Zircon U-Pb ages of the mafic gneiss and leucogneiss from the Bailey Peninsula: Constraints on the timing of the tectonothermal events related to the amalgamation of Rodinia in the Windmill Islands, East Antarctica
-
摘要:
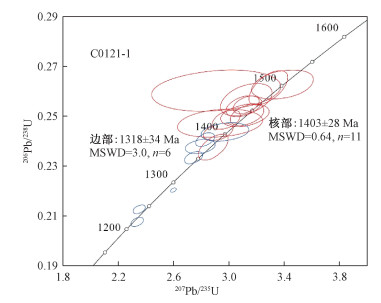
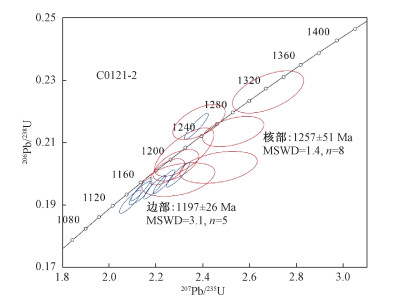
东南极Windmill群岛变质杂岩经历的变质和岩浆事件与西澳大利亚Albany-Fraser造山带在时间上相对应,并可能与罗迪尼亚超大陆的拼合有关。Windmill群岛Bailey半岛的镁铁质片麻岩(角闪石-单斜辉石-斜方辉石-黑云母-斜长石-石英-磁铁矿-锆石)被认为具有较早的形成年龄,其中还出露属于正片麻岩的淡色片麻岩(斜长石-钾长石-石英-黑云母-锆石)。对这两种片麻岩中的锆石分别进行了SHRIMP U-Pb年龄测定,首次获得该区镁铁质片麻岩锆石核部207Pb/206Pb加权平均年龄1403±28 Ma,该年龄记录了本区中元古代早期岩浆事件,这是Windmill群岛地区记录的最早一期岩浆事件,可能受到了东部莫森大陆(Mawson Continent)构造岩浆活动的影响。铁镁质片麻岩锆石增生边的年龄为1318±34 Ma,则记录了早期构造热事件。淡色片麻岩中锆石核部年龄为1257±51 Ma,与Bailey半岛的片麻状含石榴子石花岗岩侵位年龄一致,共同记录了该区的一期岩浆活动。淡色片麻岩中锆石增生边的年龄为1197±26 Ma,记录了晚期的变质事件。这些新的年龄数据强烈支持1375~1151 Ma期间东南极Windmill群岛与西澳大利亚Albany-Fraser造山带相连接的构造模型,同时也为罗迪尼亚超大陆拼合过程提供了重要的年代学约束。
-
关键词:
- SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 镁铁质片麻岩 /
- 淡色片麻岩 /
- Windmill群岛 /
- 东南极 /
- 罗迪尼亚
Abstract:We report new geochronological data of the mafic gneiss and leucogneiss from the Windmill Islands, East Antarctica, in order to unravel the tectonothermal events related to the amalgamation of Rodinia. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating from the mafic gneiss (Hbl-Cpx-Opx-Bt-Pl-Qtz-Mag-Zrn) yielded early Mesoproterozoic magmatic ages of 1403±28 Ma from igneous cores, and middle Mesoproterozoic metamorphic ages of 1318±34 Ma from overgrown rims. The leucogneiss (Pl-Kfs-Qtz-Bt-Zrn) in the Bailey Peninsula has intrusive ages of 1257±51 Ma from magmatic origin zircon cores, and metamorphic ages of 1197±26 Ma from overgrown rims and/or structureless grains. The intrusive age of mafic gneiss indicates the existence of a ca.1.40 Ga igneous activity in the Windmill Islands. This is likely the earliest igneous record of the Windmill Islands, possibly relating to the final period of igneous activity of the Mawson Continent. The age of high-grade metamorphism of the mafic gneiss from the Bailey Peninsula can be constrained by the metamorphic zircon overgrowth at 1318±34 Ma, suggesting that the Windmill Islands was possibly involved in the Albany-Fraser-Windmill (East Antarctic) orogeny during the 1375~1151 Ma period. This study further supports the tectonic model in which the Windmill Islands and the Albany-Fraser Orogeny are parallel convergence during the Mesoproterozoic Rodinia amalgamation.
-
Key words:
- SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages /
- mafic gneiss /
- leucogneiss /
- Windmill Islands /
- East Antarctica /
- Rodinia
-

-
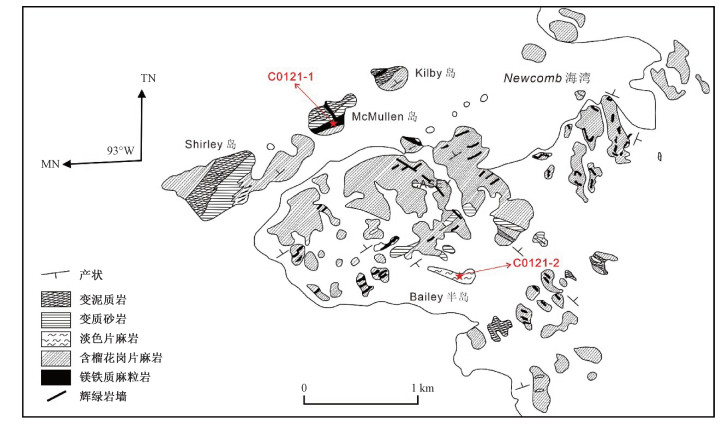
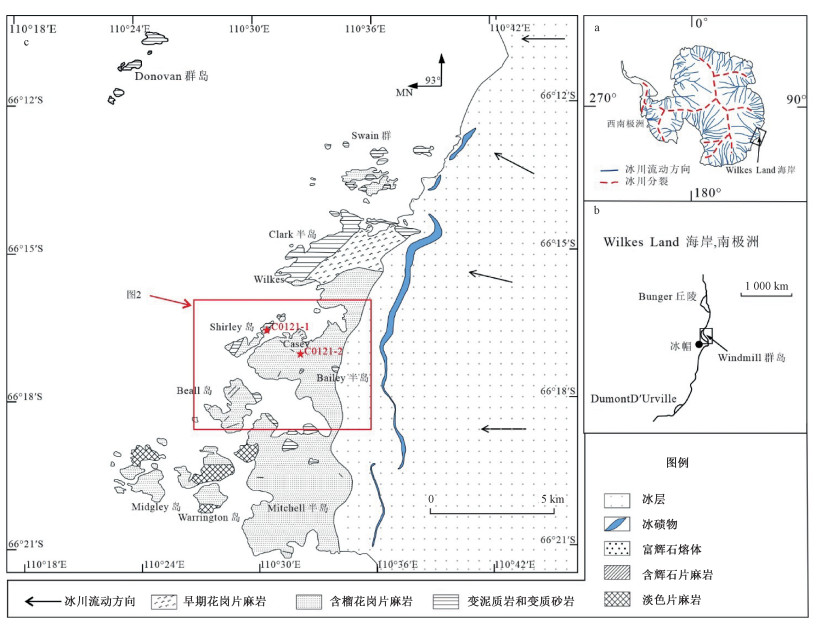
图 1 Windmill群岛地质简图(据Zhang et al., 2012修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 Bailey半岛地质简图(据Paul et al., 1995修改)
Figure 2.
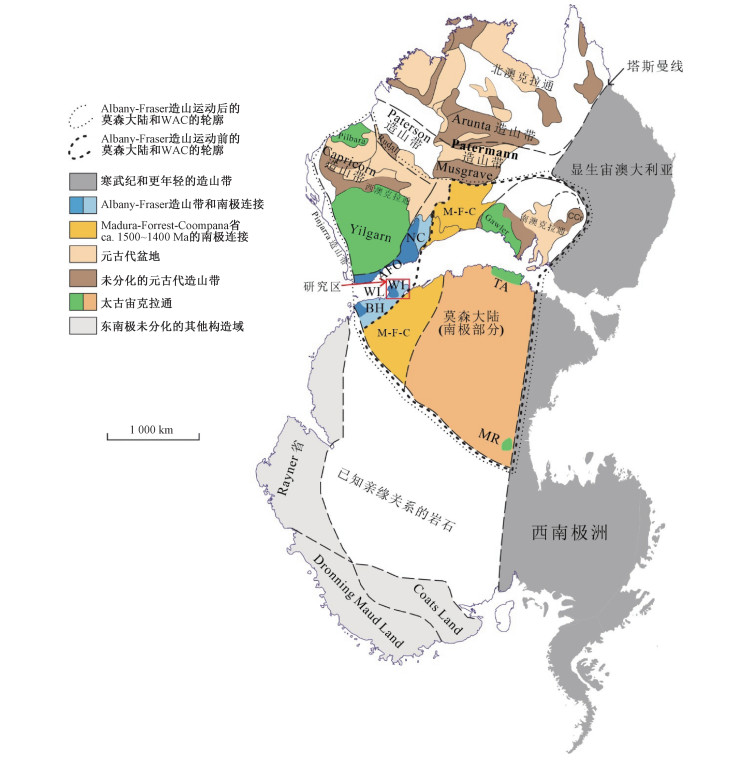
图 7 南极洲和澳大利亚的冈瓦纳大陆构造图(据Liu et al., 2018修改)
Figure 7.
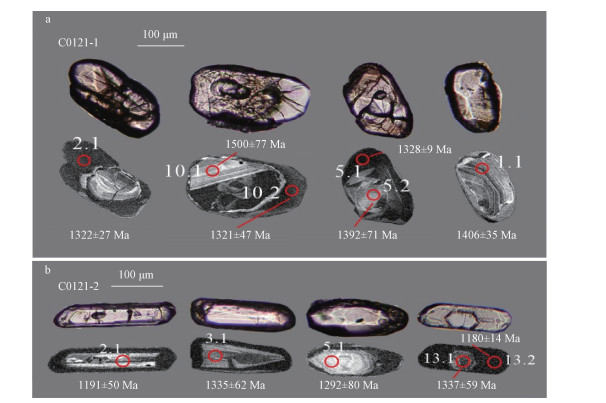
表 1 Bailey半岛镁铁质片麻岩和淡色片麻岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb同位素数据
Table 1. SHRIMP U-Pb isotopic analytical data of the mafic gneiss and leucogneiss from the Bailey Peninsula, Windmill Islands
点号 206Pbc/% 含量/×10-6 232Th/238U 年龄/Ma 同位素比值 U Th 206Pb* 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 不和谐度 207Pb*/206Pb* ±/% 207Pb*/235U ±/% 206Pb*/238U ±/% 误差 C0121-1镁铁质片麻岩 1.1c 0.07 117 60 25.7 0.53 1406 35 1462 12 -4 0.0891 1.8 3.126 2.0 0.2545 0.91 0.4 2.1r 0.07 218 7 43.7 0.03 1322 27 1352 8 -2 0.0853 1.4 2.745 1.5 0.2334 0.7 0.4 3.1c 2.5 26 11 6.02 0.42 1224 200 1490 28 -22 0.0811 10.0 2.91 11.0 0.2601 2.1 0.2 4.1c 0.15 79 42 17.1 0.54 1439 44 1441 15 0 0.0906 2.3 3.13 2.6 0.2505 1.1 0.4 5.1r 0.04 1910 0 362 0.00 1328 9.1 1284 3 3 0.08556 0.47 2.599 0.55 0.22032 0.29 0.5 5.2r 1.35 127 1 27 0.01 1392 71 1406 12 -1 0.0884 3.7 2.97 3.8 0.2437 0.99 0.3 6.1c 0.29 118 47 24.8 0.41 1359 42 1406 12 -3 0.0869 2.2 2.922 2.4 0.2438 0.97 0.4 7.1c 0.27 92 30 20.1 0.34 1399 48 1458 14 -4 0.0888 2.5 3.107 2.7 0.2539 1.1 0.4 8.1c 0.0 70 38 15.8 0.56 1451 43 1497 23 -3 0.0912 2.3 3.288 2.9 0.2614 1.8 0.6 9.1c 0.1 108 39 23 0.37 1361 39 1431 13 -5 0.087 2.0 2.982 2.3 0.2486 1.0 0.5 10.1c 0.92 66 23 14.9 0.36 1500 77 1503 20 0 0.0936 4.1 3.39 4.3 0.2626 1.5 0.3 10.2r 0.08 200 5 40.9 0.03 1321 47 1375 10 -4 0.0853 2.4 2.795 2.6 0.2378 0.77 0.3 11.1c 0.34 80 24 17.3 0.31 1433 67 1440 15 0 0.0904 3.5 3.12 3.7 0.2503 1.2 0.3 12.1c 0.57 39 11 8.74 0.28 1389 69 1473 22 -6 0.0883 3.6 3.13 3.9 0.2567 1.7 0.4 13.1r 0.0 202 5 41.8 0.02 1324 27 1389 9 -5 0.0854 1.4 2.832 1.6 0.2405 0.73 0.5 14.1r 0.0 388 25 70.9 0.07 1205 22 1242 6 -3 0.08032 1.1 2.353 1.2 0.2125 0.55 0.4 15.1c 1.19 54 25 11.6 0.48 1343 130 1423 20 -6 0.0862 6.7 2.94 6.9 0.247 1.5 0.2 16.1c 0.29 108 32 22 0.31 1387 39 1374 18 1 0.0882 2.0 2.888 2.5 0.2375 1.5 0.6 17.1r 0.0 387 22 68.9 0.06 1239 22 1215 6 2 0.08173 1.1 2.338 1.3 0.2074 0.56 0.4 C0121-2淡色片麻岩 1.1r 0.02 1698 33 314 0.02 1196 11 1256 15 -5 0.07996 0.54 2.373 1.4 0.2152 1.3 0.9 2.1c 0.2 92 170 17.1 1.91 1191 50 1264 19 -6 0.0798 2.6 2.382 3.1 0.2166 1.7 0.6 3.1c 0.48 55 112 10.8 2.09 1335 62 1315 23 2 0.0859 3.2 2.68 3.7 0.2262 2.0 0.5 4.1r 0.02 2484 127 418 0.05 1229 11 1152 13 6 0.08132 0.56 2.195 1.4 0.1957 1.3 0.9 5.1c 0.82 106 125 18.2 1.22 1292 80 1166 19 10 0.084 4.1 2.29 4.5 0.1982 1.8 0.4 6.1r 0.04 3400 194 577 0.06 1247 10 1161 14 7 0.08207 0.53 2.233 1.4 0.1973 1.3 0.9 7.1c 0.69 153 411 26.7 2.78 1395 78 1186 18 15 0.0886 4.1 2.47 4.4 0.2021 1.7 0.4 8.1r 0.02 3436 233 576 0.07 1181 11 1149 13 3 0.07936 0.54 2.135 1.4 0.1951 1.3 0.9 9.1c 0.34 129 217 22.6 1.73 1240 45 1189 18 4 0.0818 2.3 2.285 2.8 0.2026 1.6 0.6 10.1c 0.28 150 183 26.7 1.26 1229 51 1213 27 1 0.0813 2.6 2.321 3.6 0.207 2.5 0.7 11.1r 0.09 2648 110 455 0.04 1277 11 1173 14 8 0.08331 0.56 2.293 1.4 0.1996 1.3 0.9 12.1c 0.51 506 305 87.7 0.62 1226 34 1179 15 4 0.0812 1.7 2.246 2.2 0.2006 1.4 0.6 13.1c 1.33 328 288 61.1 0.9 1337 59 1248 17 7 0.0859 3.1 2.53 3.4 0.2135 1.5 0.4 13.2r 0.08 2336 76 384 0.03 1180 14 1127 13 5 0.07932 0.7 2.089 1.5 0.191 1.3 0.9 14.1r 0.35 2191 73 366 0.03 1192 16 1142 14 4 0.07979 0.81 2.133 1.5 0.1939 1.3 0.8 注:误差为1s;Pbc和Pb*分别表示普通铅和放射成因铅;标准校正值的误差为1.03%;普通铅校正应用204Pb实测值;c: 锆石核(core);r: 锆石增生边(rim) 表 2 东南极Windmill群岛地质演化的锆石和独居石U-Pb年龄和石榴子石-全岩Sm-Nd同位素年龄记录
Table 2. Summary of litho-tectonic and metamorphic evolution as determined by U-Pb SHRIMP zircon and monazite analyses and Grt-WR Sm-Nd data
地质事件 样品地点及形式 年龄/Ma 分析方法 参考文献 Balaena岛辉长岩侵位 519 斜长石K-Ar Webb et al., 1963 晚期粗玄岩墙侵位 细晶岩墙侵位 Robinson脊 1138±9 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post,2000 变形作用(D4) 北东-南西向左旋剪切和脆性断裂 橄榄石辉长岩墙侵位 变形作用(D3) 早期构造单元的南北向褶皱 变形作用(D2) 紧闭到等斜F2褶皱 Ardery紫苏花岗岩侵位 Bosner岛 1163±7 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post,2000 Robinson脊 1178±7, 1178±6 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2017b Robinson脊 1196±8, 1205±13 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Zhang et al., 2012 Ford岛花岗岩侵位 Ford岛 1173±9 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post,2000 黑云母花岗岩侵入变沉积岩 Mitchell半岛 1235±7 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2017b 麻粒岩相和部分熔融和变形作用(M2/D2) Mitchell半岛混合岩淡色体 1137±3 Sm-Nd(Grt-WR) Post, 2000 Herring岛麻粒岩变质事件 1142±7 独居石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Bailey半岛正片麻岩 1156±17 Sm-Nd(Grt-WR) Post, 2000 Clark半岛正片麻岩 1169±7 独居石HRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Herring岛麻粒岩锆石变质增长边 1171±9 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Bailey半岛含正片麻岩 1171±13 独居石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Clark半岛石榴黑云片麻岩淡色体 1171±6 独居石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Cameron岛、Herring岛、Mitchell半岛和Robinson脊变沉积岩锆石变质边 ca.1325~1170 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2017b Mitchell半岛、Herring岛变泥质岩 1177±4, 1200~1170,1185±8 独居石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2007a Bailey半岛正片麻岩同变质至变形后D2a锆石变质增生 1214±10 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Bailey半岛淡色片麻岩锆石变质增生边 1197±26 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 文中 麻粒岩相重结晶 ca.1210~1180 锆石和独居石SHRIMP U-Pb,Sm-Nd(Grt-WR) Post et al., 1997 花岗质岩石的侵位 Bailey含石榴子石花岗片麻岩侵位和片麻状含石榴子石花岗岩 1242±13, 1247±13, 1258±12 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Zhang et al., 2012 Bailey半岛淡色片麻岩原岩侵位 1257±51 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 文中 Clark半岛正片麻岩 1315±6 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Clark半岛正片麻岩 1323±7 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2017b 高角闪岩-麻粒岩相变质作用和变形作用(M1/D1) 角闪岩相重结晶 ca.1400~1300 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post et al., 1997 Mitchell半岛变泥质岩 1305±7 独居石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2007a Bailey半岛镁铁质片麻岩变质 1318±34 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 文中 Clark半岛石榴黑云片麻岩淡色体 1342±21 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 变沉积岩原岩沉积时代 Cameron岛、Herring岛、Mitchell半岛和Robinson脊变沉积岩 ca.1350~1315 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Morrissey et al., 2017b Herring岛石榴堇青黑云片麻岩 ca.1400~1350 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post, 2000 Chappel岛 1450±80 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Williams et al., 1983 ca.2500~1700 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb Post et al., 1997 花岗岩的侵位 Bailey半岛石榴花岗片麻岩、片麻状石榴花岗岩(继承锆石) 1372±13 锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb Zhang et al., 2012 镁铁质岩石的侵位 Bailey半岛 1403±28 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 文中 -
AITKEN A R A, BETTS P G, YOUNG D A, et al., 2016. The Australo-Antarctic Columbia to Gondwana transition[J]. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 136-152. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.10.019
AITKEN A R A, YOUNG D A, FERRACCIOLI F, et al., 2014. The subglacial geology of Wilkes land, East Antarctica[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(7): 2390-2400. doi: 10.1002/2014GL059405
BLIGHT D F, OLIVER R L, 1977. The metamorphic geology of the Windmill Islands, Antarctica: a preliminary account[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 24(5-6): 239-262. doi: 10.1080/00167617708728986
BLIGHT D F, OLIVER R L, 1982. Aspects of the geologic history of the Windmill Islands, Antarctica[M]//CRADDOCK C. ed. Antarctic geoscience. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press: 445-454.
BOGER S D, 2011. Antarctica-Before and after Gondwana[J]. Gondwana Research, 19(2): 335-371. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.09.003
CLARK D J, HENSEN B J, KINNY P D, 2000. Geochronological constraints for a two-stage history of the Albany-Fraser Orogen, Western Australia[J]. Precambrian Research, 102(3-4): 155-183. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00063-2
FITZSIMONS I C W, 2000. A review of tectonic events in the East Antarctic Shield and their implications for Gondwana and earlier supercontinents[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 31(1): 3-23. doi: 10.1016/S0899-5362(00)00069-5
FITZSIMONS I C W, 2003. Proterozoic basement provinces of southern and southwestern Australia, and their correlation with Antarctica[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 206(1): 93-130. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.206.01.07
ARRIS L B, 1995. Correlation between the Albany, Fraser And Darling mobile belts of western Australia and Mirny to Windmill Islands in the east Antarctic Shield: Implications for Proterozoic Gondwanaland reconstructions[M]//YOSHIDA S M. India and Antarctica during the Precambrian. Memoir of the Geological Society of India, vol. 34. Bangalore: Geological Society of India: 47-71.
HAWKESWORTH C, CAWOOD P, KEMP T, et al., 2009. A matter of preservation[J]. Science, 323(5910): 49-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1168549
HE X F, HAND M, SANTOSH M, et al., 2018. Long-lived metamorphic P-T-t evolution of the Highland Complex, Sri Lanka: insights from mafic granulites[J]. Precambrian Research, 316: 227-243. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.08.008
HIRAYAMA E, TSUNOGAE T, MALAVIARACHCHI S P K, et al., 2020. Prolonged Neoproterozoic high-grade metamorphism of the Wanni Complex, Sri Lanka: New insights from petrology, phase equilibria modelling, and zircon U-Pb geochronology of partially melted cordierite gneiss from Walpita[J]. Geological Journal, 55(9): 6147-6168. doi: 10.1002/gj.3792
KADOWAKI H, TSUNOGAE T, HE X F, et al., 2019. Pressure-temperature-time evolution of ultrahigh-temperature granulites from the Trivandrum Block, southern India: Implications for long-lived high-grade metamorphism[J]. Geological Journal, 54(5): 3041-3059. doi: 10.1002/gj.3422
KILPATRICK J A, ELLIS D J, 1992. C-type magmas: igneous charnockites and their extrusive equivalents[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 83(1-2): 155-164. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007847
KINNY P D, WIJBRANS J R, FROUDE D O, et al., 1990. Age constraints on the geological evolution of the Narryer Gneiss Complex, Western Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 37(1): 51-69. doi: 10.1080/08120099008727905
LI Z X, BOGDANOVA S V, COLLINS A S, et al., 2008. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: a synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 160(1-2): 179-210. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021
LIU Y B, LI Z X, PISAREVSKY S A, et al., 2018. First Precambrian palaeomagnetic data from the Mawson Craton (East Antarctica) and tectonic implications[J]. Scientific Reports, 8: 16403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34748-2
LUDWIG K R. 2001. Squid 1.02: A user's manual[M]. Bakeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: 1-19.
MAAS R, KINNY P D, WILLIAMS I S, et al., 1992. The Earth's oldest known crust: a geochronological and geochemical study of 3900~4200 Ma old detrital zircons from Mt. Narryer and Jack Hills, Western Australia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(3): 1281-1300. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90062-N
MARITATI A, HALPIN J A, WHITTAKER J M, et al., 2019. Fingerprinting Proterozoic Bedrock in Interior Wilkes Land, East Antarctica[J]. Scientific Reports, 9: 10192. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46612-y
MÖLLER A, POST N J, HENSEN B J, 2002. Crustal residence history and garnet Sm-Nd ages of high-grade metamorphic rocks from the Windmill Islands area, East Antarctica[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 91(6): 993-1004. doi: 10.1007/s00531-002-0291-x
MORRISSEY L J, HAND M, KELSEY D E, 2017a. A curious case of agreement between conventional thermobarometry and phase equilibria modelling in granulites: New constraints on P-T estimates in the Antarctica segment of the Musgrave-Albany-Fraser-Wilkes Orogen[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 35(9): 1023-1050. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12266
MORRISSEY L J, PAYNE J L, HAND M, et al., 2017b. Linking the Windmill Islands, east Antarctica and the Albany-Fraser Orogen: insights from U-Pb zircon geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 293: 131-149. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.005
OLIVER R L, COOPER J A, TRUELOVE A J, 1983. Petrology and zircon geochronology of Herring Island and Commonwealth Bay and evidence for Gondwana reconstruction[C]//OLIVER R L, JAMES P R, JAGO J B. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 64-68.
PAUL E, STÜWE K, TEASDALE J, et al., 1995. Structural and metamorphic geology of the Windmill Islands, east Antarctica: field evidence for repeated tectonothermal activity[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 42(5): 453-469. doi: 10.1080/08120099508728216
PAYNE J L, HAND M, BAROVICH K M, et al., 2009. Correlations and reconstruction models for the 2500~1500 Ma evolution of the Mawson Continent[M]//REDDY S M, MAZUMDER R, EVANS D A D, et al., Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 323(1): 319-355.
POST N J, 2000. Unravelling Gondwana fragments: An integrated structural, isotopic and petrographic investigation of the Windmill Islands, East Antarctica[D]. Sydney: University of New South Wales.
POST N J, HENSEN B J, KINNY P D, 1997. Two metamorphic episodes during a 1340~1180 Ma convergent tectonic event in the Windmill Islands, East Antarctica[M]//RICCI C A. The Antarctic Region: Geological Evolution and Processes. Sienna: Terra Antarctica Publication: 157-161.
SONG B, 2015. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age measurement: Sample preparation, measurement, data processing and explanation[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(10): 1777-1788. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201510001.htm
SPAGGIARI C V, KIRKLAND C L, PAWLEY M J, et al., 2011. The geology of the east Albany-Fraser Orogen: a field guide[M]. Perth: Geological Survey of Western Australia.
SPAGGIARI C V, SMITHIES R H, 2015. Eucla basement stratigraphic drilling results release workshop: Extended abstracts[M]. Perth: Geological Survey of Western Australia.
STARK J C, WANG X C, LI Z X, et al., 2018. In situ U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of a 1.13 Ga mafic dyke suite at Bunger Hills, East Antarctica: The end of the Albany-Fraser Orogeny[J]. Precambrian Research, 310: 76-92. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.02.023
TUCKER N M, HAND M, CLARK C, 2020. The Bunger Hills: 60 years of geological and geophysical research[J]. Antarctic Science, 32(2): 85-106. doi: 10.1017/S0954102019000403
TUCKER N M, HAND M, KELSEY D E, et al., 2018. A tripartite approach to unearthing the duration of high temperature conditions versus peak metamorphism: An example from the Bunger Hills, East Antarctica[J]. Precambrian Research, 314: 194-220. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.06.006
TUCKER N M, PAYNE J L, CLARK C, et al., 2017. Proterozoic reworking of Archean (Yilgarn) basement in the Bunger Hills, east Antarctica[J]. Precambrian Research, 298: 16-38. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.05.013
WEBB A W, MCDOUGALL I, COOPER J A, 1963. Potassium-argon dates from the Vincennes Bay region and Oates Land[C]//ADIE R J. Proceedings of the 1st international symposium on Antarctic geology. North Holland, Amsterdam: 597-602.
WILLIAMS I S, COMPSTON W, Collerson K D, et al. 1983. A reassessment of the age of the Windmill metamorphics, Casey area[C]//OLIVER R L. JAMES P R. JAGO J B. eds. Antarctic earth science, Australian Academy of Science, Canberra: 3-76.
WHITNEY D L, EVANS B W, 2010. Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals[J]. American Mineralogist, 95(1): 185-187. doi: 10.2138/am.2010.3371
WILLIAMS I S, 1998. U-Th-Pb geochronology by ion microprobe[M]//MCKIBBEN M A, SHANKS W C III, RIDLEY W I. Applications of microanalytical techniques to understanding mineralizing processes. Reviews in Economic Geology, 7: 1-35.
WILLIAMS I S, 2001. Response of detrital zircon and monazite, and their U-Pb isotopic systems, to regional metamorphism and host-rock partial melting, Cooma Complex, southeastern Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 48(4): 557-580. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00883.x
WILLIAMS I S, BUICK I S, CARTWRIGHT I, 1996. An extended episode of early Mesoproterozoic metamorphic fluid flow in the Reynolds Range, central Australia[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 14(1): 29-47. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034680705310_e156.html
WILLIAMS I S, CLAESSON S, 1987. Isotopic evidence for the Precambrian provenance and Caledonian metamorphism of high grade paragneisses from the Seve Nappes, Scandinavian Caledonides: II. Ion microprobe zircon U-Th-Pb[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 97(2): 205-217. doi: 10.1007/BF00371240
XU Q Q, ZHAO L, NIU B G, 2015. Determination of the early Paleozoic granite in Zhifang area, East Junggar, Xinjiang and its geological implications[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 21(4): 502-516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAI M G, 2019. Tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 722-745. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201905008.htm
ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, LIU X C, et al., 2012. U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the bedrocks and moraine sediments from the Windmill Islands: implications for Proterozoic evolution of East Antarctica[J]. Precambrian Research, 206-207: 52-71. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.02.019
宋彪, 2015. 用SHRIMP测定锆石U-Pb年龄的工作方法[J]. 地质通报, 34(10): 1777-1788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.002
徐芹芹, 赵磊, 牛宝贵, 2015. 新疆东准噶尔纸房地区早古生代花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 21(4): 502-516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2015.04.006 https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20150406&journal_id=dzlxxb
翟明国, 2019. 华北克拉通构造演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 722-745. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190507&journal_id=dzlxxb
-



 下载:
下载: