Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils in the Yuanzhou District of Guyuan City, Ningxia
-
摘要:
研究目的 通过研究宁夏固原市原州区表层土壤重金属含量及空间分布特征,对该地区进行生态风险评价,明确原州区表层土壤重金属累积情况。
研究方法 系统采集了研究区表层土壤样品12988件,获取了As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn等8种重金属含量,采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法和潜在生态危害指数法进行土壤重金属生态风险评价。
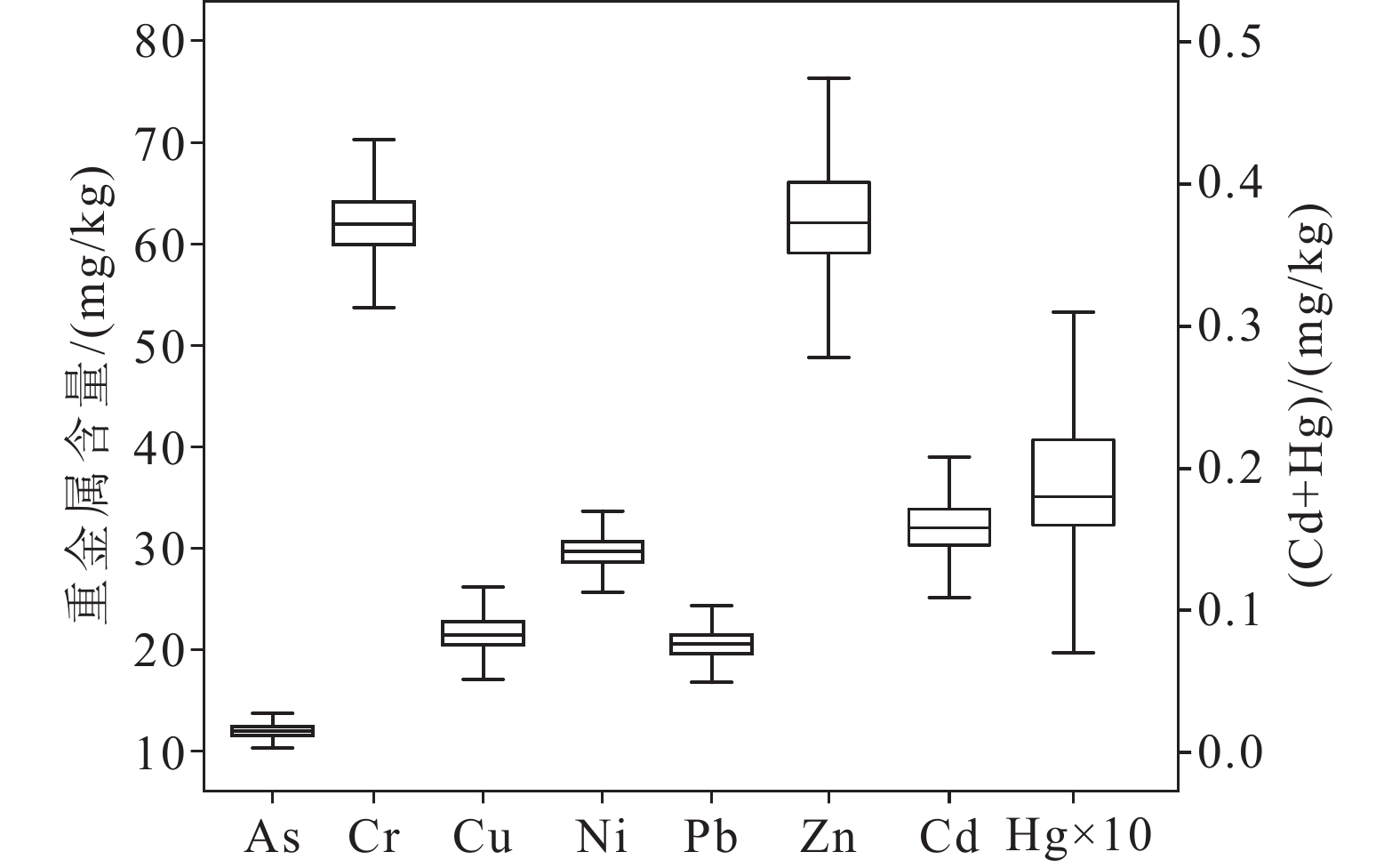
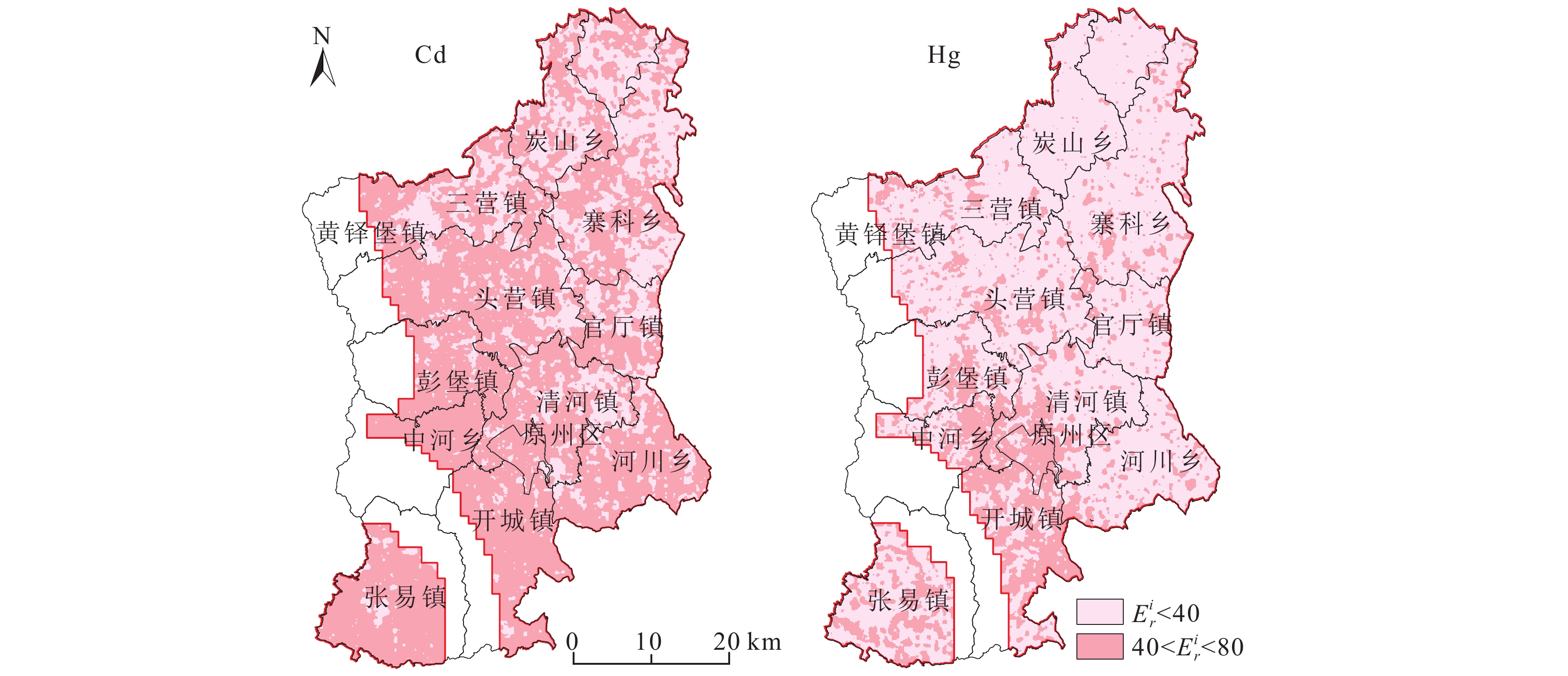
研究结果 与宁夏自治区表层土壤元素背景值相比,原州区表层土壤8种重金属富集系数分别为As(1.01)、Cd(1.42)、Cr(1.04)、Cu(0.99)、Hg(1.03)、Ni(0.81)、Pb(1.01)和Zn(1.07)。土壤中8种重金属空间分布特征相似,高值区主要分布在六盘山东西两侧、固原市区、张易镇和黄铎堡镇等人类活动频繁区域,在东北部第四纪黄土覆盖区的炭山乡、寨科乡土壤重金属富集程度较低。单因子指数法评价结果显示,原州区土壤整体清洁,无污染。内梅罗综合污染指数法分析结果显示,土壤各重金属元素污染指数均小于0.7,属清洁水平,污染风险等级为安全。潜在生态危害指数法分析结果显示,Cd和Hg单元素潜在危害指数达到中等风险水平,重金属综合潜在生态危害指数为轻微风险。
结论 固原市原州区土壤重金属生态风险较低,受人类活动影响的区域,表层土壤重金属存在轻微富集。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective This study investigated the contents and spatial distributions of heavy metals in surface soils in Yuanzhou District, Guyuan City, Ningxia, evaluating heavy metal accumulation and its associated ecological risk.
Methods A total of 12988 soil samples were collected and the levels of eight heavy metals, namely, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn, were measured. The single−factor index, Nemerow comprehensive pollution index, and potential ecological hazard index were used to estimate the ecological risks associated with heavy metal contamination in soils.
Results Compared to the background values of the Ningxia Autonomous Region, the average enrichment coefficients of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn were 1.01, 1.42, 1.04, 0.99, 1.03, 0.81, 1.01, and 1.07, respectively. Similar distributions of the eight heavy metals, with high concentrations, were observed in areas characterized by high human activity, such as the east and west sides of Liupan Mountain, as well as Guyuan City, Zhangyi Town, and Huangduobao Town. In contrast, low concentrations were observed in Tanshan Township and Zhaike Township in the northeast Quaternary areas with loess−covered soil. Single−factor index evaluation revealed that the soil was "clean" in the Yuanzhou area. Evaluation using the Nemerow comprehensive pollution index indicated that the soil pollution index of all heavy metals was less than 0.7, which is considered "clean." While the single−element potential hazard index of Cd and Hg showed a level of moderate risk, the comprehensive potential ecological hazard index of the heavy metals showed slight risk levels.
Conclusions The soil quality in Yuanzhou District, Guyuan City, is in good condition, although slight enrichment of heavy metals was seen in the topsoil due to human activities in some areas.
-

-
表 1 实验室元素分析测试方法
Table 1. Laboratory elemental analysis and testing methods
元素 实验室分析方法 Cu、Zn、Ni、Cr 粉末压片–X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) Cd 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法(GF–AAS) Hg 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) As 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) Pb 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP–MS) 表 2 单因子污染指数分级标准
Table 2. Grading standard of single factor pollution index
指标范围 Pi<1.0 1.0≤Pi<2.0 2.0≤Pi<3.0 Pi≥3.0 污染等级 无污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 表 3 内梅罗综合污染指数分级标准
Table 3. Grading standard of Nemerow comprehensive pollution index
等级划分 PI 污染等级 污染水平 Ⅰ PI≤0.7 安全 清洁 Ⅱ 0.7<PI≤1.0 警戒线 尚清洁 Ⅲ 1.0<PI≤2.0 轻污染 土壤开始受到污染 Ⅳ 2.0<PI≤3.0 中污染 土壤已受中度污染 Ⅴ PI>3.0 重污染 土壤已受重度污染 表 4 土壤重金属潜在生态危害指数分级标准
Table 4. Grading standard of potential ecological hazard index of heavy metals in soil
评价指标 指标范围 潜在生态危害程度 $E_r^i $ 或RI$E_r^i $ ≤40或RI≤150轻微风险 40< $E_r^i $ ≤80或150<RI≤300中等风险 80< $E_r^i $ ≤160或300<RI≤600较强风险 160< $E_r^i $ ≤320或600<RI≤1200很强风险 $E_r^i $ ≥320或RI>1200极强风险 表 5 研究区表层土壤重金属含量特征(n=12988)
Table 5. Characteristics of heavy metal concentrations in surface soils of the study area (n=12988)
项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 最小值/(mg/kg) 5.0 0.043 17.3 4.1 0.002 5.8 11.6 10.8 最大值/(mg/kg) 25.3 0.423 87.8 46.0 1.441 43.3 92.9 164.1 中位值/(mg/kg) 12.0 0.158 61.9 21.5 0.018 29.7 20.5 62.1 平均值/(mg/kg) 12.1 0.159 62.1 21.8 0.022 29.7 20.7 63.0 标准差/(mg/kg) 0.9 0.020 4.0 2.1 0.027 2.1 1.9 6.4 变异系数/% 7.8 12.7 6.5 9.8 125.8 7.0 9.1 10.2 宁夏土壤元素背景值/
(mg/kg)11.9 0.112 60 22.1 0.021 36.6 20.6 58.8 富集系数
(元素含量/背景值)1.01 1.42 1.04 0.99 1.03 0.81 1.01 1.07 表 6 原州区土壤重金属风险指数评价
Table 6. Risk index evaluation of heavy metal in soils of the Yuanzhou District
项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 单因子指数 $ {P}_{i} $ 0.48 0.27 0.25 0.22 0.006 0.16 0.12 0.21 内梅罗综合污染指数 $ \mathrm{P}\mathrm{I} $ 0.69 0.53 0.304 0.36 0.297 0.20 0.40 0.42 单个元素潜在生态危害指数 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 10.13 42.72 2.07 4.94 41.37 4.06 5.03 1.07 多种重金属综合潜在生态危害指数 $ \mathrm{R}\mathrm{I} $ 111.39 表 7 土壤重金属含量的Pearson相关性系数
Table 7. Pearson correlation coefficient of heavy metal concentrations in soils
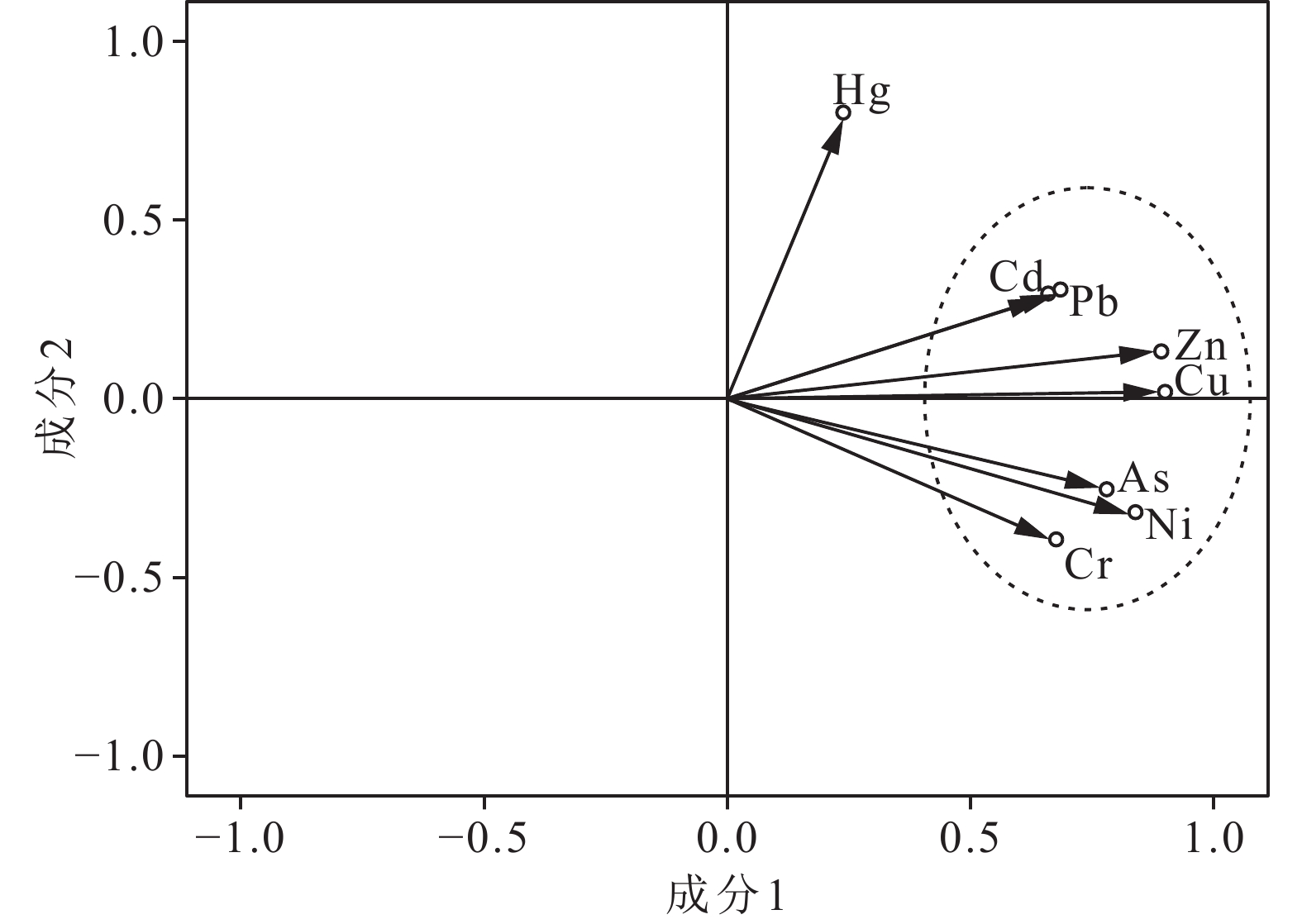
重金属 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn As 1 0.366** 0.489** 0.639** 0.052** 0.700** 0.390** 0.601** Cd 1 0.227** 0.477** 0.164** 0.372** 0.408** 0.552** Cr 1 0.566** 0.025** 0.658** 0.344** 0.468** Cu 1 0.219** 0.705** 0.562** 0.833** Hg 1 0.044** 0.240** 0.243** Ni 1 0.419** 0.681** Pb 1 0.599** Zn 1 注:**代表相关性在0.01水平上显著(双尾)。 表 8 土壤重金属主成分分析
Table 8. Principal component analysis of heavy metal in soils
成分 初始特征值 提取载荷平方和载入 总计 方差/% 累积/% 总计 方差/% 累积/% 1 4.271 54.188 53.388 4.271 54.188 53.388 2 1.154 14.525 68.713 1.154 14.525 67.813 3 0.759 9.486 77.299 4 0.572 7.148 84.447 5 0.489 6.107 90.554 6 0.367 4.587 95.141 7 0.239 2.99 98.131 8 0.15 1.869 100 -
[1] Cai L M, Xu Z C, Ren M Z, Guo Q W, Hu X B, Hu G C, Wan H F, Peng P A. 2012. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78: 2−8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.07.004
[2] Cao Shengwei, Liu Chunlei, Li Yasong, Li Jing, Hao Qichen, Gao Jie, Dong Yan, Lu Chenming. 2022. Sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of offshore area in Quanzhou Bay, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1481−1496 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Z Y, Zhao Y Y, Chen D L, Huang H T, Zhao Y, Wu Y J. 2023. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal cumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area, Henan Province, central China[J]. China Geology, 6(1): 15−26.
[4] China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. 1990. Background Value of Soil Elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 330–381 (in Chinese).
[5] Chu Tianshu, Wang Bingxiong, Gao Sicheng, Cheng Tianyi, Yang Zengling. 2021. Estimation on farmland carrying capacity for livestock and poultry manure based on risk screening values for farmland soil heavy metal contamination[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 26(2): 125−138 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Dang Mintuan, Liu Juan, Yang Shan. 2020. Advance of heavy mental pollution in soil and its control[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 66(6): 94−96 (in Chinese).
[7] Dong Q Y, Wen H T, Pan W, Song C, Lai S Y, Yang Z J, Zhao Y Y, Yan M J. 2023. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and crops in a mining area (Au−Ag−Cu−trona−oil et al. ) of the Nanyang Basin, Henan Province, China[J]. China Geology, 6: 1−13.
[8] Hakanson L. 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975−1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[9] Hu Qi, Liu Shaoyu, Liu Pengfei, Zhang Wenqiang. 2020. Evaluation of heavy pollution of farmland soil in eastern area of Fuyang City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(7): 68−73 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Huang S S, Tu J, Jin Y, Hua M, Wu X M, Xu W W, Yang Y B, Wang H O, Su Y M, Cai L M. 2018. Contamination assessment and source identification of heavy metals in river sediments in Nantong, Eastern China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 12(3): 373−389. doi: 10.1007/s41742-018-0097-8
[11] Liang Yongfeng. 2012. Measurement and evaluation on soil nutrient content in Yuanzhou County of Guyuan City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural, 40(36): 17576−17577 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Liang Yongfeng. 2013. Soil nutrient status and wheat planting suitability in Yuanzhou County of Guyuan City[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 52(16): 3788−3790 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Liu Fenglian, Yu Liping, Wu Huizhong, Xu Bingzhong. 2015. Survey of the content of cadmium and lead in rural soil, Ningxia[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 42(5): 798−800 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Liu Tong, Liu Chuanpeng, Deng Jun, Kang Pengyu, Wang Kaikai, Zhao Yuyan. 2022. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in eastern Yinan County, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1497−1508 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Ma Gui, Han Xinning, Wei Weixing, Li Meiyuan, Li Guodong. 2021. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil of urban areas of Guyuan city[J]. Journal of Ningxia Normal University, 42(4): 51−60.
[16] Ma Yibo, Li Longbo, Zhang Meixue, Mo Chunhu, Meng Wei. 2020. Discussion on soil forming rock type and its relation with cultivated land soil in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 37(4): 425−429 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Mu Hongyu, Zhuang Zhong, Li Yanming, Qiao Yuhui, Chen Qing, Xiong Jing, Guo Lili, Jiang Rongfeng, Li Huafen. 2020. Heavy metal contents in animal manure in China and the related soil accumulation risks[J]. Environmental Science, 41(2): 986−996 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Pan L B, Ma J, Wang X L, Hou H. 2016. Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution[J]. Chemosphere, 148: 248−254. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.049
[19] Pezzarossa B, Malorgio F, Lubrano L, Tognoni F, Petruzzelli G. 1990. Phosphatic fertilizers as a source of heavy metals in protected cultivation[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 21(9/10): 737−751.
[20] Song H Y, Hu K L, An Y, Chen C, Li G D. 2018. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of the heavy metals in the agricultural soil in a regional scale[J]. Journal of Soils & Sediments: Protection, Risk Assessment, & Remediation, 18(3): 852–862.
[21] Song Yuting, Lei Ningfei. 2018. China's cadmium pollution land status and restoration measures[J]. Journal of Xichang University (Natural Science Edition), 32(3): 79−83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Tang Doudou, Yuan Xuyin, Wang Yimin, Ji Junfeng, Wen Yubo, Zhao Wanfu. 2018. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background[J]. Journal of Agro−Environment Science, 37(1): 18−26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Temmerman L D, Vanongeval L, Boon W, Hoenig M, Geypens M. 2003. Heavy metal content of arable soils in northern Belgium[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 148(1): 61–76.
[24] Wang Mei’e, Peng Chi, Chen Weiping. 2016. Impacts of industrial zone in arid area in Ningxia Province on the accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils[J]. Environmental Science, 37(9): 3532−3539 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Wei Yihua, Qiu Suyan, Zhang Jinyan, Chen Qinglong, Chen Liumeng, Tu Tianhua, Dai Tingcan. 2019. Characteristic of heavy metal contents in agricultural wastes and agricultural risk assessment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 35(14): 212−220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Xu Xiaowei, Hu Siyi, Pan Rouhe. 2014. Determination of heavy metals and organochlorine pesticides in lycium barbarum[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 24(10): 1487−1492 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Xu Zhengqi, Ni Shijun, Tuo Xianguo, Zhang Chengjiang. 2008. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(2): 112−115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Yang Bingxue, Ma Qin, Fang Chen, Xu Xinhong, Ma Yuandan. 2020. Investigation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution of farmland soil in Linan district of Hangzhou City[J]. Sichuan Environment, 39(3): 132−138 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Zhang Qian, Liu Xiangwei, Shui Yong, Tang Ting. 2021. Distribution of heavy metals in the upstream of Yellow River and ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 57(2): 333−340 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Zhang Renduo. 2005. Spatial Variation Theory and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 82–91 (in Chinese).
[31] Zhang Shuhai, Wei Guning. 2012. Evaluation and Formula Fertilization in Yuanzhou District, Guyuan City, Ningxia[M]. Yinchuan: Sunshine Press, 3–9 (in Chinese).
[32] Zhang Tengjiao, Liu Hong, Ouyang Yuan, Huang Hanxiao, Zhang Jinghua, Li Fu, Xiao Qiliang, Zeng Jian, Hou Qian, Wen Dengkui, Duan Shengyi. 2020. A preliminary discussion on the physical and chemical characteristics and main controlling factors of soil and parent material in the middle and high mountain area: Take Xichang as an example[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 106−114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Zhang Xiaomin, Zhang Xiuying, Zhong Taiyang, Jiang Hong. 2014. Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metal in arable land soil of China[J]. Environmental Science, 35(2): 692−702 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Zhang X W, Yang L S, Li Y H, Li H R, Wang W Y, Ye B X. 2012. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 184(4): 2261−2273. doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6
[35] Zhou Qinli, Wang Xuedong, Li Zhitao, Wang Xiahui, He Jun, Ji Guohua. 2019. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metal in Helan County of Ningxia, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 36(4): 513−521 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Zhuang Guotai. 2015. Current situation of national soil pollution and strategies on prevention and control[J]. Journal of China Academy of Sciences, 30(4): 476−483 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] 曹胜伟, 刘春雷, 李亚松, 李静, 郝奇琛, 高婕, 董岩, 陆晨明. 2022. 福建泉州湾近岸海域沉积物重金属来源分析与生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1481−1496. doi: 10.12029/gc20220508
[38] 楚天舒, 王柄雄, 高思程, 成天一, 杨增玲. 2021. 基于农田土壤重金属污染风险筛选值的畜禽粪污农田承载力估算[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 26(2): 125−138.
[39] 党民团, 刘娟, 杨珊. 2020. 土壤重金属污染及治理研究进展[J]. 陕西农业科学, 66(6): 94−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2020.06.030
[40] 胡琪, 刘少玉, 刘鹏飞, 张文强. 2020. 阜阳市东部地区农田土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(7): 68−73.
[41] 梁永峰. 2012. 固原市原州区土壤养分含量的测定与评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 40(36): 17576−17577. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.36.049
[42] 梁永锋. 2013. 固原市原州区土壤养分含量及小麦种植适宜性[J]. 湖北农业科学, 52(16): 3788−3790.
[43] 刘凤莲, 于丽萍, 吴惠忠, 许秉忠. 2015. 宁夏农村土壤重金属镉和铅含量调查与分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 42(5): 798−800.
[44] 刘同, 刘传朋, 邓俊, 康鹏宇, 王凯凯, 赵玉岩. 2022. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1497−1508.
[45] 马贵, 韩新宁, 魏卫星, 李美媛, 李国栋. 2021. 固原市表层土壤重金属空间分布及健康风险评价[J]. 宁夏师范学院学报, 42(4): 51−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1331.2021.04.009
[46] 马义波, 李龙波, 张美雪, 莫春虎, 孟伟. 2020. 贵州成土母岩类型及其与耕地土壤关系探讨[J]. 贵州地质, 37(4): 425−429.
[47] 穆虹宇, 庄重, 李彦明, 乔玉辉, 陈清, 熊静, 郭丽莉, 江荣风, 李花粉. 2020. 我国畜禽粪便重金属含量特征及土壤累积风险分析[J]. 环境科学, 41(2): 986−996.
[48] 宋玉婷, 雷泞菲. 2018. 我国土壤镉污染的现状及修复措施[J]. 西昌学院学报(自然科学版), 32(3): 79−83.
[49] 唐豆豆, 袁旭音, 汪宜敏, 季峻峰, 文宇博, 赵万伏. 2018. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(1): 18−26. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0801
[50] 王美俄, 彭驰, 陈卫平. 2016. 宁夏干旱地区工业区对农田土壤重金属累积的影响[J]. 环境科学, 37(9): 3532−3539.
[51] 魏益华, 邱素艳, 张金艳, 陈庆隆, 陈柳萌, 涂田华, 戴廷灿. 2019. 农业废弃物中重金属含量特征及农用风险评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(14): 212−230.
[52] 徐晓卫, 胡思一, 潘柔和. 2014. 宁夏枸杞中重金属元素和有机氯农药残留的分析[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 24(10): 1487−1492.
[53] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 张成江. 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 31(2): 112−115.
[54] 杨冰雪, 马勤, 方晨, 许鑫红, 马元丹. 2020. 杭州市临安区农田土壤重金属污染调查与评价[J]. 四川环境, 39(3): 132−138.
[55] 张倩, 刘湘伟, 税勇, 王婷. 2021. 黄河上游重金属元素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 57(2): 333−340.
[56] 张仁铎. 2005. 空间变异理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 23–39.
[57] 张树海, 魏固宁. 2012. 宁夏固原市原州区耕地地力评价与测土配方施肥[M]. 银川: 阳光出版社, 3–9.
[58] 张腾蛟, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 黄瀚霄, 张景华, 李富, 肖启亮, 曾建, 侯谦, 文登奎, 段声义. 2020. 中高山区土壤成土母质理化特征及主控因素初探—以西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(1): 106−114.
[59] 张小敏, 张秀英, 钟太洋, 江洪. 2014. 中国农田土壤重金属富集状况及其空间分布研究[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 692−702.
[60] 中国环境监测总站. 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 330–381.
[61] 周勤利, 王学东, 李志涛, 王夏晖, 何俊, 季国华. 2019. 宁夏贺兰县土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 36(4): 513−521.
[62] 庄国泰. 2015. 我国土壤污染现状与防控策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 30(4): 476−483.
-



 下载:
下载: