Distribution and genesis of global Na-carbonate deposits and its prospecting potential
-
摘要:
研究目的 天然碱矿主要用于制纯碱,和合成碱相比,具有绿色环保、成本低的优势。其下游产业遍布各个领域,如玻璃、医药等。光伏等新能源产业的蓬勃发展给纯碱带来了新需求。中国是纯碱消费大国,天然碱或成为稀缺资源。天然碱矿是一种蒸发岩矿床,成矿过程具有重要的研究意义,国内蒸发岩矿床研究领域对天然碱矿的关注较少。理清世界天然碱矿产资源类型、分布特征,总结碱矿成因对深化中国天然碱矿成矿规律研究、预测找矿远景、寻找天然碱矿床具有积极意义。
研究方法 搜集已公开发表或出版的天然碱矿床资料,对世界典型矿床区域概况、物源、成因等内容进行系统总结。
研究结果 绝大部分天然碱矿床分布于北美洲、亚洲和非洲,主要形成于新生代。类型以现代天然碱矿床居多,古代天然碱矿床较少,但资源规模大。古代天然碱矿以美国绿河组、河南泌阳凹陷安棚天然碱矿最为典型,现代天然碱矿以肯尼亚马加迪湖和内蒙古查干诺尔泡碱矿床为典型。
结论 天然碱矿需要在封闭的构造环境、干旱的气候条件、充足的碳酸钠型卤水补给等成矿因素耦合条件成矿。与其他蒸发岩不同的是,维持碳酸钠型卤水所需的CO2来源具有复杂性。中国天然碱矿找矿远景应聚焦内蒙古第四纪盐湖、白垩纪封闭凹陷,以及河南始新世白云岩、油页岩发育的封闭盆地等地。积极开展天然碱矿成矿理论研究和找矿工作具有重要意义。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective Natural soda-ash deposits, also called sodium carbonate evaporites, are mainly used to produce soda ash. In the soda industry, compared with synthetic soda, this process has advantages for environmental protection and lower cost. The downstream industries contain various fields, including glass, medicine, and so on. The booming of new energy industries such as photovoltaic has brought new demand for soda ash. China consumes loads of soda ash annually; thus, soda may become a scarce resource in the future. Mineralization process of natural soda-ash evaporites is of great significance in evaporite community. In China however, soda-ash deposits have received little attention and have great research potential. Investigations on types and distribution characteristics of global soda-ash deposits and their genesis are helpful and useful for deepening research and prospecting of Nacarbonate deposits in China.
Methods Compiling published data and systematically summarizing the regional setting, provenance, genesis of typical soda-ash deposits.
Results Most deposits are Cenozoic in age and located in North America, Asia and Africa. Modern soda-ash deposits predominate in number, but resources size of ancient deposits is tremendous. Specific ancient deposits include the Green River Formation, United States and the Anpeng soda deposit in Biyang Depression in Henan, the counterparts, typical modern alkaline lake deposits formed in Lake Magadi, Kenya and Chaganor, Inner Mongolia.
Conclusions The requirement for Na-carbonate deposits precipitation are (1) hydrologically-closed basins, (2) arid climate, and (3) sufficient sodium carbonate supply. Unlike other evaporites, the sources of CO2 required to maintain Na-carbonate brines are complicated. Efforts for prospecting in China should focus on Quaternary saline lakes, Cretaceous restrict basins in Inner Mongolia, and tectonically-closed depression in which dolomite and oil shale develops in Henan. It is of great significance to carry out the metallogenic theory research and mine prospecting.
-

-
图 1 世界主要天然碱矿分布图(据Warren, 2010)
Figure 1.
图 2 形成天然碱矿的不饱和卤水演化路径(改自Hardie and Eugster, 1970)
Figure 2.
图 3 苏打石-天然碱-泡碱随温度、CO2的变化的稳定图(改自Jagniecki et al., 2015)
Figure 3.
图 5 贝帕扎里盆地地质简图及天然碱矿床地层柱状简图(据Helvaci, 2010)
Figure 5.
图 6 泌阳凹陷地质简图及安棚天然碱矿床岩性柱状简图(据杨江海等, 2014; 易承龙, 2016)
Figure 6.
图 7 东非大裂谷东支区域图(a)与马加迪湖区地质图(b)(改自Eugster and Blair, 1968; Schubel and Simonson, 1990; Damnati et al., 1992; Owen et al., 2019)
Figure 7.
图 8 查干诺尔区域地质简图和泡碱矿床岩性柱状简图(改自张晨鼎, 2013)
Figure 8.
表 1 纯碱矿物产量及碳酸钠储量(据USGS, 2023)
Table 1. Soda-ash mine production and reserves (after USGS, 2023)
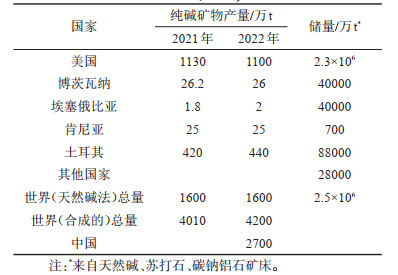
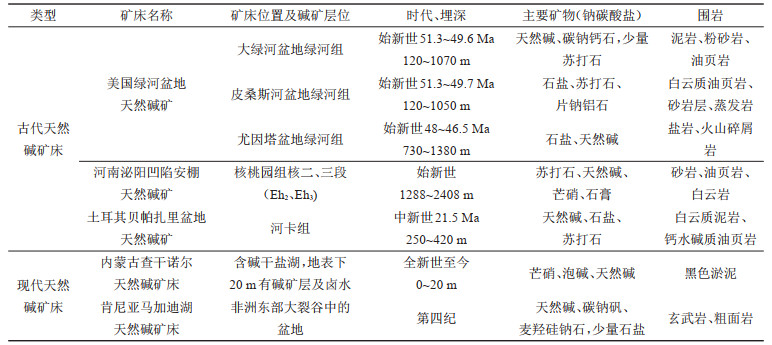
表 2 世界典型天然碱矿床(据张晨鼎, 2013; 叶铁林, 2013; Warren, 2016)
Table 2. Typical Na-carbonate deposits in the world (after Zhang Chending, 2013; Ye Tielin, 2013; Warren, 2016)
-
Baker B H, Mitchell J G. 1976. Volcanic stratigraphy and geochronology of the Kedong-Olorgesailie area and the evolution of the South Kenya rift valley[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 132: 467-484. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.132.5.0467
Baker B H. 1986. Tectonics and volcanism of the southern Kenya Rift Valley and its influence on rift sedimentation[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 25(1): 45-57. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.025.01.05
Chen Jianli. 2013. Geological characteristics, genesis and ore prediction of natural soda deposit in Biyang depression: Taking Anpeng trona deposit as an example[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 28(3): 393-400 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Crossley R. 1979. The Cenozoic stratigraphy and structure of the western part of the Rift Valley in southern Kenya[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 136(4): 393-405. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.136.4.0393
Culbertson W C. 1972. Trona and Halite resources in Wilkins Peak Member of Green river Formation, Green River Basin, Wyoming: Abstract[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 56: 612-612.
Cumming V M, Selby D, Lillis P G. 2012. Re-Os geochronology of the lacustrine Green River Formation: Insights into direct depositional dating of lacustrine successions, Re-Os systematics and paleocontinental weathering[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 359/360: 194-205. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.012
Cumming V M, Selby D, Lillis P G, Lewan M D. 2014. Re-Os geochronology and Os isotope fingerprinting of petroleum sourced from a Type Ⅰ lacustrine kerogen: Insights from the natural Green River petroleum system in the Uinta Basin and hydrous pyrolysis experiments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 138: 32-56. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.016
Damnati B, Taieb M, Williamson D. 1992. Laminated deposits from Lake Magadi (Kenya); climatic contrast effect during the maximum wet period between 12, 000-10, 000 yrs BP[J]. Bulletin De La Société Géologique De France, 163(4): 407-414.
Demicco R V, Lowenstein T K, Hardie L A. 2003. Atmospheric pCO2 since 60 Ma from records of seawater pH, calcium, and primary carbonate mineralogy[J]. Geology, 31(9): 793-796. doi: 10.1130/G19727.1
Dickinson W R, Klut M A, Hayes M J, Janecke S U, Lundin E R, McKittrick M A, Olivares M D. 1988. Paleogeographic and paleotectonic setting of Laramide sedimentary basins in the central Rocky Mountain region[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 100: 1023-1039. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1988)100<1023:PAPSOL>2.3.CO;2
Earman S, Phillips F M, McPherson B J O L. 2005. The role of "excess" CO2 in the formation of trona deposits[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 20(12): 2217-2232. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.08.007
Eugster H P. 1967. Hydrous sodium silicates from lake Magadi, Kenya: Precursors of bedded chert[J]. Science, 157(3793): 1177-1180. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3793.1177
Eugster H P, Blair F J. 1968. Gels composed of sodium-aluminum silicate, Lake Magadi, Kenya[J]. Science, 161(3837): 160-163. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.160
Eugster H P. 1969. Inorganic bedded cherts from the Magadi area, Kenya[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 22(1): 1-31. doi: 10.1007/BF00388011
Eugster H P, Hardie L A. 1975. Sedimentation in an ancient PlayaLake Complex: The Wilkins peak member of the Green River Formation of Wyoming[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 86(3): 319-334. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<319:SIAAPC>2.0.CO;2
Eugster H P, Jones B F, Shirley L R. 1977. Hydrochemistry of the Lake Magadi basin, Kenya[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41(1): 53-72. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(77)90186-7
Eugster H P. 1980. Hypersaline Brines and Evaporitic Environments[M]. Netherland: Elsevier Science.
Garcia-Veigas J, Gundogan I, Helvacı C, Prats E. 2013. A genetic model for Na-carbonate mineral precipitation in the Miocene Beypazari trona deposit, Ankara province, Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 294: 315-327. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.06.011
Hardie L A, Eugster H P. 1970. The evolution of closed-basin brines[J]. Mineralogical Society of America Special Publication, 3: 253-273.
Helvaci C, Inci U, Yilmaz H, Yaǧmurlu F. 1989. Geology and Neogene trona deposit of the Beypazari region, Turkey[J]. Turkish Journal of Engineering and Environmental Sciences, 13: 245-256.
Helvaci C. 1998. The Beypazari Trona Deposit, Ankara Province, Turkey[C]//Wyoming State Geological Survey Public Information Circular 40.
Helvaci C. 2010. Geology of the Beypazari trona field, Ankara, Turkey. Mid-congress field excursion guide book, tectonic crossroads: Evolving orogens of Eurasia-Africa-Arabia[C]//Tectonic Crossroads: Evolving Orogens of Eurasia-AfricaArabia, Ankara, Turkey.
Hyland E G, Sheldon N. 2013. Coupled CO2-climate response during the Early Eocene climatic optimum[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 369: 125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.10.011
Inci U. 1991. Miocene alluvial fan-alkaline playa lignite-trona bearing deposits from an inverted basin in Anatolia: Sedimentology and tectonic controls on deposition[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 71(1): 73-97.
Jagniecki E A, Lowenstein T K, Jenkins D M, Demicco R V. 2015. Eocene atmospheric CO2 from the nahcolite proxy[J]. Geology, 43(12): 1075-1078.
Jagniecki E A, Lowenstein T K, Demicco R V, Baddouh M, Carroll A R, Beard B L, Johnson C M. 2021. Spring origin of Eocene carbonate mounds in the Green River Formation, Northern Bridger Basin, Wyoming, USA[J]. Sedimentology, 68(6): 2334-2364. doi: 10.1111/sed.12852
Jin Qiang, Xiong Shousheng, Lu Peide. 1998. Volcanic activity in major source rocks in faulted basins of China and its significance in main source rocks of fault basins in China [J]. Geological Review, 44: 136-142 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.02.004
Lee H, Muirhead J. D, Fischer T P, Ebinger C J, Sharp Z. D, Kianji G. 2016. Massive and prolonged deep carbon emissions associated with continental rifting[J]. Nature Geoscience, 9: 145-149. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2622
LeGall B, Nonnotte, P, Rolet J, Benoit M, Guillou, H, MousseauNonnotte M, Albaric J, Deverchère J. 2008. Rift propagation at craton margin. Distribution of faulting and volcanism in the North Tanzanian Divergence (East Africa) during Neogene times[J]. Tectonophysics, 448, 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.005
Lowenstein T K, Demicco R V. 2006. Elevated Eocene atmospheric CO2 and its subsequent decline[J]. Science, 313(5795): 1928-1928. doi: 10.1126/science.1129555
Lowenstein T K, Lauren A D, García-Veigas, J. 2016. Influence of magmatic-hydrothermal activity on brine evolution in closed basins: Searles Lake, California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 128: 1555-1568. doi: 10.1130/B31398.1
Lowenstein T K, Jagniecki E A, Carroll A R, Smith M E, Renaut R W, Owen R B. 2017. The Green River salt mystery: What was the source of the hyperalkaline lake waters?[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 173: 295-306. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.014
Lowenstein T K, Demicco R V. 2019. When evaporites are not formed by evaporation-The role of temperature and pCO2 on saline deposits of the Eocene Green River Formation, Colorado, USA[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 132: 1365-1380.
McNulty E. 2017. Lake Magadi and the Soda Lake Cycle: A Study of the Modern Sodium Carbonates and of Late Pleistocene and Holocene Lacustrine Core Sediments[D]. Binghamton: Binghamton University.
Muirhead J D, Simon A K, Hyunwoo L, Sara M, Brent D T, Tobias P F, Kianji G W, Sarah S D. 2016. Evolution of upper crustal faulting assisted by magmatic volatile release during early-stage continental rift development in the East African Rift[J]. Geosphere, 12: 1670-1700. doi: 10.1130/GES01375.1
Ogola J S, Behr H J. 2000. Mineralogy and Trona Formation in lake Magadi, Kenya[C]//Applied Mineralogy in Research, Economy, Technology, Ecology and Culture: Proceedings of the Sixth International Congress on Applied Mineralogy. Göttingen, GER: ICAM, 383-386.
Olson K J, Lowenstein T K. 2021. Searles Lake evaporite sequences Indicators of late Pleistocene-Holocene lake temperatures, brine evolution, and pCO2[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 133(11): 2319-2334.
Owen R B, Muiruri V M, Lowenstein T K, Renaut R W, Rabideaux N, Luo S, Deino A L, Sier M J, Dupont-Nivet G, McNulty E P, Leet K, Cohen A, Campisano C, Deocampo D, Shen C, Billingsley A, Mbuthia A. 2018. Progressive aridification in East Africa over the last half million years and implications for human evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(44): 11174-11179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1801357115
Owen R B, Renaut R W, Muiruri V M, Rabideaux N M, Lowenstein T K, McNulty E P, Leet K, Deocampo, D, Luo S, Deino A L, Cohen, A, Sier M J, Campisano, C, Shen C, Billingsley A, Mbuthia A, Stockhecke M. 2019. Quaternary history of the Lake Magadi Basin, southern Kenya Rift: Tectonic and climatic controls[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 518: 97-118. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.01.017
Qi Bingde, Xie Xing, Deng Liangwu, Zeng Qingliang, Ma Lanlan. 2011. Analysis on metallogenic conditions of Chaganur natural alkali deposit in Sunite Right Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Sichuan Geology, 31(S1): 8-10 (in Chinese).
Renaut R W, Ashley G M. 2002. Sedimentation in Continental Rifts[M]. US: SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology.
Renaut R W, Owen R B, Lowenstein T K, De C G, Mcnulty E, Scott J J, Mbuthia A. 2021. The role of hydrothermal fluids in sedimentation in saline alkaline lakes: Evidence from Nasikie Engida, Kenya Rift Valley[J]. Sedimentology, 68(1): 108-134. doi: 10.1111/sed.12778
Schubel K A, Simonson B M. 1990. Petrography and diagenesis of cherts from Lake Magadi, Kenya[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 60(5): 761-776.
Smith M E, Carroll A R, Scott J J, Singer B S. 2014. Early Eocene carbon isotope excursions and landscape destabilization at eccentricity minima: Green River Formation of Wyoming[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 403: 393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.06.024
USGS. 2023. Mineral Commodity Summaries[R]. United States Geological Survey.
Wang Aiyun, Chen Wenxi. 2022. Trona: From ancient washing powder to the mother of chemical industry[J]. Earth, (1): 6-11 (in Chinese).
Wang Jiuyi, Liu Chenglin, Wang Chunlian, Yu Xiaocan, Yan Kai, Gao Chao. 2021. Tectono-paleoclimatic coupling process for mineralization of Late Cretaceous-Paleogene evaporites in South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(7): 2041-2051 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Warren J K. 2010. Evaporites through time: Tectonic, climatic and eustatic controls in marine and nonmarine deposits[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 98(3/4): 217-268.
Warren J K. 2016. Evaporites: Sediments, Resources and Hydrocarbons[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG.
Xu Hong, Peng Qiming, Martin R Palmer. 2004. Origin of tourmalinerich rocks in a Paleoproterozoic terrene (N.E. China): Evidence for evaporite-derived boron[J]. Geology in China, (3): 240-253 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Yang, Cao Yangtong, Liu Chenglin. 2021. Whether the middle Eocene salt-forming brine in the Kuqa Basin reached the potashforming stage: Quantitative evidence from halite fluid inclusions[J]. Geofluids, 2: 1-12.
Xu Yang, Liu Chenglin, Cao Yangtong. 2021. Salt-forming evolution characteristics of Middle Eocene in the Kuqa basin, Xinjiang: A case study of borehole KL4[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(7): 2183-2192 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Kai, Liu Chenglin, Wang Chunlian, Fan Meiling, Xu Haiming, Wang Jiuyi. 2021. Mineral deposition and paleoenvironment of Cretaceous evaporite in Southwestern Congo[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 40(3): 525-534 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jianghai, Yi Chenglong, Du Yuansheng, Zhang Zongheng, Yan Jiaxin. 2014. Geochemical characteristics of Paleogene alkalibearing rock series in Biyang Depression and their indicative significance for alkali-formation[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 44(10): 2172-2184 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/zd-2014-44-10-2172
Ye Tielin. 1978. Trona and its genesis briefly[J]. Industrial Minerals and Processing, 6: 18-23 (in Chinese).
Ye Tielin. 2013. Trona Resources, Geology, Mining and Processing, 3rd Edition[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press (in Chinese).
Yi Chenglong. 2016. Sequence stratigraphy characteristics and its significance of alkaliferous strata of the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in Anpeng area, Biyang sag in Henan Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 18(1): 93-100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zachos J C, Dickens G R, Zeebe R E. 2008. An Early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics[J]. Nature, 451: 279-283. doi: 10.1038/nature06588
Zhang Chending. 1979. Soda-ash deposits[J]. Soda Industry, 3: 56-64(in Chinese).
Zhang Chending. 2004. Development of the Trona deposit in Beypazari, Turkey [J]. Soda ash Industry, (2): 15-18 (in Chinese).
Zhang Chending. 2013. Development of the Trona Deposit[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press (in Chinese).
Zhang Tianfu, Zhang Yun, Cheng Xianyu, Sun Lixin, Cheng Yinhang, Zhou Xiaoxi, Wang Shaooyi, Ma Hailin, Lu Chao. 2020. Borehole databases and 3D geological model of Jurassic-Cretaceous strata in Dongsheng area, North Odors Basin[J]. China Geology, 47(S1): 220-245 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhong Yisi, Wang Licheng, Dong Haowei. 2022. Evaporite sedimentary characteristics and environment: A review[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 40(5): 1188-1214 (in Chinese with English abstract).
陈建立. 2013. 泌阳凹陷碱矿床地质特征、成因及成矿预测——以安棚碱矿床为例[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 28(3): 393-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201303010.htm
金强, 熊寿生, 卢陪德. 1998. 中国断陷盆地主要生油岩中的火山活动及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 44: 136-142. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.1998.02.005
齐兵德, 谢星, 邓良武, 曾清亮, 马兰兰. 2011. 内蒙古苏尼特右旗查干诺尔天然碱矿成矿条件浅析[J]. 四川地质学报, 31(S1): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB2011S1005.htm
王爱云, 陈文西. 2022. 天然碱: 从古代洗衣粉到化工之母[J]. 地球, (1): 6-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIQU202201003.htm
王九一, 刘成林, 王春连, 余小灿, 颜开, 高超. 2021. 晚白垩世-古近纪华南蒸发岩矿床形成的构造和气候耦合控制[J]. 地质学报, 95(7): 2041-2051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202107004.htm
许虹, 彭齐鸣, Martin R Palmer. 2004. 辽宁古元古代地体中富电气石岩石的成因: 蒸发岩硼源的证据(英文)[J]. 中国地质, (3): 240-253. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20040302?st=search
徐洋, 刘成林, 曹养同. 2021. 新疆库车盆地中始新世成盐演化特征——以KL4钻孔为例[J]. 地质学报, 95(7): 2183-2192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202107017.htm
颜开, 刘成林, 王春连, 范美玲, 徐海明, 王九一. 2021. 刚果盆地西南部白垩纪蒸发岩矿物与古环境特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 40(3): 525-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202103006.htm
杨江海, 易承龙, 杜远生, 张宗恒, 颜佳新. 2014. 泌阳凹陷古近纪含碱岩系地球化学特征对成碱作用的指示意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 44(10): 2172-2184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201410006.htm
叶铁林. 1978. 天然碱及其成因简述[J]. 化工矿山技术, 6: 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ197806003.htm
叶铁林. 2013. 天然碱资源·地质·开采·加工第3版[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社.
易承龙. 2016. 河南省泌阳凹陷安棚地区古近系核桃园组含碱地层层序特征及其意义[J]. 古地理学报, 18(1): 93-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201601008.htm
张晨鼎. 1979. 天然碱矿床[J]. 纯碱工业, 3: 56-64.
张晨鼎. 2004. 土耳其贝帕扎里天然碱矿床的开发[J]. 纯碱工业, (2): 15-18.
张晨鼎. 2013. 天然碱矿床开发[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社.
张天福, 张云, 程先钰, 孙立新, 程银行, 周小希, 王少轶, 马海林, 鲁超. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部东胜地区侏罗系-白垩系钻孔数据库与三维地质模型[J]. 中国地质, 47(S1): 220-245. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/2020S120?st=search
钟逸斯, 王立成, 董浩伟. 2022. 蒸发岩沉积特征及环境综述[J]. 沉积学报, 40(5): 1188-1214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202205003.htm
-




 下载:
下载:







