Distribution characteristics, ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil of Beizhen agricultural area, Jinzhou City, Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 查明辽宁省锦州市北镇农业区重金属分布特征,可以为当地特色农业开发、全域旅游和土壤重金属污染管控提供科学依据。
研究方法 本文通过地质调查查明成土母质,采集表层土壤样品,以元素含量分布特征、富集程度为基础,开展土壤环境质量评价,利用地累积指数法进行重金属污染程度评价, Hakanson生态风险指数法识别研究区潜在生态风险程度,并通过Pearson相关性分析和聚类分析,定量分析不同重金属的主要来源。
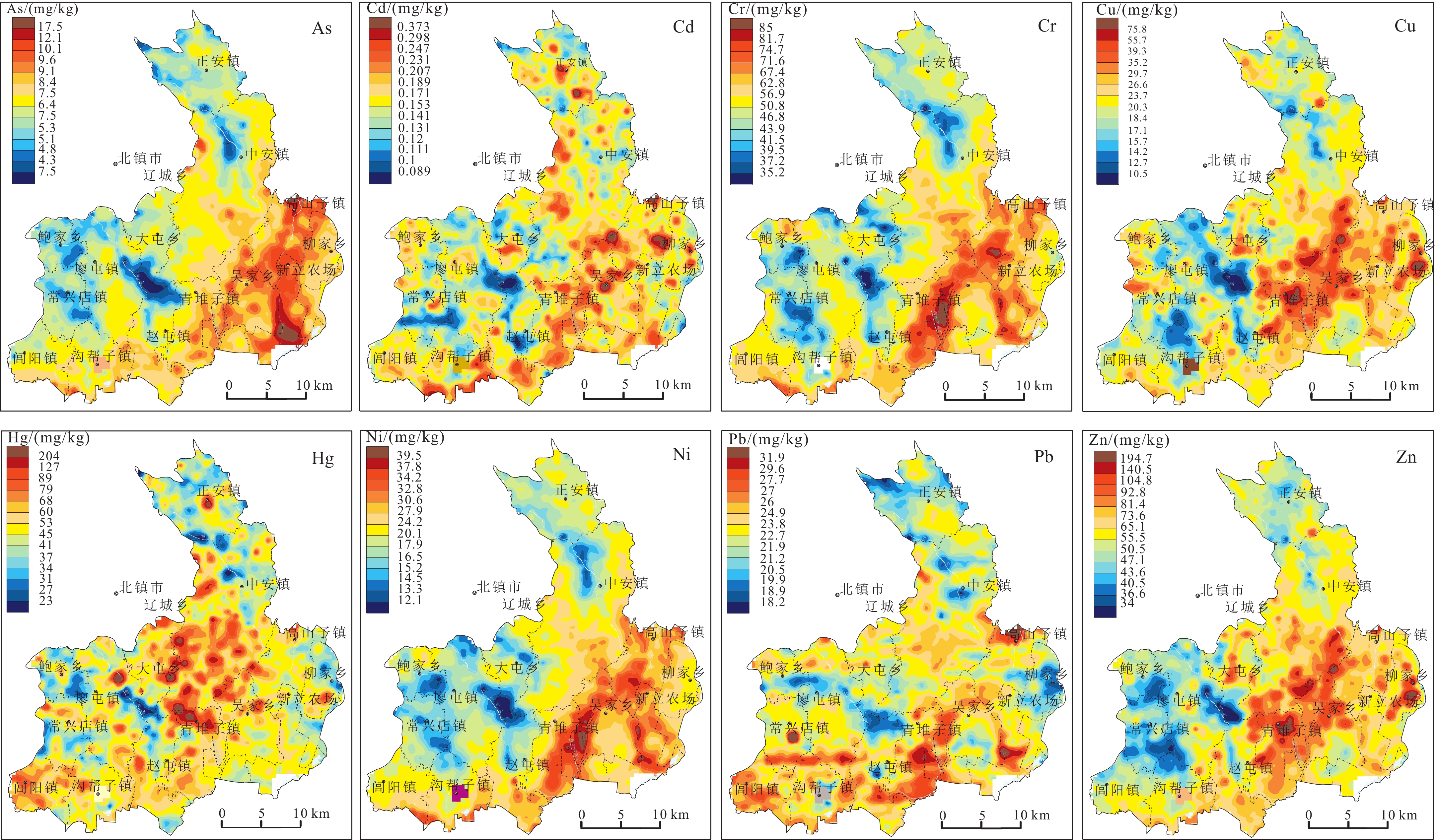
研究结果 北镇农业区土壤中Cr和Pb的均值低于辽宁省辽河流域背景值,表层土壤重金属富集程度由大到小排序为Hg>As>Cd>Pb>Zn>Cu>Cr>Ni。研究区土壤质量总体良好,在超标样品中Cd、Cu和Zn含量超过风险筛选值的占比分别为45.56%、29.11%和11.47%,占总超标数的86.12%;As和Cd为轻度污染状态,大部分土壤样品的重金属为无—轻度的污染状态,仅Hg元素个别采样点位为强—极强污染。单指标潜在生态风险由高到低排序为:Hg>Cd>As>Cu>Ni>Pb>Cr>Zn,土壤潜在生态风险综合指数RI分布范围为29.7~2358.16,平均值为141.9,以低度风险为主,其次中度风险。相关性分析和聚类分析结果表明,Ni、Cr、As、Pb主要受母岩自然风化影响,Cu、Zn、Cd、Hg受农业生产、工业生产、交通运输,甚至建筑活动等多种来源影响。
结论 农用物质的不合理施用、大气沉降、工业生产、生活垃圾和煤炭燃烧等产生的物质在土壤中富集可能对研究区生态环境质量造成污染风险,未来需要加强对Hg、Cd、Cu和Zn元素在不同地块中富集趋势监测和研究。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective To investigate the distribution characteristics of heavy metals and provide a scientific basis for local characteristic agricultural development, comprehensive tourism, and soil heavy metal pollution control.
Methods Through geological investigation, the soil parent material was identified, and topsoil samples were collected. Soil environmental quality evaluation was carried out based on the distribution characteristics and enrichment degree of element content. The degree of heavy metal pollution was evaluated using the ground accumulation index method. The Hakanson ecological risk index method was used to identify the degree of potential ecological risk in the study area. Furthermore, Pearson correlation analysis and cluster analysis were employed to quantitatively determine the main sources of different heavy metals.
Results The average values of Cr and Pb in the soil of the Beizhen agricultural area were lower than the background values of the Liaohe River Basin in Liaoning Province. The enrichment degree of heavy metals in the topsoil, from high to low, was Hg > As > Cd > Pb > Zn > Cu > Cr > Ni. The soil quality in the study area is generally good. The proportion of Cd, Cu, and Zn contents exceeding the risk screening values in the exceeding standard samples was 45.56%, 29.11%, and 11.47%, respectively, accounting for 86.12% of the total number of exceeding standards. The evaluation results of heavy metal pollution showed that As and Cd were in a mildly polluted state, most heavy metals in soil samples were in no to mild pollution, and only Hg elements had strong to extremely strong pollution at individual sampling points. The order of potential ecological risk of single indices from high to low is Hg > Cd > As > Cu > Ni > Pb > Cr > Zn. The distribution range of the potential ecological risk comprehensive index (RI) of surface soil in the whole region is 29.7 to 2358.16, with an average value of 141.9, primarily indicating low risk, followed by moderate risk. The results of correlation analysis and cluster analysis show that Ni, Cr, As, and Pb are mainly affected by the natural weathering of the parent rock, while Cu, Zn, Cd, and Hg are influenced by agricultural production, industrial production, transportation, and even construction activities.
Conclusions The enrichment of substances produced by the unreasonable application of agricultural substances, atmospheric deposition, industrial production, domestic garbage, and coal combustion in the soil may pose pollution risks to the ecological environment quality of the study area. In the future, it is necessary to strengthen the monitoring and research on the enrichment trend of Hg, Cd, Cu, and Zn elements in different plots.
-

-
表 1 农用地土壤污染风险筛选值
Table 1. Pollution risk screening value of agricultural land soil
序号 项目 风险筛选值/(mg/kg) pH≤5.5 5.5<pH≤6.5 6.5<pH≤7.5 pH>7.5 1 Cd 水田 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.8 其他 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.6 2 Hg 水田 0.5 0.5 0.6 1.0 其他 1.3 1.8 2.4 3.4 3 As 水田 30 30 25 20 其他 40 40 30 25 4 Pb 水田 80 100 140 240 其他 70 90 120 170 5 Cr 水田 250 250 300 350 其他 150 150 200 250 6 Cu 果园 150 150 200 200 其他 50 50 100 100 7 镍 60 70 100 190 8 锌 200 200 250 300 表 2 农用地土壤污染风险管制值
Table 2. Pollution risk control value of agricultural land soil
序号 项目 风险管制值/(mg/kg) pH≤5.5 5.5<pH≤6.5 6.5<pH≤7.5 pH>7.5 1 Cd 1.5 2.0 3.0 4.0 2 Hg 2.0 2.5 4.0 6.0 3 As 200 150 120 100 4 Pb 400 500 700 1000 5 Cr 800 850 1000 1300 表 3 土壤环境地球化学等级划分
Table 3. Geochemical classification of soil environment
等级 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 土壤环境 Pi≤1 1<Pi≤2 2<Pi≤3 3<Pi≤5 Pi>5 清洁 轻微污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 表 4 地质累积指数分级标准
Table 4. Classification standard of geological accumulation index
等级 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 6级 7级 Igeo <0 0~1 1~2 2~3 3~4 4~5 >5 描述 无污染 无到中度污染 中度污染 中度到强度污染 强度污染 强度到极强污染 极强污染 表 5 重金属潜在生态风险等级
Table 5. Potential ecological risk levels of heavy metals
生态风险指数 生态风险等级 低度 中度 重度 严重 Eri <40 40~80 80~160 >160 RI <150 150~300 300~600 >600 表 6 表层土壤重金属元素地球化学参数特征
Table 6. Characteristics of chemical parameters of heavy metal elements in surface soil
元素 最大值 最小值 平均值 中位数 标准差 偏度 峰度 变异系数 剔除3倍离差
后平均值富集
系数辽河流域
背景值As 75.5 0.001 7.23 6.8 2.63 6.27 124.44 0.36 7.03 1.05 6.70 Cd 1.98 0.03 0.17 0.16 0.09 6.37 84.28 0.55 0.16 1.23 0.13 Cr 112.7 17.4 55.3 53.1 13.24 0.64 0.21 0.24 55.04 0.92 60.00 Hg 1.73 0 0.05 0.05 0.06 14.87 321.78 1.15 0.045 1.50 0.03 Pb 134.5 10.1 23.54 23.1 4.04 8.52 207.99 0.17 23.34 0.97 24.00 Ni 95.2 5.7 23.08 21.7 7.38 0.88 2.13 0.32 22.94 1.00 23.00 Cu 313.2 2.4 24.13 20.8 17.56 7.21 78.26 0.73 21.1 1.13 18.70 Zn 712.4 14.8 65.82 56.6 43.52 6.88 69.79 0.66 58.37 1.08 54.00 注:标准差/富集系数/变异系数/偏度/峰度均无量纲;其他指标值的质量分数单位为mg/kg;土壤背景值来自于辽宁省辽河流域农业地质调查数据背景值。 表 7 农用地土壤污染风险筛选情况统计
Table 7. Statistics of pollution risk screening of agricultural land soil
pH值范围 样品数量/个 重金属风险筛选超标数/个 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn ≤5.5 1308 0 32 0 11 1 1 1 2 5.5~6.5 1091 1 54 0 59 0 0 1 34 6.5~7.5 881 0 49 0 15 0 0 0 14 >7.5 753 15 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 合计 4033 16 136 0 85 1 1 2 51 超标率/% — 0.40 3.37 0 2.12 0.025 0.025 0.05 1.27 表 8 农用地土壤污染风险管制情况统计
Table 8. Statistics of pollution risk control of agricultural land soil
pH值范围 Cd Hg As Pb Cr 管制值 超标数/个 管制值 超标数/个 管制值 超标数/个 管制值 超标数/个 管制值 超标数/个 ≤5.5 1.5 1 2 0 200 0 400 0 800 0 5.5~6.5 2 0 2.5 0 150 0 500 0 850 0 6.5~7.5 3 0 4 0 120 0 700 0 1000 0 >7.5 4 0 6 0 100 0 1000 0 1300 0 合计 1 0 0 0 0 超标率/% 0.025 0 0 0 0 表 9 研究区土壤环境元素等级统计
Table 9. Statistics of soil environmental element levels in the study area
元素 一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 Cu 面积/km2 1114.199 5.449 0.774 0.673 0.056 比例/% 99.38 0.486 0.069 0.06 0.005 Ni 面积/km2 1121.15 比例/% 100.00 Cd 面积/km2 1105.017 15.337 0.482 0.280 0.022 比例/% 98.561 1.368 0.043 0.025 0.002 Pb 面积/km2 1120.99 0.16 比例/% 99.99 0.01 As 面积/km2 1118.88 2.27 比例/% 99.80 0.20 Hg 面积/km2 1119.832 1.313 比例/% 99.88 0.12 Zn 面积/km2 1117.986 2.218 0.912 0.029 比例/% 99.72 0.198 0.081 0.003 Cr 面积/km2 1121.15 比例/% 100.00 综合 面积/km2 1095.168 23.461 1.406 0.982 0.078 比例/% 97.683 2.093 0.125 0.093 0.007 表 10 研究区单元素地累积指数分级统计
Table 10. Classification statistics of single element ground accumulation index in the study area
等级 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 6级 7级 Igeo
均值受污染点位占比% 描述 无污染 无—中度污染 中度污染 中度—强度污染 强度污染 强—极强污染 极强污染 As 1940 2037 51 4 1 0 0 0.04 51.90 Hg 2041 1706 213 53 13 4 3 0.03 49.39 Cr 3989 44 0 0 0 0 0 −0.74 1.09 Pb 4018 13 2 0 0 0 0 −0.63 0.37 Cd 3001 961 59 10 2 0 0 −0.33 25.59 Cu 3233 684 88 22 6 0 0 −0.38 19.84 Zn 3399 540 71 20 3 0 0 −0.44 15.72 Ni 3699 333 1 0 0 0 0 −0.65 8.28 表 11 研究区重金属元素潜在生态风险指数分级统计
Table 11. Classification statistics of potential ecological risk index of heavy metal elements in the study area
风险等级 潜在生态风险指数 各风险等级样本数/个 最小值 最大值 平均值 低度 中度 重度 严重 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ As 0.0015 112.61 10.79 4028 4 1 0 Cd 7.25 455.85 39.21 2516 1408 93 16 Cr 0.58 3.76 1.84 4033 0 0 0 Hg 0.0013 2311.42 72.48 592 2596 689 156 Pb 2.1 28.03 4.9 4033 0 0 0 Ni 1.23 20.69 5.02 4033 0 0 0 Cu 0.65 83.76 6.45 4017 15 1 0 Zn 0.27 13.19 1.22 4033 0 0 0 RI 29.7 2358.16 141.9 2842 1091 80 20 表 12 研究区表层土壤重金属元素含量相关性
Table 12. Correlation of heavy metal elements in surface soil of study area
重金属 As Cd Cr Hg Pb Ni Cu Zn As 1 Cd 0.3039 1 Cr 0.6444** 0.2807 1 Hg 0.0639 0.1725 0.092 1 Pb 0.4505* 0.2987 0.4201* 0.0612 1 Ni 0.7019** 0.2457 0.935** 0.0528 0.3924 1 Cu 0.2485 0.4099* 0.2797 0.2482 0.1237 0.2776 1 Zn 0.2729 0.3801 0.2913 0.2729 0.1284 0.2975 0.9304** 1 注:**表示P<0.01,为极显著相关;*表示P<0.05,为显著相关。 表 13 表层土壤重金属元素含量主成分
Table 13. Principal component of heavy metal elements content in surface soil
成分 初始特征值 提取平方和荷载 旋转成分矩阵 特征值 贡献率/% 累积贡献率/% 特征值 贡献率/% 累积贡献率/% 重金属 F1 F2 1 3.49 43.58 43.58 3.49 43.58 43.58 As 0.828 0.145 2 1.69 21.1 64.68 1.69 21.1 64.68 Cd 0.311 0.531 3 0.89 11.09 75.77 Cr 0.902 0.153 4 0.83 10.4 86.17 Hg −0.031 0.490 5 0.59 7.34 93.52 Pb 0.636 0.050 6 0.39 4.91 98.43 Ni 0.914 0.136 7 0.07 0.86 99.28 Cu 0.147 0.925 8 0.06 0.72 100 Zn 0.16 0.921 -
[1] Bao Liran, Deng Hai, Jia Zhongmin, Li Yu, Dong Jinxiu, Yan Mingshu, Zhang Fenglei. 2020. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1625−1636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Bao Shihai. 2013. Current status and analysis of soil environmental quality of basic farmland in Jinzhou City[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (12): 184–185(in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Xiaomin, Zhu Baohu, Yang Wen. 2015. Sources, spatial distribution and contamination assessments of heavy metals in gold mine area soils of Miyun Reservoir upstream, Beijing, China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(12): 2248−2256 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Yali, Weng Liping, Ma Jie, Wu Xiaojuan, Li Yongtao. 2019. Research progress on source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in Chinese soil in the past decade[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Science, 38(10): 2219−2238 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Cui Xingtao, Luan Wenlou, Song Zefeng. 2016. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 43(2): 683−690 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fan Sheng. 2014. Accumulation and Risk Study of Heavy Metal Element Pollution in Mining Areas[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 1–65(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Forstner U, Ahlf W, Calmano W. 1993. Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany[J]. Water Science and Technology, 28(8): 307−314.
[8] Hakanson L. 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sediment to logical approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975−1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[9] Hao Libo, Lu Jilong, Ma Li. 2005. The relationship and significance between soil chemical composition and bedrock chemical composition in shallow covering areas: A case study of the northern Daxing'an Mountains[J]. Geology in China, 32(3): 477–482(in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Huang Yong, Duan Xuchuan, Yuan Guoli, Li Huan, Zhang Qinrui. 2022. Geochemistry and source identification of heavy metals in the top and sub–soil of Yanqing District in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 36(2): 634–644 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Jiang Baiwen, Lu Lei, Wang Chunhong, Gao Qiang, Zhang Di, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling, 2020. Effect of organic fertilizer application on heavy metals accumulation in soil and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 51(4): 37–44(in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Lei Guojian, Chen Zhiliang, Liu Qianjun, Peng Xiaochun, Jiang Xiaolu, Ou Yingjuan, Zhou Ding, Li Fanghong. 2013. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution level and potential ecological hazards in suburban areas of Guangzhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Sciences, 33(S1): 49–53 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Li Fengguo, Chen ming, Shi Yanli, Zheng Xiaojun, Liu Yan, Liu Youcun, Tao Meixia, Hu Lanwen. 2020. Spatial distribution and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in sediments of the upper reaches of Ganjiang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(3): 920−927(in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Qiuyan, Wei Minghui, Dai Huimin, He Pengfei, Liu Kai. 2021. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in Jinzhou City[J]. Geology and Resources, 30(4): 465−472 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Lin Yanping, Zhao Yang, Hu Gongren, Su Guangming. 2011. Application of multivariate statistics in source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution[J]. Earth and Environment, 39(4): 536−542(in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Liu Tong, Liu Chuanpeng, Deng Jun, Kang Pengyu, Wang Kaikai, Zhao Yuyan. 2022. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in eastern Yinan County, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1497−1508 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Lü Jianshu, Zhang Zulu, Liu Yang, Dai Jeirui, Wang Xue, Wang Maoxiang. 2012. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(7): 971−984 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Ma Zhenghu, Qu Xiangning, He Zhirun, Zhao Xini, Liu Yaqing, Zhang Yuxun, Yang Lei. 2022. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Ningxia Yuehai Lake[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 43(2): 116−124 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Ma Z, Chen K, Li Z, Bi J, Huang L. 2016. Heavy metals in soils and road dusts in the mining areas of Western Suzhou, China: A preliminary identification of contaminated sites[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(1): 204–214.
[20] Muller G. 1969. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhime River[J]. Geological Journals, 2: 109−118.
[21] Ning Zengping, Lan Xiaolong, Huang Zhengyu, Chen Haiyan, Liu Yizhang, Xiao Tangfu, Zhao Yanlong. 2017. Spatial distribution characteristics, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Hejiang River[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(8): 3036−3047 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Ren Yu, Cao Wengeng, Xiao Shunyu, Li Xiangzhi, Pan Deng, Wang Shuai. 2024. Research progress on distribution, harm and control technology of heavy metals in soil[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 118−142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Shao Li, Xiao Huayun, Wu Daixun, Tang Congguo. 2012. Research progress on heavy metal pollution from transportation sources[J]. Earth and Environment, 40(3): 445−459 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Sun Chao 2010. Distribution and Accumulation Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil of Chongming Island[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 1–155(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Sun L G, Liu D K, Ke M, Hui Z, Yuan Y J, Zhu F Q, Gang H. 2019. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China[J]. Catena, 175: 101−109. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.014
[26] Sun Wenxian, Niu Xiaoyin, Zheng Jiawen, Liu Aiju, Li Menghong. 2021. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in facility farmland soil in Gaoqing County[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 35(3): 17−23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Tang Jinlai, Zhao Kuan, Hu Ruixin, Xu Tao, Wang Yixuan, Yang Yang, Zhou Baohua. 2023. Characteristics, source apportionment, and pollution assessment of heavy metal content in surface soil of Chuzhou City[J]. Environmental Science, 44(6): 3562−3572 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Tang Jiang. 2005. Study on the Regularity of Move, Enrichment, and Translation of Cadmium and Other Heavy Metals in the District of the Three Gorges Reservoir[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1–117 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Tume P, González E, Reyes F, Fuentes J P, Roca N, Bech J, Medina G. 2019. Sources analysis and health risk assessment of trace elements in urban soils of Hualpen, Chile[J]. Catena, 175: 304−316. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.030
[30] Wang A T, Wang Q, Li J, Yuan G L, Albanese S, Petrik A. 2019. Geo–statistical and multivariate analyses of potentially toxic elements' distribution in the soil of Hainan Island (China): A comparison between the topsoil and subsoil at a regional scale[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 197: 48−59. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.11.008
[31] Wang H Y, Lu S G. 2011. Spatial distribution, source identification and affecting factors of heavy metals contamination in urban–suburban soils of Lishui City, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(7): 1921−1929. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1005-0
[32] Wang Weipeng, Lu Hongwei, Feng Sansan. 2020. Ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the central area of one river and two rivers in Tibet[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(6): 970−980 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Wang Zhongyang. 2018. Cultivated Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Risk Assessment and Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in chaoyang area[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 1–133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wei Xiao. 2017. Soil geochemistry and heavy metal accumulation characteristics in Jiangxinzhou, Anhui section of the Yangtze River [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 1–68(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Xiao J Q, Yuan X Y, Li J Z. 2010. Characteristics and transformation of heavy metal pollution in soil and rice of Yangtze River Delta Region[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, (4): 148−151.
[36] Xu Zhengqi, Ni Shijun, Tuo Xianguo, Zhang Chengjiang. 2008. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(2): 112−115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yan Hongze, Zhou Guohua, Sun Binbin, He Ling, Liu Yinfei, Hou Shujun. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of the bayberry producing area in Longhai, Fujian[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1155−1166 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, Duan Q, Huang L, Bi J. 2018. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 642: 690−700. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.068
[39] Yang Yu, Guo Tingting, Liu Xiaoli, Tie Baiqing. 2023. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils in typical agricultural small watersheds in southern mining areas[J]. Environmental Science, 44(3): 1602−1610 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Yin Dechao, QI Xiaofan, Wang Yushan, Xu Rongzhen, An Yonghui, Wang Xuqing, Geng Hongjie. 2022. Geochemical characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals insurface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, Xiong'an New District[J]. Geology in China, 49(3): 979−992 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Yu Chao, Wang Hongjin. 2014. Agro–ecological Geochemical Survey and Evaluation in Linyi City, Shandong Province[R]. Jinan: Shandong Institute of Geological Survey.
[42] Yu Rui, Wang Yang, Wang Chenxu, Wang Qicun, Cui Zhengwu. 2017. Analysis of heavy metal pollution status and sources in black soil of corn planting area in Yushu City[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 26(10): 1788−1794 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Yuan G L, Sun T H, Han P, Li J. 2013. Environmental geochemical mapping and multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils of a closed steel smelter: Capital Iron & Steel Factory, Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 130: 15−21. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.02.010
[44] Zhang Ding, Huang Rong, Gao Xuesong. 2022. Spatial characteristics and potential ecological risk factors of heavy metals in cultivated land in transition zone of mountain plain[J]. Environmental Science, 43(2): 946−956 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhang Xianyi, Pang Chengbao, Wang Anting, Yuan Guoli, Sang Xuezhen, Li Yuanzhong, Yang Yi. 2020. Distribution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in topsoils and subsoils of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 34(5): 970−978 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Zhao Yan, Guo Changlai, Li Xuguang, Sun Xiubo. 2021. Geological heritage resource endowment and protective utilization in Jinzhou City, Liaoning Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(10): 1688−1696 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 2020. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1625−1636.
[48] 鲍士海. 2013. 锦州市基本农田土壤环境质量现状及分析[J]. 绿色科技, (12): 184−185.
[49] 陈小敏, 朱保虎, 杨文, 季宏兵. 2015. 密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属空间分布、来源及污染评价[J]. 环境化学, 34(12): 2248−2256.
[50] 陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 武晓娟, 李永涛. 2019. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(10): 2219−2238.
[51] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 马云超. 2016. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质, 43(2): 683−690.
[52] 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 2022. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 36(2): 634−644.
[53] 凡生. 2014. 矿集区重金属元素污染累积与风险研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 1−65.
[54] 郝立波, 陆继龙, 马力. 2005. 浅覆盖区土壤化学成分与基岩化学成分的关系及其意义—以大兴安岭北部地区为例[J]. 中国地质, 32(3): 477−482.
[55] 姜佰文, 陆磊, 王春宏, 高强, 张迪, 陈曦, 王艳玲. 2020. 施用有机肥对土壤重金属累积的影响及风险评价[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 51(4): 37−44.
[56] 雷国建, 陈志良, 刘千钧, 彭晓春, 蒋晓璐, 欧英娟, 周鼎, 李方鸿. 2013. 广州郊区土壤重金属污染程度及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 33(S1): 49−53.
[57] 李凤果, 陈明, 师艳丽, 郑小俊, 刘燕, 刘友存, 陶美霞, 胡兰文. 2020. 赣江上游沉积物重金属空间分布及污染特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 920−927.
[58] 李秋燕, 魏明辉, 戴慧敏, 贺鹏飞, 刘凯. 2021. 锦州市土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 地质与资源, 30(4): 465−472.
[59] 林燕萍, 赵阳, 胡恭任, 苏光明. 2011. 多元统计在土壤重金属污染源解析中的应用[J]. 地球与环境, 39(4): 536−542.
[60] 刘同, 刘传朋, 邓俊, 康鹏宇, 王凯凯, 赵玉岩. 2022. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1497−1508.
[61] 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 代杰瑞, 王学, 王茂香. 2012. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 67(7): 971−984.
[62] 马正虎, 璩向宁, 何志润, 赵希妮, 刘雅清, 张矞勋, 杨蕾. 2022. 宁夏阅海底泥重金属空间分布特征及来源解析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 43(2): 116–124.
[63] 宁增平, 蓝小龙, 黄正玉, 陈海燕, 刘意章, 肖唐付, 赵彦龙. 2017. 贺江水系沉积物重金属空间分布特征、来源及潜在生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(8): 3036−3047.
[64] 任宇, 曹文庚, 肖舜禹, 李祥志, 潘登, 王帅. 2024. 重金属在土壤中的分布、危害与治理技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 118−142.
[65] 邵莉, 肖化云, 吴代赦, 唐从国. 2012. 交通源重金属污染研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 40(3): 445−459.
[66] 孙超. 2010. 崇明岛农田土壤重金属的分布与累积特征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 1−155.
[67] 孙文贤, 牛晓音, 郑家文, 刘爱菊, 李梦红. 2021. 高青县设施农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 山东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 35(3): 17−23.
[68] 汤金来, 赵宽, 胡睿鑫, 徐涛, 王宜萱, 杨扬, 周葆华. 2023. 滁州市表层土壤重金属含量特征、源解析及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 44(6): 3562−3572.
[69] 唐将. 2005. 三峡库区镉等重金属元素迁移富集及转化规律[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 1–117.
[70] 王伟鹏, 卢宏玮, 冯三三. 2020. 西藏一江两河流域中部地区土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(6): 970−980.
[71] 王中阳. 2018. 朝阳地区耕地土壤重金属污染风险评价与来源解析研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 1–133.
[72] 魏晓. 2017. 长江安徽段江心洲土壤地球化学及重金属累积特征[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 1–56.
[73] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 张成江. 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 31(2): 112−115.
[74] 严洪泽, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 刘银飞, 候树军. 2018. 福建龙海杨梅产地元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1155−1166.
[75] 杨宇, 郭婷婷, 刘孝利, 铁柏清. 2023. 南方典型矿区农业小流域耕地土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 44(3): 1602−1610.
[76] 尹德超, 祁晓凡, 王雨山, 徐蓉桢, 安永会, 王旭清, 耿红杰. 2022. 雄安新区白洋淀表层沉积物重金属地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(3): 979−992.
[77] 喻超, 王红晋. 2014. 山东省临沂市农业生态地球化学调查与评价[R]. 济南: 山东省地质调查院.
[78] 于锐, 王洋, 王晨旭, 王其存, 崔政武. 2017. 榆树市玉米种植区黑土重金属污染状况及来源浅析[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(10): 1788−1794.
[79] 张丁, 黄容, 高雪松. 2022. 山地平原过渡带耕地土壤重金属空间特征及潜在生态风险因素探析[J]. 环境科学, 43(2): 946−956.
[80] 张宪依, 庞成宝, 王安婷, 袁国礼, 桑学镇, 李元仲, 杨毅. 2020. 海南岛表层及深层土壤重金属分布特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 34(5): 970−978.
[81] 赵岩, 郭常来, 李旭光, 孙秀波. 2021. 辽宁锦州市地质遗迹资源禀赋及保护性利用[J]. 地质通报, 40(10): 1688−1696.
-




 下载:
下载: