Petrogenesis of the Hughes Bluff granitic pluton in the Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica
-
摘要:
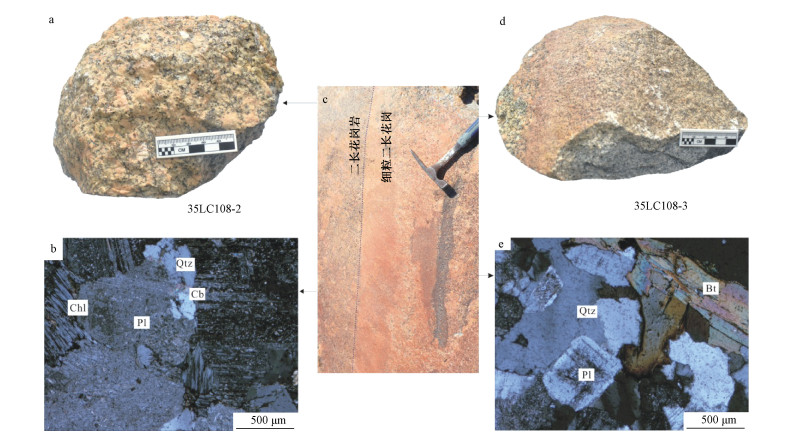
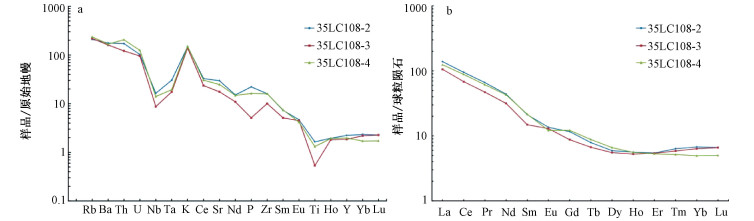
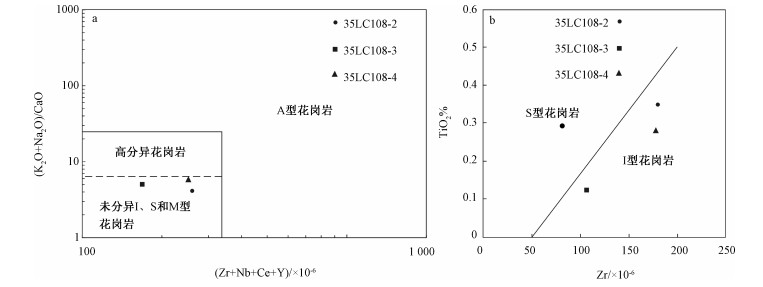
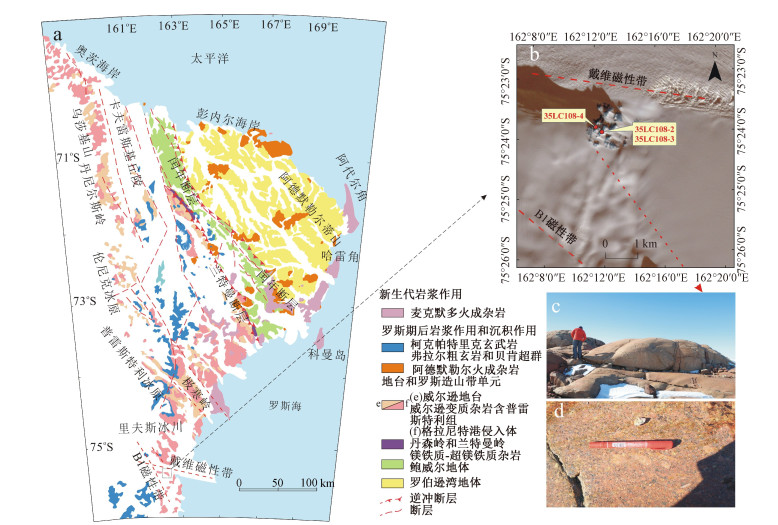
为了探讨横贯南极山脉休斯陡崖花岗质岩体的岩石成因,对其开展了岩相学和岩石化学分析。结果表明,休斯陡崖岩体主体岩石为二长花岗岩,后期被细粒二长花岗岩岩脉侵入。二者都具有高硅、富碱和高钾特征,里特曼指数小于3,岩石铝饱和指数(A/CNK)值小于1;微量元素原始地幔标准化分布型式具有Rb、Th、U和K元素富集,Nb、Ta、Nd和Ti等元素亏损特征;稀土元素总量偏低,轻稀土富集。主期二长花岗岩的稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布型式具有轻微的负Eu异常,而岩脉具有正的Eu异常。休斯陡崖岩体的岩石类型为钙碱性准铝质I型花岗岩,源区为下陆壳,并伴有幔源物质的混入。在源区,岩浆发生了不同程度的斜长石、钛铁矿、金红石和磷灰石的分离结晶作用,其形成的构造环境为与俯冲作用有关的火山岛弧环境。
Abstract:In order to elucidate the petrogenesis of the Hughes Bluff granitic pluton, the petrological and geochemical studies were conducted, and the results show that the Hughes Bluff granitic pluton is composed of monzogranite, intruded by fine-grained monzogranite dikes in the later period. They both are characterized by high abundance of silicon, alkali and potassium, enriched in Rb, Th, U and K and depleted in Nb, Ta, Nd and Ti relative to those of the primitive mantle, with the Rittmann Indexes less than 3 and the A/CNK values less than 1. They both also have a low total amount of rare earth elements and an abundance of light rare earth, showing weakly negative Eu anomaly and slightly positive Eu anomaly in the chondrite-normalized REE pattern for the monzogranite and granitic monzogranite dike respectively. All the data show that the rocks from the Hughes Bluff granitic pluton belong to the I-type granites, and the source region is probably the lower continental crust, but the contribution of mantle material cannot be ruled out. The magma in the source region underwent varying degrees of fractional crystallization of plagioclase, ilmenite, rutile and apatite, and was derived from a volcanic island arc environment related to subduction.
-
Key words:
- the Transantarctic Mountains /
- Petrogenesis /
- Pluton /
- I-type granite
-

-
图 3 休斯陡崖岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图与微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(球粒陨石和原始地幔数据据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 3.
表 1 休斯陡崖岩体主量元素分析结果
Table 1. Major element results of the Hughes Bluff pluton
主量元素含量/% SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 LOI 总和 Mg# 石英 斜长石 正长石 刚玉 透辉石 紫苏辉石 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 磷灰石 35LC108-2 70.5 0.35 14.00 2.43 0.04 0.87 2.01 3.86 4.42 0.48 0.84 99.8 41.55 25.55 40.22 26.71 0.64 0.00 3.95 0.53 0.29 0.83 35LC108-3 74.47 0.12 13.36 1.53 0.02 0.22 1.63 4.06 4.17 0.11 0.64 100.33 22.28 30.92 40.45 24.76 0.00 1.28 1.88 0.23 0.22 0.25 35LC108-4 71.20 0.28 14.00 1.94 0.04 0.62 1.49 4.07 4.44 0.35 0.61 99.04 38.92 25.87 40.00 26.48 0.36 0.00 5.14 0.66 0.36 1.14 注:矿物含量来自于CIPW标准矿物的计算结果;Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+) 表 2 休斯陡崖岩体微量元素分析结果
Table 2. Trace element results of the Hughes Bluff pluton
微量元素含量/×10-6 Ba Sr Zn Zr Li Be Sc V Cr Co Ni Cu Ga Ge Rb Y Nb Mo Cd Cs Hf Ta W Tl Pb Bi Th U 35LC108-2 1231.89 625.32 48.06 179.72 36.12 2.91 2.48 9.45 1.06 2.54 0.8 4.19 19.17 0.84 133.03 10.14 11.64 0.78 - 2.07 4.76 1.24 0.27 0.84 23.67 0.03 14.55 2.14 35LC108-3 1124.32 369.72 28.62 112.33 26.15 2.15 1.21 2.17 0.44 0.96 0.27 0.65 13.29 0.92 138.87 8.42 6.19 4.60 0.02 1.85 3.16 0.71 0.33 0.71 37.77 0.03 10.32 2.00 35LC108-4 1172.63 521.56 52.35 178.86 27.12 2.52 1.59 8.29 1.36 2.37 0.55 0.41 17.16 0.99 149.48 8.98 9.99 0.11 0.02 4.20 4.90 0.79 0.28 0.69 30.40 0.03 17.46 2.61 注:-低于检测限 表 3 休斯陡崖岩体稀土元素分析结果
Table 3. Rare earth element results of the Hughes Bluff pluton
稀土元素含量/×10-6 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ΣREE LaN/YbN EuN 35LC108-2 32.89 58.20 6.27 20.49 3.24 0.79 2.39 0.30 1.51 0.32 0.90 0.16 1.15 0.17 128.76 19.36 0.83 35LC108-3 25.04 41.73 4.47 14.76 2.27 0.75 1.80 0.25 1.41 0.30 0.89 0.15 1.08 0.17 95.05 15.71 1.10 35LC108-4 29.47 54.01 5.81 19.97 3.30 0.70 2.50 0.33 1.68 0.32 0.88 0.13 0.84 0.13 120.06 23.70 0.72 -
ALLIBONE A H, COX S C, GRAHAM I J, et al., 1993. Granitoids of the Dry Valleys area, southern Victoria Land, Antarctica: plutons, field relationships, and isotopic dating[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 36(3): 281-297. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1993.9514576
ANTONINI P, PICCIRILLO E M, PETRINI R, et al., 1999. Enriched mantle-dupal signature in the genesis of the Jurassic Ferrar tholeiites from Prince Albert Mountains (Victoria Land, Antarctica)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 136(1-2): 1-19. doi: 10.1007/s004100050520
ARMIENTI P, GHEZZO C, INNOCENTI F, et al., 1990. Isotope geochemistry and petrology of granitoid suites from Granite Harbour Intrusives of the Wilson Terrane, North Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2(1): 103-124. doi: 10.1127/ejm/2/1/0103
BARRETT P J, 1981. History of the Ross Sea region during the deposition of the Beacon Supergroup 400~180 million years ago[J]. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 11(4): 447-458. doi: 10.1080/03036758.1981.10423334
BORG S G, STUMP E, CHAPPELL B W, et al., 1987. Granitoids of northern Victoria Land, Antarctica; Implications of chemical and isotopic variations to regional crustal structure and tectonics[J]. American Journal of Science, 287(2): 127-169. doi: 10.2475/ajs.287.2.127
CAPPONI G, CRISPINI L, MECCHERI M, 1999. Structural history and tectonic evolution of the boundary between the Wilson and Bowers terranes, Lanterman Range, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Tectonophysics, 312(2-4): 249-266. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00174-2
CAPPONI G, MONTOMOLI C, CASALE S, et al., 2020. Geology of the northern Convoy Range, Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Maps, 16(2): 702-709. doi: 10.1080/17445647.2020.1822218
CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R, 2001. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 48(4): 489-499. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00882.x
COOPER A K, RAYMOND C, DIGGLES M, et al., 2007. Guidelines for extended abstracts in the 10th ISAES X online proceedings[C]//COOPER A K, RAYMOND C R. Antarctica: a keystone in a changing world-online proceedings of the 10th ISAES X. USGS Open-File Report 2007-1047.
COTTLE J M, COOPER A F, 2006. Geology, geochemistry, and geochronology of an A-type granite in the Mulock Glacier area, southern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 49(2): 191-202. doi: 10.1080/00288306.2006.9515159
DALLAI L, GHEZZO C, TURI B, et al., 2002. Oxygen isotope geochemistry of the Granite Harbour Intrusives, Wilson Terrane, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 75(3-4): 223-241. doi: 10.1007/s007100200025
DALLAI L, GHEZZO C, SHARP Z D, 2003. Oxygen isotope evidence for crustal assimilation and magma mixing in the Granite Harbour Intrusives, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Lithos, 67(1-2): 135-151. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00267-0
DI VINCENZO G, PALMERI R, TALARICO F, et al., 1997. Petrology and geochronology of eclogites from the Lanterman Range, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Petrology, 38(10): 1391-1417. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.10.1391
DI VINCENZO G, ROCCHI S, ROSSETTI F, et al., 2004. 40Ar-39Ar dating of pseudotachylytes: the effect of clast-hosted extraneous argon in Cenozoic fault-generated friction melts from the West Antarctic Rift system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 223(3-4): 349-364. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.04.042
ENCARNACIÓN J, GRUNOW A, 1996. Changing magmatic and tectonic styles along the paleo-Pacific margin of Gondwana and the onset of early Paleozoic magmatism in Antarctica[J]. Tectonics, 15(6): 1325-1341. doi: 10.1029/96TC01484
ENCARNACIÓN J, ROWELL A J, GRUNOW A M, 1999. A U-Pb age for the Cambrian Taylor Formation, Antarctica: Implications for the Cambrian time scale[J]. The Journal of Geology 107(4): 497-504. doi: 10.1086/314361
ESTRADA S, LÄUFER A, ECKELMANN K, et al., 2016. Continuous Neoproterozoic to Ordovician sedimentation at the East Gondwana margin-implications from detrital zircons of the Ross Orogen in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Gondwana Research, 37: 426-448. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.006
FAURE G, MENSING T M, 2011. The transantarctic mountains: rocks, ice, meteorites and water[M]. Dordrecht: Springer: 1-804.
FEDERICO L, CRISPINI L, CAPPONI G, 2010. Fault-slip analysis and transpressional tectonics: a study of Paleozoic structures in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 32(5): 667-684. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2010.04.001
FERRACCIOLI F, BOZZO E, 1999. Inherited crustal features and tectonic blocks of the Transantarctic Mountains: an aeromagnetic perspective (Victoria Land, Antarctica)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B11): 25297-25319. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900041
FERRACCIOLI F, BOZZO E, 2003. Cenozoic strike-slip faulting from the eastern margin of the Wilkes Subglacial Basin to the western margin of the Ross Sea Rift: an aeromagnetic connection[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 210(1): 109-133. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.210.01.07
FERRACCIOLI F, ARMADILLO E, ZUNINO A, et al., 2009. Magmatic and tectonic patterns over the Northern Victoria Land sector of the Transantarctic Mountains from new aeromagnetic imaging[J]. Tectonophysics, 478(1-2): 43-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.11.028
GOODGE J W, WALKER N W, HANSEN V L, 1993. Neoproterozoic-Cambrian basement-involved orogenesis within the Antarctic margin of Gondwana[J]. Geology, 21(1): 37-40. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0037:NCBIOW>2.3.CO;2
GOODGE J W, 2007. Metamorphism in the Ross Orogen and its bearing on Gondwana margin tectonics[M]//CLOOS M, CARLSON W D, GILBERT M C, et al. Convergent Margin Terranes and Associated Regions: A Tribute to W.G. Ernst. Boulder, CO, USA: Geological Society of America: 185-203.
GOODGE J W, FANNING C M, NORMAN M D, et al., 2012. Temporal, Isotopic and Spatial Relations of Early Paleozoic Gondwana-Margin Arc Magmatism, Central Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Petrology, 53(10): 2027-2065. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egs043
GOODGE J W, FANNING C M, 2016. Mesoarchean and Paleoproterozoic history of the nimrod complex, central Transantarctic mountains, Antarctica: Stratigraphic revisions and relation to the Mawson Continent in East Gondwana[J]. Precambrian Research, 285: 242-271. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.09.001
GOODGE J W, 2020. Geological and tectonic evolution of the Transantarctic Mountains, from ancient craton to recent enigma[J]. Gondwana Research, 80: 50-122. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.11.001
GREEN T H, 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 347-359. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-X
GUNN B M, WARREN G, 1962. Geology of Victoria Land between Mawson and Mullock Glaciers, Antarctica[J]. New Zealand Geological Survey Bulletin, 71: 1-157. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313662583_Geology_of_the_basement_rocks_between_the_Mawson_and_Mullock_glaciers_south_Victoria_Land_Antarctica
GUO X Z, JIA Q Z, LI J C, et al., 2019. The forming age and geochemistry characteristics of the granodiorites in Harizha, East Kunlun and its tectonic significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2): 286-300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE P, LU X Z, YANG R N, et al., 2020. Petrogeochemistry, zircon U-Pb chronology of I type granite from Yaolesayi estuary, Northern Altun[J]. Mineral Exploration, 11(9): 1822-1830. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HOFMANN A W, 1988. Chemical differentiation of the earth: The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90(3): 297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X
ISBELL J L, 1999. The Kukri Erosion Surface; a reassessment of its relationship to rocks of the Beacon Supergroup in the central Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica[J]. Antarctic Science, 11(2): 228-238. doi: 10.1017/S0954102099000292
LÄUFER A L, KLEINSCHMIDT G, HENJES-KUNST F, et al., 2005. Geological map of the cape Adare Quadrangle Victoria Land, Antarctica, 1: 250000[R]. PERTUSATI P C, ROLAND N W. German-Italian Geological Antarctic Map Programme (GIGAMAP), Hannover: BGR.
LI J Y, Gao L M, SUN G H, et al., 2007. Shuangjingzi midge Triassic syn-collisional crust derived granite in the east Inner Mongolia and its constraint on the timing of collision between Siberian and Sino-Korean paleo-plates[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3): 565-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279908280_Shuangjingzi_middle_Triassic_syn-collisional_crust-derived_granite_in_the_east_Inner_Mongolia_and_its_constraint_on_the_timing_of_collision_between_Siberian_and_Sino-Korean_paleo-plates?ev=auth_pub
LIU H, ZHANG H, LI G M, et al., 2016. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Qingcaoshan strongly peraluminous S-type granitic pluton, Southern Qiangtang, Northern Tibet: Constraints from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 52(5): 848-860. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-BJDZ201605010.htm
MA C Q, LI Z C, EHLERS C, et al., 1998. A post-collisional magmatic plumbing system: Mesozoic granitoid plutons from the Dabieshan high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone, east-central China[J]. Lithos, 45(1-4): 431-456. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00043-7
MENG Y K, XU Z Q, GAO C S, et al., 2018. The identification of the Eocene magmatism and tectonic significance in the middle Gangdese magmatic belt, southern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(3): 513-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201803001.htm
PEARCE J, 1996. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 19(4): 120-125. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G, 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
RAPP R P, WATSON E B, 1995. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
READ S E, COOPER A F, WALKER N W, 2002. Geochemistry and U-Pb geochronology of the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian Koettlitz Glacier Alkaline province, Royal Society range, Transantarctic mountains, Antarctica[J]. Royal Society of New Zealand Bulletin, 35: 143-151. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/312974347_Geochemistry_and_U-Pb_Geochronology_of_the_Neoproterozoic-Cambrian_Koettlitz_Glacier_Alkaline_Province_Royal_Society_Range_Transantarctic_Mountains_Antarctica
ROCCHI S, DI VINCENZO G, GHEZZO C, et al., 2009. Granite-lamprophyre connection in the latest stages of the Early Paleozoic Ross Orogeny (Victoria Land, Antarctica)[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121(5-6): 801-819. doi: 10.1130/B26342.1
ROCCHI S, BRACCIALI L, DI VINCENZO G, et al., 2011. Arc accretion to the early Paleozoic Antarctic margin of Gondwana in Victoria Land[J]. Gondwana Research, 19(3): 594-607. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.08.001
ROSSETTI F, STORTI F, SALVINI F, 2000. Cenozoic noncoaxial transtension along the western shoulder of the Ross Sea, Antarctica, and the emplacement of McMurdo dyke arrays[J]. Terra Nova, 12(2): 60-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2000.00270.x
SALVINI F, BRANCOLINI G, BUSETTI M, et al., 1997. Cenozoic geodynamics of the Ross Sea region, Antarctica: crustal extension, intraplate strike-slip faulting, and tectonic inheritance[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B11): 24669-24696. doi: 10.1029/97JB01643
STUMP E, 1995. The ross orogen of the transantarctic mountains[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press: 1-284.
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F, 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[M]//SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345.
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M, 1985. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. Palo Alto, California: Blackwell Scientific: 1-312.
VETTER U, TESSENSOHN F, 1987. S-and I-type granitoids of North Victoria Land, Antarctica, and their inferred geotectonic setting[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 76(1): 233-243. doi: 10.1007/BF01820585
WANG J F, LI Y J, LI H Y, et al., 2018. Zircon U-Pb dating of the Shijiangshan Late Jurassic-early cretaceous a-type granite in Xi Ujimqin Banner of Inner Mongolia and its tectonic setting[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(2-3): 382-396. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/325904120_Zircon_U-Pb_dating_of_the_Shijiangshan_Late_Jurassic-Early_Cretaceous_A-type_granite_in_Xi_Ujimqin_Banner_of_Inner_Mongolia_and_its_tectonic_setting
WAREHAM C D, STUMP E, STOREY B C, et al., 2001. Petrogenesis of the Cambrian Liv Group, a bimodal volcanic rock suite from the Ross orogen, Transantarctic Mountains[J]. GSA Bulletin, 113(3): 360-372. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<0360:POTCLG>2.0.CO;2
WEAVER S D, BRADSHAW J D, LAIRD M G, 1984. Geochemistry of Cambrian volcanics of the Bowers Supergroup and implications for the early Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of northern Victoria Land, Antarctica[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 68(1): 128-140. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90145-6
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. 1987. A-Type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
WU F Y, LI X H, YANG J H, et al., 2007. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1217-1238. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/1492686
WU F Y, LIU X C, JI W Q, et al., 2017. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(7): 1201-1219. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5139-1
ZHANG Y F, LIN X W, GUO Q M, et al., 2015. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating and Geochemistry of Aral Granitic Plutons in Koktokay Area in the Southern Altay Margin and Their Source Significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2): 339-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502010.htm
国显正, 贾群子, 李金超, 等, 2019. 东昆仑哈日扎花岗闪长岩形成时代、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(2): 286-300. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190214&journal_id=dzlxxb
何鹏, 芦西战, 杨睿娜, 等, 2020. 阿尔金北缘尧勒萨依河口I型花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 11(9): 1822-1830. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2020.09.003
李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 等, 2007. 内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 23(3): 565-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703006.htm
刘洪, 张晖, 李光明, 等, 2016. 藏北羌塘南缘早白垩世青草山强过铝质S型花岗岩的成因: 来自地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学的约束[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 52(5): 848-860. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201605010.htm
孟元库, 许志琴, 高存山, 等, 2018. 藏南冈底斯带中段始新世岩浆作用的厘定及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报. 34(3): 513-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201803001.htm
王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等, 2018. 内蒙古西乌旗石匠山晚侏罗世-早白垩世A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 37(2-3): 382-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2018Z1018.htm
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等, 2007. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001
吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等, 2017. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 47(7): 745-765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201707001.htm
张亚峰, 蔺新望, 郭岐明, 等, 2015. 阿尔泰南缘可可托海地区阿拉尔花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学特征及其源区意义[J]. 地质学报, 89(2): 339-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502010.htm
-



 下载:
下载: