Influence mechanism and ecological effect of water saving irrigation on water balance in the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia
-
摘要:
研究目的 宁夏引黄灌区是中国重要的粮食生产基地之一,自实施节水灌溉以来,渠系衬砌、田间节水等节水工程影响了区域水平衡状况,研究节水灌溉对水平衡的影响机制及其生态效应对于区域水资源优化管理具有重要意义。
研究方法 通过构建宁夏引黄灌区“水-土-气-生”多元化数据库,运用秩相关分析和Spearman相关分析方法,研究了2000—2020年宁夏引黄灌区的水平衡要素演变趋势、水平衡演化机制及其生态效应。
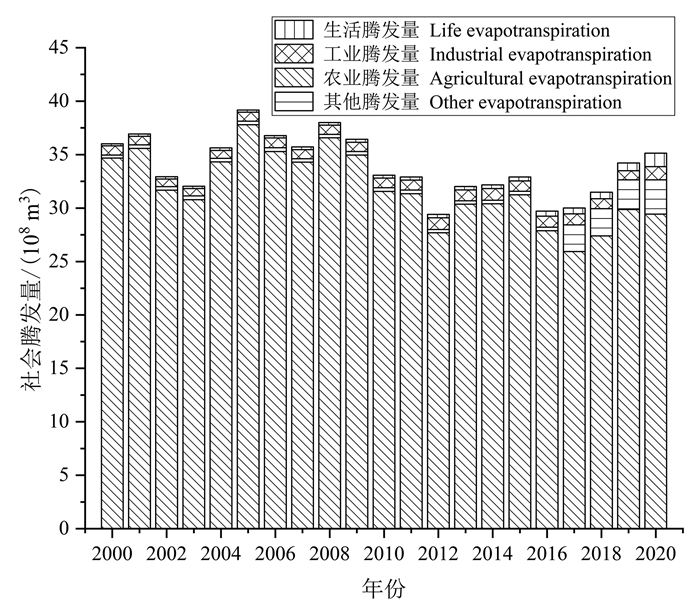
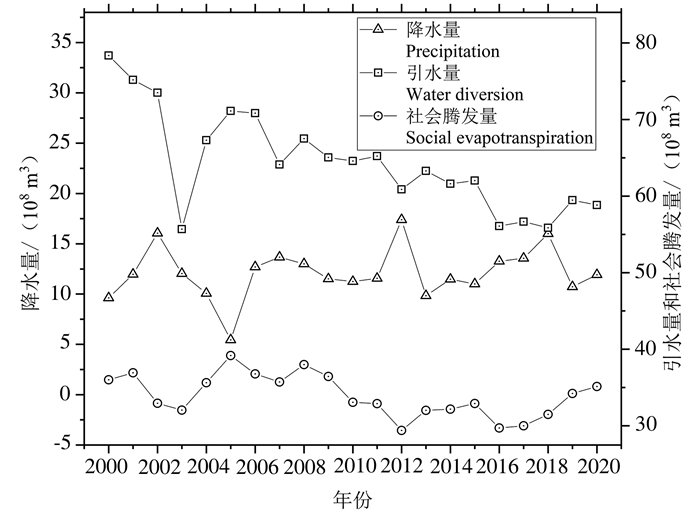
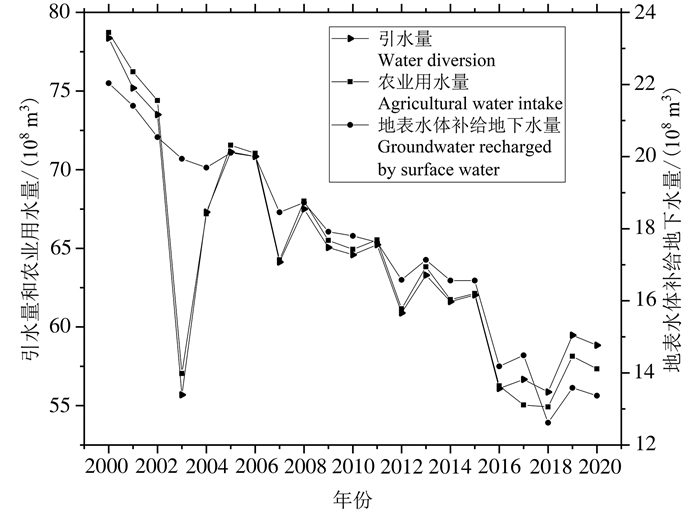
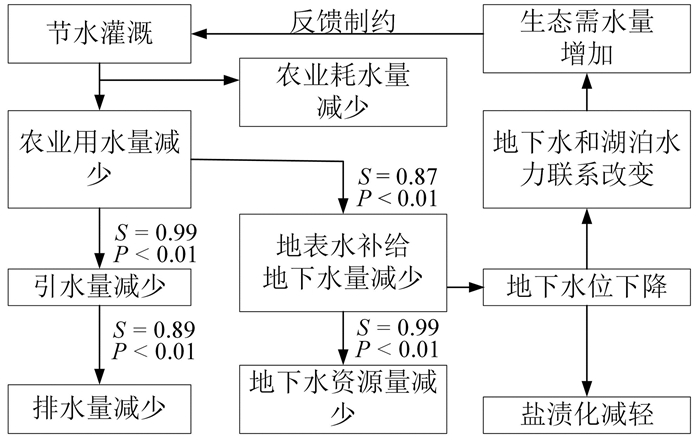
研究结果 宁夏引黄灌区社会经济发展主要依赖过境黄河水,节水灌溉后水循环通量显著减少,2000—2020年农业用水量减少21.38×108 m3,引黄水量减少19.52×108 m3,排水量减少19.11×108 m3;节水灌溉是水平衡演化的主要驱动因子,农业用水量减少直接导致引黄水量与地表水体补给地下水资源量减少(P < 0.01);节水灌溉后地表水体补给地下水量减少8.68×108 m3,地下水资源量减少8.89×108 m3,地下水位普遍下降,盐渍化程度有所减轻,但改变了湖泊和地下水的水力联系,导致生态需水量增加。
结论 节水灌溉后农业用水效率得到提高,水循环通量显著减少,地下水位下降对生态环境造成一定影响,建议以生态安全为底线进一步优化节水方案,相关研究成果为区域自然资源管理及生态保护修复提供支撑。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
Objectives The Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia is one of the important grain production bases in China. Since the implementation of water-saving irrigation, projects such as canal lining and field water-saving have affected the regional water balance. It is of great significance to study the influence mechanism and ecological effect of water-saving irrigation on water balance for the optimal management of regional water resources.
Methods By constructing the water-soil-gas-generation diversified database of the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia, adopting rank correlation analysis and Spearman correlation analysis methods, the evolution trend of water balance elements, water balance evolution mechanism and ecological effect of the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia from 2000 to 2020 were studied.
Results The economic development of the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia mainly depends on the Yellow River water. Since the implementation of water-saving irrigation, the water circulation flux decreased significantly. From 2000 to 2020, the amount of agricultural water intake, water diversion and water discharge decreased by 21.38×108 m3, 19.52×108 m3 and 19.11×108 m3, respectively. Water-saving irrigation is the main driving factor of water balance evolution, and the decrease of agricultural water intake directly leads to the decrease of the amount of water diversion and groundwater recharged by surface water (P < 0.01). After the implementation of water-saving irrigation, the amount of groundwater recharged by surface water decreased by 8.68×108 m3, and the amount of groundwater resources decreased by 8.89×108 m3. The groundwater table decreased, and the degree of salinization reduced. In addition, the decline of the groundwater table changed hydraulic connection between lakes and groundwater, resulting in an increase in ecological water demand.
Conclusions After the implementation of water-saving irrigation, the utilization efficiency of agricultural water has been improved, water circulation flux has been significantly reduced, and the decline of groundwater table has affected the ecological environment. It is suggested to further optimize the water-saving scheme based on ecological security. Relevant research results provide support for regional natural resource management and ecological protection and restoration.
-

-
图 7 湿地地表水-地下水交互模式简图(据罗杰,2020修改)
Figure 7.
表 1 宁夏引黄灌区水平衡要素的Spearman相关系数
Table 1. Spearman correlation coefficients of water balance elements in the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia

表 2 宁夏引黄灌区水平衡要素变化
Table 2. Changes in water balance elements in the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia

表 3 2000—2020年土地利用转移矩阵
Table 3. Land-use transfer matrix from 2000 to 2020

-
Beran A, Hanel M, Nesládková M, Vizina A, VyskočP, Kožín R. 2019. Climate change impacts on water balance in western Bohemia and options for adaptation[J]. Water Science and Technology, 19(1/2): 323-335.
Chen Sheming, Liu Futian, Zhang Zhuo, Zhang Qian, Wang Wei. 2021. Changes of groundwater flow field of Luanhe River Delta under the human activities and its impact on the ecological environment in the past 30 years[J]. China Geology, 4(3): 455-462.
Fan G, Zhang D, Zhang J, Li Z, Sang W, Zhao L, Xu M. 2022. Ecological environmental effects of Yellow River irrigation revealed by isotope and ion hydrochemistry in the Yinchuan Plain, Northwest China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 135: 108574. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108574
Gan Yueyun, Wang Kaiyan, Gan Shengwei. 2019. Analysis of the water balance in the Taihu Basin in recent years[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 39(1): 89-92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Shushu. 2018. Study on Spatiotemporal Evolution and Regulation of Soil Salinization in Hetao Irrigation Districe, Inner Mongolia, China Using Remote Sensing and CLUE-S Model[D]. Beijing: China Inestitute of Water Reources and Hydropower Research, 1-124 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Shuangbao, LI Fucheng, Wang Sai, LI Haixue, Yuan Lei, Liu Jingtao, Shen Haoyong, Zhang Xueqing, Li Changqing, Wu Xi, Ma Tao, Wei Shibo, Zhao Minmin. 2021. Groundwater resource and eco-environmental problem of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1001-1019 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Xiaoqin, Zhang Yibing, Li Ying, Zhang Bo, Meng Xuchen, Xu Lei. 2019. Conversion relationship between lake and groundwater in Yinchuan City: A case study for the Yuehai Lake[J]. Arid Zone Research, 36(6): 1344-1356 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Imran K, Mostafa A. 2019. Potential changes to the water balance of the Teesta River Basin due to climate change[J]. American Journal of Water Resources, 7(3): 95-105.
Jin H, Chen X, Wang Y, Zhong R, Zhao T, Liu Z, Tu X. 2021. Spatiotemporal distribution of NDVI and its influencing factors in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 603(Part D): 127129.
Jin Xiaohui, Fan Yumei, Duan Hao, Yang Jian, Song Changji, Jia Qian, Hu Yawei. 2021. Temporal and spatial response of groundwater depth in Yinchuan Plain to the integrated water regulation of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 32(4): 45-51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jin Xiaomei, Hu Guangcheng, Shi Xiaojie. 2009. Relathionship between soil salinization and the vegetation growing, groundwater depth in the Yinchuan Plain[J]. Geoscience, 23(1): 23-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.01.004
Liu Sheng, Lou Huajun, Jia Shaofeng, Yan Guozhen, Xiang Yangxu. 2014. Quantitative relationship between vegetaiton and groundwater depth in Mahai Oasis area[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science and Technology, 12(6): 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Z, Chen H, Huo Z, Wang F, Shock C C. 2016. Analysis of the contribution of groundwater to evapotranspiration in an arid irrigation district with shallow water table[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 171: 131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2016.04.002
Luo Jie. 2020. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Ecological Effects of Lake-Groundwater Hyporheic Zone in Yuehai Lake, Yinchuan Plain[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 1-94 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Prǎvǎlie R, Piticar A, Roşca B, Sfîcǎ L, Bandoc G, Tiscovschi A, Patriche C. 2019. Spatio-temporal changes of the climatic water balance in Romania as a response to precipitation and reference evapotranspiration trends during 1961-2013[J]. Catena, 172: 295-312. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.08.028
Ruan Benqing, Zhang Renduo, Li Huian. 2008. Study on Water Balance Mechanism and Water Consumption in Hetao Irrigation District[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Song Bo, Zhang Fawang, Yang Huifeng, Liu Chunlei, Meng Ruifang, Nan Tian. 2021. Ecological priority-based source-division evaluation and application on water resources carrying capacity: Take Baoding plain of Hebei Province as a case study[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1156-5116(in Chinese with English abstract).
Song Ge, Huang Jinting, Ning Bohan, Wang Jiawei, Zeng Lei. 2021. Effects of groundwater level on vegetation in the arid area of western China[J]. China Geology, 4(3): 527-535.
Statistics Bureau of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. 2000-2020. Ningxia Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Press(in Chinese).
Sun Yufang. 2019. Study on soil salinization dynamics in Yinchuan Plain based on remotesending monitoring index model[J]. Ground Water, 41(5): 80-82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiaowei, Shao Jingli, Wang Zhuoran, Cui Yali, Zhang Qiuli. 2020. A study of the determination of indicators of dual control of groundwater abstraction amount and water table in northwest China: A case study of the Minqin Basin[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 47(2): 17-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Z, Wang W, Zhang Z, Hou X, Yao D. 2021. Assessment of the effect of water-table depth on riparian vegetation along the middle and lower reaches of the Manasi River, Northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 29(2): 1-11.
Xu Ying, Ge Zhou, Wang Juan, Li Wei, Feng Shaoyuan. 2019. Study on relationship between soil salinization and groundwater table depth based on indicator Kriging[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(1): 123-130 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yue Yong, Hao Fanghua, Li Peng, Ma Guifen, Du Xiaowen. 2008. The land water circle mode in Hetao Irrigation Area[J]. Jounral of Irrigation and Drainage, 27(3): 69-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai Jiaqi, Zhang Yue, He Guohua, Ren Changjia, Fu Wenqi. 2016. Influences of water saving on regional water and salt balance in Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 37(6): 24-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang H, Wang X S. 2020. The impact of groundwater depth on the spatial variance of vegetation index in the Ordos Plateau, China: A semivariogram analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 588: 125096.
Zhang Jinping, Guo Bingtuo, Hou Hongyu, Liu Junge. 2010. Research on water balance mechanism for Yellow River irrigation area in Ningxia[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 338(12): 38-41(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Liang. 2010. Proportion Analysis of Natural and Artificial Water Circulation Fluxes in Manas River Basin[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 1-62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang R, Wu J, Yang Y, Peng X, Li C, Zhao Q. 2022a. A method to determine optimum ecological groundwater table depth in semiarid areas[J]. Ecological Indicators, 139: 108915.
Zhang Teng, Zhang Zhen, Xu Yan. 2016. Simulation and emulation on the equilibrium of supply anddemand of water resources in Haidian District based on the SD model[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 37(2): 29-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Hou K, Qian H, Gao Y, Fang Y, Xiao S, Tang S, Zhang Q, Qu W, Ren W. 2022b. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 837: 155808.
Zhong X, Sun F, Wu C, Shi J, Zhan J. 2016. The impact of land use change on water balance in Zhangye city, China[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Parts, 96: 64-73.
Zhu Hongbin, Lu Wendai. 2011. Application Statistics and SPSS Application[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry(in Chinese).
甘月云, 王凯燕, 甘升伟. 2019. 近年来太湖流域水量平衡分析[J]. 水文, 39(1): 89-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWZZ201901016.htm
郭姝姝. 2018. 基于遥感及CLUE-S模型的内蒙古河套灌区土壤盐渍化时空演变与调控研究[D]. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院, 1-124.
韩双宝, 李甫成, 王赛, 李海学, 袁磊, 刘景涛, 申豪勇, 张学庆, 李长青, 吴玺, 马涛, 魏世博, 赵敏敏. 2021. 黄河流域地下水资源状况及其生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1001-1019. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210402?st=search
黄小琴, 张一冰, 李英, 张勃, 孟旭晨, 徐磊. 2019. 银川市湖泊-地下水转化关系——以阅海湖为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(6): 1344-1356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201906003.htm
靳晓辉, 樊玉苗, 段浩, 杨健, 宋常吉, 贾倩, 胡亚伟. 2021. 银川平原地下水位对黄河流域水量统一调度的时空响应分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 32(4): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ202104007.htm
金晓媚, 胡光成, 史晓杰. 2009. 银川平原土壤盐渍化与植被发育和地下水埋深关系[J]. 现代地质, 23(1): 23-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200901004.htm
刘圣, 娄华君, 贾绍凤, 闫国振, 项洋旭. 2014. 马海绿洲区植被与地下水位埋深的定量关系[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 12(6): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201406001.htm
罗杰. 2020. 银川平原阅海湖-地下水交互带水文地球化学特征及生态效应[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 1-94.
宁夏回族自治区统计局. 2000~2020. 宁夏统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社.
阮本清, 张仁铎, 李会安. 2008. 河套灌区水平衡机制及耗水量研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
宋博, 张发旺, 杨会峰, 刘春雷, 孟瑞芳, 南天. 2021. 基于生态优先的水资源承载力分源评价及应用——以河北保定平原为例[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1156-5116. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210412?st=search
孙玉芳. 2019. 基于遥感监测指数模型的银川平原土壤盐渍化动态研究[J]. 地下水, 41(5): 80-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201905033.htm
王晓玮, 邵景力, 王卓然, 崔亚莉, 张秋兰. 2020. 西北地区地下水水量-水位双控指标确定研究——以民勤盆地为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 47(2): 17-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202002004.htm
徐英, 葛洲, 王娟, 李伟, 冯绍元. 2019. 基于指示Kriging法的土壤盐渍化与地下水埋深关系研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(1): 123-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU201901016.htm
岳勇, 郝芳华, 李鹏, 马桂芬, 杜晓文. 2008. 河套灌区陆面水循环模式研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 27(3): 69-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS200803020.htm
翟家齐, 张越, 何国华, 任长江, 付雯琪. 2016. 内蒙古河套灌区节水对区域水盐平衡的影响分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报: 自然科学版, 37(6): 24-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBSL201606005.htm
张金萍, 郭兵托, 侯红雨, 刘俊阁. 2010. 宁夏引黄灌区水平衡机制研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 338(12): 38-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD201012011.htm
张亮. 2010. 玛纳斯河流域天然水循环通量和人工水循环通量比例分析研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 1-62.
张腾, 张震, 徐艳. 2016. 基于SD模型的海淀区水资源供需平衡模拟与仿真研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 37(2): 29-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNZ201602004.htm
朱红兵, 卢纹岱. 2011. 应用统计与SPSS应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社.
-




 下载:
下载: