Sinoprobe and parameters study on deep karst geothermal reservoir in the Donglihu Area, Tianjin and its exploitable potential analysis
-
摘要:
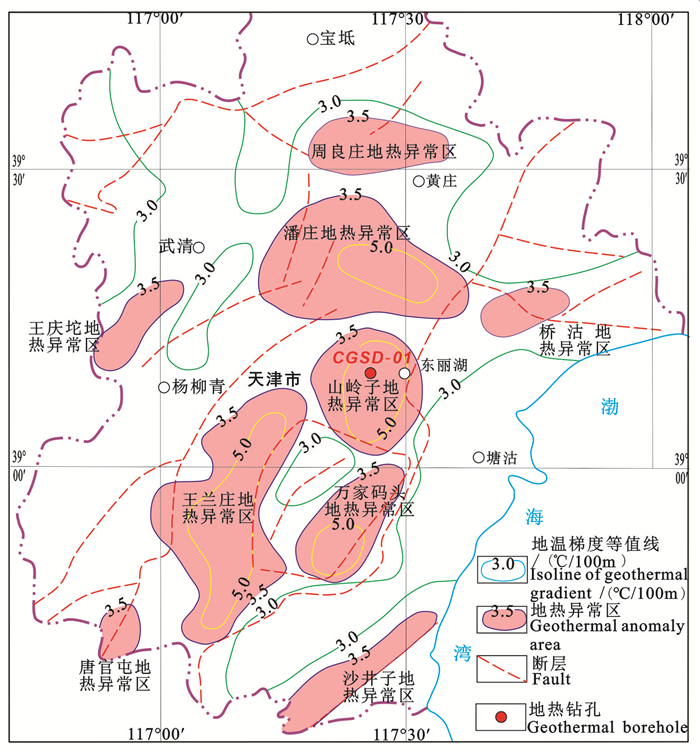
研究目的 天津市地热资源储量丰富、开发利用程度高,蓟县系雾迷山组三、四段白云岩热储是目前的主力开采层位,随着开发强度不断增大,部分地区开采潜力已达极限。探测深部地热资源、增加可开采资源量,成为保障天津地区地热可持续开发的有效途径之一。
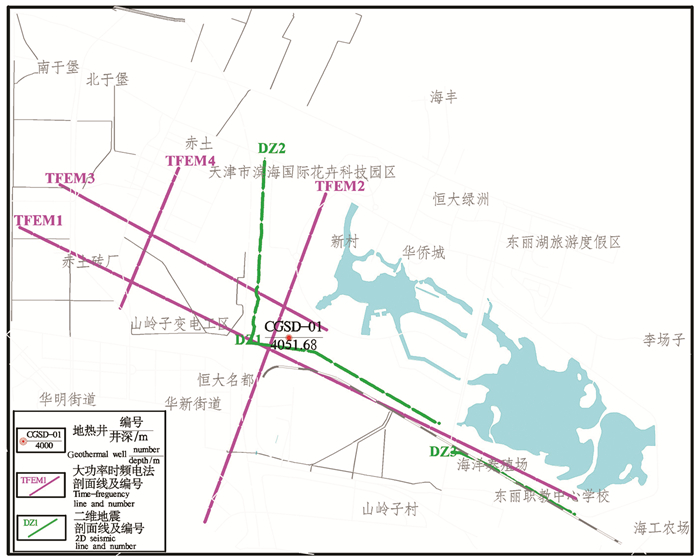
研究方法 本次研究以东丽湖为重点研究区,开展深部热储地球物理探测,实施地热科学钻探CGSD-01井。
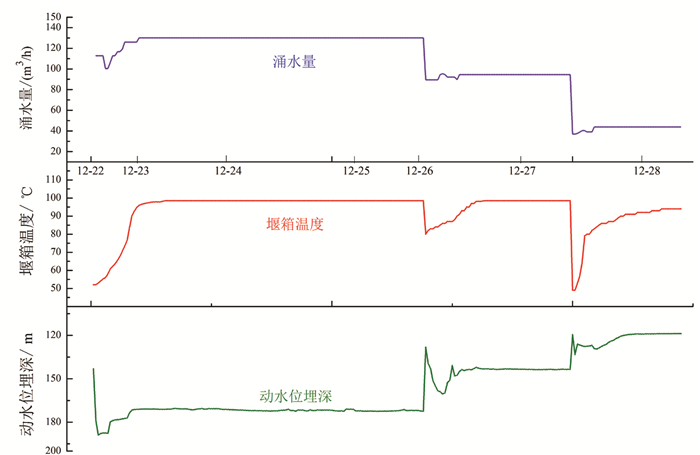
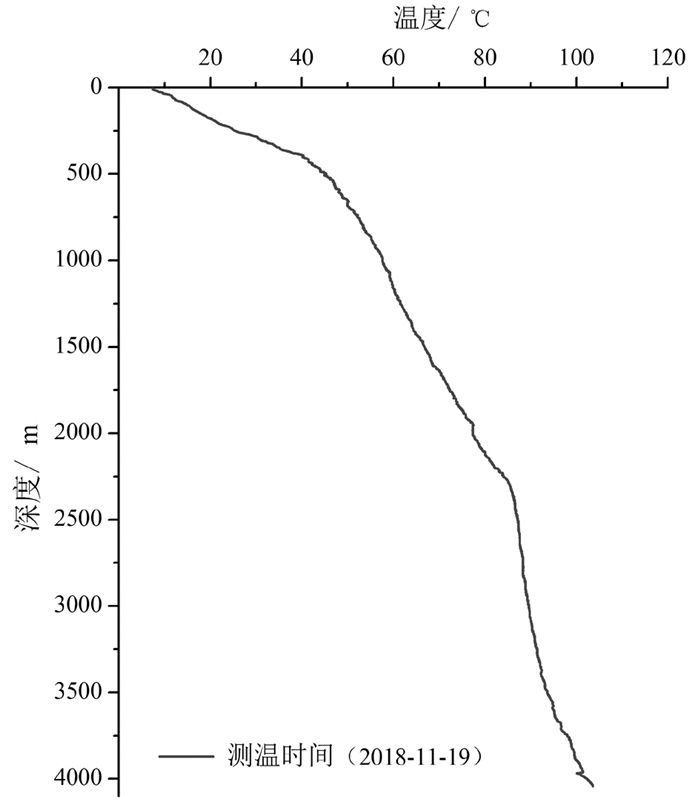
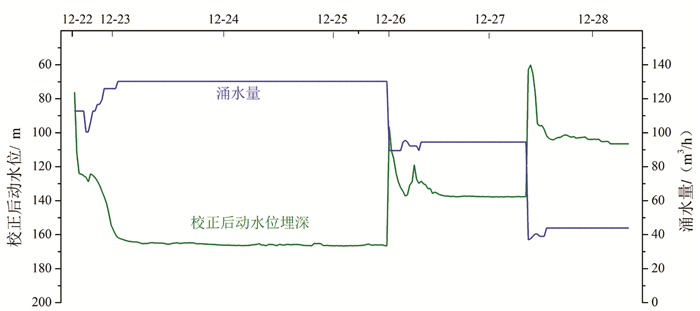
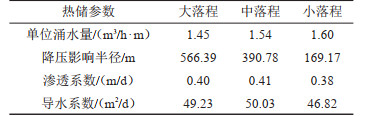
研究结果 主要结果包括:(1)CGSD-01井在3715m钻遇雾迷山组二段,上覆雾迷山组三段底部发育一套紫红色泥质白云岩夹浅灰色细晶白云岩,厚度约73m,裂隙不发育,具有隔水-弱透水性质;(2)CGSD-01井成井深度4051.68m,孔底温度105℃,单位涌水量1.53m3/h·m,渗透系数0.40m/d,导水系数48.69m2/d;(3)雾迷山组二段地热水类型为Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na型,矿化度1.7g/L,初步推断地热水来源于大气降水,主要发生混合、阳离子交替吸附、碳酸盐岩溶解、硫酸盐还原等作用,且未达到平衡;(4)蓟县系雾迷山组二段单井最大涌水量可达130m3/h,出水温度100℃,单井可满足约30万m2建筑物供暖需求。
结论 在天津地区深部热储第二空间首次探获高产能雾迷山组二段新储层,探明了热储结构和主要参数,显示出良好的资源前景。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geothermal resource survey engineering.
Objective Tianjin is abundant in geothermal resources with high utilization level, and section 4-3 in Wumishan Formation of Jixian system is the main development dolomite reservoir at present. With the development intensity of geothermal fluid increasing, the exploitation potential of some areas has reached the limit. Exploring the deep geothermal resources and increasing the allowable productions have become one of the effective ways to ensure the sustainable development of geothermal resources in Tianjin.
Methods Donglihu area is the key research region in this study. Deep geophysical detection had been carried out and geothermal scientific exploration well CGSD-01 had been drilled.
Results The main results are listed as follows: (1)CGSD-01 drilling encountered the section 2 of Wumishan Formation at 3715 m, a set of purplish red argillaceous dolomite with light gray fine-grained dolomite is developed at the bottom of the section 3 of Wumishan Formation overlying, the thickness is about 73 m, and the fissures are not developed, which can be considered as aquiclude or aquitard; (2)The completion depth of CGSD-01 is 4051.68 m, and the bottom temperature is 106℃, specific field is 1.53 m3/h·m, permeability is 0.40 m/d, conductivity is 48.69 m2/d; (3)The geothermal fluid type of the section 2 of Wumishan Formation is Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na, salinity is 1.7 g/L. It is preliminarily inferred that the geothermal water is originated from atmospheric precipitation, and mainly occurs mixing, cation alternating adsorption, carbonate dissolution, sulfate reduction, and does not reach equilibrium state; (4)The maximum outflow rate of CGSD-01 can be reach to 130 m3/h, and the temperature is 100℃, which can meet the heating load of 300 thousand square meters building area.
Conclusions The high-yield new reservoir section 2 in Wumishan Formation of Jixian system was exposed for the first time in the second space of deep thermal reservoir in Tianjin area, and the thermal reservoir structure and main parameters of the reservoir were proved up, showing a good resource prospect.
-

-
表 1 天津东丽湖地区综合地层简表
Table 1. The simplified table of geological strata in Donglihu area, Tianjin

表 2 天津东丽湖CGSD-01井钻遇地层表
Table 2. Geological stratum of well CGSD-01 in the Tianjin
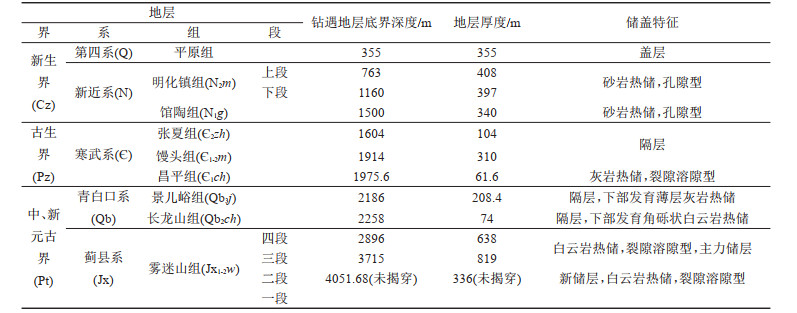
表 3 CGSD-01井雾迷山组二段热储热导率测试值
Table 3. Thermal conductivity test results of Wumishan Formation section 2 in well CGSD-01
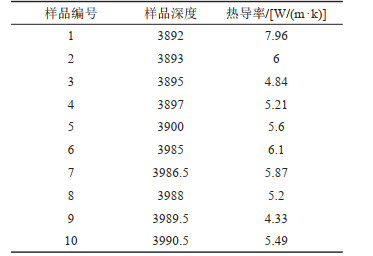
表 4 CGSD-01井热储参数计算基本参数
Table 4. Reservoir parameters of well CGSD-01
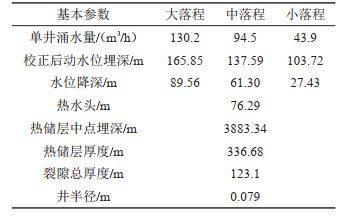
表 5 CGSD-01井地热热储参数计算结果
Table 5. Interpretation results of pumping test for well CGSD-01
-
Chen Moxiang. 1988. Geothermal in North China[M]. Beijing: Science Press(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong Weibin, Zhao Ming, Liu Fang, Zhao Guo. 2008. The time-frequency electromagnetic method and its application in Western China[J]. Applied Geophysics, 5: 127-135. doi: 10.1007/s11770-008-0020-8
Gao Chang. 2003. Comprehensive Geophysical Survey Report on 1: 50000 Regional Geological Survey in Deep Coverage Area of Tianjin[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Geological Survey Research Institute(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Li, Zhao Sumin, Ruan Chuanxia. 2007. The inhomogeneity characteristics of geothermal storing karst caves of Wumishan reservoir of Jixian System in the deep part of Tianjin[J]. Geoscience, 21(4): 600-604(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.002
Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli, Wang Guiling. 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 40(1): 312-321(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
Song Dan. 2020. Influences of Dongli Lake Water Reinjection in Tianjin City on the Scaling Characteristics of Geothermal Reservoirs in Wumishan Formation, Jixian System[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-125(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tianjin Geothermal Exploration and Development Designing Institute. 2000. Deep Geothermal Resources Survey Report in Tianjin[R]. Tianjin(in Chinese).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Lin Wenjing, Liu Feng, Zhu Xi, Liu Yanguang, Li Jun. 2017. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1074-1085(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jige, Chen Ruijun, Yi Zhidong, Wu Peiliang. 2013. Analysis on the Ordovician geothermal well construction risk in the Panzhuang Uplift[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 36: 71-75(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2013.01.008
Wang Kun. 2008. Background History and Status of Geothermal Utilization in Tianjin. Lectures on Geothermal Areas in China[R]. Reykjavik: 12-23.
Wang Weixing, Sun Yudong, Yang Yongjiang. 2010. Geology and hydrogeochemical characteristics geothermal paired wells in Dongli Lake Area, Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 34: 44-48(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Aimin, Ma Feng, Wang, Guiling, Liu Jinxia, Hu Qiuyun. 2018. A study of deep-seated karst geothermal reservoir exploration and huge capacity geothermal well parameters in Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(5): 523-532(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Baiming, Lin Li, Zhao Sumin. 2006. Analysis on mechanism of geothermal origin in Tianjin area[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, (2): 104-107(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.02.025
Zhang Baojian, Wen Dongguang, Shen Zhaoli, Qi Lin. 2009. Geothermal resource of structural trap type: An important geothermal resource conceptual model[J]. Geology in China, 36(4): 927-931(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.04.022
Zhang Wei, Wang Guiling, Liu Feng, Xing Linxiao, Li Man. 2019. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 255-268(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Sumin, Gao Baozhu., Li Xuemei. 2006. Character and water-temperature conductivity of the Cangdong Fault (Tianjin Segment)[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 30: 121-127(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yu, Lei Xiaodong, Zhao Xuchen, Sun Mingguo. 2020. Application of 2D seismic exploration in geothermal resource exploration in Beijing Municipal Administrative Center[J]. Urban Geology, 15(3): 336-341(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Yinming, Hu Xiaoying, Zhang Zhaofang. 2013. Application of time-frequency electromagnetic method in detecting water-rich geological anomalies in coal mine, proceedings[C]//Chinese Geophysics 2013-Proceedings of the 24th Meeting(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Yinming, Liu Xuejun, Zhang Chunhe. 2015. The TFEM technology for quick identification of 'sweet spot' of shale gas and its applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 39: 60-63(in Chinese with English abstract).
陈墨香. 1988. 华北地热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
高昌. 2003. 天津市深覆盖地区1: 50000区域地质调查综合物探研究报告[R]. 天津: 天津市地质调查研究所, 6-33.
林黎, 赵苏民, 阮传侠. 2007. 天津地区深部蓟县系雾迷山组热储岩溶非均一性特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 21(4): 600-604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.002
蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 王贵玲. 2013. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 40(1): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20130121?st=search
宋丹. 2020. 天津东丽湖地表水回灌对蓟县系雾迷山组地热储层结垢特征影响研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-125.
天津地热勘查开发设计院. 2003. 天津深部地热资源普查报告[R]. 天津.
天津市地质调查研究所. 2003. 天津区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 刘峰, 朱喜, 刘彦广, 李郡. 2017. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1074-1085. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20170603?st=search
王继革, 陈瑞军, 易志东, 武佩良. 2013. 潘庄凸起奥陶系地热井施工风险分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 36(1): 71-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201301009.htm
王卫星, 孙玉东, 杨永江. 2010. 天津市东丽湖地热对井的地质与水文地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 34(1): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201001010.htm
吴爱民, 马峰, 王贵玲, 刘金侠, 胡秋韵, 苗青壮. 2018. 雄安新区深部岩溶热储探测与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地球学报, 39(5): 523-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805002.htm
张百鸣, 林黎, 赵苏民. 2006. 天津地区地热形成机理[J]. 水文地质工程地质, (2): 104-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200602027.htm
张保建, 文冬光, 沈照理, 亓麟. 2009. 一种值得重视的地热资源概念模式——构造圈闭型地热资源[J]. 中国地质, 36(4): 927-931. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20090422?st=search
张薇, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 邢林啸, 李曼. 2019. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 255-268. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20190204?st=search
赵苏民, 高宝珠, 黎雪梅. 2006. 沧东断裂(天津段)特征及导水导热性质分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 30(2): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200702008.htm
赵玉, 雷晓东, 赵旭辰, 孙明国. 2020. 二维地震勘探在北京城市副中心地热资源勘查中的应用[J]. 城市地质, 15(3): 336-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ202003018.htm
周印明, 胡晓颖, 张兆芳. 2013. 时频电磁法在探测煤矿富水地质异常体中的应用[C]//中国地球物理第二十四分会场论文集.
周印明, 刘雪军, 张春贺. 2015. 快速识别页岩气"甜点"目标的时频电磁勘探技术及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 39(1): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201501010.htm
-




 下载:
下载: