Spatial-temporal distribution, genesis and environmental impact of the shallow groundwater pH values in the Fangchenggang, Guangxi
-
摘要:
研究目的 查明防城港地区浅层偏酸性地下水时空分布、成因及环境影响。
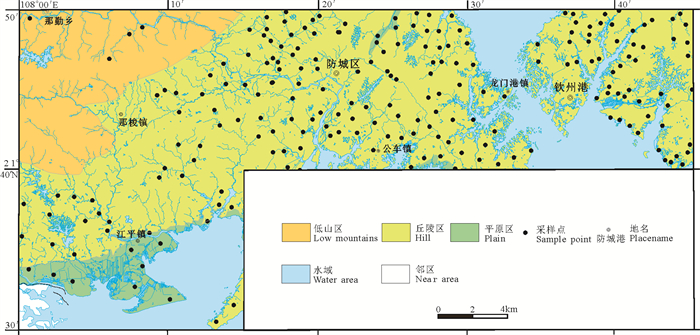
研究方法 于2013—2015年间进行了浅层地下水pH值现场测试,枯水期214组,丰水期168组;讨论了其时空分布特征、成因和生态影响。
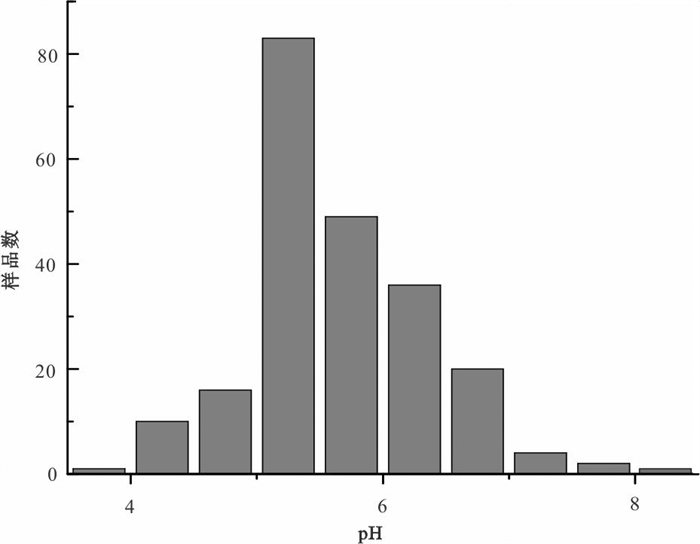
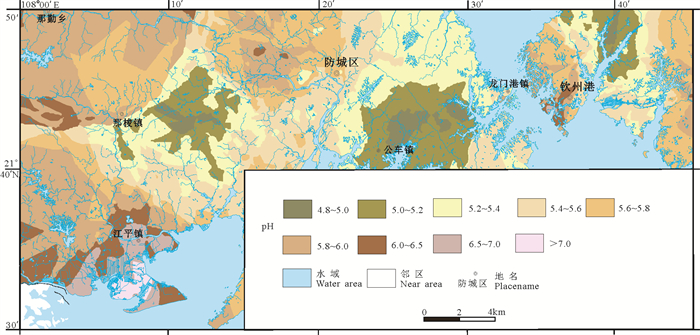
研究结果 结果表明,丰水期和枯水期偏酸性(pH < 6.5)地下水样分别占79.3%和64.3%,pH值总体上丰水期低于枯水期。地下水pH值在低山区(均在5≤pH<5.5范围,平均值5.18,n=4)<丘陵区(大多数5≤pH<6.5,平均值5.18,n=202)<平原区(大多数6.5≤pH<8.5,平均值6.77,n=8)。
结论 偏酸性地下水成因主要与偏酸性大气降水有关,其次与酸性的包气带介质及硫化物矿物的氧化有关。偏酸性大气降水入渗补给是丰水期pH值低于枯水期的主要原因。相比较而言,潮汐作用使得江平地区地下水pH值升高。偏酸性地下水影响饮水安全(研究区枯水期仅20.6%的样品pH值符合生活饮用水标准),促进某些有害组分的释放,腐蚀地下管网和建筑桩基等设施。偏酸性地下水向地表水排泄亦可对地表水环境和地表生态系统产生影响。本研究有助于研究区水资源管理。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
Objective The purpose of this study is to uncover the spatial-temporal distribution, genesis, and environmental impacts of shallow acidic groundwater in the Fangchenggang area.
Methods In-situ pH values of shallow groundwater were determined in the study area during 2013 to 2015, including 214 samples in the dry season and 168 samples in the wet season. Spatial and temporal distribution, genesis, and ecological influences of the pH values were discussed.
Results Results show that the acidic groundwater samples (pH < 6.5) account for 79.3% and 64.3%, respectively, in the wet and dry seasons. In general, pH values in the wet season are lower than in the dry season. Values are generally lower in the low mountain areas (pH 5.0-5.5, mean 5.18, n=4) relative to the hillys (pH mostly 5.0- 6.5, mean 5.97, n=202), and the plain areas (pH typically 6.5- 8.5, mean 6.77, n=8).
Conclusions Occurrence of acidic shallow groundwater can be contributed primarily to the acid rain, and partly to the acidic unsaturated zone, and oxidation of sulfide minerals. Accordingly, seasonal changes of acidic rain should principally responsible for the spatial variations of groundwater pHs. By contrast, however, tides could increase groundwater pH values in the Jiangping area. Acidic groundwater threatens safe drinking water supply, because only 20.6% samples in the dry season having pHs within the drinking water standard thresholds. Also, it may promote release of some harmful elements from aquifer sediments, and erode underground pipe networks and building pile foundations. In addition, due to discharge, acidic groundwater could influence surface water environment and surface ecosystems. This study contributes to water resources management in the study area.
-

-
表 1 按地貌分区浅层地下水枯水期pH值统计
Table 1. Statistics of pH of groundwater in different landscape
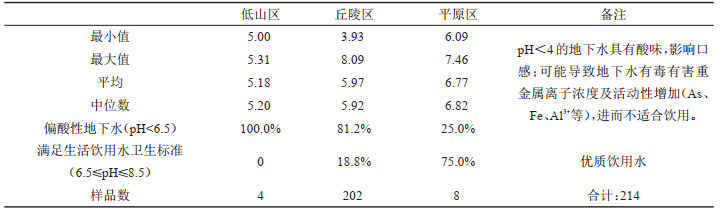
表 2 丰、枯水期地下水pH值对比统计
Table 2. Comparison of groundwater pH values in wet season and dry season
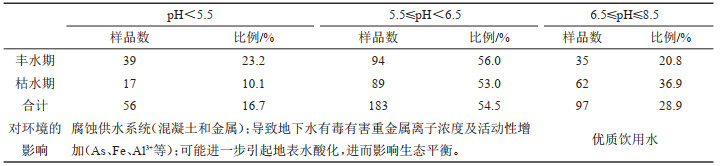
表 3 枯水期主要地下水水化学类型pH值统计
Table 3. pH statistics of major groundwater chemical types
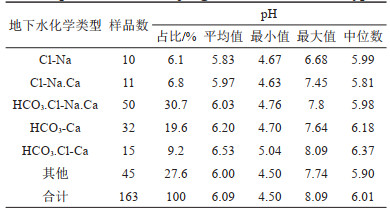
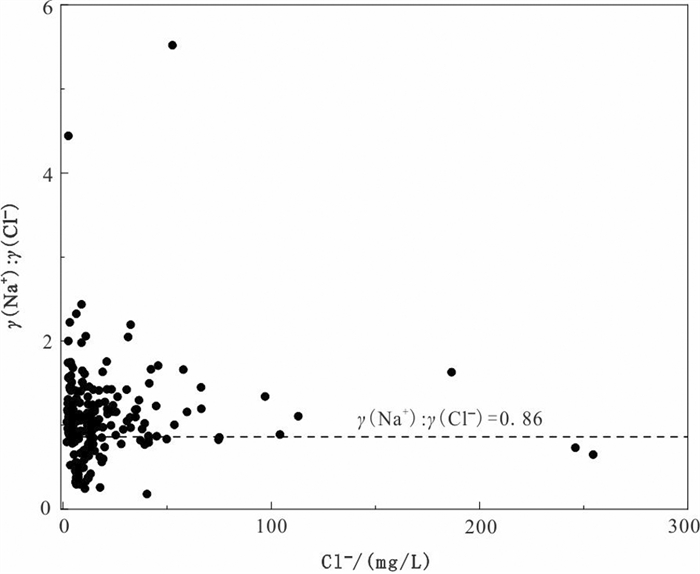
表 4 研究区地下水主要离子及pH值相关性
Table 4. Correlation coefficients of ionic concentration and pH of groundwaterin study area
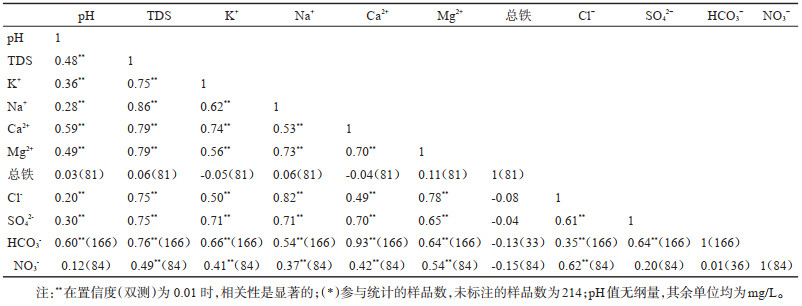
表 5 防城港地区降雨pH值统计
Table 5. pH of precipitation in the Fangchenggang area
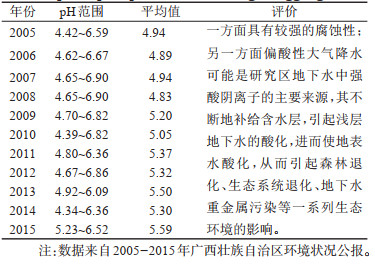
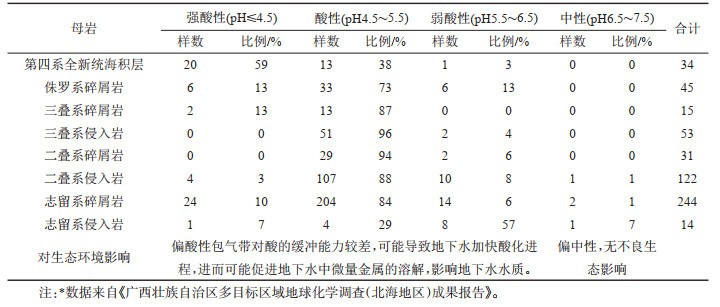
表 6 包气带介质酸碱性统计
Table 6. Statistics of pH value of unsaturated zone
-
Appleyard S, Cook T. 2008. Reassessing the management of groundwater use from sandy aquifers: Acidification and base cation depletion exacerbated by drought and groundwater withdrawal on the Gnangara Mound, Western Australia[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 17(3): 579-588.
Appleyard S, Wong S, Willis-Jones B, Angeloni J, Watkins R. 2004. Groundwater acidification caused by urban development in Perth, Western Australia: Source, distribution, and implications for management[J]. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 42(6): 579-585. doi: 10.1071/SR03074
Campbell D H, Muths E, Turk J T, Corn P S. 2004. Sensitivity to acidification of subalpine ponds and lakes in north-western Colorado[J]. Hydrological Processes, 18: 2817-2834. doi: 10.1002/hyp.1496
Cheng Aizhen, Wei Huahong. 2010. Spatial and temporal distribution and seasonal variation analysis in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 38(9): 4683-4685(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Donghui, He Jiangtao, Liu Qifeng, Zhong Zuoshen. 2006. A discussion about anthropogenic influence on groundwater in urban areas[J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 28(4): 22-25(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Huijie. 2012. Study on Environmental Characteristics and Pollution Mechanism of Rural Drinking Water in Poyang Lake Basin[D]. Nangchang: Nanchang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Min. 2009. Chemical Oceanography[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press (in Chinese).
Chen Shuangxi, Li Qinghua, Liu Huaiqing, Chen Wen, Yu Shaowen, Wang Qing, Zhang Hongxin. 2019. Dataset of Field Testing of the Groundwater in the Fangchenggang Area of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Geology in China, 46(S2): 69-73(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Wen, Li Qinghua, Yu Shaowen, Liu Huaiqing. 2017. Hydrochemical characteristics and ion sources of groundwater in Fangcheng district, Guangxi[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 33(2): 162-168(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Yuanming, Gao Zhipeng, Chen Zongliang, Li Wei, Wang Xi, Ma Xuemei, Guo Huaming. 2019. Distribution characteristics and genesis of strontium-bearing mineral water in Tailai basin[J]. Geology in China, 46(6): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Clohessy S, Appleyard S, Vogwill R. 2013. Groundwater acidification near the water table of the superficial aquifer, Gnangara Mound, Swan coastal plain, western Australia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 36(3): 140-152.
Du Yu, Liang Jun, Liang Ju. 2012. Analysis of acid rain regional distribution and variation in Guangxi based on GIS[J]. Environmental Engineering, 30(S2): 371-374(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ding Aizhong, Hao Na, Cheng Lirong, Zhang Dan, Tan Wenjie, Zhang Lizhong, Lin Xueyu. 2009. Formation origin of high concentration Fe in shallow groundwater in Deyang, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 39(5): 868-873(in Chinese with English abstract).
Fest E P M J, Temminghoff E J M, Griffioen J, Van Der Grift B, Van Riemsdijk W H. 2007. Groundwater chemistry of Al under Dutch sandy soils: Effects of land use and depth[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 22(7): 1427-1438. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.02.002
Franken G, Postma D, Duijnisveld W H M, Böttcher J, Molson J. 2009. Acid groundwater in an anoxic aquifer: Reactive transport modelling of buffering processes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 24(5): 890-899. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.001
Gower C, Rowell D L, Nortcliff S, Wild A. 1995. Soil acidification: Comparison of acid deposition from the atmosphere with inputs from the litter/soil organic layer[J]. Geoderma, 66(1/2): 85-98.
Jing Jihong, Sun Jichao, Han Shuangping, Huang Guanxing, Chen Xi, Zhang Yuxi, Liu Jingtao. 2010. Distribution characteristics of acid rain and acidified groundwater in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Shanghai Geology, 31(2): 8-12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kjoller C, Postma D, Larsen F. 2004. Groundwater acidification and the mobilization of trace metals in a sandy aquifer[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 38: 2829-2835. doi: 10.1021/es030133v
Knutson G. 1994. Acidification Effects on Groundwater-prognosis of the Risks for the Future[M]. LAHS Publ., 222: 3-17.
Lahermo P. 1991. Aspects of acidification of groundwater in Finland[J]. Geol. Surv. Finl. Spec. Pap., 9: 131-139.
Lang L O, Swedberg S. 1990. Occurrence of acidic groundwater in Precambrian crystalline bedrock aquifers, southwestern Sweden[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 49: 315-328. doi: 10.1007/BF00507071
Li Dan, Meng Qingqiang, Zhang Mingzhu. 2015. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and analyses of pH in shallow groundwater from various water source locations in Guangzhou[J]. Groundwater, 37(6): 3-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Rui, Zhou Xun, Zhang Li, Ou Yecheng, Huang Xixin. 2006. Characteristics of the pH in weak acidic groundwater near Beihai and preliminary analyses of its affecting factors[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 143(5): 46-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Yuan, Huang Baisheng. 2003. Analysis of Low pH value of shallow groundwater in Maoming[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 31(3): 32-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ou Yecheng, Chen Runling, Huang Xixin, Zhou Xun. 2009. Characteristics and genesis of natural weak acidic groundwater on Beihai Coast[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 29(4): 449-454 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Preda M, Cox M E. 2000. Sediment water interaction acidity and other water quality parameters in a subtropical setting Pimpama River southeast Queensland[J]. Environmental Geology, 39(3/4): 319-329.
Preda M, Cox M E. 2001. Trace metal in acid sediments and waters, Pimpama catchment, southeast Queensland, Australia[J]. Environmental Geology, 40(6): 755-768. doi: 10.1007/s002540100318
Reuss J O. 1983. Implications of the calcium-aluminum exchange system for the effect of acid precipitation on soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 12: 591-595.
Swedberg S. 1995. Regional groundwater monitoring and examples of acidification trend in the province of Goteborg and Bohus, southwestern Sweden[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 85: 1843-1848. doi: 10.1007/BF00477248
Shen Zhaoli, Zhu Wanhua, Zhong Zuoshen. 1993. Hydrogeochemical Basis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Takem G E, Kuitcha D, Ako A A, Mafany G T, Takounjou-Fouepe A, Ndjama J, Ntchancho R, Ateba B H, Chandrasekharam D, Ayonghe S N. 2015. Acidification of shallow groundwater in the unconfined sandy aquifer of the city of Douala, Cameroon, western Africa: Implications for groundwater quality and use[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74: 6831-6846. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4681-3
Wen Dongguang, Shen Zhaoli, Zhong Zuoshen. 1998. Geochemical Simulation Theory of Water-rock Interaction and its Application[M]. WuHan: China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese).
Xu Naizheng, Gong Jianshi, Tan Mengjiao, Ye Yonghong, Zhou Kaie, Zhu Chunfang, Shu Longcang, Meng Dan. 2021. Hydrogeochemical processes and potential exposure risk high- arsenic groundwater in Huaihe River Basin, China[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1418-1428(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Xinmin, Cai Fahe, Wang Shulan, Sun Xinzhang, Han Mei. 2010. Research progress of acid precipitation in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 23(5): 527-532(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yuxi, Sun Jichao, Chen Xi, Huang Guanxing, Jing Jihong, Liu Jingtao, Xiang Xiaoping, Wang Jincui, Zhi Bingfa. 2011. Characteristics and preliminary analyses of the formation of pH in shallow groundwater in the Pearl River delta[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 38(1): 16-21(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Jian. 1999. Seawater intrusion and hydrochemical characteristic and change of shallow underground water[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 19(6): 525-531(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Xun, Zhang Hua, Zhao Liang, Yan Xia, Ou Yecheng, Huang Xixin. 2007. A preliminary analysis of the formation of the weak acidic groundwater in Beihai, Guangxi[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 81(6): 850-856(in Chinese with English abstract).
程爱珍, 韦华红. 2010. 广西酸雨时空分布和季节变化特征分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 38(9): 4683-4685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.09.103
程东会, 何江涛, 刘起峰, 钟佐燊. 2006. 人类活动对城市地下水影响的探讨[J]. 新疆环境保护, 28(4): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2301.2006.04.006
陈慧杰. 2012. 鄱阳湖流域农村饮用水水环境特征及其污染机理研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学.
陈敏. 2009. 化学海洋学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
陈双喜, 黎清华, 刘怀庆, 陈雯, 余绍文, 王清, 张宏鑫. 2019. 广西防城港地区地下水现场测试数据集[J]. 中国地质, 46(S2): 69-73. doi: 10.12029/gc2019Z207 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2019S207&flag=1
陈雯, 黎清华, 余绍文, 刘怀庆. 2017. 广西防城区地下水水化学特征及离子来源分析[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 33(2): 162-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2017.02.007
陈远铭, 高志鹏, 陈宗良, 李伟, 王茜, 马雪梅, 郭华明. 2019. 泰莱盆地含锶矿泉水分布特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 46(6): 1-11. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1019156711.htm
杜裕, 梁俊, 梁驹. 2012. 基于GIS广西酸雨区域分布及变化特征分析[J]. 环境工程, 30(S2): 371-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC2012S2103.htm
丁爱中, 郝娜, 程莉蓉, 张丹, 谭文捷, 张礼中, 林学钰. 2009. 四川德阳浅层地下水高含铁成因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 39(5): 868-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200905016.htm
荆继红, 孙继朝, 韩双平, 黄冠星, 陈玺, 张玉玺, 刘景涛. 2010. 珠江三角洲地区酸雨及酸化地下水分布特征[J]. 上海地质, 31(2): 8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2010.02.002
李丹, 孟庆强, 张明珠. 2015. 广州市地下水源地浅层地下水pH值的时空变化及其成因分析[J]. 地下水, 37(6): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2015.06.002
李锐, 周训, 张理, 欧业成, 黄喜新. 2006. 北海市偏酸性地下水pH值的特点及其影响因素简析[J]. 勘察科学技术, 143(5): 46-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2006.05.013
梁媛, 黄柏生. 2003. 茂名市浅层地下水pH值偏低的原因分析[J]. 工程勘察, 31(3): 32-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200303009.htm
欧业成, 陈润玲, 黄喜新, 周训. 2009. 北海市滨海地下水天然偏酸性特征及其影响因素[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 29(4): 449-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2009.04.005
沈照理, 朱婉华, 钟佐燊. 1993. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
文冬光, 沈照理, 钟佐燊. 1998. 水-岩相互作用的地球化学模拟理论及应用[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
许乃政, 龚建师, 檀梦皎, 叶永红, 周锴锷, 朱春芳, 束龙仓, 孟丹. 2021. 淮河流域高砷地下水的形成演化过程及其环境健康风险[J]. 中国地质, 48(5): 1418-1428. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210508&flag=1
张新民, 柴发合, 王淑兰, 孙新章, 韩梅. 2010. 中国酸雨研究现状[J]. 环境科学研究, 23(5): 527-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201005001.htm
张玉玺, 孙继朝, 陈玺, 黄冠星, 荆继红, 刘景涛, 向小平, 王金翠, 支兵发. 2011. 珠江三角洲浅层地下水pH值的分布及成因浅析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 38(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.01.004
赵健. 1999. 海咸水入侵与浅层地下水水化学特征及变化研究[J]. 地理科学, 19(6): 525-531. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.1999.06.009
周训, 张华, 赵亮, 沈晔, 严霞, 欧业成, 黄喜新. 2007. 浅析广西北海市偏酸性地下水的形成原因[J]. 地质学报, 81(6): 850-856. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.06.015
-



 下载:
下载: