Distribution and causes of karst collapse in Yangtze River Economic Belt and its influence on engineering construction
-
摘要:
研究目的 岩溶塌陷是长江经济带主要环境地质问题之一,开展长江经济带岩溶塌陷分布、成因及其对工程建设的影响研究,对长江经济带立体综合交通走廊建设和新型城镇化建设地质环境安全保障具有重要意义。
研究方法 本文系统梳理了长江经济带岩溶塌陷研究成果,从岩溶环境特征、岩溶塌陷的成因类型和机制、发育及分布规律、对工程建设的影响及防控措施几个方面进行论述。
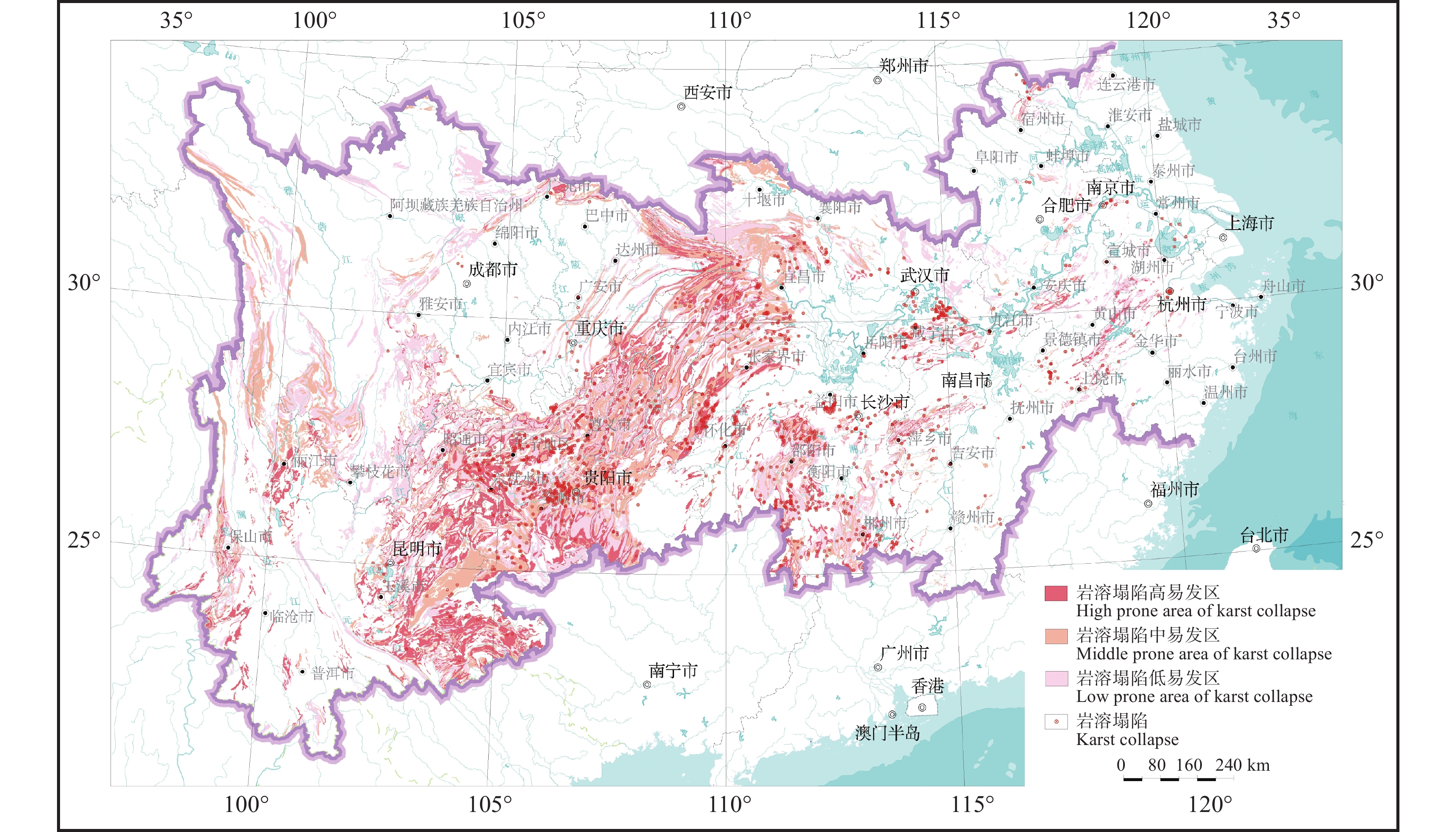
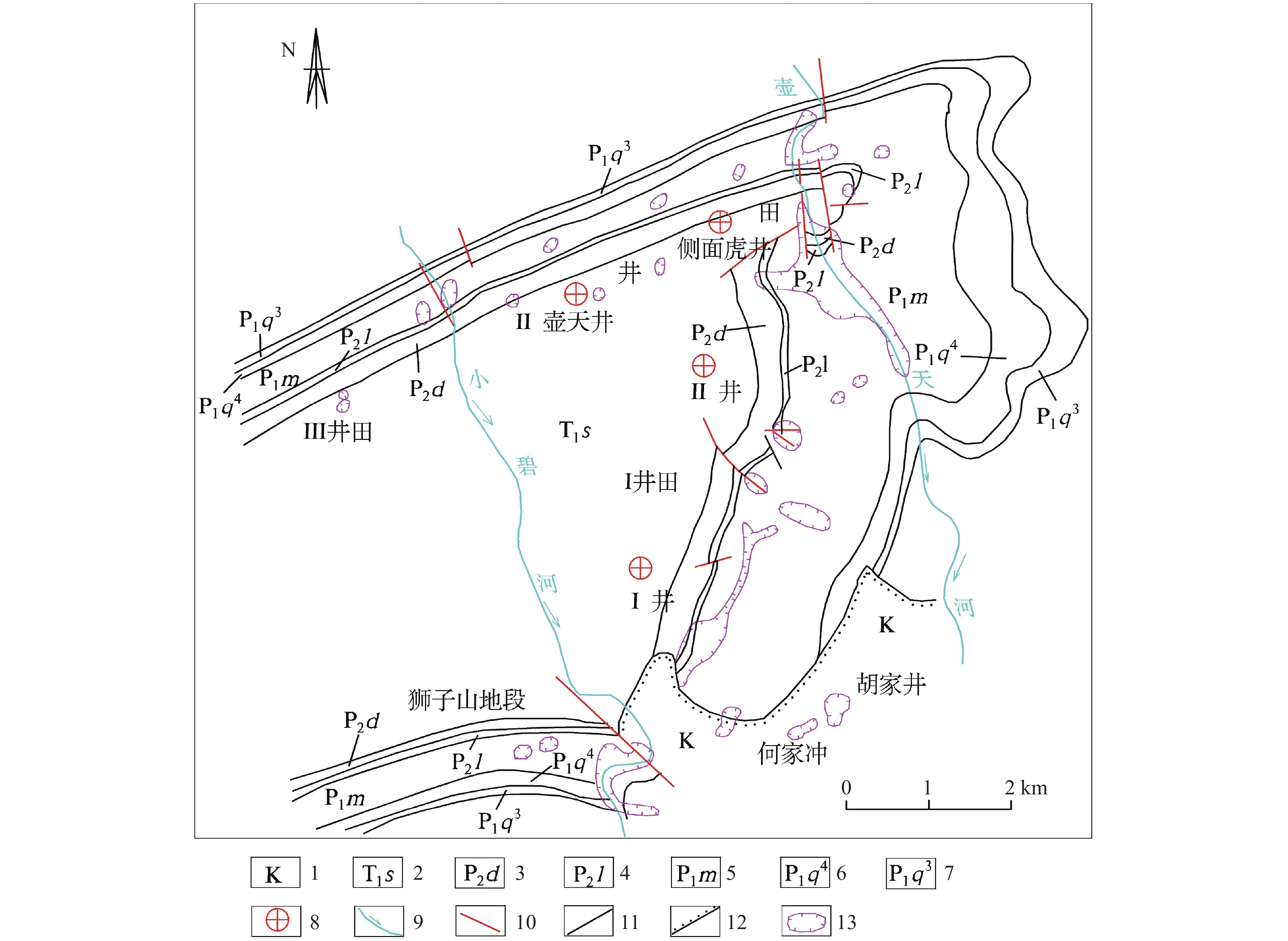
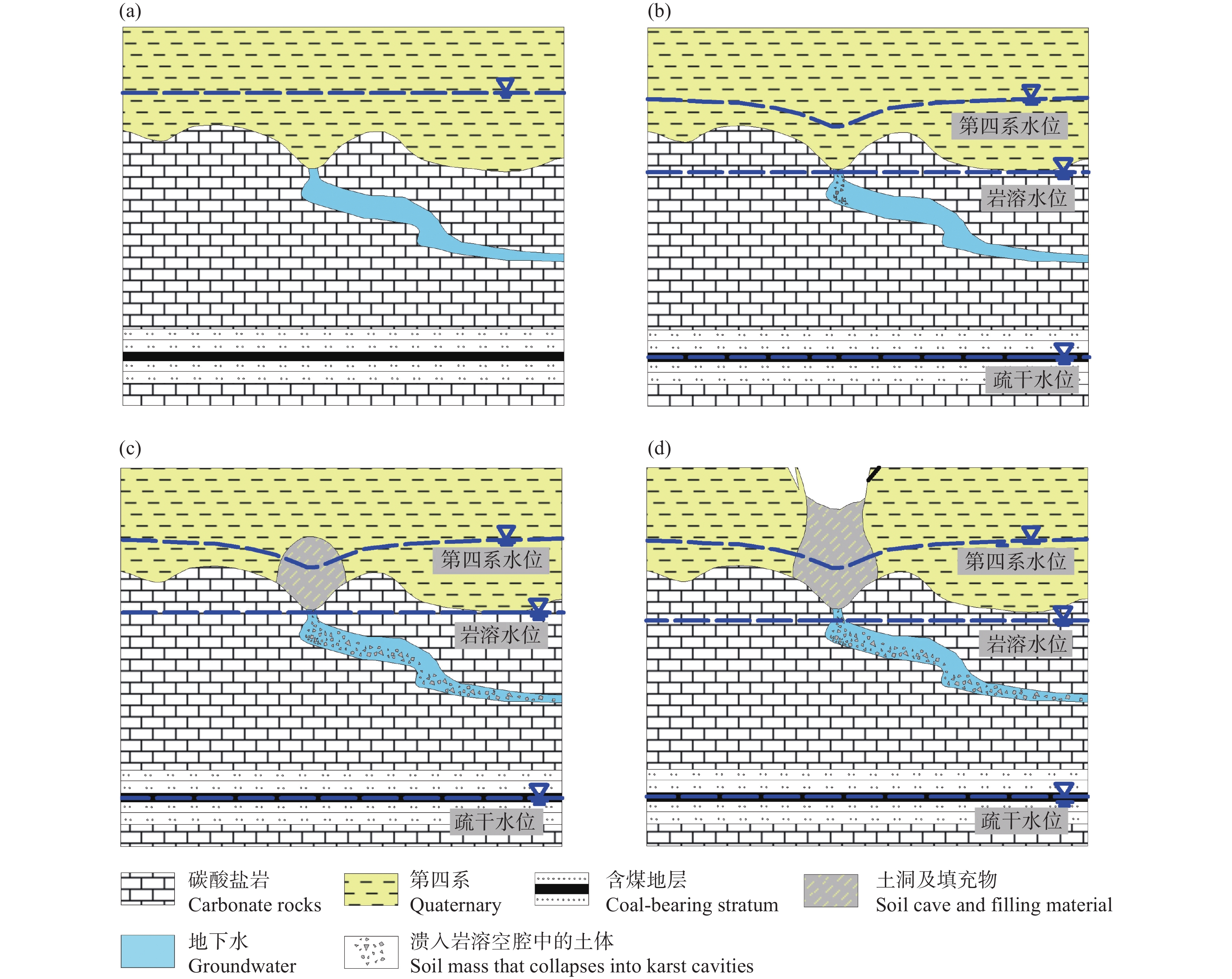
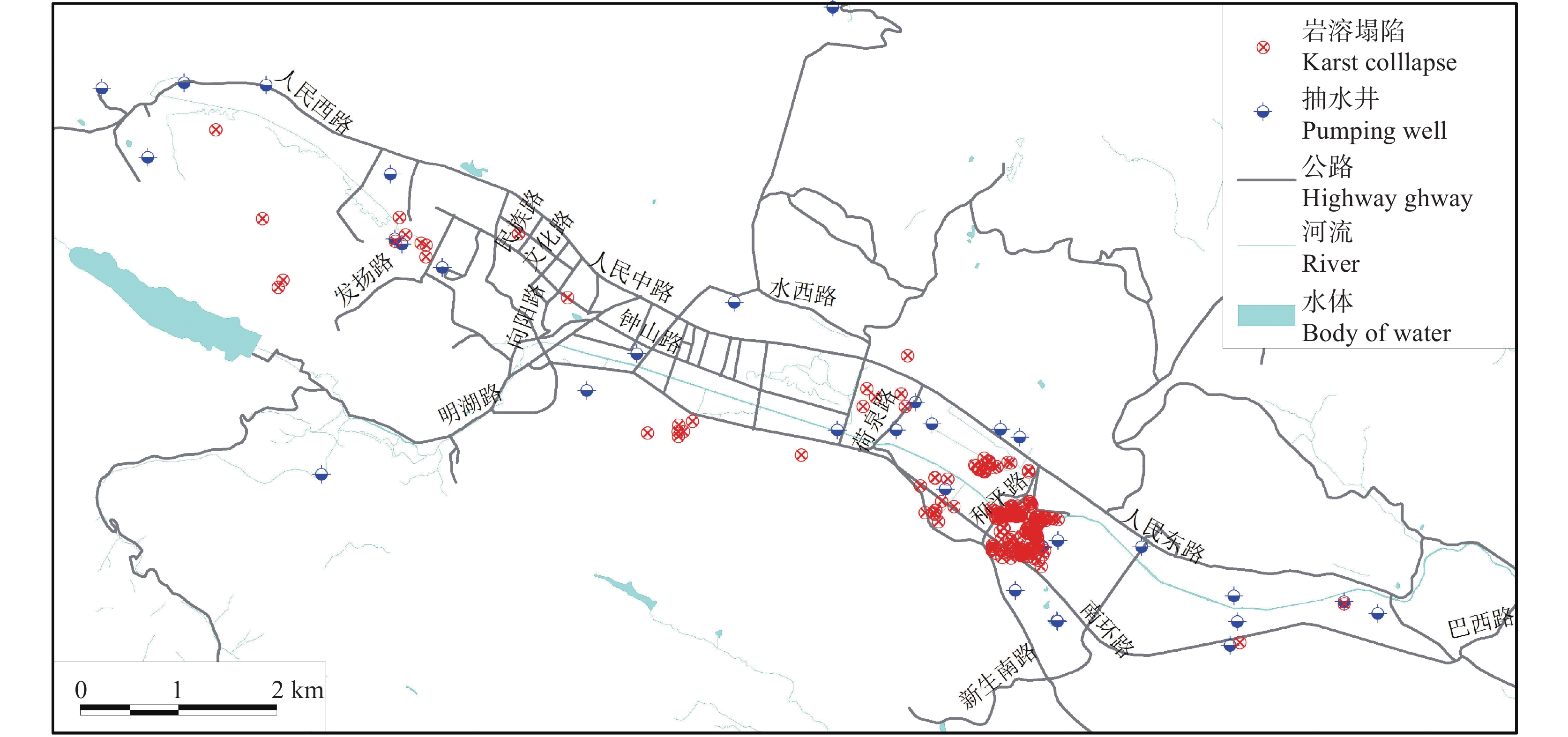
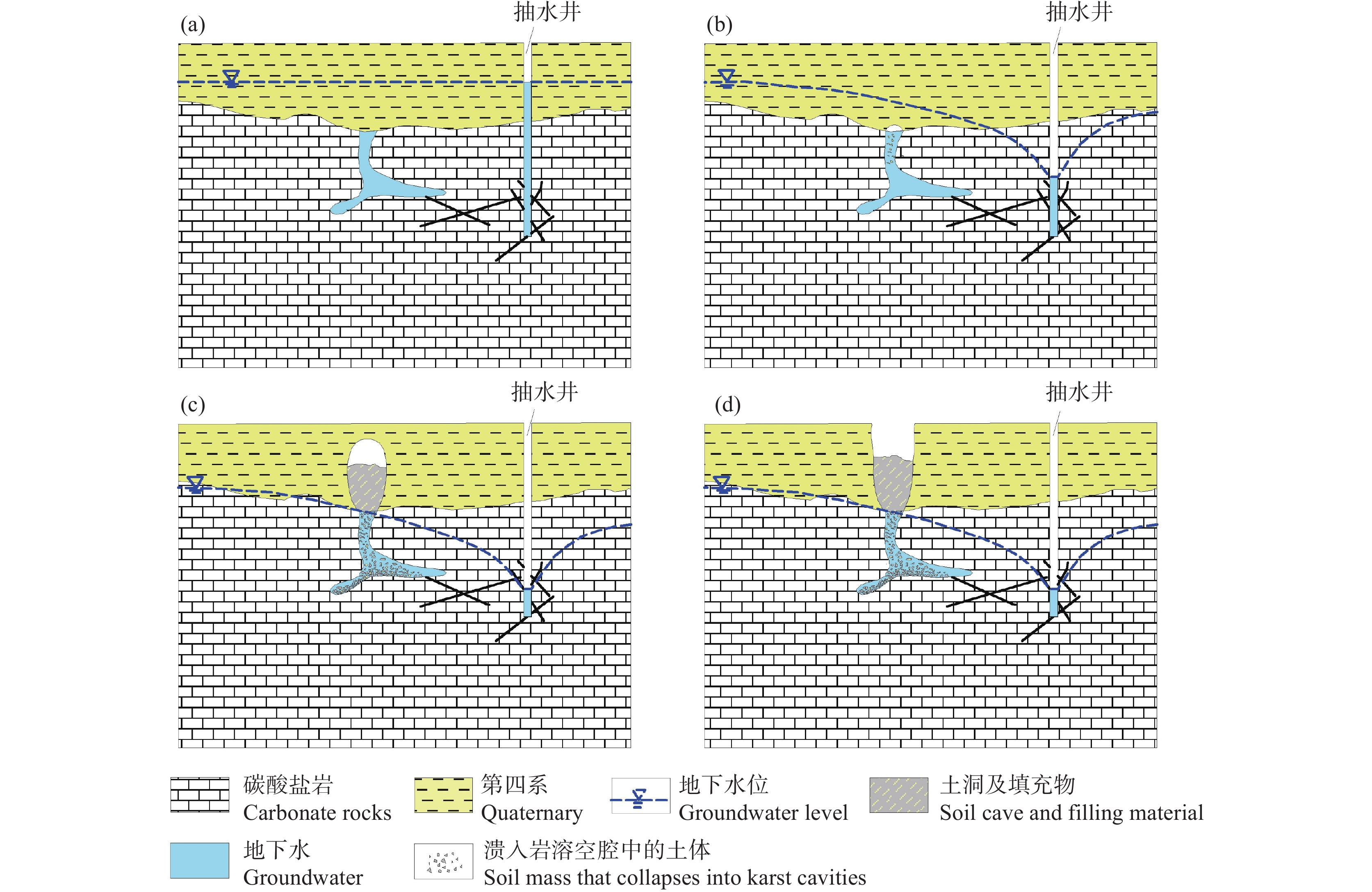
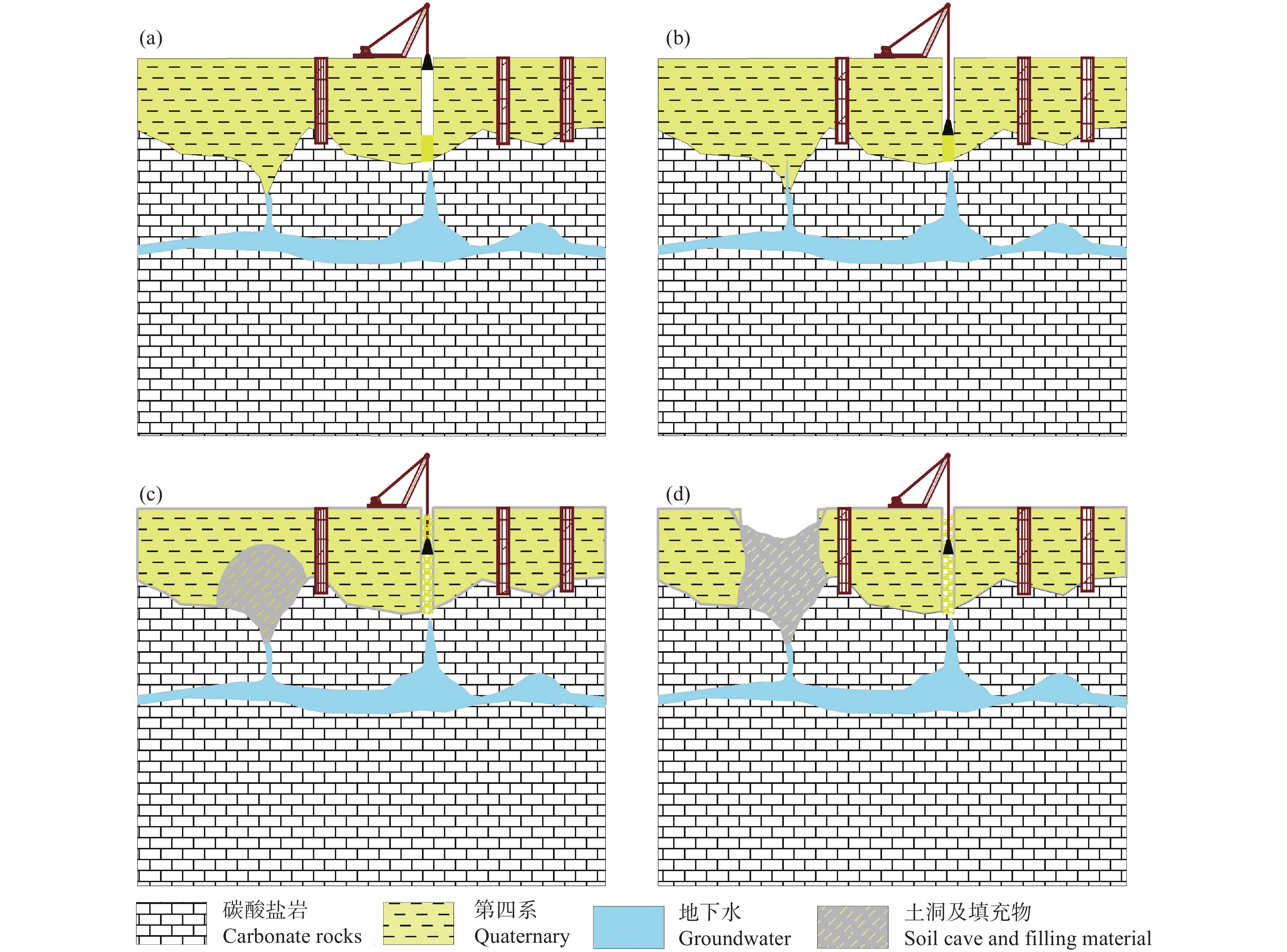
研究结果 研究结果表明,长江经济带岩溶塌陷易发区面积约25.4 万km2,有记录的岩溶塌陷灾害2146处,矿山疏干排水、抽水、工程施工等是这一地区岩溶塌陷的主要诱发因素。长江经济带岩溶塌陷具有以下发育分布规律:一是具有区域性和地带性的分布特征;二是发育地层一般为均匀状纯碳酸盐岩,沿断裂破碎带、褶皱轴部裂隙发育带、可溶岩与非可溶岩接触地带等岩溶洞隙密集发育带分布;三是多发生在岩溶地下水强径流带、河流两岸等地下水位变化幅度大、水动力条件易发生急剧变化的地段;四是多发生在人类工程活动强烈的地区,塌陷的规模取决于人类活动的性质和强度。为了降低岩溶塌陷对工程建设和安全运营影响,本文同时提出了相关建议和对策。
结论 长江经济带岩溶塌陷分布广、危害大,高易发区内线性工程、重要城市群等规划建设应对这一环境地质问题引起重视,该研究成果可为长江经济带国土空间规划、地质灾害防治提供基础支撑和理论依据。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
Objective Karst collapse is one of the main environmental geological problems in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Conducting research on the distribution, causes, and impact on engineering construction of karst collapse in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is of great significance for the geological environment safety guarantee faced by the construction of multimodal transport corridor and urbanization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
Methods This article systematically summarizes the survey results of karst collapse implemented by China Geological Survey since 2016, including the geological background, cause types and mechanisms, development and distribution patterns, impact on engineering construction, and prevention and control measures of karst collapse.
Results The research results indicate that the area of potential karst collapse in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is about 254000 square kilometers, with 2146 documented karst collapse disasters events. Mine drainage, pumping and engineering construction are the main inducing factors for karst collapse in this area. The karst collapse in the Yangtze River Economic Belt has the following formation and distribution characteristics: firstly, it has regional and zonal distribution characteristics; The second is that the underlying strata are generally homogeneous pure carbonate rocks, distributed along strong karstification zones such as fault fracture zones, the axis of strata fold and contact zones between soluble and non-soluble rocks; Thirdly, it often occurs in areas with large amplitude, high speed, and high frequency of groundwater level fluctuation such as concentrated flow zone of karst and river terraces; Finally, it often occurs in areas with strong human engineering activities, and the scale and quantity mainly depend on the type and intensity of human activities. In order to reduce the impact of karst collapse on engineering, this article also proposes relevant suggestions and countermeasures.
Conclusions The karst collapse in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is widely distributed and has a great impact. The planning and construction of linear engineering and Megalopolis in high risk areas should pay attention to this issue. The research results can provide basic support and theoretical basis for the spatial planning of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the prevention and control of geological disasters.
-

-
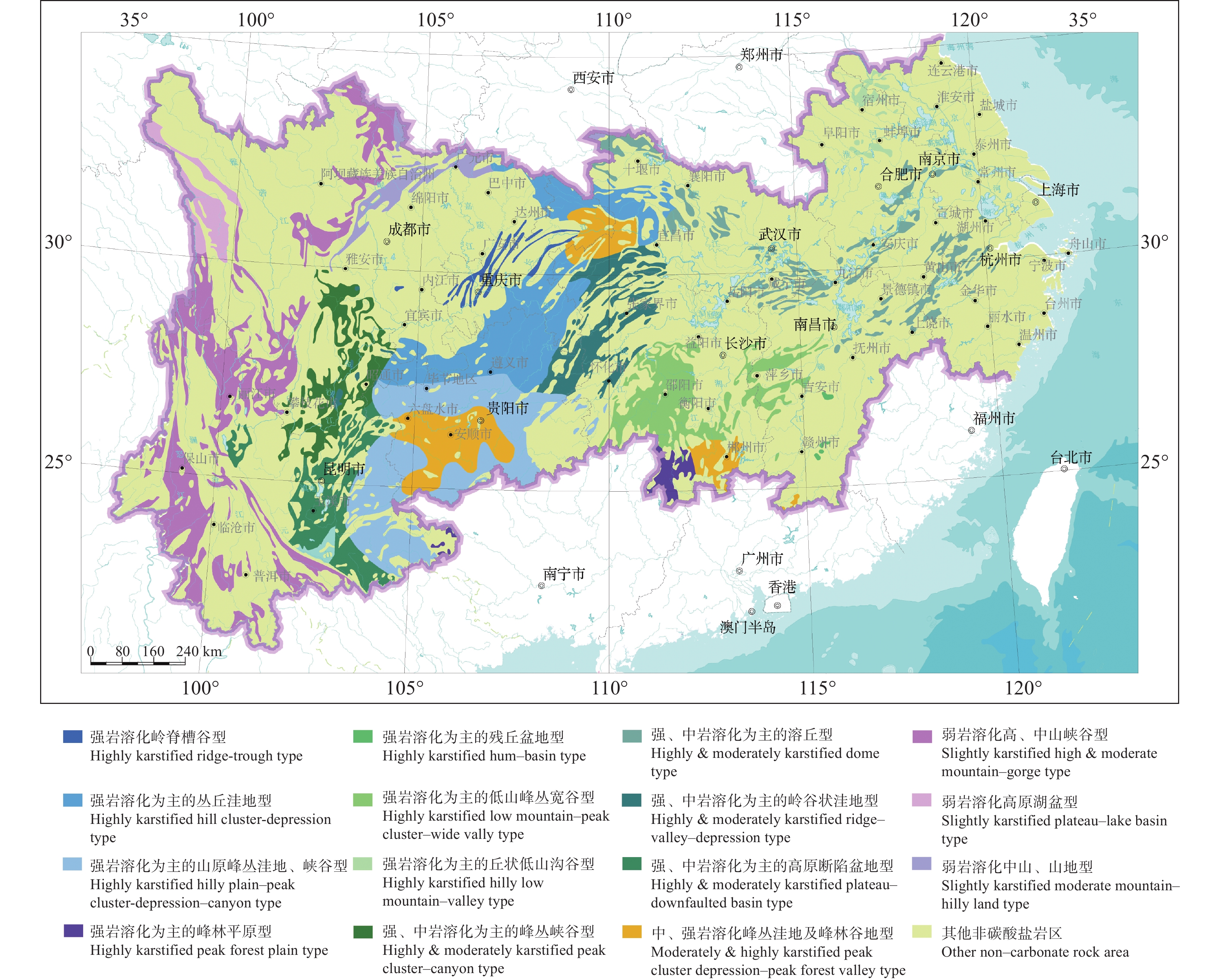
表 1 长江经济带岩溶环境一览
Table 1. List of environmental geology of karst in Yangtze River Economic Belt
编号 岩溶地质环境类型 分布范围 面积/km2 1 强岩溶化岭脊槽谷型 四川盆地东部 9504.39 2 强岩溶化为主的丛丘洼地型 黔北、川东南的一部分(云贵高原的北延部分) 94580.27 3 强岩溶化为主的山原峰丛洼地、峡谷型 滇东、黔中、黔南 97213.08 4 强岩溶化为主的峰林平原型 湘南永州西南地区 7328.42 5 强岩溶化为主的残丘盆地型 赣中南 986.38 6 强岩溶化为主的低山峰丛宽谷型 湘中、湘东及赣西 49714.31 7 强岩溶化为主的丘状低山沟谷型 皖中、皖北、苏西北地区 5979.38 8 强、中岩溶化为主的峰丛峡谷型 川西南—滇东北,云贵高原西部 34258.77 9 强、中岩溶化为主的溶丘型 长江中、下游两岸的大片地区 44129.11 10 强、中岩溶化为主的岭谷状洼地型 湘西、鄂西和黔东北的部分地区 37908.02 11 强、中岩溶化为主的高原断陷盆地型 滇中高原 40092.05 12 中、强岩溶化峰丛洼地及峰林谷地型 贵州都匀—贵阳—安顺地区以及湘南郴州一带 58883.16 13 弱岩溶化高、中山峡谷型 横断山脉大雪山一带 121371.64 14 弱岩溶化高原湖盆型 川西,与西藏交界地带 17229.91 15 弱岩溶化中山、山地型 高原、高山周围地形递降的斜坡带上 17442.03 表 2 长江经济带岩溶塌陷易发区及塌陷点数量统计
Table 2. Statistics of karst collapse prone areas and collapse points in Yangtze River Economic Belt
省 岩溶塌陷易发区面积/km2 岩溶塌陷/处 省 岩溶塌陷易发区面积/km2 岩溶塌陷/处 湖南省 29664 663 江苏省 446 58 贵州省 66867 603 重庆市 24653 67 湖北省 28892 348 安徽省 2451 29 云南省 71006 186 四川省 28719 20 江西省 4758 156 浙江省 2166 14 表 3 长江经济带岩溶塌陷与岩溶发育程度的关系
Table 3. Relationship between karst collapse and karst development degree in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
省区 Є O D C P T J K 岩溶发育程度 Є1 Є2 Є3 O1 O2 O3 D1 D2 D3 C1 C2 C3 P1 P2 T1 T2 T3 J K1 K2 强 中 弱 云南 2 1 1 1 76 6 46 9 5 3 137 5 8 四川 1 3 17 21 重庆 3 1 5 39 4 43 4 5 贵州 39 16 11 11 5 1 3 5 17 7 51 117 169 67 5 4 366 162 0 湖北 9 33 12 21 51 3 114 10 168 75 10 湖南 5 22 41 10 4 8 95 92 90 59 52 25 26 2 9 5 14 17 291 264 21 江西 3 3 16 32 6 2 51 9 2 安徽 2 1 2 13 14 4 江苏 2 22 6 28 2 浙江 7 2 5 14 合计 192 81 272 234 398 485 5 37 1133 525 46 百分比/% 11.27 4.75 15.96 13.73 23.36 28.46 0.29 2.17 66.49 30.81 2.70 -
[1] Bi Xueli, Shi Jian. 2018. Environmental Geological Map of Karst in China (attached instructions) 1: 500000 [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
[2] Brinkmann R, Parise M, Dye D. 2008. Sinkhole distribution in a rapidly developing urban environment: Hills borough country, Tampa Bay area, Florida[J]. Engineering Geology, 99(3/4): 169−184.
[3] Chen Guoliang, Chen Yuchang, Tan Hongzeng, Zhang Jianghua, Li Naifei. 1990. Research on mechanism, prediction and countermeasure for land-collapse in karst area[J]. Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1(3): 39–48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Cheng Xing, Huang Runqiu. 2003. Study on train–induced vibration and its influence on karst collapse[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 22(12): 2062−2066 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Deng Qijiang, Li Xingyu, Lu Qiong, Li Jianfeng. 2009. Development characters and prevention measures of the karst collapse in Kunming[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 28(1): 23−29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fu Kailong. 2005. An analysis of the karst ground collapse and water yield of the Zhongliangshan Tunnel in the Yusui Expressway[J]. Hydrogeological and Engineering Geology, (2): 107−110 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Gutierrez F, Parise M, De Waele J, Jourde H. 2014. A review on natural and human−induced geohazards and impacts in karst[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 138: 61−88. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.08.002
[8] He Fang, Xu Youning, Qiao Gang, Liu Ruiping. 2010. Regional distribution characteristics of mine environmental geological problems in China[J]. Geology in China, 37(5): 1520−1529 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Huang Jingjun, Cui Longyu, Wu Xin, Jiang Su, Jiang Guoqing, Xu Shiyin. 2019. The control of the old (abandoned course of ) Yellow River fault zone in Xuzhou on the karst collapse[J]. Geology in China, 46(2): 389−397 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Kang Yanren, Xiang Shijun. 1990. Karst Collapse in South China[M]. Nanning: Guangxi Science and Technology Press (in Chinese).
[11] Liu Lu. 2021. Research on mine geological environmental problems and prevention techniques in Huainan City[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 35(2): 200−205 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Luu L H, Noury G, Benseghier Z, Philippe P. 2019. Hydro–mechanical modeling of sinkhole occurrence processes in covered karst terrains during a flood[J]. Engineering Geology, 260: 1−12.
[13] Jiang Xiaozhen, Lei Mingtang, Guan Zhende. 2016. Character of water or barometric pressure jump within karst conduit in large strong drainage area of karst water filling mine in Dachengqiao, Ningxiang, Hunan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 35(2): 179−189 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Jiang Xiaozhen, Lei Mingtang. 2018. New karst sinkhole formation mechanism discovered in a mine dewatering area in Hunan, China[J]. Mine Water Environ, (37): 625−635.
[15] Jiang Yuehua, Lin Liangjun, Chen Lide, Ni Huayong, Ge Weiya, Cheng Hangxin, Zhai Gangyi, Wang Guiling, Ban Yizhong, Li Yuan, Lei Mingtang, Tan Chengxuan, Su Jingwen, Zhou Quanping, Zhang Taili, Li Yun, Liu Hongying, Peng Ke, Wang Hanmei. 2017. Research on conditions of resources and environment and major geological problems in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1045−1061 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Jiang Yuehua, Ni Huayong, Zhou Quanping, Cheng Zhiyan, Duan Xuejun, Zhu Zhimin, Wu Jichun, Ren Haiyan, Fan Chenzi, Yang Jinwei, Chen Chao, Hu Jian, Wang Xiaolong, Jiang Xiaye, Liu Yongbing, Yang Hai, Guo Wei, Feng Naiqi, Wei Guangqing, Jin Yang, Yang Hui, Liu Lin, Mei Shijia, Zhang Hong, Chen Pengjun, Yuan Jihai, Qi Qiuju, Lü Jinsong, Gu Xuan, Liu Peng. 2021. Key technology of ecological restoration demonstration in the Yangtze River Economic Zone and its application[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1305−1333 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Meng Yan, Lei Mingtang. 2019. Analysis of situation and trend of sinkhole collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(3): 411−417 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Pan Zongyuan, Jiang Xiaozhen, Dai Jianling, Guan Zhende, Wu Yuanbin. 2017. Study on the mechanism of groundwater level restoration process to karst sinkholes in karst deposit drainage area: A case of Dachengqiao, Ningxiang county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(6): 786−794 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Tan Kelong, Zhou Chunguang. 1996. Research on karst collapse in Enkou–Doulishan mine district of middle Hunan province[J]. Journal of Xi'an Mining Institute, 16(2): 130−134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Waltham T, Fred GB, Martin GG. 2005. Sinkholes and Subsidence[M]. Chichester: Praxis Publishing Ltd.
[21] Wu Mengjie, Shen Huizhen, Liu Sixi. 2013. Status quo and prevention measures of karst collapses in Zhejiang[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 24(4): 18−24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Wu Yuanbin, Yin Renchao, Lei Mingtang, Dai Jianling, Jia Long, Pan Zongyuan, Ma Xiao, Zhou Fubiao. 2021. Triggering factors and prevention–control countermeasures of karst collapses caused by tunnel construction in the Zhongliangshan area, Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 40(2): 246−252 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Xiang Shijun, Kang Yanren, Liu Zhiyun, Xie Daixing, Chen Jian, Yan Zhiwei. 1986. Karst collapse in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 5 (4): 255–272(in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Yang Decai. 2002. Study on pumping collapse in Shuicheng karst basin[J]. Geotechnical Engineering, 5(6): 27−29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Zhou W F, Lei M T. 2017. Conceptual site models for sinkhole formation and remediation[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(24): 818. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-7129-0
[26] Zhou Zheng, Li Dahua, Liao Yunping, Lin Junzhi, Zhang Ye, Chen Hongkai, Qi Yongai, Wang He. 2022. Characteristics and formation mechanism of karst ground collapse in Zhongliangshan area, Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 41(1): 67−78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] 毕雪丽, 时坚. 2018. 中国岩溶环境地质图(附说明书)1: 500000[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[28] 陈国亮, 陈裕昌, 谭鸿增, 张江华, 李乃飞. 1990. 岩溶地面塌陷机制、预测及整治研究[J]. 地质灾害与防治, 1(3): 39−48.
[29] 程星, 黄润秋. 2003. 铁路振动及其在岩溶塌陷中的致塌力研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 22(12): 2062−2066. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.12.021
[30] 邓启江, 李星宇, 吕琼, 李坚峰. 2009. 昆明市岩溶塌陷发育特征和防治措施[J]. 中国岩溶, 28(1): 23−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.01.005
[31] 付开隆. 2005. 渝遂高速公路中梁山隧道岩溶塌陷及涌水量分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, (2): 107−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.02.024
[32] 何芳, 徐友宁, 乔冈, 刘瑞平. 2010. 中国矿山环境地质问题区域分布特征[J]. 中国地质, 37(5): 1520−1529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.05.028
[33] 黄敬军, 崔龙玉, 武鑫, 姜素, 姜国庆, 徐士银. 2019. 徐州废黄河断裂带对岩溶塌陷的控制作用[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 389−397. doi: 10.12029/gc20190215
[34] 康彦仁, 项式均. 1990. 中国南方岩溶塌陷[M]. 南宁: 广西科学技术出版社.
[35] 刘璐. 2021. 淮南市矿山地质环境问题及防治技术研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 35(2): 200−205.
[36] 蒋小珍, 雷明堂, 管振德. 2016. 湖南宁乡大成桥充水矿山疏干区岩溶系统水气压力监测及突变特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 35(2): 179−189. doi: 10.11932/karst20160207
[37] 姜月华, 林良俊, 陈立德, 倪化勇, 葛伟亚, 成杭新, 翟刚毅, 王贵玲, 班宜忠, 李媛, 雷明堂, 谭成轩, 苏晶文, 周权平, 张泰丽, 李云, 刘红樱, 彭柯, 王寒梅. 2017. 长江经济带资源环境条件与重大地质问题[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1045−1061. doi: 10.12029/gc20170601
[38] 姜月华, 倪化勇, 周权平, 程知言, 段学军, 朱志敏, 吴吉春, 任海彦, 范晨子, 杨晋炜, 陈超, 胡建, 王晓龙, 姜夏烨, 刘永兵, 杨海, 郭威, 冯乃琦, 魏广庆, 金阳, 杨辉, 刘林, 梅世嘉, 张鸿, 陈澎军, 袁继海, 齐秋菊, 吕劲松, 顾轩, 刘鹏. 2021. 长江经济带生态修复示范关键技术及其应用[J]. 中国地质, 48(5): 1305−1333. doi: 10.12029/gc20210501
[39] 蒙彦, 雷明堂. 2019. 岩溶塌陷研究现状及趋势分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(3): 411−417. doi: 10.11932/karst20190311
[40] 潘宗源, 蒋小珍, 戴建玲, 管振德, 吴远斌. 2017. 岩溶矿床疏干区地下水位恢复对岩溶塌陷作用机制的研究: 以湖南宁乡大成桥为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 36(6): 786−794. doi: 10.11932/karst2017y41
[41] 谭克龙, 周春光. 1996. 湘中恩口—斗笠山矿区岩溶塌陷研究[J]. 西安矿业学院学报, 16(2): 130−134.
[42] 吴孟杰, 沈慧珍, 刘思秀. 2013. 浙江省岩溶地面塌陷现状及防治措施[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 24(4): 18−24.
[43] 吴远斌, 殷仁朝, 雷明堂, 戴建玲, 贾龙, 潘宗源, 马骁, 周富彪. 2021. 重庆中梁山地区隧道工程影响下岩溶塌陷形成演化模式及防治对策[J]. 中国岩溶, 40(2): 246−252. doi: 10.11932/karst20210204
[44] 项式均, 康彦仁, 刘志云, 谢代兴, 陈健, 阎志为. 1986. 长江流域的岩溶塌陷[J]. 中国岩溶, 5(4): 255−272.
[45] 杨德才. 2002. 水城岩溶盆地抽水塌陷研究[J]. 岩土工程界, 5(6): 27−29.
[46] 周正, 李大华, 廖云平, 林军志, 张烨, 陈洪凯, 祁永爱, 王贺. 2022. 重庆中梁山岩溶地面塌陷特征及形成机理[J]. 中国岩溶, 41(1): 67−78. doi: 10.11932/karst20220103
-



 下载:
下载: