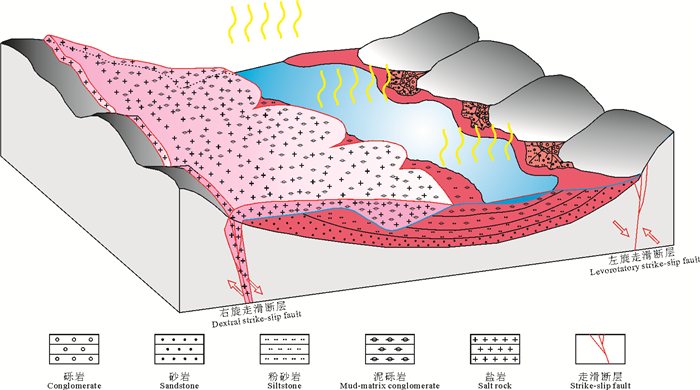
The deep source and shallow mineralization model of potash deposits in the Simao Basin: Evidence from Sr isotope
-
摘要:
研究目的 思茅盆地赋存有中国唯一的前第四纪固体钾盐矿床,该矿床的成因一直存在争议。客观地认识矿床成因、合理地构建矿床成因模式,不仅是钾盐矿床学研究中亟需解决的基础科学问题,而且关乎盆地内钾盐资源勘查方向的选择。
研究方法 本项研究以思茅盆地L-2井和MZK-3井的盐岩、盐岩上覆和下伏碎屑岩、盐岩中的碎屑岩为主要研究对象,重点分析其锶同位素地球化学特征。
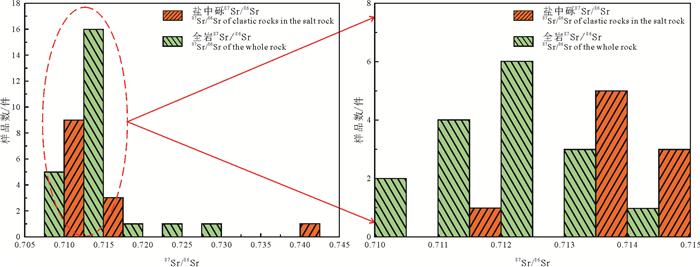
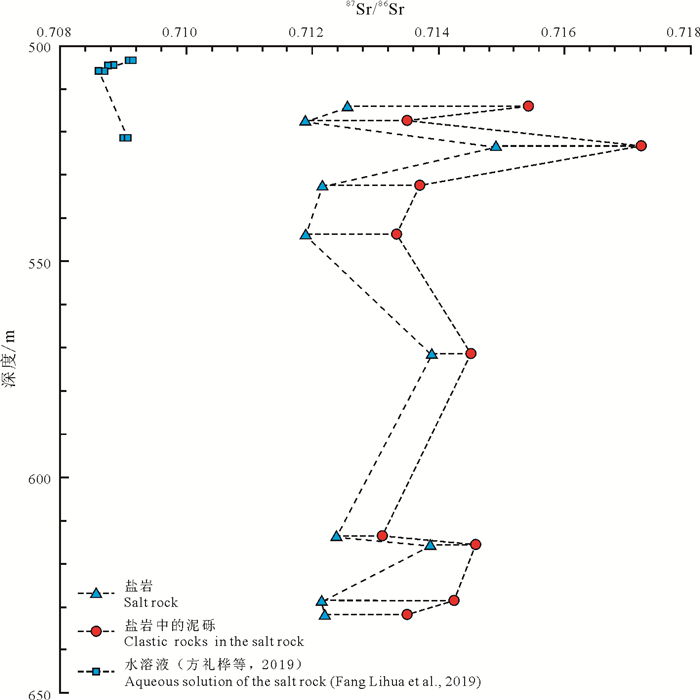
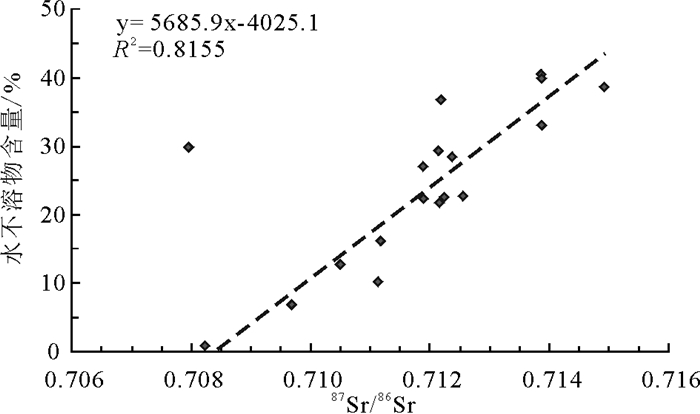
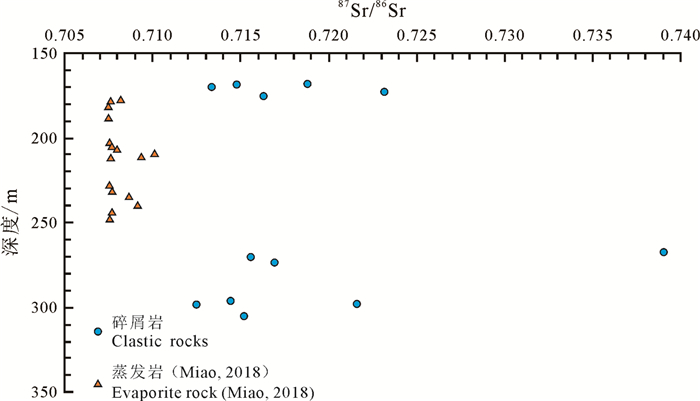
研究结果 结果表明:(1)L-2井全岩样品87Sr/86Sr值为0.708220~0.727458,平均值为0.712776;盐岩水不溶物87Sr/86Sr值为0.711342~0.741999,平均值为0.716574;(2)MZK-3井盐岩上覆碎屑岩层87Sr/86Sr值为0.713318~0.723147,平均值为0.717255;盐岩下伏碎屑岩层87Sr/86Sr值为0.712470~0.738988,平均值为0.719307;(3)碎屑岩样品经过87Rb校正恢复至初始沉积状态的87Sr/86Sr值为0.710880~0.727678,平均值为0.712828;(4)盐岩样品87Sr/86Sr值全部明显小于大陆地表风化系统的平均值,有个别样品87Sr/86Sr值大于现代海水。
结论 基于思茅盆地基础地质和钾盐矿床地质已有的研究成果,结合盐岩和碎屑岩锶同位素地球化学特征,可以得出:思茅盆地含钾盐岩与碎屑岩处于不同的锶同位素平衡体系;含钾盐岩的物源主体为海水,成盐过程中陆源淡水的补给可使87Sr/86Sr值增大;碎屑岩沉积于陆相环境,在与固态盐岩或盐岩水溶液接触之前已处于早成岩阶段A亚期;钾盐的成矿模式为勐野井组沉积期深层源盐通过走滑拉分形成的断层迁移至地表,在由高处向汇水盆地迁移过程中捕获了处于早成岩阶段A亚期的碎屑颗粒,形成了现今的含泥砾盐岩;部分含泥砾盐岩在迁移进入汇水盆地之后,经历了溶解-重结晶的过程,形成了盆地内成分较纯的盐岩;后续沉积的碎屑颗粒形成了防止盐岩溶蚀破坏的保护层;新生代的喜山运动使早期形成的钾盐矿床发生调整改造。
Abstract:This paper is the result of the geological survey engineering.
Objective The Simao Basin hosts the only pre-Quaternary solid potash deposit in China, but the genesis of this deposit has been still controversial. An objective understanding of deposit genesis as well as rational construction of a metallogenic model is not only fundamental scientific issues that need to be addressed urgently in the study of potash mineral deposits, but also have a bearing on the choice of the direction for potash resource exploration in the basin.
Methods This study focuses on Sr isotope geochemical characteristics of the samples from salt rocks, overlying and underlying clastic rocks and clastic rocks within the salt rocks in Wells L-2 and MZK-3 of the Simao Basin.
Results The results show that: (1) The bulk-rock 87Sr/86Sr values from the Well L-2 samples are 0.708220-0.727458, with an average of 0.712776; the 87Sr/86Sr values of water-insoluble matter within the salt rock are 0.711342-0.741999, with an average of 0.716574; (2) The 87Sr/86Sr values of the clastic rock overlying and underlying the salt layer in Well MZK-3 range from 0.713318-0.723147 and 0.712470-0.738988, with an average of 0.717255 and 0.719307, respectively; (3) The 87Sr/86Sr values of the clastic rock corrected by 87Rb tore cover their initial sedimentary state are 0.710880-0.727678, with an average of 0.712828; (4) The 87Sr/86Sr values of salt rock are all significantly lower than the average value of the continental weathering system, with some individual samples having 87Sr/86Sr values larger than modern seawater.
Conclusions Based on the existing research results of the basic geology and potash deposit geology in the Simao Basin, combined with the Sr isotope geochemical characteristics of salt rocks and clastic rocks, it can be concluded that: The potash-bearing salt rocks and clastic rocks are in different Sr isotope equilibrium systems; the matter source of potash-bearing salt rock is mainly seawater, and the recharge of terrestrial freshwater into the evaporation basin during the salinization process would increase 87Sr/86Sr values of the samples. The clastic rocks were deposited in the terrestrial environment and were in the eodiagenesis substage A before contacting with solid salt rock or brine; a more rational potash metallogenic model is that the deep source salt migrated to the surface through faults formed by strike-slip pull-apart process during the deposition period of the Mengyejing Formation, capturing the unconsolidated clastic rocks in the eodiagenesis substage As they migrated from the height to the catchment basin, and forming the present-day clastic-bearing salt rocks. After migrating into the catchment basin, parts of the clastic-bearing salt rocks underwent dissolution and recrystallization, resulting in the formation of salt rock with relatively purer composition. The subsequent deposition of the clastic rocks formed a protective layer against rock salt dissolution. Early-formed potash deposits were influenced by the Cenozoic Himalayan movement, leading to the modification not only in physical structure but also in mineral component.
-
Key words:
- potash deposit /
- material source /
- metallogenic model /
- Sr isotope /
- geological survey engineering /
- Simao Basin
-

-
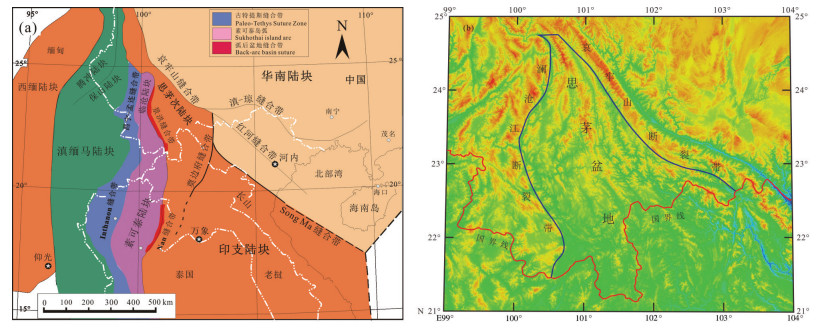
图 2 L-2井地理位置及周围地质简图(据苗忠英等, 2019a, b)
Figure 2.
表 1 思茅盆地L-2井蒸发岩及其水不溶物锶同位素地球化学特征
Table 1. 87Sr/86Sr values of the evaporite and its water-insoluble matter of the L-2 well cores in the Simao basin
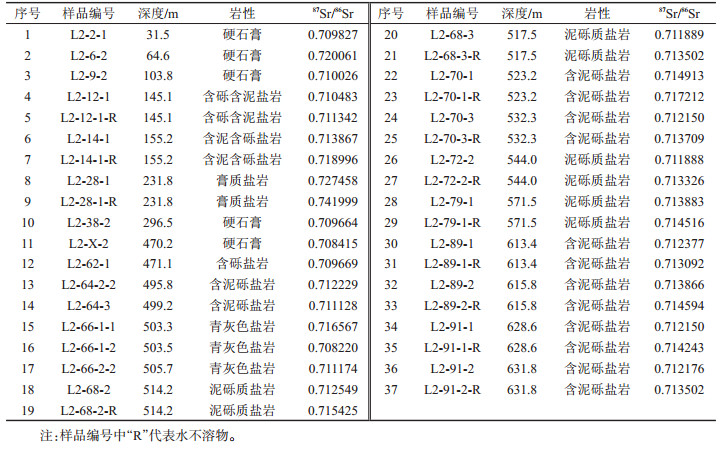
表 2 MZK-3井盐岩上覆和下伏碎屑岩锶同位素地球化学特征
Table 2. 87Sr/86Sr values of clastic rocks being upon and beneath salt rock layer, in the MZK-3 well
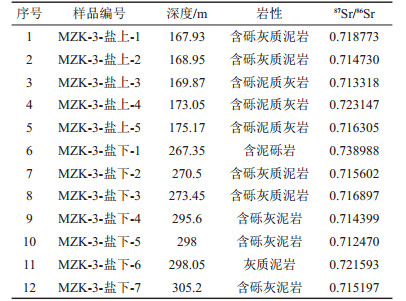
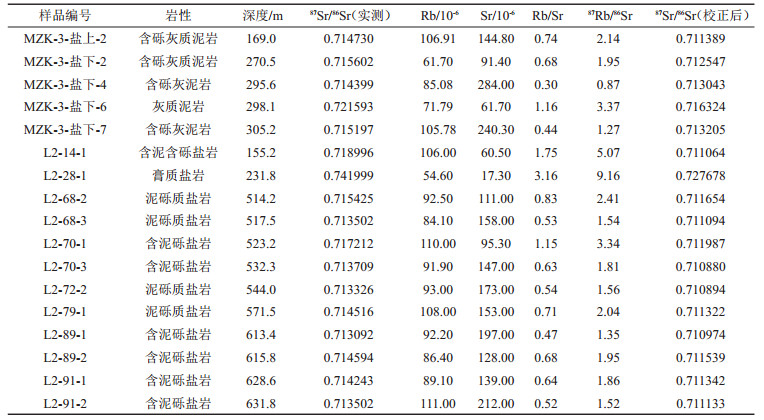
表 3 样品的Rb-Sr含量及校正后的87Sr/86Sr值
Table 3. Rb and Sr concent and adjusted 87Sr/86Sr values
-
Butterfield D A, Nelson B K, Wheat C G, Mottl M J, Roe K K. 2011. Evidence for basaltic Sr in midocean ridge-flank hydrothermal systems and implications for the global oceanic Sr isotope balance[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(22): 4141-4153.
Chen Yaokun, Liao Zongting, Wei Zhihong, Li Minghui. 2004. Characteristics and tectonic evolution of the Lanping-Simao mesozoic basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 26(3): 219-222(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dessert C, Dupr B, Franois L M, Schott J, Gaillardet J, Chakrapani G, Bajpai S. 2001. Erosion of deccan traps determined by river geochemistry: Impact on the global climate and the 87Sr/86Sr ratio of seawater[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188(3): 459-474.
Dickin A P. 2005. Radiogenic Isotope Geology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Eglington B M, Talma A S, Marais S, Matthews P E, Dixon J G P. 2003. Isotopic composition of pongola supergroup limestones from the buffalo river gorge, south Africa: Constraints on their regional depositional setting[J]. South African Journal of Geology, 106(1): 1-10. doi: 10.2113/1060001
Fang Lihua, Xia Zhiguang, Li Weiqiang, Yin Hongwei, Miao Zhongying, Liu Bin, Shao Chunjing. 2019. Sr isotope characteristics of salt rocks in Simao Basin, southwestern Yunnan and its implications[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 25(5): 679-685(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Sijing, Shi He, Zhang Meng, Shen Licheng, Wu Wenhui. 2002. Application of strontium isotope stratigraphy to diagenesis research[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 20(3): 359-366(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liao Zongting, Chen Yaokun. 2005. Nature and evolution of Lanping-Simao basin prototype[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 33(11): 109-113(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Ying, Zheng Mianping, Zhang Zhen, Yu Changqing, Miao Zhongying, Zhang Kai, Gao Lei. 2017. Salt tectonic and prospecting potassium research in Simao Basin[J]. Geological Review, 63(3): 568-580(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma Haizhou, Li Yongshou, Cheng Huaide, Qin Xiwei, Zhang Xiying, Miao Weiliang, Xu Jianxin, Li Binkai, Hai Qingyu. 2019. Metallogenic model and processes of the cretaceous potassium-bearing evaporites involving Changdu, Lanping-Simao and Khorat Basin[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 27(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract).
Metcalfe I. 2002. Permian tectonic framework and palaeogeography of SE Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20: 551-566. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00022-6
Miao Z Y. 2018. New Sr isotope evidence to support the material source of the mengyejing potash deposit in the Simao Basin from ancient marine halite or residual sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 92(2): 866-867. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13564
Miao Zhongying, Zheng Mianping, Zhang Xuefei, Zhang Zhen, Gao Yunzhi. 2019a. Geochemistry and sedimentology significance of sulfur isotope in the evaporite: A case from the MZK-3 well in the Simao Basin, southwestern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(5): 1166-1179(in Chinese with English abstract).
Miao Zhongying, Zheng Mianping, Zhang Xuefei, Zhang Zhen, Liu Jianhua, Gao Yunzhi, Zhai Xuefeng. 2019b. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of the Lower Cretaceous evaporite and its significance for potash mineralization in the Simao basin, southwest China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(2): 279-290(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qu Yihua. 1997. On affinity of potassium bearing brine in Lanping-Simao basin, China to that in Ale basin, Thailand, and location of target areas for potassium hunting in former basin[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 19(2): 10-13(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shuai Kaiye. 1987. Geologic-tectonic evolution and evaporite formation of Mesozoic-Cenozoic era in Yunnan[J]. Geoscience, 1(2): 207-229(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sone M, Metcalfe I. 2008. Parallel Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia: New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 340: 166-179. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2007.09.008
Tan Fuwen. 2002. The sedimentary characteristics of Simao triassic rear arc foreland basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 20(4): 560-567(in Chinese with English abstract).
Veizer J, Compston W. 1974. 87Sr/86Sr composition of seawater during the Phanerozoic[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 38: 1461-1484. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(74)90099-4
Wang L C, Liu C L, Fei M M, Shen L J, Zhang H, Zhao Y J. 2015. First SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of the potash-bearing Mengyejing Formation, Simao Basin, southwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Cretaceous Research, 52: 238-250. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2014.09.008
Wang Licheng, Liu Chenglin, Shen Lijian, Bo Ying. 2018. Research advances in potash forming of the Simao Basin, Eastern Tethyan Realm[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(8): 1707-1723(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Nanping, Jiang Shaoyong, Liao Qilin, Pan Jiayong, Dai Baozhang. 2003. Lead and sulfur isotope geochemistry and the ore sources of the vein-type copper deposits in Lanping-Simao Basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(4): 799-807(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Tianzhu. 1981. Origin of the Mengyejing potash deposit in Yunnan[J]. Chemical Geology, (1): 1-8(in Chinese).
Xie Tao, Hu Shixue, Zhou Changyong, Zhang Qiyue, Huang Jinyuan, Wen Wen. 2019. Composition and evolution of strontium isotope from the fossiliferous layers of the Luoping biota, Yunnan[J]. Geology in China, 46(3): 642-650(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Li Wenchang, Li Huaqi, Cai Zhihui, Yan Zhen, Ma Changqian. 2013. Paleo-Tethys system and accretionary orogen in the Xizang plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6): 1847-1860(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jianxu, Yin Hongwei, Zhang Zhen, Zheng Mianping. 2013. Geologic setting of the potassium in the Lanping-Simao Basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(4): 633-640(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Xin, Zheng Jianjing, Liu Xingwang, Su Long, Liu Yuhu, Liu Yanhong. 2011. Dynamic basin-orogen coupling and sequence response process: Taking Lanping-Simao Basin, western Yunnan as a case[J]. Geoscience, 25(3): 447-455(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Fuguang, Pan Guitang, Wan Fang, Li Xingzhen, Wang Fangguo. 2006. Tectonic facies along the Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinshajiang orogenic belt in southwestern China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 26(4): 33-39(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Hongfu, Wu Shunbao, Du Yuansheng, Peng Yuanqiao. 1999. South China defined as part of tethyan archipelagic ocean system[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24(1): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Jiyun, Sun Zhiming, Yang Zhenyu, Liang Qizhong. 1999. Cretaceous and Early Tertiary paleomagnetic results from the Lanping Basin and its geological implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(5): 648-659(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Mianping, Zhang Zhen, Yin Hongwei, Tan Xiaohong, Yu Changqing, Shi Linfeng, Zhang Xuefei, Yang Jianxu, Jiao Jian, Wu Guopeng. 2014. A new viewpoint concerning the formation of the Mengyejing potash deposit in Jiangcheng, Yunnan[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(1): 11-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Mianping, Zhang Zhen, Zhang Yongsheng, Liu Xifang, Yin Hongwei. 2012. Potash exploration characteristics in China: New understanding and research progress[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 33(3): 280-294(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Zhijie, Yin Hongwei, Zhang Zhen, Zheng Mianping, Yang Jianxu. 2012. Strontium isotope characteristics and the origin of salt deposits in Mengyejing, Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 48(6): 719-727(in Chinese with English abstract).
陈跃昆, 廖宗廷, 魏志红, 李明辉. 2004. 兰坪-思茅中生代盆地的特征及构造演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 26(3): 219-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200403001.htm
方礼桦, 夏芝广, 李伟强, 尹宏伟, 苗忠英, 刘斌, 邵春景. 2019. 滇西南思茅盆地盐岩Sr同位素特征及其对区域成盐作用的启示[J]. 高校地质学报, 25(5): 679-685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201905004.htm
黄思静, 石和, 张萌, 沈立成, 武文慧. 2002. 锶同位素地层学在碎屑岩成岩研究中的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 20(3): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200203000.htm
廖宗廷, 陈跃昆. 2005. 兰坪-思茅盆地原型的性质及演化[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 33(11): 109-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ200511021.htm
刘璎, 郑绵平, 张震, 于常青, 苗忠英, 张凯, 高磊. 2017. 滇西南思茅盆地盐构造研究及找钾初探[J]. 地质论评, 63(3): 568-580. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201703003.htm
马海州, 李永寿, 程怀德, 秦西伟, 张西营, 苗卫良, 许建新, 李斌凯, 海擎宇. 2019. 昌都-兰坪-呵叻成盐带白垩纪成盐成钾过程[J]. 盐湖研究, 27(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ201901002.htm
苗忠英, 郑绵平, 张雪飞, 张震, 高运志. 2019a. 蒸发岩中硫同位素的地球化学特征及其沉积学意义——以思茅盆地MZK-3井为例[J]. 地质学报, 93(5): 1166-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201905013.htm
苗忠英, 郑绵平, 张雪飞, 张震, 刘建华, 高运志, 翟雪峰. 2019b. 思茅盆地下白垩统蒸发岩硫同位素地球化学特征及其钾盐成矿意义[J]. 地球学报, 40(2): 279-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201902004.htm
曲懿华. 1997. 兰坪-思茅盆地与泰国呵叻盆地含钾卤水同源性研究——兼论该区找钾有利层位和地区[J]. 化工矿产地质, 19(2): 10-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC702.001.htm
帅开业. 1987. 云南中、新生代地质构造演化与蒸发岩建造[J]. 现代地质, 1(2): 207-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ198702004.htm
谭富文. 2002. 云南思茅三叠纪弧后前陆盆地的沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报, 20(4): 560-567. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200204004.htm
王立成, 刘成林, 沈立建, 伯英. 2018. 东特提斯域思茅盆地钾盐成矿研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 92(8): 1707-1723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201808013.htm
吴南平, 蒋少涌, 廖启林, 潘家永, 戴宝章. 2003. 云南兰坪-思茅盆地脉状铜矿床铅、硫同位素地球化学与成矿物质来源研究[J]. 岩石学报, 19(4): 799-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200304022.htm
吴天柱. 1981. 云南勐野井钾盐矿床的成因[J]. 化工地质, (1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC198101000.htm
谢韬, 胡世学, 周长勇, 张启跃, 黄金元, 文芠. 2019. 云南含罗平生物群层位锶同位素组成与演化[J]. 中国地质, 46(3): 642-650. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20190314?st=search
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李文昌, 李化启, 蔡志慧, 闫臻, 马昌前. 2013. 青藏高原中的古特提斯体制与增生造山作用[J]. 岩石学报, 29(6): 1847-1860. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201306002.htm
杨尖絮, 尹宏伟, 张震, 郑绵平. 2013. 滇西兰坪-思茅盆地成钾地质条件分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(4): 633-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201304009.htm
杨鑫, 郑建京, 刘兴旺, 苏龙, 刘玉虎, 刘燕红. 2011. 动态"盆山"耦合关系及其层序响应过程: 以滇西兰坪-思茅盆地为例[J]. 现代地质, 25(3): 447-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201103006.htm
殷鸿福, 吴顺宝, 杜远生, 彭元桥. 1999. 华南是特提斯多岛洋体系的一部分[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 24(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX901.000.htm
尹福光, 潘桂棠, 万方, 李兴振, 王方国. 2006. 西南"三江"造山带大地构造相[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 26(4): 33-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200604004.htm
尹济云, 孙知明, 杨振宇, 梁其中. 1999. 滇西兰坪盆地白垩纪-早第三纪古地磁结果及其地质意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 42(5): 648-659. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199905008.htm
郑绵平, 张震, 尹宏伟, 谭筱虹, 于常青, 施林峰, 张雪飞, 杨尖絮, 焦建, 武国朋. 2014. 云南江城勐野井钾盐成矿新认识[J]. 地球学报, 35(1): 11-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201401003.htm
郑绵平, 张震, 张永生, 刘喜方, 尹宏伟. 2012. 我国钾盐找矿规律新认识和进展[J]. 地球学报, 33(3): 280-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201203002.htm
郑智杰, 尹宏伟, 张震, 郑绵平, 杨尖絮. 2012. 云南江城勐野井盐类矿床Sr同位素特征及成盐物质来源分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 48(6): 719-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ201206006.htm
-



 下载:
下载: