Identification and risk assessment of coal mining-induced landslides in Guizhou Province by InSAR and optical remote sensing
-
摘要:
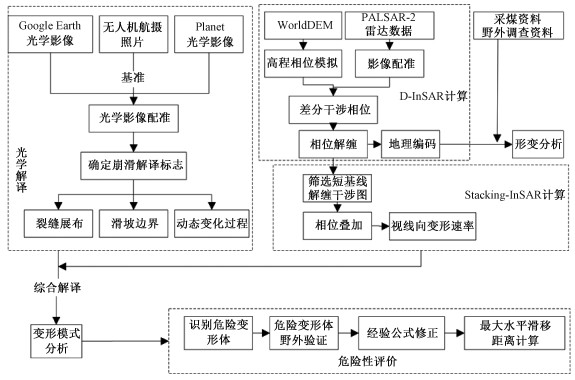
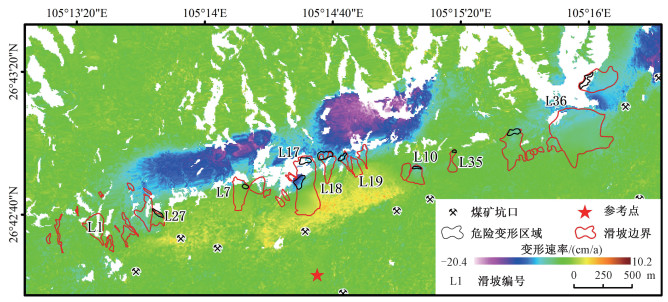
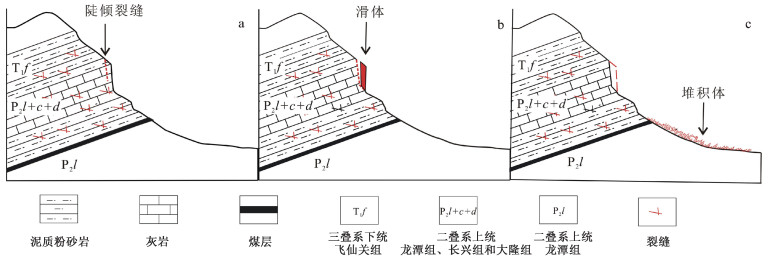
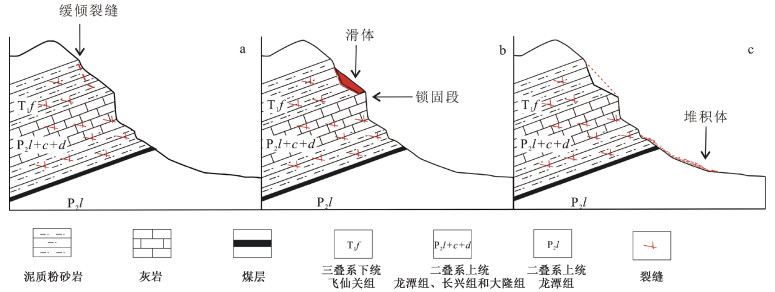
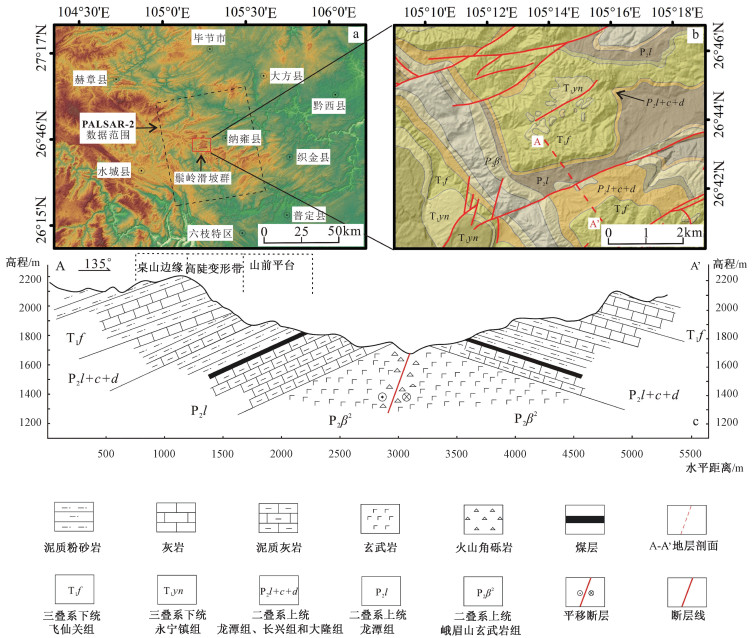
贵州鬃岭滑坡群具有孕灾规律性强、发育集中密集、威胁严重等特点。文章利用InSAR和光学遥感进行精细识别,获取了区域滑坡灾害信息,总结了鬃岭区域滑坡变形破坏模式,基于此建立了该地区的滑坡风险评价的体积-距离统计公式,并对典型灾害体进行了计算,获得了一些重要认识。地下采煤活动是引起鬃岭桌山边缘山体变形的主要原因;InSAR观测结果显示鬃岭地区变形具有明显的带状特征,年平均变形速度为-20.4~10.2 cm/a,与下部采空区具有较好的对应关系,大位移区域集中在采煤沉降和斜坡重力叠加的桌山边缘地带;鬃岭地区现存变形现象64处,其中滑坡37处,裂缝27条,危险变形体2处;滑坡主要发生在飞仙关组深灰色灰岩岩层和暗紫红色泥质粉砂岩岩层中,根据滑源岩性及变形特征将滑坡划分为拉裂-倾倒和拉裂-剪断两种类型,其中拉裂-倾倒型滑坡堆积体粒径大,运动距离远,威胁较大;文中建立的岩质滑坡碎屑流滑移距离计算公式,对鬃岭地区上硬下软地层中发育的采煤滑坡滑移距离具有良好的适用性,验证误差在5%以内,利用该公式对鬃岭滑坡群左家营和箐脚危险变形体进行计算,预测危险避让距离在220~386 m。文章提出的基于差分干涉测量技术和光学影像的采煤滑坡危险性评价方法对黔西、滇东地区的采矿滑坡防治工作具有重要的示范意义。
Abstract:The Zongling landslide group in Guizhou Province is characterized by strong regularity of disaster formation, concentrated development and severe threat. It is represented in the coal mining-induced geological hazards in western Guizhou and eastern Yunnan. In this paper, InSAR and optical remote sensing were used for nuanced identification to obtain the regional landslide information, and the landslide deformation-failure mode in the Zongling region was summarized. Based on this, the volume-distance statistical formula suitable for landslide risk assessment in this region was established, and the typical disaster bodies ware calculated. Some important insights are gained: Underground coal mining is the major contributor to the deformation of the edge of Table Mountain in Zongling. InSAR observation results show that the deformation in the Zongling area has prominent zonal characteristics, and the annual average deformation velocity is between -20.4~10.2 cm/a, which corresponds well with the lower goaf. The areas with great displacement are concentrated in the edge zone of cuesta, with coal mining subsidence and slope gravity superimposed; There are 64 deformations in the Zongling area, including 37 landslides, 27 cracks, and 2 dangerous deformed bodies. Landslides mainly occur in the dark grey limestone strata and dark purplish-red argillaceous siltstone strata of the Feixianguan Formation. According to the lithology and deformation characteristics of the slip source, the landslides can be classified into two types: pull-toppling and pull-clipping, and the former is distinguished by large particle size, long movement distance, and severe threat. The formula for calculating the slip distance of rock landslide debris flow has good applicability to the slip distance of coal mining-induced landslide developed in the "upper hard and lower soft" strata in the Zongling area, and the verification error is less than 5%. The formula is used to calculate the dangerous deformed bodies of Zuojiaying and Jingjiao in the study area, and the danger avoidance distance is predicted to be 220~386 m. The proposed method of coal mining-induced landslide risk assessment based on differential interferometry and optical image play an exemplary role for the prevention and control of coal mining-induced landslides in western Guizhou and eastern Yunnan.
-
Key words:
- Zongling landslide group /
- optical remote sensing /
- InSAR /
- landslide slip distance /
- risk assessment
-

-
表 1 研究采用的光学和雷达数据表
Table 1. Optical and radar data sets used in the study
数据 数量 分辨率/m 采集时间 用途 PALSAR-2 8 1.43×2.21(Az×Rg) 2017-05至2018-08 InSAR数据处理 Planet光学影像 8 3 2016-10至2019-11 动态解译 Google Earth光学影像 3 0.61 2017-05至2018-04 动态解译 无人机航摄照片 1 0.1 2019-11-01 精细化解译 航摄数字地表模型 1 0.1 2019-11-01 精细化解译 WorldDEM 1 12 2011 InSAR数据处理 表 2 模型修正采用的滑坡参数
Table 2. Landslide parameters used to modify the calculation model
滑坡 l1实际值/m d/m B/m α/m V/m3 H/m 修正前l1值/m 修正后l1值/m 修正前误差 修正后误差 贵州鬃岭左家营滑坡 614 12 170 27 507700 301 960.13 603.87 56.4% -1.7% 贵州鬃岭中岭滑坡 522 11 334 26 1142100 213 820.24 520.92 57.1% -0.2% 贵州鬃岭中岭2号滑坡 333 10 152 33 38307 216 531.81 337.74 59.7% 1.4% 贵州尖山营1号滑坡 242 4 110 27 78500 129 393.72 250.04 62.7% 3.3% 贵州尖山营2号滑坡 244 2.5 100 28 103500 133 387.75 246.25 58.9% 0.9% 重庆甑子岩滑坡 683 8 210 39 500000 315 1079.00 685.24 58.0% 0.3% 湖北宜昌盐池河滑坡 604 5 150 33 1000000 246 998.32 634.01 65.3% 5.0% 贵州纳雍张家湾滑坡 718 14 200 32 493000 264 1053.15 668.83 46.7% -6.8% 贵州纳雍煤冲滑坡 280 8 124 32 30348 176 461.76 293.25 64.9% 4.7% 贵州都匀马达岭滑坡 580 5 120 25 1900000 150 893.28 567.30 54.0% -2.2% 表 3 改进后计算模型验证表
Table 3. Verification table of the improved calculation model
滑坡(编号) l1实际值/m d/m B/m α/m V/m3 H/m l1计算值/m 误差 代家屋脊滑坡(L10) 160 7 110 31 5269 120 166.86 4.29% 箐脚2#滑坡(L19) 267 7 82 36 8429 228 274.60 2.85% 大土寨滑坡(L7) 260 8 105 35 9857 205 261.62 0.62% 张家麻窝滑坡(L35) 200 3 21 31 2984 160 201.65 0.83% 半边街滑坡(L1) 270 7 130 41 7800 230 262.20 -2.89% -
CHENG Y, ZHANG J, CHEN J, 2019. Analysis on stability and hazard zone of dangerous rock mass in Zongling Town, Nayong of Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 30(4): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DONG J, ZHANG L, LI M H, et al., 2018. Measuring precursory movements of the recent Xinmo landslide in Mao County, China with sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets[J]. Landslides, 15(1): 135-144. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0914-8
FAN J H, GUO H D, GUO X F, et al., 2008. Monitoring subsidence in tianjin area using interferogram stacking based on coherent targets[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 12(1): 111-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAN X M, XU Q, SCARINGI G, et al., 2019. The "long" runout rock avalanche in Pusa, China, on August 28, 2017: a preliminary report[J]. Landslides, 16(1): 139-154. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1084-z
FAN X Y, HU X B, ZHANG R X, et al., 2018. Study on the open topography influence on the moving distances of landslides[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 27(5): 188-196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GAO Y, HE K, LI Z, et al., 2020. An analysis of disaster types and dynamics of landslides in the southwest karst mountain areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(4): 14-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HAN D J, YANG C S, DONG J H, 2020. InSAR monitoring and analysis of landslide deformation after the earthquake in the Zhangmu port, Xizang[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 565-574. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG R Q, 2007. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 26(3): 433-454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI L J, YAO X, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2014. SBAS-InSAR technology based identification of slow deformation of geologic mass along section of China-Pakistan highway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(5): 921-927. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI W L, XU Q, LU H Y, et al., 2019. Tracking the deformation history of large-scale rocky landslides and its enlightenment[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 1043-1053. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Z H, SONG C, YU C, et al., 2019. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring: challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 967-979. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU G W, WANG C J, LI G H, et al., 2019. Application research on the remote sensing technology in geological disaster prevention and control of existing railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 36(6): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU X H, YAO X, ZHOU Z K, et al., 2018. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2): 229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LU H Y, LI W L, XU Q, et al., 2019. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the baige landslide, the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(9): 1342-1354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
STROZZI T, WEGMULLER U, WERNER C, et al., 2000. Measurement of slow uniform surface displacement with mm/year accuracy[C]//IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. Taking the pulse of the planet: the role of remote sensing in managing the environment. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37120). Honolulu: IEEE: 2239-2241.
TANG R, XU Q, WU B, et al., 2018. Method of sliding distance calculation for translational landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 39(3): 1009-1019, 1070. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG J, WANG C, XIE C, et al., 2020. Monitoring of large-scale landslides in Zongling, Guizhou, China, with improved distributed scatterer interferometric SAR time series methods[J]. Landslides, 17(8): 1777-1795. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01407-5
XU C, XU X W, SHEN L L, et al., 2016. Optimized volume models of earthquake-triggered landslides[J]. Scientific Reports, 6: 29797. doi: 10.1038/srep29797
YANG X Z, XUE L G, 1994. Natural resources for Tourism in Maoshi, Northen Suburb of Zunyi city and their classification[J]. Guizhou Geology, 11(2): 161-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Z P, JIANG Y W, LI B, et al., 2020. Study on the mechanism of deep and large fracture propagation and transfixion in karst slope under the action of mining[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 459-470. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAN W W, HUANG R Q, PEI X J, et al., 2017. Empirical prediction model for movement distance of gully-type rock avalanches[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 25(1): 154-163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG M, WU L Z, ZANG J C, et al., 2019. The 2009 Jiweishan rock avalanche, Wulong, China: deposit characteristics and implications for its fragmentation[J]. Landslides, 16(5): 893-906. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01142-6
ZHANG Y, WANG Y J, YAN S Y, 2016. Ground subsidence detection of peibei mining area based on stacking InSAR technology[J]. Coal Technology, 35(7): 102-105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO J J, MA Y T, LIN B, et al., 2016. Geomechanical mode of Mining landslides with gently counter-inclined bedding: a case study of madaling landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 35(11): 2217-2224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHENG D, FROST J D, HUANG R Q, et al., 2015. Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: a case study of kaiyang phosphorite mine rockfalls[J]. Engineering Geology, 197: 145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
ZHENG G, XU Q, PENG S Q, 2019. Calculation model of the long-runout distance of rock avalanche[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(12): 4897-4906. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU J J, LI Z W, HU J, 2017. Research progress and methods of InSAR for deformation monitoring[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 46(10): 1717-1733. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHUO B X, 2011. Remote sensing interpretation & application of geology engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Railway Press. (in Chinese)
程宇, 张健, 陈进, 等, 2019. 贵州纳雍骔岭镇危岩带稳定性及危害范围分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 30(4): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201904003.htm
范景辉, 郭华东, 郭小方, 等, 2008. 基于相干目标的干涉图叠加方法监测天津地区地面沉降[J]. 遥感学报, 12(1): 111-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB200801015.htm
樊晓一, 胡晓波, 张睿骁, 等, 2018. 开阔型地形条件对滑坡运动距离的影响研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 27(5): 188-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201805021.htm
高杨, 贺凯, 李壮, 等, 2020. 西南岩溶山区特大滑坡成灾类型及动力学分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 47(4): 14-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202004003.htm
韩冬建, 杨成生, 董继红, 2020. 西藏樟木口岸震后滑坡灾害变形InSAR监测分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 565-574. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.049
黄润秋, 2007. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 26(3): 433-454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
李凌婧, 姚鑫, 张永双, 等, 2014. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的中巴公路(公格尔-墓士塔格段)地质体缓慢变形识别研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(5): 921-927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201405023.htm
李为乐, 许强, 陆会燕, 等, 2019. 大型岩质滑坡形变历史回溯及其启示[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 44(7): 1043-1053. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907010.htm
李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等, 2019. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 44(7): 967-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907003.htm
刘桂卫, 王长进, 李国和, 等, 2019. 遥感技术在既有铁路地灾防治中应用方法研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 36(6): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.06.006
刘星洪, 姚鑫, 周振凯, 等, 2018. 滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(2): 229-237. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.02.024
陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等, 2019. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 44(9): 1342-1354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201909011.htm
唐然, 许强, 吴斌, 等, 2018. 平推式滑坡运动距离计算模型[J]. 岩土力学, 39(3): 1009-1019, 1070. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201803030.htm
杨秀忠, 薛立根, 1994. 遵义毛石旅游自然资源特征及景点类型划分[J]. 贵州地质, 11(2): 161-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ402.008.htm
杨忠平, 蒋源文, 李滨, 等, 2020. 采动作用下岩溶山体深大裂隙扩展贯通机理研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 459-470. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.039
詹威威, 黄润秋, 裴向军, 等, 2017. 沟道型滑坡-碎屑流运动距离经验预测模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 25(1): 154-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201701021.htm
张洋, 汪云甲, 闫世勇, 2016. 基于Stacking InSAR技术的沛北矿区沉降监测[J]. 煤炭技术, 35(7): 102-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS201607042.htm
赵建军, 马运韬, 蔺冰, 等, 2016. 平缓反倾采动滑坡形成的地质力学模式研究: 以贵州省马达岭滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 35(11): 2217-2224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201611006.htm
郑光, 许强, 彭双麒, 2019. 岩质滑坡-碎屑流的运动距离计算公式研究[J]. 岩土力学, 40(12): 4897-4906. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201912040.htm
朱建军, 李志伟, 胡俊, 2017. InSAR变形监测方法与研究进展[J]. 测绘学报, 46(10): 1717-1733. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170350
卓宝熙, 2011. 工程地质遥感判释与应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国铁道出版社.
-



 下载:
下载: