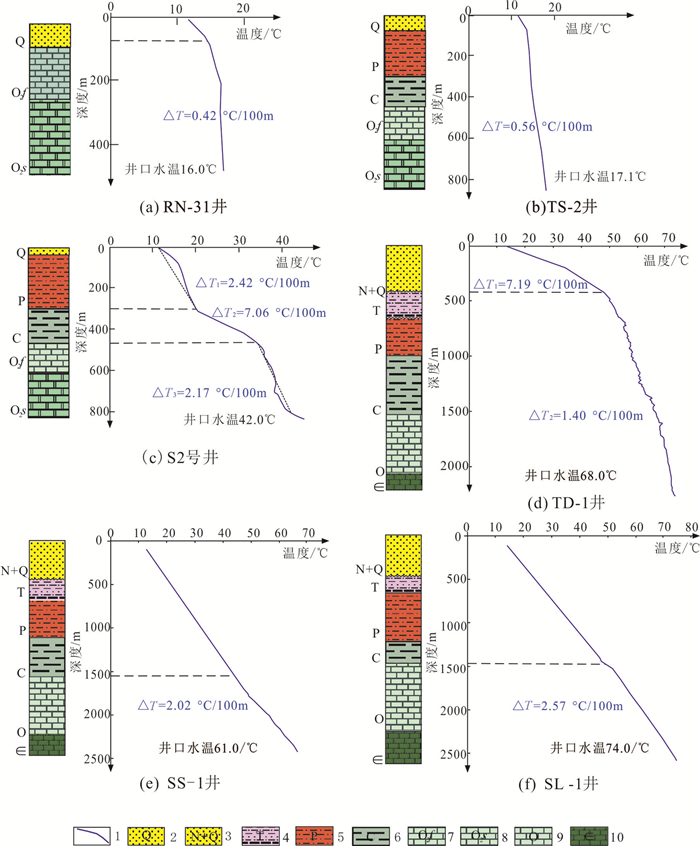
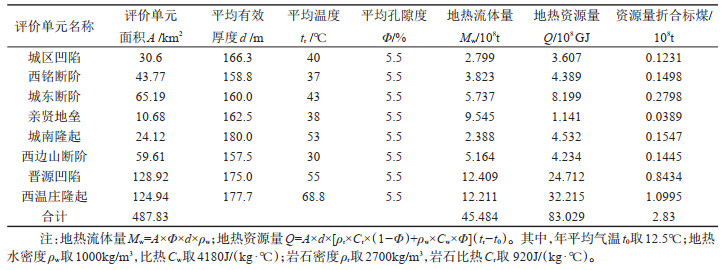
研究结果 结果表明,岩溶热储发育的层位主要为华北板块广泛分布的下古生界奥陶系,经历了早古生代末的表生岩溶、晚古生代的直接盖层沉积、中生代岩溶地热系统初始形成、新近纪的改造与第四纪最终定型等5个阶段。该地热系统的热源来自于新生代裂谷盆地产生的高大地热流(最高达79.12 mW/m2),热传递方式可分为强烈对流型(盆地边缘)和热传导型(盆地内部)截然不同的两类。热储储集性能具纵向分层、平面分带特征。在纵向上识别出15~20层有效储集段,累计厚度160~180 m,可划分为3~4层主力含水段;在平面上有利储集带主要受NE向隐伏构造的控制,且主力含水层在运移过程中易发生“越流”现象。盆地中段的奥陶系热储因埋藏适中(约400~1900 m)、且储层温度较高(30~75℃),是最有利的勘探开发区。依据热储体积法评价出太原盆地岩溶地热系统可利用的静态地热资源量为83.03×108 GJ,折合标煤2.83×108 t。
结论 年开采地热资源量可满足1502万m2的供暖面积。鉴于目前已开发资源仅占可开发的23.3%,开发潜力巨大。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
Objective The Taiyuan Basin is one of the areas where its distribution of beneficial Karst geothermal reservoir and demand of urban heating are well matched. The research on the evolution of Karst geothermal system and the characteristics of genetic elements in Taiyuan Basin has a great significance for the overall development of geothermal resources in this area and the understanding of the distribution of geothermal resources in rift basins.
Methods Based on the previous research and the latest data of 54 geothermal wells, we analyze the heat source, geothermal reservoir distribution and hydrothermal dynamic characteristics of karst geothermal system in Taiyuan Basin, and also evaluate the geothermal resources by 8 effective structural units.
Results The results show as flow: (1) The strata of karst thermal reservoir in Taiyuan Basin are mainly developed in the Lower Paleozoic Ordovician, ,which is widely distributed in North China Plate. And the evolution of the karst geothermal reservoir has gone through five stages, i.e. the epigenic karstification at the end of the Early Paleozoic, the direct caprock deposition in the Late Paleozoic, the initial formation of the karst geothermal system during Mesozoic, the transformation during the Neogene and the final setting during the Quaternary. (2)The heat source of the geothermal system comes from the high terrestrial heat flow (up to 79.12mW/m2) generated by the Cenozoic rift basin, and the heat transfer mode can be divided into two different types: the strong convection type at the edge of the basin and the heat conduction type inside the basin. (3) The geothermal reservoir property is in the longitudinal and horizontal zonation. In the vertical direction, 15-20 effective reservoir sections are identified, with a accumulated thickness of 160~180m, which can be divided into 3-4 layers of main water-bearing section; on the plane, the favorable reservoir belt is mainly controlled by NE trending concealed structure, and the main water-bearing layer is easy to generate a "over-flow" phenomenon during the migration process. The Ordovician reservoir in the middle of the basin with moderately buried (about 400~1900 m) and high temperature (30-75℃) charcteristics is the most favorable exploration and development area. (4) According to the geothermal reservoir volume method, the total geothermal resources of the karst geothermal system in Taiyuan Basin are estimated to be 8.303 billion GJ, which is equivalent to 283 million tons of standard coal.
Conclusions The annual exploitation of geothermal resources can meet the heating area of 15.02 million square meters. At present, the developed resources only account for 23.3% of the exploitable resources, the development potential is huge.
-

-
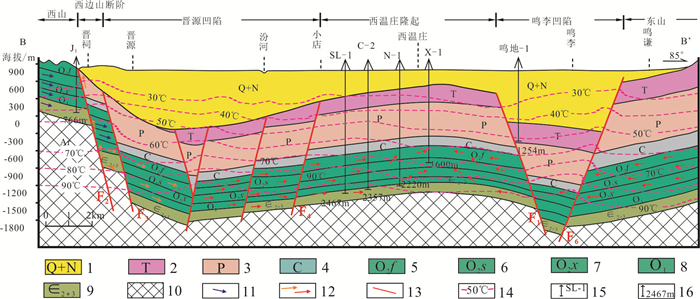
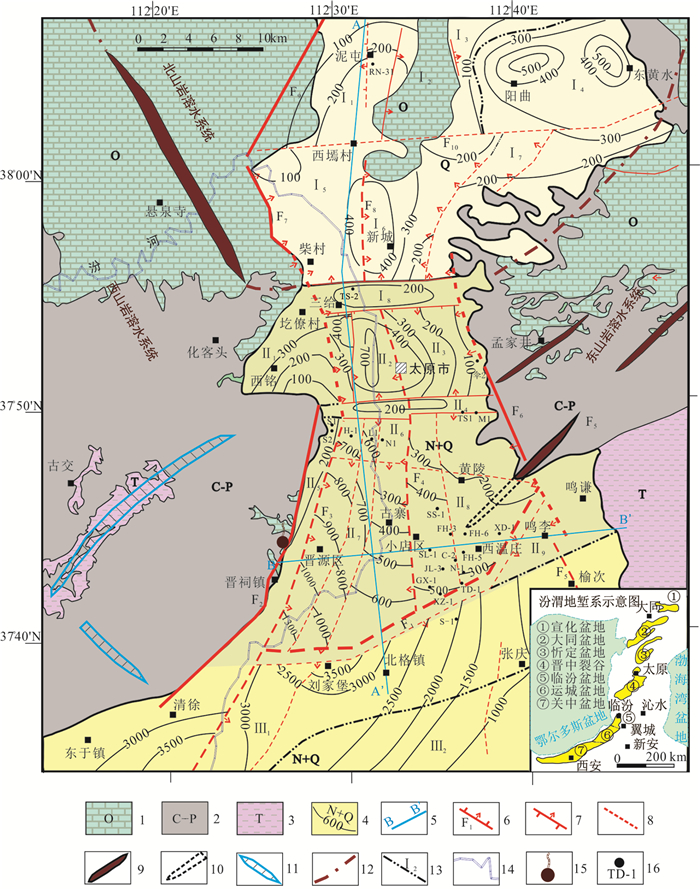
图 8 太原盆地岩溶地热系统地热水运移模式图(剖面位置见图 1B—B’)
Figure 8.
表 1 太原盆地GX-2井测井解释对应表
Table 1. Corresponding tables for log interpretation of GX-2 well in Taiyuan Basin
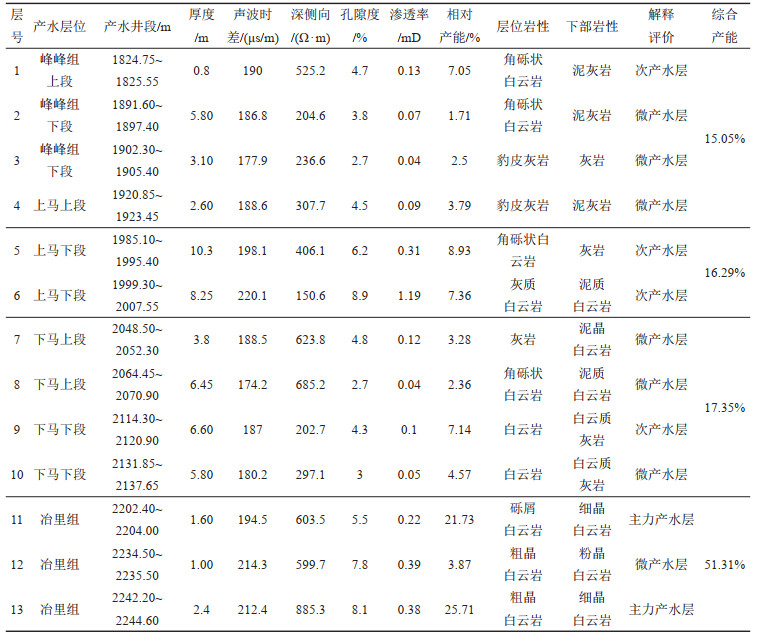
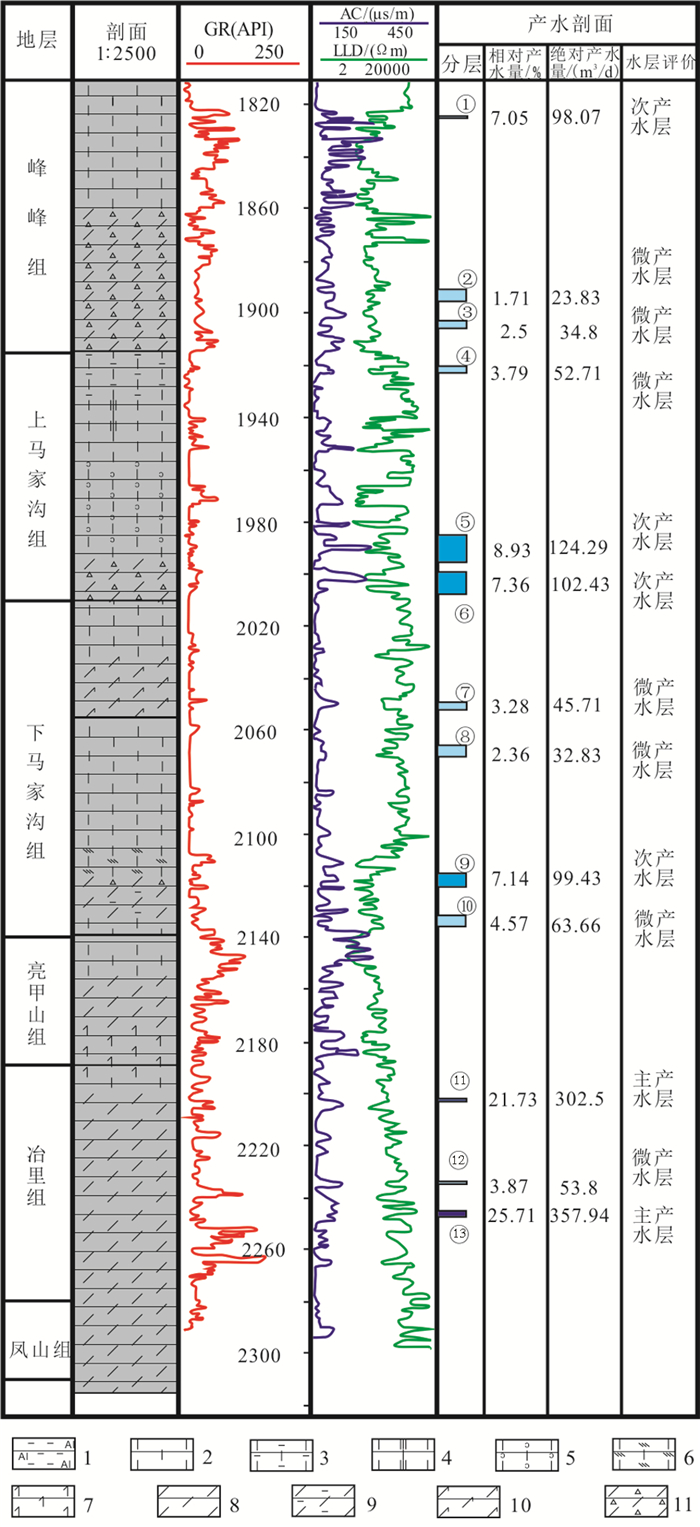
表 2 西温庄地热田地热井产液剖面测试结果统计
Table 2. Statistical table of liquid-producing profile test results of geothermal wells in Xiwenzhuang geothermal field
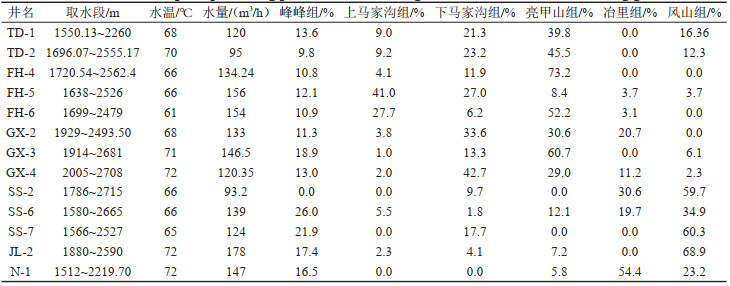
表 3 太原盆地奥陶系岩溶热储地热资源评价参数取值与计算结果
Table 3. Summary of evaluation parameters and calculation results of geothermal resources for Ordovician in Taiyuan Basin
-
Arnórsson S. 1995. Geothermal systems in Iceland: Structure and conceptual models-I high-temperature areas[J]. Geothermics, 24(5/6): 561-602. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(95)00025-9.
Chen Guangping. 2011. Thermal analysis of geological conditions of Xiwenzhuang geothermal field in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Huabei Landand Resources, (3): 5-7(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng Qidong, Cheng Shaoping, Min Wei, Yang Guizhi, Ren Dianwei. 1999. Discussion on Cenozoic tectonics and dynamics of Ordos block[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 5(3): 13-21(in Chinese with English abstract).
Deon F, Moeck I, Jaya M, Wiegand B, Scheytt T, Putriatni D J. 2012. Preliminary assessment of the geothermal system in the Tiris volcanic area, East Java, Indonesia[C]//Proceedings of the 74th EAGE Conference and Exhibition. Copenhagen, Denmark: Earthdoc Eage Publications, June 4-7.
Faulds J E, Coolbaugh M, Bouchot V, Moeck I, Oguz K. 2010. Characterizing structural controls of geothermal reservoirs in the basin and range, USA, and western Turkey: Developing successful exploration strategies in extended terranes[C]//Proceedings of the WGC. Bali, Indonesia, April 25-30: 1163-1173.
Guan Yingbin, Li Haimei. 2001. The structural framework and evolution of Taiyuan area[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science), 20(1): 32-35(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ha Chengyou, Tang Bangyi, Lu Rongan. 1989. Characteristics of fissure karst in the Middle Ordovician limestone and groundwater natural resources in the west mountain of Taiyuan, Shanxi Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 8 (1): 41-46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Ying, Bai Xuefeng, Zhang Xin. 2018. Discussion on geothermal resources and its exploitation and utilization model in Shanxi Province[J]. China Geological Survey, 5(5): 13-20(in Chinese with English abstract).
He Ying. 2010. Geological Features of Xiwenzhuang uplift geothermal field in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Shanxi Coking Coal Science & Technology, 6: 47-49(in Chinese with English abstract).
He Zhiliang, Feng Jianhua, Zhang Ying, Li Pengwei. 2017. A tentative discussion on an evaluation system of geothermal unit ranking and classification in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(3): 168-179(in Chinese with English abstract).
Helgeson H C. 1968. Geologic and thermodynamic characteristics of the Salton Sea geothermal system[J]. American Journal of Science, 266(3): 129-166. doi: 10.2475/ajs.266.3.129
Hou Yuxin. 2002. Research on the geothermal resources in border mount fracture zone in Taiyuan region[J]. Coal Geology of China, 14(4): 38-41(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Xiangquan, Hou Xinwei, Zhang Hongda, Zhang Li. 2006. Study on the geochemistry-isotope characteristics of the groundwater systems in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 20(5): 109-114(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli, Wang Guiling. 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 40(1): 312-321(in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo Huanyan, Kong Xianghong, Gao Wei'an. 1988. Numerical modeling of formation mechanism of Shanxi en-echelon graben[J]. Seismology and Geology, 10 (1): 71-77(in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo Ping, Zhang Jing, Liu Wei, Song Jinmin, Zhou Gang, Sun Ping, Wang Daochuan. 2008. Characteristics of marine carbonate hydrocarbon reservoirs in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(1): 36-50(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Teng, Wang Yanxin, Guo Qinghai, Yan Chunmiao, Ma Rui, Huang Zheng. 2009. Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence of origin of thermal karst water at Taiyuan, northern China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 20(5): 879-889. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0074-4.
Ma Teng, Wang Yanxin, Ma Rui, Yan Chunmiao, Shan Huimei, Chen Liuzhu. 2012. Evolution of Middle-Low temperature carbonate geothermal system in Taiyuan, Northern China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(2): 229-237(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Rui, Wang Yanxin, Sun Ziyong, Zheng Chunmiao, Ma Teng, Prommer H. 2011. Geochemical evolution of groundwater in carbonate aquifers in Taiyuan, Northern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 26(5): 884-897. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.008.
Moeck I S. 2014. Catalog of geothermal play types based on geologic controls[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 37: 867-882. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.032
Muffler L P J. 1976. Tectonic and hydrologic control of the nature and distribution of geothermal resources, Proceedings, Second U. N[J]. Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources, 1: 499-507.
Muffler L J P, Christiansen R L. 1978. Geothermal resource assessment of the United States[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 117(1): 160-171.
Rybach L, Muffler L J P. 1981. Geothermal System: Principle and Analysis of Typical Geothermal System[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-6.
Song Diannan. 2001. Re-recognization of Huaiyuan Movement[J]. Shandong Geology, 17(1): 19-23(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Lin Wenjing, Liu Feng, Zhu Xi, Liu Yanguang, Li jun. 2017. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-TianjinHebei region[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1074-1085 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jiyang. 2015. Geothermics and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xinwei, Wang Tinghao, Zhang Xuan, Mao Xiang, Luo Lu, Wang Di, Wu Minghu. 2019. Genetic mechanism of Xiwenzhuang geothermal field in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Earth Scienc, 44(3): 1042-1056(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Qianbo, Lianyu Fang, Zu Jinhua, Xie Yizhen. 1991. Geothermal study of fault depression zone in Shanxi[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 7: 532-534(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Zhiwei. 2008. Influences of SO42- on the solubility of calcite and dolomite[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 27(1): 24-31(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Zhiwei, Liu Huili, Zhang Zhiwei. 2009. Influences of temperature and CO2 on the solubility of calcite and dolomite[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 28(1): 7-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jianzhong. 2010. Talking about the structural environment of Xiwenzhuang area in Taiyuan City and Xiwenzhuang geothermal resources[J]. Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy, 20(1): 163-165 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Jinyan, Li Zihong, Chen Wen, Hu Guiren, Liu Yanchun. 2016. Preliminary study on exploration and activity of east segment of Tianzhuang fault in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 39(2): 261-269 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Hongwei, Deng Qidong. 1992. A study on the mechanism of the asymmetry basin——A case of the Weihe basin[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 8 (1): 26-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Shouquan. 1990. The study on karst hydrogeological structure system in Taiyuan area, Shanxi Province[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2: 173-182 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Wei, Wang Guiling, Liu Feng, Xing Linxiao, Li Man. 2019. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 255-268(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Ying, Feng Jianyun, He Zhiliang, Li Pengwe. 2017. Classification of geothermal systems and their formation key factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(3): 190-198 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈光平, 2011. 太原盆地西温庄地热田地热地质条件分析[J]. 华北国土资源, (3): 5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2011.03.002
邓起东, 程绍平, 闵伟, 杨桂枝, 任殿卫. 1999. 鄂尔多斯块体新生代构造活动和动力学的讨论[J]. 地质力学学报, 5(3): 13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.003
关英斌, 李海梅, 2001. 太原地区构造格局及其演化[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 20(1): 32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2001.01.010
哈承佑, 汤邦义, 鲁荣安, 1989. 太原西山岩溶发育特征及地下水天然资源的研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 8(1): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198901006.htm
韩颖, 白雪峰, 张欣. 2018. 山西省地热资源及其开发利用模式探讨[J]. 中国地质调查, 5(5): 13-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201805002.htm
贺鹰. 2010. 太原盆地西温庄隆起地热田地质特征[J]. 山西焦煤科技, 6: 47-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XSKJ201006017.htm
何治亮, 冯建赟, 张英, 李朋威. 2017. 试论中国地热单元分级分类评价体系[J]. 地学前缘, 24(3): 168-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703019.htm
侯玉新. 2002. 太原边山断裂带地热资源研究[J]. 中国煤田地质, 14(4): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2002.04.016
李向全, 侯新伟, 张宏达, 张莉. 2006. 太原盆地地下水系统水化学-同位素特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 20(5): 109-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2006.05.022
蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 王贵玲. 2013. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 40(1): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
罗焕炎, 孔祥红, 高维安. 1988. 山西断陷盆地带形成机制的初步数值模拟[J]. 地震地质, 10(1): 71-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198801008.htm
罗平, 张静, 刘伟, 宋金民, 周刚, 孙萍, 王道串. 2008. 中国海相碳酸盐岩油气储层基本特征[J]. 地学前缘, 15(1): 38-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200801005.htm
马腾, 王焰新, 马瑞, 闫春淼, 单慧媚, 陈柳竹. 2012. 太原盆地区碳酸盐岩中-低温地热系统演化[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 37(2): 229-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201202006.htm
Rybach L, Muffler L J P. 1981. 地热系统: 原理和典型地热系统分析[M]. 佟伟, 译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-6.
宋奠南, 2001. 对怀远运动的再认识[J]. 山东地质, 17(1): 19-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI200101003.htm
王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 刘峰, 朱喜, 刘彦广, 李郡. 2017. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1074-1085. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170603&flag=1
汪集旸. 2015. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-6.
汪新伟, 王婷灏, 张瑄, 毛翔, 罗璐, 王迪, 武明辉. 2019. 太原盆地西温庄地热田的成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 44(3): 1042-1056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903030.htm
吴乾蕃, 廉雨方, 祖金华, 谢毅真. 1991. 山西断陷带地热研究[J]. 科学通报, 7: 532-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199107015.htm
闫志为, 2008. 硫酸根离子对方解石和白云石溶解度的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 27(1): 24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.005
闫志为, 刘辉利, 张志卫, 2009. 温度及CO2对方解石、白云石溶解度影响特征分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 28(1): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.01.002
杨建中, 2010. 太原市西温庄一带构造环境与西温庄地热[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 20(1): 163-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2010.01.079
曾金艳, 李自红, 陈文, 扈桂让, 刘艳春. 2016. 太原盆地田庄断裂东段探测和活动性初步研究[J]. 地震研究, 39(2): 261-269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2016.02.012
张宏卫, 邓起东. 1992. 不对称盆地形成机制探讨——以渭河盆地为例[J]. 中国地震, 8 (1): 26-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199201003.htm
张寿全. 1990. 山西省太原地区的岩溶水文地质结构系统[J]. 地质科学, 2: 173-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199002007.htm
张薇, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 邢林啸, 李曼. 2019. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 255-268. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190204&flag=1
张英, 冯建赟, 何治亮, 李朋威. 2017. 地热系统类型划分与主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 24(3): 190-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703022.htm
-



 下载:
下载: