Pollution characteristics, source analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around a gold mine in Jiaodong Peninsula
-
摘要:
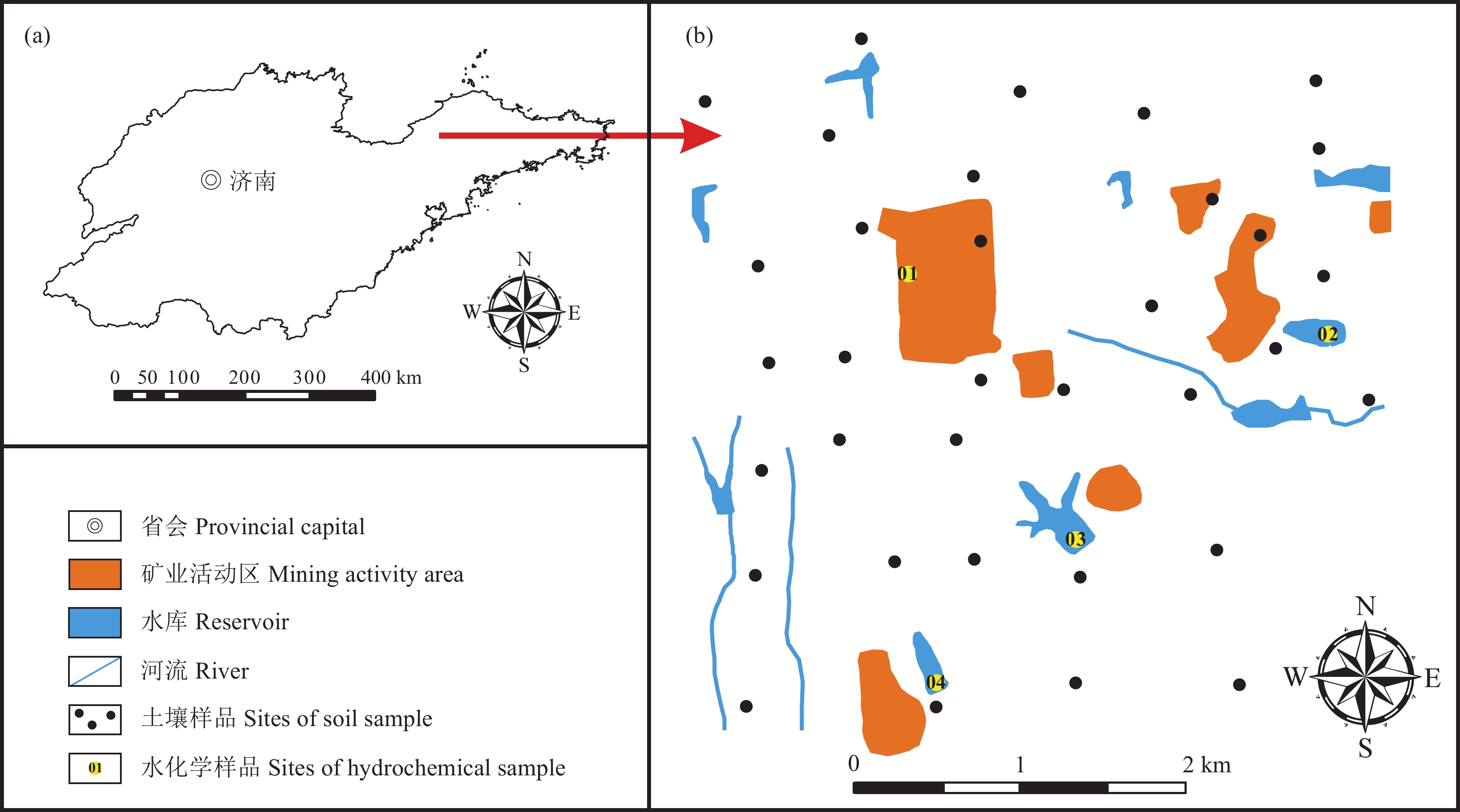
研究目的 本文采集了表层土壤样品34件,分析测定Hg、Cd、As、Pb、Cu、Cr、Zn、Ni等8种重金属元素含量;获取胶东半岛某金矿周边土壤重金属污染特征,分析土壤重金属来源并进行风险评价。
研究方法 运用相关性分析和主成分分析方法探索土壤重金属的来源,运用单项污染评价和地累积指数法确定其污染程度,采用潜在生态风险评价和人体健康风险评价的方法评估其风险。
研究结果 (1)全区仅存在3处点源污染,1处为Hg元素污染,2处为Cd元素污染;(2)元素Ni、Cr和As主要来自于土壤母质,元素Pb、Cd、Zn和Hg主要来自于矿业活动,Cu元素主要来自土壤母质和农业活动;(3)个别点状区域存在较高的潜在生态风险,风险主要来自于元素Hg和Cd,其他元素基本上不存在风险;(4)人体健康风险评价结果表明,全区土壤中的重金属元素未对人体产生明显的健康风险。
结论 该金矿周边的土壤受到了矿业活动的影响,并出现了点状污染,但程度较轻,风险可控,应当加强对该区域土壤重金属的监测和评价。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective This paper collected 34 surface soil samples to analyze and determine the concentrations of eight heavy metal, including Hg, Cd, As, Pb, Cu, Cr, Zn, and Ni. The objective was to characterize the heavy metal pollution in the soil around a gold mine, identify the sources of heavy metals in the soil, and conduct a risk assessment.
Methods Correlation analysis and principal component analysis were used to explore the sources of heavy metals in the soil. Single pollution evaluation and geo−accumulation index method were employed to determine the degree of pollution. Potential ecological risk assessment and human health risk assessment methods were utilized to evaluate the risks.
Results (1) Only three point source pollutions were found in the study area: one for Hg contamination and two for Cd contamination. (2) Nickel, chromium, and arsenic mainly originated from soil parent materials, while lead, cadmium, zinc, and mercury primarily came from mining activities. Copper was derived from both soil parent materials and agricultural activities. (3) Some localized areas demonstrated high potential ecological risks, mainly due to Hg and Cd, while other elements posed minimal risks. (4) Human health risk assessment indicated that the heavy metal elements in the soil did not pose significant health risks to humans.
Conclusions The soil around the gold mine was influenced by mining activities and exhibited localized pollution, albeit at a low level. The risks were manageable, but monitoring and assessment of heavy metals in this area should be strengthened.
-

-
表 1 重金属单项污染评价标准
Table 1. Evaluation standards of single factor
等级 重金属浓度(Ci) 污染水平 Ⅰ Ci<Si 无风险 Ⅱ Si≤Ci<Gi 风险可控 Ⅲ Ci≥Gi 风险较高 表 2 地累积指数污染程度分级
Table 2. Evaluation standards of the geological accumulation index assessment
地累积指数 级别 污染程度 Igeo<0 0 无污染 0≤Igeo<1 1 无污染到中度污染 1≤Igeo<2 2 中度污染 2≤Igeo<3 3 中度污染到强污染 3≤Igeo<4 4 强污染 4≤Igeo<5 5 强污染到极强污染 Igeo≥5 6 极强污染 表 3 重金属潜在风险指数评价标准
Table 3. Evaluation standards of the potential ecological risk index
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 潜在生态风险程度 RI 潜在生态风险程度 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ <40轻微 RI<150 轻微 40≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ <80中等 150≤RI<300 中等 80≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ <160强 300≤RI<600 强 160≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ <320很强 600≤RI<1200 很强 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ ≥320极强 RI≥1200 极强 表 4 重金属元素健康风险评价暴露因子参数
Table 4. Calculation parameters of human intake of heavy metals
参数 含义 单位 参考值 数据来源 成人 儿童 IngR 每日经口摄入土壤量 mg/d 100 200 USEPA,2011 InhR 每日呼吸吸入土壤量 m3/d 14.5 7.5 ABS 皮肤吸附因子 无量纲 0.01 0.01 ED 暴露年限 a 25 6 BW 平均体重 kg 56.8 15.9 AT 非致癌 平均暴露时长 d 9125 2190 致癌 26280 26280 PEF 颗粒物释放因子 m3/kg 1.36×109 1.36×109 EF 暴露频率 d/a 350 350 环境保护部,2014 SL 皮肤黏着因子 mg/(cm2·d) 0.07 0.2 SA 皮肤暴露面积 cm2 2011 1078 王喆等,2008 表 5 土壤重金属不同暴露途径的RFD和SF
Table 5. Reference values of RFD and SF
元素 RFD/(mg·kg−1·d−1) SF/(kg·d·mg−1) 经口摄入 呼吸吸入 皮肤接触 经口摄入 呼吸吸入 皮肤接触 As 3×10−4 1.5×10−5 3×10−4 1.5 4.3×10−3 1.5 Cd 1×10−3 1×10−5 2.5×10−5 6.1 6.3 6.1 Cr 3×10−3 2.55×10−5 7.5×10−5 — 42 — Cu 4×10−2 — 4×10−2 — — — Hg 3×10−4 3×10−4 2.1×10−5 — — — Ni 2×10−2 2.3×10−5 8×10−4 — 0.84 — Pb 3.5×10−3 3.5×10−3 5.3×10−4 — — — Zn 3×10−1 — 3×10−1 — — — 表 6 研究区土壤重金属含量特征
Table 6. Characteristics of soil heavy metal concentration in the study area
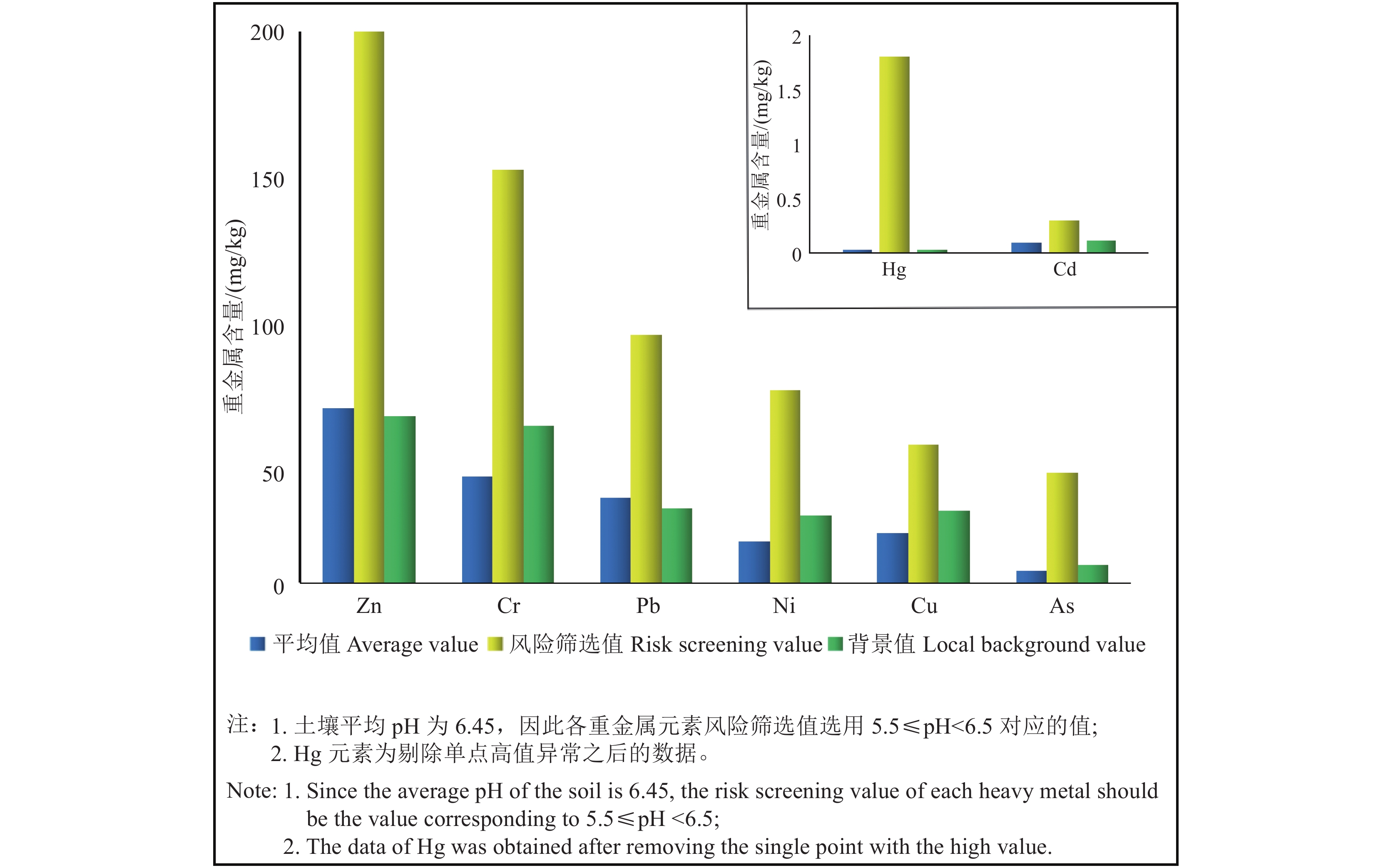
元素 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准差 变异
系数/%背景值
(庞绪贵等, )
2019As 1.13 9.19 4.53 2.57 56.82 6.4 Cd 0.03 0.396 0.098 0.077 78.62 0.117 Cr 14.8 95.3 38.54 16.26 42.19 57 Cu 4.55 41.5 18.05 11.12 61.59 26 Hg 0.00658 2.415 0.101 0.41 405.53 0.034 Hg* 0.00658 0.109 0.031 0.024 77.69 0.034 Ni 3.33 47.9 15.17 9.20 60.62 24.6 Pb 13.6 85.9 30.87 14.81 47.99 27.2 Zn 34 157 63.29 26.87 42.45 60.4 pH 4.75 8.08 6.31 0.91 14.49 6.45 注:Hg*为剔除单点高值异常后,对应的数值;含量单位为mg/kg。 表 7 土壤重金属元素的Pearson相关性分析
Table 7. Pearson correlation analysis of soil heavy metals
相关性 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn pH As 1 Cd −0.014 1 Cr 0.428* 0.003 1 Cu 0.043 0.341* 0.629** 1 Hg −0.028 0.101 −0.012 0.288 1 Ni 0.458** 0.030 0.944** 0.524** −0.034 1 Pb −0.099 0.629** −0.263 −0.121 0.023 −0.187 1 Zn −0.079 −0.079 −0.043 0.150 0.319 0.037 0.815** 1 pH −0.184 0.265 0.170 0.365* 0.012 0.135 0.079 0.120 1 注:**为在0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著;*为在0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 8 土壤重金属元素主成分分析
Table 8. Principal component analysis of soil heavy metals
指标 主成分1 主成分2 主成分3 主成分4 As 0.634 0.024 −0.557 −0.106 Cd 0.102 0.807 0.268 0.028 Cr 0.953 −0.101 0.133 0.023 Cu 0.615 0.081 0.528 0.396 Hg −0.013 0.104 −0.026 0.965 Ni 0.945 −0.02 0.050 −0.026 Pb −0.200 0.935 −0.050 −0.091 Zn 0.008 0.892 0.010 0.259 pH 0.122 0.135 0.843 −0.079 特征值 2.647 2.368 1.394 1.184 累积/% 29.411 55.725 71.219 84.373 表 9 研究区土壤重金属元素非致癌日摄入量
Table 9. Non-carcinogenic daily intake of soil heavy metals in the study area
元素 ADDiing ADDiinh ADDiderm ADD 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 As 7.64×10−6 5.46×10−5 8.15×10−10 1.51×10−9 1.08×10−7 5.89×10−7 7.75×10−6 5.52×10−5 Cd 1.65×10−7 1.18×10−6 1.76×10−11 3.25×10−11 2.32×10−11 1.27×10−11 1.67×10−7 1.19×10−6 Cr 6.51×10−5 4.65×10−4 6.94×10−9 1.28×10−8 9.16×10−7 5.01×10−6 6.60×10−5 4.70×10−4 Cu 3.05×10−5 2.18×10−4 3.2×10−9 6.00×10−9 4.29×10−7 2.35×10−6 3.09×10−5 2.20×10−4 Hg 1.70×10−7 1.22×10−6 1.82×10−11 3.36×10−11 2.40×10−9 1.31×10−8 1.73×10−7 1.23×10−6 Ni 2.56×10−5 1.83×10−4 2.73×10−9 5.05×10−9 3.61×10−7 1.97×10−6 2.60×10−5 1.85×10−4 Pb 5.21×10−5 3.72×10−4 5.56×10−9 1.03×10−8 7.34×10−7 4.01×10−6 5.29×10−5 3.76×10−4 Zn 1.07×10−4 7.63×10−4 1.14×10−8 2.11×10−8 1.50×10−6 8.23×10−6 1.08×10−4 7.72×10−4 ADD 2.88×10−4 2.06×10−3 3.07×10−8 5.68×10−8 4.06×10−6 2.22×10−5 2.92×10−4 2.08×10−3 表 10 研究区土壤重金属元素致癌日摄入量
Table 10. Carcinogenic daily intake of soil heavy metals in the study area
元素 ADDiing ADDiinh ADDiderm ADD 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 As 2.65×10−6 4.55×10−6 2.83×10−10 1.25×10−10 3.74×10−8 4.91×10−8 2.69×10−6 4.60×10−6 Cd 5.73×10−8 9.83×10−8 6.11×10−12 2.71×10−12 8.07×10−10 1.06×10−9 5.81×10−8 9.93×10−8 Cr 2.26×10−5 3.87×10−5 2.41×10−9 1.07×10−9 3.18×10−7 4.18×10−7 2.29×10−5 3.92×10−5 Ni 8.89×10−6 1.53×10−5 9.48×10−10 4.21×10−10 1.25×10−7 1.64×10−7 9.02×10−6 1.54×10−5 ADD 3.42×10−5 5.86×10−5 3.65×10−9 1.62×10−9 4.81×10−7 6.32×10−7 3.47×10−5 5.93×10−5 表 11 研究区土壤重金属元素非致癌风险指数
Table 11. Non-carcinogenic risk index of soil heavy metals in the study area
元素 统计值 HQiing HQiinh HQiderm HQ 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 As 平均值 2.55×10−2 1.82×10−1 5.43×10−5 1.00×10−4 3.07×10−4 1.68×10−3 2.58×10−2 1.84×10−1 最大值 5.17×10−2 3.69×10−1 1.10×10−4 2.04×10−4 6.24×10−4 3.41×10−3 5.24×10−2 3.73×10−1 Cd 平均值 1.65×10−4 1.18×10−3 1.76×10−6 3.25×10−6 9.29×10−5 5.08×10−4 2.60×10−4 1.69×10−3 最大值 6.69×10−4 4.78×10−3 7.13×10−6 1.32×10−5 3.76×10−4 2.06×10−3 1.05×10−3 6.85×10−3 Cr 平均值 2.17×10−2 1.55×10−1 2.72×10−4 5.03×10−4 1.22×10−2 6.68×10−2 3.42×10−2 2.22×10−1 最大值 5.36×10−2 3.83×10−1 6.73×10−4 1.24×10−3 3.02×10−2 1.65×10−1 8.45×10−2 5.50×10−1 Cu 平均值 7.62×10−4 5.44×10−3 — — 1.07×10−5 5.87×10−5 7.73×10−4 5.50×10−3 最大值 1.75×10−3 1.25×10−2 — — 2.47×10−5 1.35×10−4 1.78×10−3 1.26×10−2 Hg 平均值 5.68×10−4 4.06×10−3 6.06×10−8 1.12×10−7 1.14×10−4 6.25×10−4 6.83×10−4 4.69×10−3 最大值 1.36×10−2 9.71×10−2 1.45×10−6 2.68×10−6 2.73×10−3 1.50×10−2 1.63×10−2 1.12×10−1 Ni 平均值 1.28×10−3 9.15×10−3 1.19×10−4 2.19×10−4 4.51×10−4 2.47×10−3 1.85×10−3 1.18×10−2 最大值 4.04×10−3 2.89×10−2 3.75×10−4 6.93×10−4 1.42×10−3 7.79×10−3 5.84×10−3 3.74×10−2 Pb 平均值 1.49×10−2 1.06×10−1 1.59×10−6 2.93×10−6 1.38×10−3 7.57×10−3 1.63×10−2 1.14×10−1 最大值 4.14×10−2 2.96×10−1 4.42×10−6 8.16×10−6 3.85×10−3 2.11×10−2 4.53×10−2 3.17×10−1 Zn 平均值 3.56×10−4 2.54×10−3 — — 5.01×10−6 2.74×10−5 3.61×10−4 2.57×10−3 最大值 8.83×10−4 6.31×10−3 — — 1.24×10−5 6.80×10−5 8.96×10−4 6.38×10−3 HQ 平均值 6.52×10−2 4.66×10−1 4.48×10−4 8.29×10−4 1.46×10−2 7.97×10−2 8.02×10−2 5.46×10−1 最大值 1.02×10−1 7.29×10−1 1.07×10−3 1.98×10−3 3.27×10−2 1.79×10−1 1.23×10−1 8.39×10−1 表 12 研究区土壤重金属元素致癌风险指数
Table 12. Carcinogenic risk index of soil heavy metals in the study area
元素 统计值 CRiing CRiinh CRiderm CR 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 As 平均值 3.98×10−6 6.83×10−6 1.22×10−12 5.40×10−13 5.60×10−8 7.36×10−8 4.04×10−6 6.90×10−6 最大值 8.08×10−6 1.39×10−5 2.47×10−12 1.10×10−12 1.14×10−7 1.49×10−7 8.19×10−6 1.40×10−5 Cd 平均值 3.50×10−7 5.99×10−7 3.73×10−11 1.65×10−11 5.08×10−9 6.67×10−9 3.55×10−7 6.06×10−7 最大值 1.42×10−6 2.43×10−6 1.51×10−10 6.69×10−11 2.06×10−8 2.70×10−8 1.44×10−6 2.45×10−6 Cr 平均值 — — 1.01×10−7 4.49×10−8 — — 1.01×10−7 4.49×10−8 最大值 — — 2.50×10−7 1.11×10−7 — — 2.50×10−7 1.11×10−7 Ni 平均值 — — 7.97×10−10 3.53×10−10 — — 7.97×10−10 3.53×10−10 最大值 — — 2.51×10−9 1.12×109 — — 2.51×10−9 1.12×10−9 CR 平均值 4.33×10−6 7.43×10−6 1.02×10−7 4.52×10−8 6.10×10−8 8.01×10−8 4.49×10−6 7.55×10−6 最大值 8.29×10−6 1.42×10−5 2.53×10−7 1.12×10−7 1.17×10−7 1.53×10−7 8.54×10−6 1.44×10−5 表 13 水化学样品超标指标情况
Table 13. Quality of Hydrochemical Samples
点号 硫酸盐含量/(mg/L) 汞含量/(mg/L) 01 1022 0.000995 02 641 0.000395 03 363 0.000365 04 894 0.002295 标准限值 250 — Ⅲ类水限值 — 0.0001 Ⅵ类水限值(灌溉水限值) — 0.001 Ⅴ类水限值 — 0.001 -
[1] Al−Osman M, Yang Fei, Massey I Y. 2019. Exposure routes and health effects of heavy metals on children[J]. Biometals, 32: 563−573. doi: 10.1007/s10534-019-00193-5
[2] Bao Liran, Deng Hai, Jia Zhongmin, Li Yu, Dong Jinxiu, Yan Mingshu, Zhang Fenglei. 2020. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1625−1636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Bernard A. 2008. Cadmium and its adverse effects on human health[J]. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 128(4): 557−564.
[4] Chen Yunfei, Zhou Jinlong, Hu Yan, Zeng Yanyan, Wang Songtao, Du Jiangyan, Sun Ying. 2022. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of the jujube producing area on the southeastern margin of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(11): 3629−3639 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Cheng Xianda, Sun Jianwei, Jia Xu, Liu Xiangdong, Zhao Yuanyi. 2023. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals infarmland soil around the molybdenum mining area in Luanchuan, Henan Province[J]. Geology in China, 50(6): 1871−1886 (in Chinese with Englishabstract).
[6] Cheng Xiaomeng, Sun Binbin, Wu Chao, He Ling, Zeng Daoming, Zhao Chen. 2022. Heavy metal concentration characteristics and health risks of farmland soils in typical pyrite mining area of the central Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Environmental Science, 43(1): 442−453 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Dai Jierui, Pang Xugui, Yu Chao, Liu Huafeng, Wang Zenghui. 2011. Geochemical features and contamination assessment of soil elements in east Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 38(5): 1387−1395 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Dai Jierui, Hu Xueping, Wang Zenghui. 2013. Characteristics of heavy metals pollution in soil and potential ecological risk assessment—A case study of blue economic zone of Shandong Peninsula[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 13(1): 134−137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Dong Q Y, Wen H T, Wang P, Song C, Lai S Y, Yang Z J, Zhao Y Y, Yan M J. 2023. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and crops in a mining area (Au–Ag–Cu–trona–oil et al.) of the Nanyang Basin, Henan Province, China[J]. China Geology, 6(4): 567−579.
[10] Fan Chenzi, Yuan Jihai, Liu Chenghai, Guo Wei, Sun Dongyang, Liu Wei, Zhao Jiujiang, Hu Jundong, Zhao Linghao. 2022. Eco–geochemical survey and evaluation of heavy metals and other elements in soil in Anning City, Yunnan Provice[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 46(3): 761−771 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Gao Jianweng, Gong Jingjing, Yang Jianzhou, Tang Shixin, Ma Shengming. 2021. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in the soil of Limu Mountain – Wanling Town, Qiongzhong, Hainan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(5): 807−816 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Granero S, Domingo J L. 2002. Levels of metals in soils of Aleaa de Henares, Spain: Human health risks[J]. Environment International, 28: 159−164. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00024-7
[13] Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew B, Beeregowda K. 2014. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals[J]. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7(2): 60. doi: 10.2478/intox-2014-0009
[14] Ju Zilong, Qin Zhijun, Wang Xiang, Yuan Hang, Zhang Xiaobo, Wang Deng. 2022. Accessing the distribution and ecological risks of heavy metals in soil in Hong’an County, Hubei Province through ecological geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 46(4): 988−998 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Hongkui, Geng Ke, Zhuo Chuanyuan. 2016. Tectonic Environment and Mineralization of Gold Mines in Jiaodong [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 338–383(in Chinese).
[16] Li Jianfeng, Feng Lixiao. 2023. Health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil of a tin mining area in Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 50(3): 897−910 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Li Qian, Qin Fei, Ji Hongbing, Huang Xingxing. 2013. Contents, sources and contami – nation assessment of soil heavy metals in gold mine area of upstream part of Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Agro–Environment Science, 32(12): 2384−2394 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Lin Jin, Liang Wenjing, Jiao Yang, Yang Li, Fan Yaning, Tian Tao, Liu Xiaomeng. 2021. Ecolcgical and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around the gold mining area in Tongguan of Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 749−763 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Ling S, Junaidi A, Mohd–Harun A, Baba M. 2023. Heavy metal contamination assessment in marine sediments in the Northwest coast of Sabah, Malaysia[J]. China Geology, 6(4): 580−593.
[20] Liu R P, Xu Y N, Zhang J H, Wang W K, Rafaey M E. 2020. Effects of heavy metal pollution on farmland soils and crops: A case study of the Xiaoqinling Gold Belt, China[J], China Geology, 3(3): 402–410.
[21] Liu Ruiping, Xu Youning, He Fang, Ke Hailing, Zhang Jianghua, Chen Huaqing, Qiao Gang. 2017. The mercury concentration time and space characterized of Shuangqiao River in the gold mine area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 50(3): 231−237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Liu Ruiping, Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Qiao Gang, Ke Hailing, Chen Huaqing, He Fang. 2019. Safe technology of crops in reclaimed farmland of heavy metals tail slag field[J]. Northwestern Geology, 52(2): 236−246 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Liu Tong, Liu Chuanpeng, Deng Jun, Kang Pengyu, Wang Kaikai, Zhao Yuyan. 2022. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in eastern Yinan County, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1497−1508 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Liu Yang, Zhang Haidong, Wang Jinya. 2017. Elements migration in tectonic–alteration zones of the Xiadian gold deposit, eastern Shandong Province and its relationship with Au precipitation[J]. Northwestern Geology, 50(4): 176−185 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Lu J Z, Lu H W, Lei K W, Wang W P, Guan Y L. 2019. Trace metal element pollution of soil and water resources caused by small–scale metallic ore mining activities: A case study from a sphalerite mine in North China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(24): 24630−24644. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05703-z
[26] Lü Jianshu. 2022. Source apportionment and spatial prediction of heavy metals in soils of Yantai coastal zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(3): 713−725 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Pang Xugui, Dai Jierui, Chen Lei, Liu Huafeng, Yu Chao, Han Lu, Ren Tianlong, Hu Xueping, Wang Hongjin, Wang Zenghui, Zhao Xiqiang, Zeng Xiantong, Ren Wenkai, Wang Cunlong. 2019. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 35(1): 46−56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Shi Wenjing, Zhou Hanpeng, Sun Tao, Jin Tao, Yang Wenhuan, Li Weiping. 2022. Research on priority control factors and health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil around mining areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(8): 1616−1628 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Shi Yang, Li Jiahao, Yu Yue, Yang Yuwei, Li Bin, Chen Siqi, Chen Ji, Zhao Ke, Huang Jin. 2022. Progress and prospect of plant remediationte chnology joint with other technologies for heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 44(2): 244−250 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Sun Houyun, Wei Xiaofeng, Sun Xiaoming, Zhang Huiqiong, Yin Zhiqiang. 2023. An overview of evaluation criteria and model for heavy metal pollution ecological risk in small–scale drainage catchment of mountainous area[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 36−51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Sun Jianwei, Jia Xu, Liu Xiangdong, Cheng Xianda, Shang Liannan. 2023. Influence of mining activities in the gold ore concentration area in Western Henan on the heavy metals in surrounding farmland soil[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 42(1): 192−202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Sun Zehang. 2020. Soil and Crops Heavy Metal Pollution and Potential Health Risk Assessment for the Residents Around Small–Scale Polymetallic Mine[D]. Guangzhou: University of Chinese Academy of Science, 1–155 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Sun Zhijia, Li Baofei, Chen Yuhai, Yuan Qingzheng, Yan Xingguo, Zhao Mingjie. 2022. Assessment of agricultural land on soil heavy metals pollution and ecological risk in the northeast of Zhanjiang City[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 45(1): 61−68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Tian Wen, Zong Dapeng, Fang Chenggang, Wang Chengchen, Wang Jianmin, Xiang Ping. 2022. Health risk and toxic effect of heavy metals in soils from typical vegetable planting areas in southwest China[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(10): 4901−4908 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Tu Chunlin, Yang Kun, He Chengzhong, Zhang Liankai, Li Bo, Wei Zong, Jiang Xin, Yang Minghua. 2023. Sources and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of small watersheds in typical coal mining areas of Eastern Yunnan[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 206−221 (in Chinese with English abstract
[36] USEPA. 2011. Exposure Factors Handbook[R]. Washington, DC: Environment Protection Agency.
[37] Wang Changyu, Zhang Surong, Liu Jihong, Xing Yi, Li Mingzhe, Liu Qingxue. 2021. Pollution level and risk assessment of heavy metals in a metal smelting area of Xiong'an New District[J]. Geology in China, 48(6): 1697−1709 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Wang Cunlong, Pang Xugui, Hu Shenghong, Zheng Weijun, Liu Huafeng, Zeng Xiandong. 2011. The ecological effects of soil heavy metals in Yantai, Shandong Province: A case study of As[J]. Geology in China, 38(6): 1620−1630 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Wang Cunlong, Zeng Xiandong, Liu Huafeng, Yang Liyuan, Wang Hongjin, Pang Xugui. 2015. The present situation of soil environmental quality and the distribution and migration regularity of heavy metals in soil of Yantai[J]. Geology in China, 42(1): 317−330 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Wang Haiyang, Han Ling, Xie Danni, Hu Huijuan, Liu Zhiheng, Wang Zhen. 2022. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soil around mining areas and pollution assessment[J]. Environmental Science, 43(4): 2104−2114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Wang Jinya. 2021. Evolution of Au Ore–forming Fluid and Metallogenetic Regularity Research in Eastern Shandong[D]. Xi'an: Chang’an University, 1–122 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Wang J, Zhang X X, Chen A F, Wang B, Zhao Q, Liu G N, Xiao X, Cao J N. 2022. Source analysis and risk evaluation of heavy metal in the river sediment of polymetallic mining area: Taking the Tonglüshan skarn type Cu–Fe–Au deposit as an example, Hubei section of the Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. China Geology, 5(4): 649−661.
[43] Wang Zhe, Liu Shaoqing, Chen Xiaomin, Lin Chunye. 2008. Estimates of the exposed dermal surface area of Chinese in view of human health risk assessment[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 8(4): 152−156 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Xi Chaozhuang, Wu Linfeng, Zhang Pengfei, Fan Yunfei, Yang Mingtai, Xia Haodong, Deng Huijuan. 2022. Evaluation of heavy metals in crop−soil profiles of Huishui County in Guizhou Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 58(4): 822−835 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Xiong Jia, Han Zhiwei, Wu Pan, Zeng Xiangying, Luo Guangfei, Yang Wentao. 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics, contamination evaluation and health risk assessment of arsenic and antimony in soil around an antimony smelter of Dushan County[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(2): 655−664 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Xu Lei, Guan Jiyun, Ba Yong, Chen Weizhi, Huang Jiazhong, Cheng Yanxun, Zhang Ya, Qu Qiang, Zhao Mengsheng. 2024. Spatial distribution pattern and driving mechanism of heavy metal elements in soils of middle–alpine hilly region, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 304−326 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Liu Ruiping, Ke Hailing, Li Yujing. 2007. Environmental effects of heavy metal pollution of farmland soils in gold mining areas[J]. Geology in China, 34(4): 716−722 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Zhao A’ning, Ke Hailing. 2008. Evaluation of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in farmland soils in a certain gold mining area, Xiaoqinling, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(8): 1272−1278 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Ke Hailing, Chen Huaqing, Liu Ruiping, Qiao Gang, Shi Yufei. 2014. An assessment method for heavy metal cumulative risk on farmland soil in the mining area: A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold mining area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(8): 1097−1105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] Xu Zhengqi, Ni Shijun, Tuo Xianguo, Zhang Chengjiang. 2008. Calculation of heavy metals′ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(2): 112−115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Yang Ling, Tian Lei, Bai Guangyu, Pei Shengliang, Zhang Deqiang. 2022. Ecological risk assessments and source analysis of heavy metals in thesoil of Xin Barag Youqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 49(6): 1970−1983 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[52] Yang S, Ge W Y, Chen H H, Xu W L. 2019. Investigation of soil and groundwater environment in urban area during post–industrial era: A case study of brownfield in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. China Geology, 2(4): 501−511.
[53] Yang Yuzhen, Liu Senrong, Yang Yong, Li Lifen, Liu Shenghua, Kang Yihua, Fei Xinqiang, Gao Yunliang, Gao Baolong. 2021. Heavy metals in peri–urban soil of Huangshi: Their distribution, risk assessment, and source identification[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 45(5): 1147−1156 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[54] Yin Yimeng, Zhao Weituo, Huang Ting, Cheng Sheng Gao, Zhao Zhenli, Yu Congcong. 2018. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in a soil–rice system in an E–waste dismantling area[J]. Environmental Science, 39(2): 916−926 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[55] Zhang Dong, Li Yongchun, Su Rilige, Yuan Guoli, Tai Surigala, Wang Yongliang, Chen Guodong, Zhou Wenhui, Du Yuchunzi, Yang Jianyu. 2024. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Wuyuan County, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 248−263 (in Chinese withEnglish abstract).
[56] Zhao L Y, Wang Z J, Kong L H, Gu S S, Li Y C, Han X C, Liu S G, Li B F, Zhang J H. 2023. Risk assessment of soil heavy metals in mining activity areas: A case study in Eastern Shandong Province, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 82(21): 513 . doi: 10.1007/s12665-023-11204-7
[57] Zhao Xinna, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao. 2023. Review on heavy metal pollution and remediation technology in the soil of mining areas[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 84−101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[58] Zhao Z G, Jiang H S, Kong L H, Shen T Y, Zhang X H, Gu S S, Han X C, Li Y C. 2021. Assessment of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface soils of Laizhou, Eastern China[J]. Water, 13: 2940. doi: 10.3390/w13212940
[59] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 2020. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1625−1636. doi: 10.12029/gc20200602
[60] 陈云飞, 周金龙, 胡艳, 曾妍妍, 王松涛, 杜江岩, 孙英. 2022. 新疆塔里木盆地东南缘红枣产地土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 41(11): 3629−3639. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021071406
[61] 程贤达, 孙建伟, 贾煦, 刘向东, 赵元艺. 2023. 河南栾川县钼矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染特征与健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 50(6): 1871−1886. doi: 10.12029/gc20221116001
[62] 成晓梦, 孙彬彬, 吴超, 贺灵, 曾道明, 赵辰. 2022. 浙中典型硫铁矿区农田土壤重金属含量特征及健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 43(1): 442−453.
[63] 代杰瑞, 庞绪贵, 喻超, 刘华峰, 王增辉. 2011. 山东省东部地区土壤地球化学特征及污染评价[J]. 中国地质, 38(5): 1387−1395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.025
[64] 代杰瑞, 胡雪平, 王增辉. 2013. 土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价—以山东半岛蓝色经济区为例[J]. 安全与环境学报, 13(1): 134−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2013.01.030
[65] 范晨子, 袁继海, 刘成海, 郭威, 孙冬阳, 刘崴, 赵九江, 胡俊栋, 赵令浩. 2022. 云南省安宁地区土壤重金属等元素生态地球化学调查与评价[J]. 物探与化探, 46(3): 761−771.
[66] 高健翁, 龚晶晶, 杨剑洲, 唐世新, 马生明. 2021. 海南岛琼中黎母山—湾岭地区土壤重金属元素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 40(5): 807−816.
[67] 居字龙, 秦志军, 万翔, 袁航, 张小波, 王登. 2022. 湖北红安县生态地质调查土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 物探与化探, 46(4): 988−998.
[68] 李洪奎, 耿科, 禚传源. 2016. 胶东金矿构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 338–383.
[69] 李剑锋, 冯李霄. 2023. 湖南某锡矿区土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 50(3): 897−910. doi: 10.12029/gc20220825003
[70] 李倩, 秦飞, 季宏兵, 冯金国, 黄兴星. 2013. 北京市密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属含量、来源及污染评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 32(12): 2384−2394. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.12.011
[71] 林荩, 梁文静, 焦旸, 杨莉, 范亚宁, 田涛, 刘晓萌. 2021. 陕西潼关县金矿矿区周边农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 749−763. doi: 10.12029/gc20210306
[72] 刘瑞平, 徐友宁, 何芳, 柯海玲, 张江华, 陈华清, 乔冈. 2017. 某金矿带双桥河河水–底泥–悬浮物中Hg含量时程分布特征[J]. 西北地质, 50(3): 231–237.
[73] 刘瑞平, 徐友宁, 张江华, 乔冈, 柯海玲, 陈华清, 何芳. 2019. 含重金属的尾矿渣场复垦还田种植农作物的安全技术[J]. 西北地质, 52(2): 236−246.
[74] 刘同, 刘传朋, 邓俊, 康鹏宇, 王凯凯, 赵玉岩. 2022. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1497−1508. doi: 10.12029/gc20220509
[75] 刘洋, 张海东, 王金雅. 2017. 胶东地区夏甸金矿床构造蚀变带元素质量迁移与Au沉淀关系研究[J]. 西北地质, 50(4): 176−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.04.019
[76] 吕建树. 2022. 烟台海岸带土壤重金属定量源解析及空间预测[J]. 地理学报, 76(3): 713−725.
[77] 庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 刘华峰, 喻超, 韩鎏, 任天龙, 胡雪平, 王红晋, 王增辉, 赵西强, 曾宪东, 任文凯, 王存龙. 2019. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 35(1): 46−56. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.01.008
[78] 石文静, 周翰鹏, 孙涛, 黄金涛, 杨文焕, 李卫平. 2022. 矿区周边土壤重金属污染优先控制因子及健康风险评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(8): 1616−1628.
[79] 石杨, 李家豪, 于月, 杨雨薇, 李斌, 陈思奇, 陈稷, 赵珂, 黄进. 2022. 重金属污染土壤的植物修复技术与其他技术联用的进展与前景[J]. 环境污染与防治, 44(2): 244−250.
[80] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 孙晓明, 张会琼, 殷志强. 2023. 山区小流域矿集区土壤重金属污染生态风险评价基准与模型[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 36−51. doi: 10.12029/gc20200916001
[81] 孙建伟, 贾煦, 刘向东, 程贤达, 商连南. 2023. 豫西金矿集区矿业活动对周边农田土壤重金属影响研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 42(1): 192−202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2023.1.ykcs202301015
[82] 孙泽航. 2020. 小型多金属矿山周边土壤及作物重金属污染及居民潜在健康风险评估[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 1–155.
[83] 孙志佳, 李保飞, 陈玉海, 袁庆政, 闫兴国, 赵明杰. 2022. 湛江东北部农用地土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 45(1): 61−68.
[84] 田稳, 宗大鹏, 方成刚, 王成尘, 王健敏, 向萍. 2022. 西南典型菜地土壤重金属健康风险和毒性效应[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(10): 4901−4908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.10.048
[85] 涂春霖, 杨坤, 和成忠, 张连凯, 李博, 魏总, 姜昕, 杨明花. 2023. 滇东典型煤矿区小流域沉积物重金属来源及风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 206−221. doi: 10.12029/gc20220221002
[86] 王昌宇, 张素荣, 刘继红, 邢怡, 李名则, 刘庆学. 2021. 雄安新区某金属冶炼区土壤重金属污染程度及风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(6): 1697−1709. doi: 10.12029/gc20210603
[87] 王存龙, 庞绪贵, 胡圣虹, 郑伟军, 刘华峰, 曾宪东. 2011. 山东省烟台地区土壤重金属的生态效应—以砷为例[J]. 中国地质, 38(6): 1620−1630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.023
[88] 王存龙, 曾宪东, 刘华峰, 杨丽原, 王红晋, 庞绪贵. 2015. 烟台市土壤环境质量现状及重金属元素分布迁移规律[J]. 中国地质, 42(1): 317−330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.026
[89] 王海洋, 韩玲, 谢丹妮, 胡慧娟, 刘志恒, 王祯. 2022. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 43(4): 2104−2114.
[90] 王金雅. 2021. 胶东地区Au成矿流体演化与成矿规律研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 1–122.
[91] 王喆, 刘少卿, 陈晓民, 林春野. 2008. 健康风险评价中中国人皮肤暴露面积的估算[J]. 安全与环境学报, 8(4): 152−156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2008.04.038
[92] 息朝庄, 吴林锋, 张鹏飞, 范云飞, 杨茗钛, 夏浩东, 邓会娟. 2022. 贵州惠水农作物–土壤剖面重金属污染评价[J]. 地质与勘探, 58(4): 822−835. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2022.04.011
[93] 熊佳, 韩志伟, 吴攀, 曾祥颖, 罗广飞, 杨文弢. 2020. 独山锑冶炼厂周边土壤锑砷空间分布特征、污染评价及健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(2): 655−664.
[94] 徐磊, 管继云, 巴永, 陈伟志, 黄加忠, 程琰勋, 张亚, 瞿镪, 赵萌生. 2024. 云南中高山丘陵区土壤重金属元素空间分布格局及驱动机制[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 304−326. doi: 10.12029/gc20230427003
[95] 徐友宁, 张江华, 刘瑞平, 柯海岭, 李育敬. 2007. 金矿区农田土壤重金属污染的环境效应分析[J]. 中国地质, 34(4): 716−722. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.04.023
[96] 徐友宁, 张江华, 赵阿宁, 柯海玲. 2008. 小秦岭某金矿区农田土壤重金属污染的潜在生态危害评价[J]. 地质通报, 27(8): 1272−1278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.025
[97] 徐友宁, 张江华, 柯海玲, 陈华清, 刘瑞平, 乔冈, 史宇飞. 2014. 矿业活动区农田土壤重金属累积风险的评判方法——以小秦岭金矿区为例[J]. 地质通报, 33(8): 1097−1105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.002
[98] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 张成江. 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 31(2): 112−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[99] 杨玲, 田磊, 白光宇, 裴圣良, 张德强. 2022. 内蒙古新巴尔虎右旗土壤重金属生态风险与来源分析[J]. 中国地质, 49(6): 1970−1983. doi: 10.12029/gc20220619
[100] 杨育振, 刘森荣, 杨勇, 李丽芬, 刘圣华, 亢益华, 费新强, 高云亮, 高宝龙. 2021. 黄石市城市边缘区土壤重金属分布特征、风险评价及溯源分析[J]. 物探与化探, 45(5): 1147−1156.
[101] 尹伊梦, 赵委托, 黄庭, 程胜高, 赵珍丽, 余葱葱. 2018. 电子垃圾拆解区土壤–水稻系统重金属分布特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(2): 916−926.
[102] 张栋, 李永春, 苏日力格, 袁国礼, 邰苏日嘎拉, 王永亮, 陈国栋, 周文辉, 杜雨春子, 杨建雨. 2024. 内蒙古五原县某地土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 248−263. doi: 10.12029/gc20230420001
[103] 赵鑫娜, 杨忠芳, 余涛. 2023. 矿区土壤重金属污染及修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 84−101. doi: 10.12029/gc20220702001
-



 下载:
下载: