Spatial characteristics of quantitative geomorphic indices in the Taihang Mountains, north China: Implications for tectonic geomorphology
-
摘要:
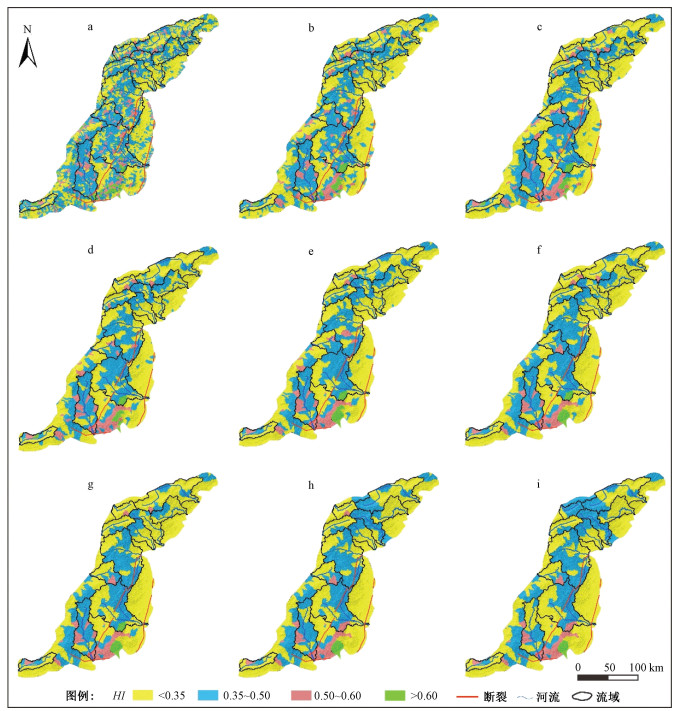
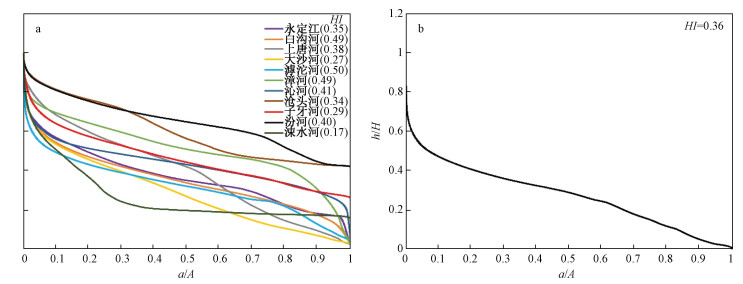
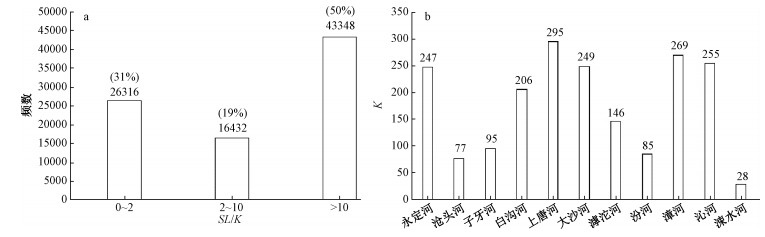
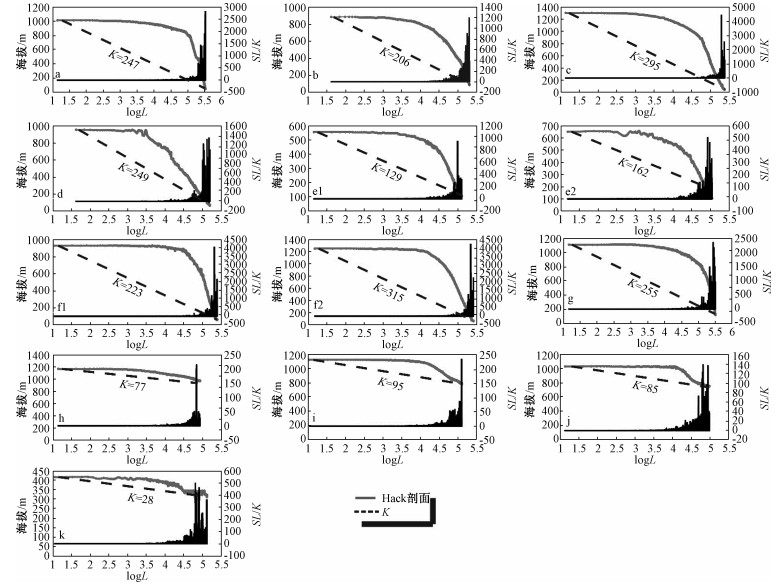
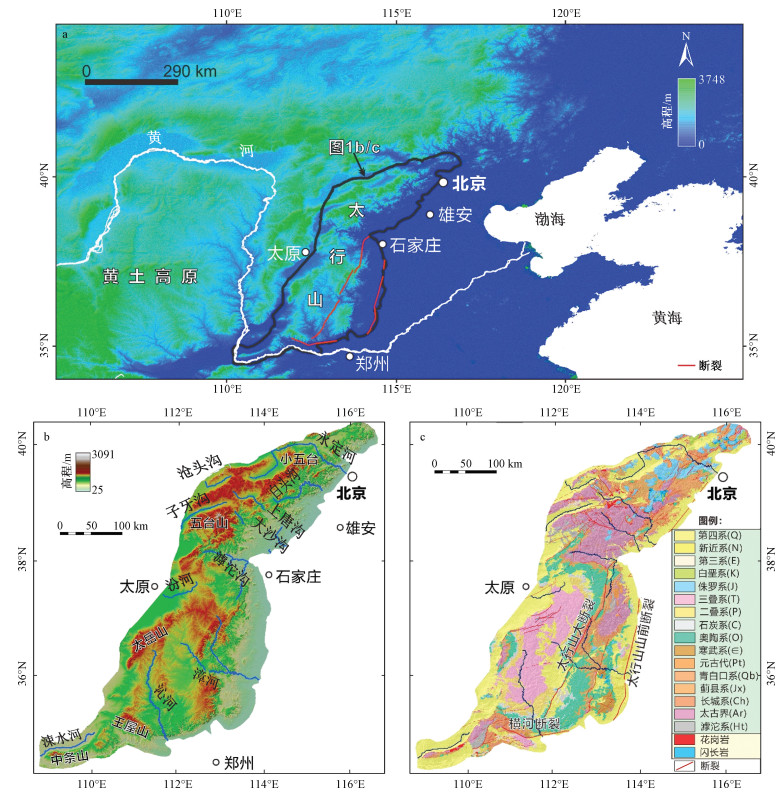
系统的地貌计量指标分析有助于理解造山带新构造活动特征与地貌演化。太行山地处中国第二、三地形阶梯的边界,具有重要的构造地貌意义。基于ASTER GDEM地形数据,对太行山按流域进行了面积高程积分、河长坡降指标(SL)和Hack剖面等地貌计量指标的分析,结合地层、构造等资料,探讨了太行山构造地貌演化特征。结果表明,在分析的11条河流中,7条河流的面积高程曲线(HC)呈S形,面积高程积分值(HI)在0.35~0.60之间,表明其地貌演化处于壮年阶段,4条河流的HC呈凹形,HI值小于0.35,表明其地貌已遭受强烈侵蚀改造,目前处于地貌演化的老年阶段;7条河流的Hack剖面呈上凸形态,均衡坡降指标值(K)偏高,表明流域所在区域新构造活动较为活跃,4条河流的Hack剖面近似直线,K值偏低,表明河流所在区域新构造活动性较弱;从整体上看,太行山的HI平均值为0.36,HC为接近凹形的S形,表明太行山地貌演化整体上处于"壮年期"向"老年期"过渡阶段;太行山新构造活动性(断裂活动)在空间上存在差异性,东部活动性较强,西部地区活动性相对较弱。
Abstract:Tectonic geomorphology focuses on the coupling relationship between tectonics and surface processes, as well as their influence on topographic evolution. Spatial analysis techniques based on digital elevation model (DEM) and geographic information system (GIS) have gradually become one of the quantitative methods of tectonic geomorphologic study. The Taihang Mountains is located at the boundary of China's second and third topographic steps, and has important tectonics and geomorphological significance. However, at present, there are still few studies on the relationship between topographic evolution status of the Taihang Mountains and geological tectonics. Based on the ASTER GDEM data (30 m×30 m) and GIS spatial analysis method, we selected the elevation, slope, hypsometric integral, stream length-gradient index SL and Hack Profile of river slopes in the mainstream of the Taihang Mountains for analysis. Combining with the lithology and tectonics, we discussed the regional landform evolution status of the Taihang Mountains. The results show that, among the 11 rivers analyzed, the HC of 7 rivers is S-shaped, the HI between 0.35 and 0.60, indicating that the geomorphy is in the prime of evolution, while that of the other 4 rivers is concave, HI less than 0.35, indicating strong erosion and destruction effect in the old age. The Hack profiles of 7 rivers are up-convex with relatively high K value, demonstrating the relatively active regional neotectonic activity, while that of the other 4 rivers are approximately straight with low K value, demonstrating the weak regional neotectonic activity. On the whole, the average HI of the Taihang Mountains is 0.36, and the HC is nearly concave S-shaped. The geomorphological evolution of this area is generally in the transitional stage from the "prime age" to the "old age". The neotectonic activity (fault activity) of the Taihang Mountains shows difference in space, with strong activity in the east and relatively weak activity in the west.
-

-
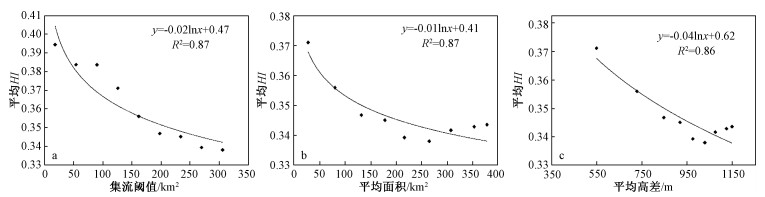
表 1 不同集流阈值下太行山次集水盆地数量、平均面积、平均高差和平均HI
Table 1. Attributes of the sub-catchment basins defined by the area threshold
集流阙值/km2 次集水盆地数量/个 平均面积/km2 平均高差/m 平均HI 4.5 20277 6.98 369 0.39 8.1 10449 13.49 439 0.38 9 9085 15.52 440 0.38 18 5072 27.63 549 0.37 54 1712 80.27 728 0.36 90 1027 132.02 847 0.35 126 749 178.12 919 0.35 162 611 216.42 975 0.34 198 493 265.36 1028 0.34 234 418 307.80 1075 0.34 270 362 353.37 1124 0.34 306 335 378.44 1149 0.34 -
ALIPOOR R, POORKERMANI M, ZARE M, et al., 2011. Active tectonic assessment around Rudbar Lorestan dam site, High Zagros Belt (SW of Iran)[J]. Geomorphology, 128(1-2): 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.10.014
AN H T, XU L Q, LI S Z, et al., 2015. Meso-cenozoic stress fields and their transition mechanisms in the eastern Taihang mountain fault zone[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(4): 571-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201504002.htm
CAO X Z, LI S Z, LIU X, et al., 2013. The intraplate morphotectonic inversion along the Eastern Taihang Mountain Fault Zone, North China and its mechanism[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(4): 88-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304010.htm
CAO X Z, XU L Q, LI S Z, et al., 2018. Neotectonics in the central North China block[J]. Chinese Journal of geology, 53(3): 835-859. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/331972830_Neotectonics_in_the_central_North_China_block
CHANG J, QIU N S, LIU S, et al., 2019. Post-Triassic multiple exhumation of the Taihang Mountains revealed via low-T thermochronology: Implications for the paleo-geomorphologic reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 68: 34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.11.007
CHANG Z Y, WANG J, BAI S B, et al., 2014. Appraisal of active tectonic in Bailongjiang basin based on DEM data[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 34(2): 292-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_quaternary-sciences_thesis/0201253122967.html
CHEN Y C, SUNG Q, CHENG K Y, 2003. Along-strike variations of morphotectonic features in the Western Foothills of Taiwan: tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis[J]. Geomorphology, 56(1-2): 109-137. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(03)00059-X
CHENG L, WU D Y, JIN W, et al., 2017. Geomorphic evolution of the Qiantang River drainage basin based on the analysis of topographic indexs[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 37(2): 343-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_quaternary-sciences_thesis/0201253121039.html
CHENG S X, LI S Z, XU L Q, et al., 2014. Junction and transition of meso-cenozoic intraplate deformation between Taihang mountains and Qinling mountains[J]. Geological Review, 60(6): 1245-1258. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201406006.htm
DAVIS W M, 1899. The geographical cycle[J]. The Geographical Journal, 14(5): 481-504. doi: 10.2307/1774538
EL HAMDOUNI R, IRIGARAY C, FERNÁNDEZ T, et al., 2008. Assessment of relative active tectonics, southwest border of the Sierra Nevada (Southern Spain)[J]. Geomorphology, 96(1-2): 150-173. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.08.004
FAN K F, YANG D C, 2006. Geomorphologic system in Taihang Mountain area[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 7(1): 51-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CGCZ200601015.htm
GAO Y F, JIAO H Y, 2007. Landform features of Zhangshiyan and Yuntai mountain at the middle-south section of the Taihang mountains[J]. Urban Geology, 2(4): 44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ200704012.htm
GONG M Q, 2010. Uplift process of southern Taihang mountain in Cenozoic[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HACK J T, 1973. Stream-profile analysis and stream-gradient index[J]. Journal of Research of the U.S. Geological Survey, 1(4): 421-429. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/311898307_Stream_profile_analysis_and_stream_gradient_index/amp
HAN M K, ZHU S L, ZHAO J Z, et al., 1983. Geomorphic expressions of Quaternary tectonic stress field in the southern section of the eastern piedmont fault zone of Taihangshan Mountain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 38(4): 348-357. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB198304002.htm
HE D F, SHAN S Q, ZHANG Y Y, et al., 2018. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong'an New Area: Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(8): 1007-1022. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9188-4
HU X F, PAN B T, KIRBY E, et al., 2010. Spatial differences in rock uplift rates inferred from channel steepness indices along the northern flank of the Qilian Mountain, northeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(27): 3205-3214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4024-4
HU X M, FU J L, LI Y L, 2002. Response of landform development to the tectonic movement and the climate changes in Fenhe drainage basin[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 27(3): 310-318. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Q W, SHI Y, QIN K L, et al., 2019. Geochronology and geochemistry of intrusions in the Qinling Complex: implications for the Paleozoic Tectonic evolution[J]. Geology and Exploration, 55(5): 1185-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKT201905007.htm
JI Y P, GAO H S, PAN B T, et al., 2011. Implication of active structure in the upper reaches of Weihe river basin from stream length-gradient index (SL index) and Hack profile[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 47(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201104000.htm
LEE C S, TSAI L L, 2010. A quantitative analysis for geomorphic indices of longitudinal river profile: A case study of the Choushui River, central Taiwan[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(7): 1549-1558. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0140-3
LI L B, XU G, HU J M, et al., 2012. Quantitative analysis of relative active tectonics of the upstream region of Weihe river based on DEM[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 32(5): 866-879. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DSJJ201205008.htm
LIANG O B, REN J J, LV Y W, 2018. The response of fluvial geomorphologic characteristics of the Fujiang drainge basin to activity of the Huya fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(1): 42-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU J, ZHANG J Y, GE Y K, et al., 2018. Tectonic geomorphology: An interdisciplinary study of the interaction among tectonic climatic and surface processes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(30): 3070-3088. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/N972018-00498
LIU K, QU G S, NING B K, et al., 2012. The application of slope analysis method in fault segmentation in Kunming basin[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster-prevention Science and Technology, 2012, 14(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-FZJS201204002.htm
LIU K M, XU Q M, DUAN L F, et al., 2020. Quaternary stratigraphic architecture and sedimentary evolution from borehole GB014 in the western Xiong'an New Area[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(20): 2145-2160. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/342894393_Quaternary_stratigraphic_architecture_and_sedimentaryevolution_from_borehole_GB014_in_the_westernXiong'an_New_Area
MENG Y K, WANG X W, CHEN J, 2015. Geological evidence of the Cenozoic tectonic uplifting in Taihang Mountains-Apatite fission track evidence from Well Qincan 1[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 35(1): 15-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201501003.htm
PEDRERA A, PÉREZ-PEÑA J V, GALINDO-ZALDÍVAR J, et al., 2009. Testing the sensitivity of geomorphic indices in areas of low-rate active folding (eastern Betic Cordillera, Spain)[J]. Geomorphology, 105(3-4): 218-231. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.09.026
QIAN C, HAN J E, ZHU D G, et al., 2012. An analysis of geomorphologic characteristics of the Yellow River source region based on ASTER-GDEM[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(5): 1247-1260. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286611957_An_analysis_of_geomorphologie_characteristics_of_the_Yellow_River_source_region_based_on_ASTER-GDEM
SEEBER L, GORNITZ V, 1983. River profiles along the Himalayan arc as indicators of active tectonics[J]. Tectonophysics, 92(4): 335-337, 341-367. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(83)90201-9
SHI X M, YANG J C, LI Y L, et al., 2004. Deformation of Manas river terraces and neotectonics in northern front of the Tianshan mountains[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 40(6): 971-978. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-BJDZ200406015.htm
SILVA P G, GOY J L, ZAZO C, et al., 2003. Fault-generated mountain fronts in Southeast Spain: Geomorphologic assessment of tectonic and seismic activity[J]. Geomorphology, 50(1-3): 203-225. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00215-5
STRAHLER A N, 1952. Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography[J]. GSA Bulletin, 63(11): 1117-1142. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1952)63[1117:HAAOET]2.0.CO;2
SUN Q K, HE Q L, LI L Y, et al., 2018. Evolution characteristics of the crust vertical deformation and the faults activity analysis in the northern area of North China[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 41(3): 438-445. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DZYJ201803014&dbcode=CJFD&year=2018&dflag=pdfdown
WALCOTT R C, SUMMERFIELD M A, 2008. Scale dependence of hypsometric integrals: an analysis of southeast African basins[J]. Geomorphology, 96(1-2): 174-186. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.08.001
WANG A, WANG G C, 2005. Review on morphotectonic and its analytical methods[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 24(4): 7-12, 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200504002.htm
WANG H, LI J H, WU T W, 2018. Characteristics and genesis of Geoheritage resources of Taihang mountain[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 54(3): 546-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/327526825_Characteristics_and_Genesis_of_Geoheritage_Resources_of_Taihang_Mountain
WEN L, WEI P F, LI X M, et al, 2020. Study on the river network, geomorphological features and tectonic activity in the Danjiangkou reservoir and its surrounding areas[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(2): 252-262. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU C, ZHANG X Q, MA Y H, 1999. The Taihang and Yan Mountains rose mainly in quarteranary[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 17(3): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285887689_The_Taihang_and_Yan_Mountains_rose_mainly_in_Quaternary
WU C, 2001. Geomorphologic resources of tourism landscape in Taihang Mountain Area[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 17(4): 6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT200104001.htm
WU D Y, ZHANG T Q, CHENG L, et al., 2018. Neotectonic activation of the Urumqi River basin revealed by geomorphic indices[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 38(1): 193-203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Q, 2012. Tectonic geomorphology and active tectonics in the center of the North China Block[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU J, GAO Z W, SONG C Q, et al., 2000. The structural characters of the piedmont fault zone of Taihang Mountain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(2): 111-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200002003.htm
XU Z P, JIANG L, YANG L P, et al., 2015. Structure characteristics of faults in the southeast segment of Taihang Mountain using Bouguer gravity data[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 35(3): 503-507. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/handle/00001903-5/460247
ZHANG J C, LI C C, ZHANG M, et al., 2011. Geomorphologic analysis of the Golmud river drainage basin based on hypsometric integral value[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 29(3): 257-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDYA201103001.htm
ZHANG J J, ZHU W B, ZHAO F, et al., 2018. Spatial variations of terrain and their impacts on landscape patterns in the transition zone from mountains to plains-A case study of Qihe River Basin in the Taihang Mountains[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(4): 450-461. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9158-2
ZHANG L, ZHANG X J, WU F D, et al., 2018. Characteristics of weathering crust and formation of planation surface in Wangmangling at the Southern edge of Taihang mountain[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 39(5): 635-642. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201805015.htm
ZHANG M, LI X P, 2014. Discussion on the main uplift period of the Southern segment of Taihang mountains[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Study(4): 55-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_territory-natural-resources-study_thesis/0201253447127.html
ZHANG Q Q, ZHANG S H, 2019. Devonian magmatism in the Northern margin of the North China block and its tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 125-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201901053.htm
ZHANG T Q, WANG Z, ZHANG X M, et al., 2015. Hypsometric integral analysis of the Urumqi River drainage basin and its implications for topographic evolution[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 35(1): 60-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Y Q, MA Y S, YANG N, 2003. Neotectonic activity of the southern marginal fault zone of the Taihangshan Mountains and its regional kinematic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(2): 169-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200302000.htm
ZHANG Y Q, SHI W, DONG S W, 2019. Neotectonics of North China: interplay between far-field effect of India-Eurasia collision and Pacific subduction related deep-seated mantle upwelling[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(5): 971-1001. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXE201905001.htm
ZHAO G H, LI Y, YAN Z K, et al., 2014. Tectonic Geomorphology Analysis of piedmont rivers of the middle MT. Longmenshan based on Hack profile and hypsometric integral[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 34(2): 302-311. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201402004.htm
ZHAO G S, DU Y, LING F, et al., 2012. Analysis of influencing factors on height differences between ASTER GDEM and SRTM3[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 37(4): 167-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/318108259_Analysis_of_influencing_factors_on_height_differences_between_ASTER_GDEM_and_SRTM_3
ZHAO H Z, LI Y L, YANG J C, et al., 2009. Geomorphology characteristic and tectonic response of the northern Tianshan represented by hypsometric integral[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 27(3): 285-292. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/docdown/docdownload.aspx?filename=SDYA200903006&dbcode=CJFD&year=2009&dflag=pdfdown
ZHAO H Z, LI Y L, YANG J C, et al., 2010a. Influence of area and space dependence for hypsometric integral and its geological implications[J]. Geographical Research, 29(2): 271-282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO H Z, LI Y L, YANG J C, 2010b. Implication of active structure along the northern Tianshan by stream length-gradient index and hack profile[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 46(2): 237-244. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201002012.htm
ZHU J J, LIU J T, LIANG H Z, et al., 2019. Vertical gradients of water supply and demand in Taihang Mountains, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(2): 472-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30915798
安慧婷, 许立青, 李三忠, 等, 2015. 太行山东麓断裂带中、新生代构造应力场及转换机制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(4): 571-586. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201504002.htm
曹现志, 李三忠, 刘鑫, 等, 2013. 太行山东麓断裂带板内构造地貌反转与机制[J]. 地学前缘, 20(4): 88-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304010.htm
曹现志, 许立青, 李三忠, 等, 2018. 华北地块中部新构造运动[J]. 地质科学, 53(3): 835-859.
常直杨, 王建, 白世彪, 等, 2014. 基于DEM的白龙江流域构造活动定量分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(2): 292-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.02.03
程世秀, 李三忠, 许立青, 等, 2014. 太行山-秦岭中、新生代板内变形及交接转换机制[J]. 地质论评, 60(6): 1245-1258. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201406006.htm
程璐, 武登云, 靳文, 等, 2017. 基于地貌计量指标分析的钱塘江流域地貌演化特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 37(2): 343-352.
樊克锋, 杨东潮, 2006. 论太行山地貌系统[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版), 7(1): 51-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8984.2006.01.016
高亚峰, 焦慧元, 2007. 太行山嶂石岩地貌与云台山地貌特征[J]. 城市地质, 2(4): 44-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2007.04.011
龚明权, 2010. 新生代太行山南段隆升过程研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院.
韩慕康, 朱世龙, 赵景珍, 等, 1983. 太行山东麓断裂带南段第四纪构造应力场的地貌表现[J]. 地理学报, 38(4): 348-357. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1983.04.003
何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 等, 2018. 雄安新区的三维地质结构: 来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(9): 1207-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201809007.htm
胡小飞, 潘保田, KIRBY E, 等, 2010. 河道陡峭指数所反映的祁连山北翼抬升速率的东西差异[J]. 科学通报, 55(23): 2329-2338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201023016.htm
胡小猛, 傅建利, 李有利, 2002. 汾河流域地貌发育对构造运动和气候变化的响应[J]. 地理学报, 27(3): 310-318. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2002.03.007
黄倩雯, 时毓, 覃康禾, 等, 2019. 秦岭岩群(杂岩)侵入体的年代学地球化学特征及其对古生代构造运动的启示[J]. 地质与勘探, 55(5): 1185-1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201905007.htm
吉亚鹏, 高红山, 潘保田, 等, 2011. 渭河上游流域河长坡降指标SL参数与Hack剖面的新构造意义[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 47(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2804.2011.04.001
李利波, 徐刚, 胡健民, 等, 2012. 基于DEM渭河上游流域的活动构造量化分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 32(5): 866-879. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.05.05
梁欧博, 任俊杰, 吕延武, 2018. 涪江流域河流地貌特征对虎牙断裂带活动性的响应[J]. 地震地质, 40(1): 42-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201801004.htm
刘静, 张金玉, 葛玉魁, 等, 2018. 构造地貌学: 构造-气候-地表过程相互作用的交叉研究[J]. 科学通报, 63(30): 3070-3088. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201830003.htm
刘亢, 曲国胜, 宁宝坤, 等, 2012. 坡度分析在昆明盆地断层分段中的应用[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 14(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZJS201204002.htm
刘开明, 胥勤勉, 段连峰, 等, 2020. 雄安新区西部GB014孔第四纪地层结构与演化过程[J]. 科学通报, 65(20): 2145-2160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202020011.htm
孟元库, 汪新文, 陈杰, 2015. 太行山新生代构造隆升的地质学证据-来自沁水盆地沁参1井的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 35(1): 15-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201501003.htm
钱程, 韩建恩, 朱大岗, 等, 2012. 基于ASTER-GDEM数据的黄河源地区构造地貌分析[J]. 中国地质, 39(5): 1247-1260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201205011.htm
史兴民, 杨景春, 李有利, 等, 2004. 天山北麓玛纳斯河河流阶地变形与新构造运动[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 40(6): 971-978. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200406015.htm
孙启凯, 何庆龙, 李腊月, 等, 2018. 华北北部地区地壳垂直形变演化特征及断裂活动性分析[J]. 地震研究, 41(3): 438-445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ201803014.htm
王岸, 王国灿, 2005. 构造地貌及其分析方法述评[J]. 地质科技情报, 24(4): 7-12, 20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200504002.htm
王辉, 李江海, 吴桐雯, 2018. 太行山地质遗迹特征与成因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 54(3): 546-554. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201803011.htm
文力, 魏鹏飞, 李学敏, 等, 2020. 丹江口水库库区及周边地区河网形态、地貌特征及构造活动性意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(2): 252-262. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20200210&journal_id=dzlxxb
吴忱, 张秀清, 马永红, 1999. 太行山、燕山主要隆起于第四纪[J]. 华北地震科学, 17(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD199903000.htm
吴忱, 2001. 论太行山地区旅游风景地貌资源[J]. 地理学与国土研究, 17(4): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT200104001.htm
武登云, 张天琪, 程璐, 等, 2018. 地貌形态指标揭示的北天山乌鲁木齐河流域新构造活动特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 38(1): 193-203.
吴奇, 2012. 华北地块中部构造地貌与活动构造特征[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
徐杰, 高战武, 宋长青, 等, 2000. 太行山山前断裂带的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 22(2): 111-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200002003.htm
徐志萍, 姜磊, 杨利普, 等, 2015. 利用布格重力资料研究太行山东南缘断裂构造特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 35(3): 503-507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201503035.htm
张敬春, 李川川, 张梅, 等, 2011. 格尔木河流域面积-高程积分值的地貌学分析[J]. 山地学报, 29(3): 257-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201103001.htm
张蕾, 张绪教, 武法东, 等, 2018. 太行山南缘王莽岭地区风化壳的地球化学特征与夷平面形成环境[J]. 地球学报, 39(5): 635-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805015.htm
张蒙, 李鹏霄, 2014. 太行山南段主要隆升时期探讨[J]. 国土与自然资源研究(4): 55-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZY201404020.htm
张琪琪, 张拴宏, 2019. 华北地块北缘泥盆纪岩浆活动及其构造背景[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(1): 125-138. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190112&journal_id=dzlxxb
张天琪, 王振, 张晓明, 等, 2015. 北天山乌鲁木齐河流域面积: 高程积分及其地貌意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 35(1): 60-70.
张岳桥, 马寅生, 杨农, 2003. 太行山南缘断裂带新构造活动及其区域运动学意义[J]. 地震地质, 25(2): 169-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200302000.htm
张岳桥, 施炜, 董树文, 2019. 华北新构造: 印欧碰撞远场效应与太平洋俯冲地幔上涌之间的相互作用[J]. 地质学报, 93(5): 971-1001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201905001.htm
赵国华, 李勇, 颜照坤, 等, 2014. 龙门山中段山前河流Hack剖面和面积: 高程积分的构造地貌研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(2): 302-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201402004.htm
赵国松, 杜耘, 凌峰, 等, 2012. ASTER GDEM与SRTM3高程差异影响因素分析[J]. 测绘科学, 37(4): 167-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD201204057.htm
赵洪壮, 李有利, 杨景春, 等, 2009. 天山北麓流域面积高度积分特征及其构造意义[J]. 山地学报, 27(3): 285-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200903006.htm
赵洪壮, 李有利, 杨景春, 等, 2010a. 面积高度积分的面积依赖与空间分布特征[J]. 地理研究, 29(2): 271-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201002010.htm
赵洪壮, 李有利, 杨景春, 2010b. 北天山流域河长坡降指标与Hack剖面的新构造意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 46(2): 237-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201002012.htm
朱建佳, 刘金铜, 梁红柱, 等, 2019. 太行山区水资源供需关系的垂直梯度特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(2): 472-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201902015.htm
-



 下载:
下载: