Petrogenesis and geological significance of migmatitic gneiss in Mulantou area, Hainan Island
-
摘要:
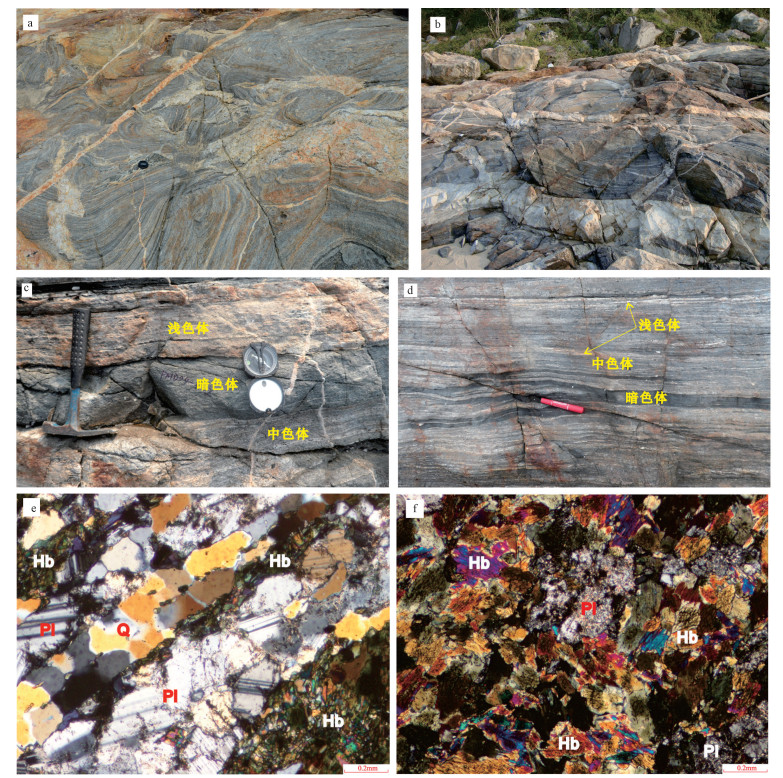
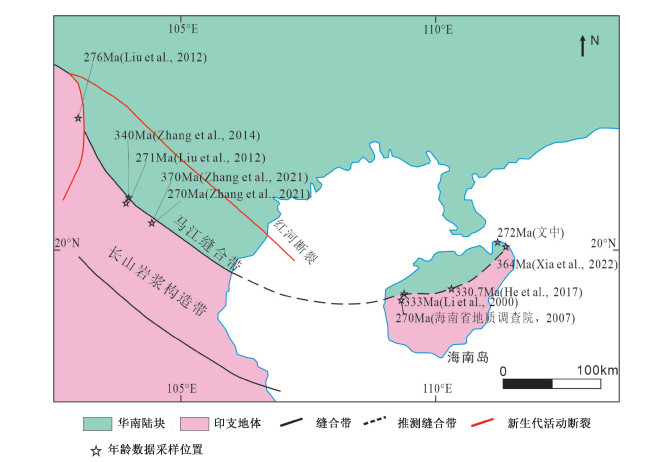
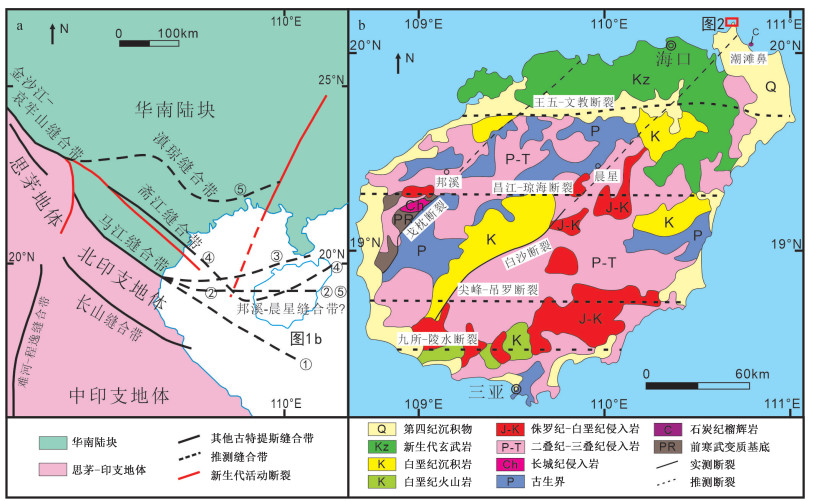
海南岛铺前-木兰头一带海边发现一套中深变质岩(木兰头杂岩), 由混合岩、大理岩、片岩和透辉石岩组成, 以混合岩为主。研究选取其中较为发育和典型的混合片麻岩为研究对象, 对其开展了锆石U-Pb同位素测年、岩石学和岩石地球化学等系统研究。结果表明, 木兰头混合片麻岩原岩为中基性火山岩, 形成时代为276 Ma, 具有活动大陆边缘的岛弧钙碱性玄武岩地球化学特征, 指示古特提斯洋俯冲的构造环境; 早期发生深熔变质作用时间为261 Ma, 指示华南和印支地块碰撞的构造环境; 后期变质作用时间为248 Ma, 指示华南和印支地块碰撞后伸展的构造环境。因此, 木兰头混合片麻岩完整记录了海南岛早二叠世—早三叠世的构造演化信息, 是古特提斯洋俯冲至关闭、华南和印支地块碰撞等地质事件的产物, 其发现为马江缝合带向东延伸的方向提供了新的思路。
Abstract:In the coastal area of Pujian to Mulantou on Hainan Island, a set of medium to deep metamorphic rocks (Mulantou complex) has been discovered, composed of migmatite, dolomite, shale, and amphibolite, with migmatite being the predominant lithology. This study selected well-developed and typical migmatitic gneisses as the research focus and conducted systematic zircon U-Pb isotope dating and petrological and geochemical studies. The results indicate that the protolith of the Mulantou migmatitic gneisses was intermediate basic volcanic rock formed around 276 Ma. These rocks exhibit geochemical characteristics of island-arc calc-alkaline basalt, suggesting a tectonic setting related to the subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Early anatectic metamorphism occurred around 261 Ma, indicating a tectonic environment related to the collision between the South China Block and the Indochina Block. Later metamorphism took place around 248 Ma, signifying a tectonic environment associated with extension following the collision between the South China Block and the Indochina Block. Therefore, the Mulantou migmatitic gneisses preserve a comprehensive record of the tectonic evolution in Hainan Island from the Early Permian to the Early Triassic. They represent the geological consequences of events such as the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, the collision between the South China Block and the Indochina Block, and the subsequent extension. The discovery of these rocks provides new insights into the eastern extension of the Song Ma suture zone.
-
Key words:
- Hainan Island /
- migmatitic gneiss /
- Early Permian-Early Triassic /
- suture zone /
- Paleotethys
-

-
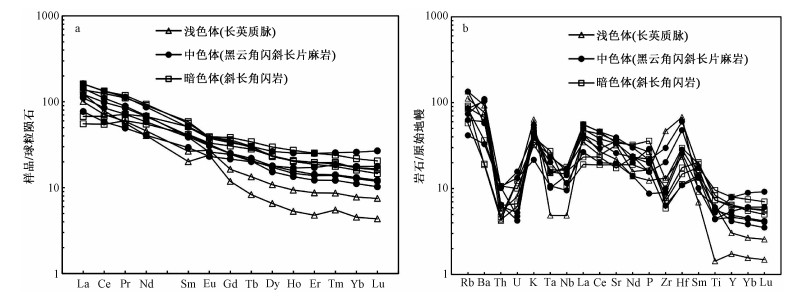
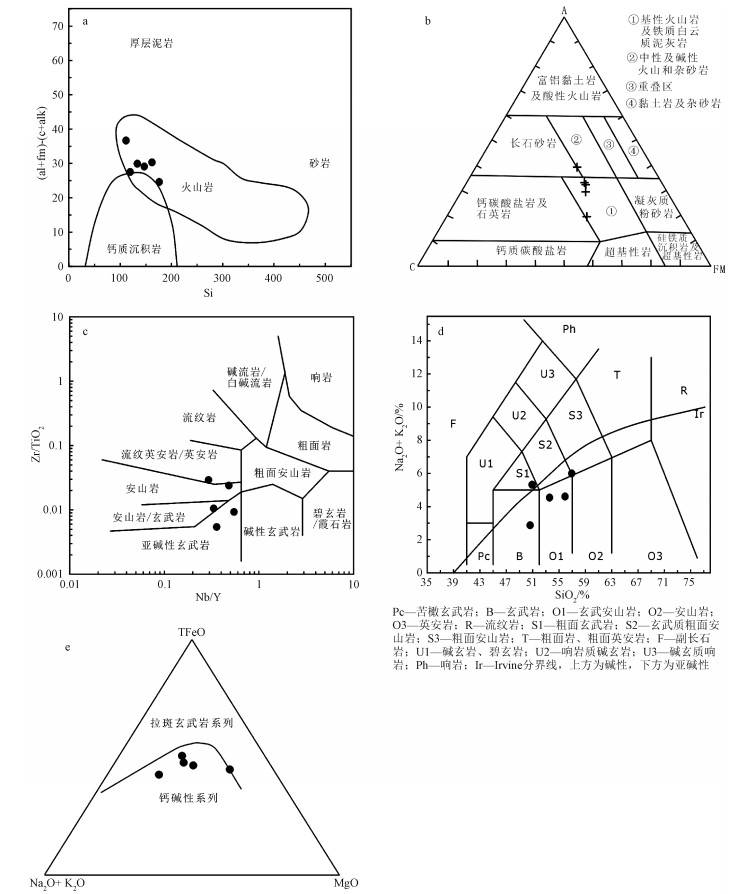
图 7 混合片麻岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(标准化值引自Sun and McDougall, 1989)
Figure 7.
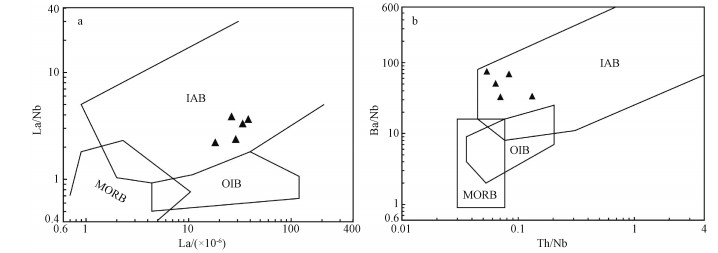
图 9 中色体(黑云角闪斜长片麻岩)的La/Nb-La和Ba/Nb-Th/Nb图解(李曙光, 1993)
Figure 9.
表 1 混合片麻岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb同位素分析数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating data of zircons from migmatitic gneiss
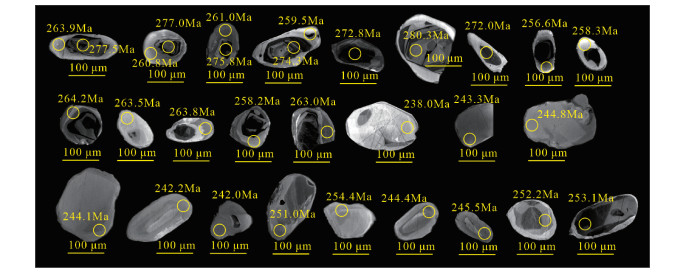
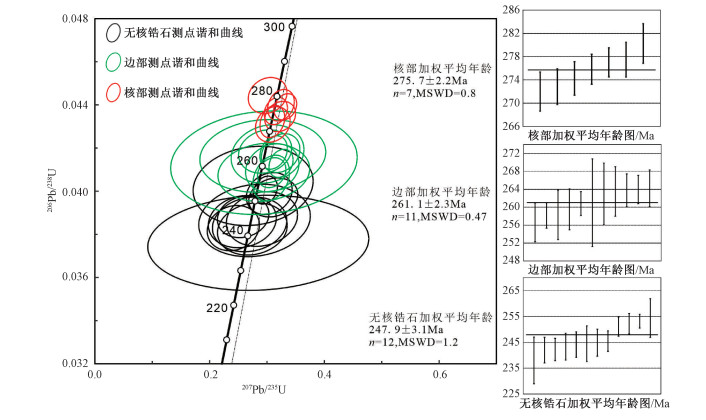
编号 元素含量/×10-6 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 锆石打点类型 Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 谐和度 01 45.66 228.54 384.93 0.0532 0.0025 0.3243 0.0154 0.0440 0.0005 344.5 105.5 285.2 11.8 277.5 3.0 97% 核 02 25.40 97.81 343.67 0.0542 0.0028 0.3115 0.0158 0.0418 0.0005 388.9 121.3 275.3 12.3 263.9 3.2 95% 边 03 100.61 549.87 479.66 0.0544 0.0021 0.3320 0.0130 0.0439 0.0004 387.1 87.0 291.1 9.9 277.0 2.5 95% 核 04 27.46 105.54 344.42 0.0568 0.0024 0.3244 0.0139 0.0413 0.0004 483.4 94.4 285.3 10.7 260.8 2.7 91% 边 05 49.22 231.91 467.50 0.0521 0.0022 0.3154 0.0134 0.0437 0.0004 300.1 98.1 278.4 10.3 275.8 2.6 99% 核 06 1.61 8.47 23.81 0.0644 0.0290 0.2947 0.1073 0.0413 0.0016 755.3 742.9 262.2 84.2 261.0 9.8 99% 边 07 26.71 116.73 275.58 0.0540 0.0030 0.3230 0.0177 0.0435 0.0005 368.6 130.5 284.2 13.6 274.3 2.9 96% 核 08 12.07 60.26 135.86 0.0565 0.0056 0.3092 0.0307 0.0411 0.0007 472.3 222.2 273.5 23.8 259.5 4.6 94% 边 09 37.91 169.48 464.35 0.0520 0.0024 0.3093 0.0142 0.0432 0.0005 283.4 105.5 273.6 11.0 272.8 3.1 99% 核 10 24.08 88.30 261.48 0.0493 0.0037 0.3011 0.0223 0.0444 0.0006 161.2 166.6 267.2 17.4 280.3 3.4 95% 核 11 39.89 222.39 271.15 0.0519 0.0033 0.3101 0.0199 0.0431 0.0005 279.7 146.3 274.3 15.5 272.0 3.4 99% 核 12 15.17 70.16 183.99 0.0563 0.0040 0.3073 0.0210 0.0406 0.0007 464.9 157.4 272.1 16.3 256.6 4.3 94% 边 13 6.40 24.95 76.84 0.0570 0.0124 0.2944 0.0528 0.0409 0.0009 500.0 410.8 262.0 41.4 258.3 5.5 98% 边 14 11.74 42.28 148.85 0.0505 0.0057 0.2967 0.0305 0.0418 0.0007 220.4 240.7 263.8 23.9 264.2 4.1 99% 边 15 20.01 86.40 202.89 0.0553 0.0079 0.3009 0.0419 0.0417 0.0009 433.4 319.4 267.1 32.7 263.5 5.5 98% 边 16 32.15 152.69 304.07 0.0562 0.0045 0.3238 0.0221 0.0418 0.0006 461.2 149.1 284.8 17.0 263.8 3.7 92% 边 17 30.48 136.25 332.86 0.0546 0.0030 0.3082 0.0164 0.0409 0.0005 394.5 91.7 272.8 12.7 258.2 2.8 94% 边 18 6.01 27.16 44.78 0.0508 0.0140 0.2927 0.0725 0.0416 0.0011 231.6 533.3 260.7 56.9 263.0 6.9 99% 边 19 2.19 13.64 21.36 0.0135 0.0730 0.2848 0.1272 0.0376 0.0015 / / 254.5 100.5 238.0 9.0 93% 无核 20 9.34 47.64 69.77 0.0538 0.0085 0.2697 0.0428 0.0385 0.0008 364.9 322.2 242.4 34.2 243.3 5.2 99% 无核 21 7.48 32.38 78.92 0.0582 0.0090 0.2912 0.0410 0.0387 0.0008 600.0 337.9 259.5 32.3 244.8 5.2 94% 无核 22 7.21 34.73 73.91 0.0526 0.0078 0.2570 0.0391 0.0386 0.0008 322.3 298.1 232.2 31.6 244.1 4.9 95% 无核 23 8.06 36.21 88.16 0.0453 0.0058 0.2413 0.0300 0.0383 0.0007 / / 219.5 24.6 242.2 4.3 90% 无核 24 7.02 33.42 85.86 0.0556 0.0084 0.2745 0.0401 0.0383 0.0008 438.9 343.3 246.3 32.0 242.0 5.0 98% 无核 25 17.04 93.30 151.74 0.0574 0.0052 0.3110 0.0282 0.0397 0.0006 509.3 200.0 274.9 21.8 251.0 3.7 90% 无核 26 5.94 40.31 45.78 0.0556 0.0155 0.2758 0.0691 0.0402 0.0012 435.2 523.7 247.3 55.0 254.4 7.5 97% 无核 27 4.35 23.90 41.22 0.0556 0.0134 0.2783 0.0642 0.0386 0.0011 438.9 462.9 249.3 51.0 244.4 6.9 98% 无核 28 19.02 92.68 183.93 0.0489 0.0062 0.2585 0.0297 0.0388 0.0006 142.7 274.0 233.5 23.9 245.5 3.9 94% 无核 29 14.42 75.77 139.44 0.0549 0.0047 0.3039 0.0264 0.0399 0.0006 409.3 189.8 269.5 20.5 252.2 4.0 93% 无核 30 38.60 204.56 317.42 0.0537 0.0025 0.2973 0.0137 0.0401 0.0004 366.7 101.8 264.3 10.7 253.1 2.7 95% 无核 表 2 混合片麻岩岩石化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of migmatitic gneiss
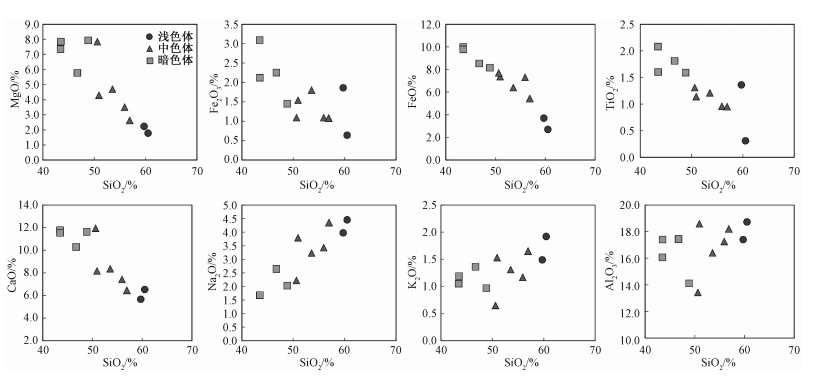
岩性 浅色体(长英质脉) 中色体(黑云角闪斜长片麻岩) 暗色体(斜长角闪岩) 样号 PMD04-5-6 PMD04-5-9 PMD04-5-1 PMD04-5-3 PMD04-5-4 PMD04-5-7 PMD04-11-1 PMD04-5-2 PMD04-5-5 PMD04-5-8 PMD04-5-10 SiO2 59.72 60.51 50.63 55.93 53.58 50.93 56.94 48.86 43.48 43.51 46.73 TiO2 1.36 0.31 1.31 0.96 1.21 1.14 0.95 1.59 2.08 1.60 1.81 Al2O3 17.39 18.72 13.42 17.25 16.4 18.58 18.18 14.1 16.06 17.4 17.43 Fe2O3 1.86 0.64 1.10 1.09 1.80 1.54 1.08 1.45 3.09 2.12 2.25 FeO 3.70 2.70 7.70 7.30 6.40 7.37 5.43 8.15 10.00 9.77 8.53 TFeO 5.37 3.28 8.69 8.28 8.02 8.76 6.40 9.45 12.78 11.68 10.55 MnO 0.13 0.09 0.19 0.19 0.20 0.18 0.15 0.21 0.24 0.21 0.21 MgO 2.23 1.78 7.84 3.50 4.69 4.29 2.64 7.93 7.35 7.85 5.77 CaO 5.67 6.53 11.94 7.42 8.36 8.16 6.45 11.62 11.77 11.53 10.29 Na2O 3.97 4.45 2.22 3.43 3.23 3.79 4.35 2.03 1.67 1.68 2.64 K2O 1.49 1.92 0.65 1.17 1.31 1.53 1.65 0.97 1.05 1.19 1.36 P2O5 0.36 0.27 0.63 0.19 0.43 0.47 0.34 0.58 0.48 0.35 0.78 CO2 0.08 0.67 0.27 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.16 0.31 0.08 0.08 0.08 H2O+ 1.81 1.19 1.85 1.31 2.09 1.63 1.42 1.94 2.44 2.52 1.86 LOI 1.12 1.78 1.35 0.69 1.26 0.82 0.78 1.70 1.35 1.52 0.95 La 23.82 29.54 26.35 18.26 28.97 38.38 33.89 32.61 15.97 13.12 38.16 Ce 43.44 48.01 51.99 35.66 60.23 81.47 67.44 76.62 41.48 33.47 81.39 Pr 5.62 5.35 6.81 4.69 8.03 10.75 8.45 10.52 6.79 5.71 11.24 Nd 21.35 18.86 27.26 19.00 31.45 40.60 32.05 42.28 31.52 25.65 43.75 Sm 4.06 3.07 5.92 4.48 6.21 7.71 5.98 8.97 7.84 6.36 8.58 Eu 1.58 1.39 1.51 1.34 1.85 2.18 1.78 2.24 2.27 1.92 2.26 Gd 3.36 2.43 5.01 4.42 5.15 6.84 5.12 7.42 7.87 6.28 7.07 Tb 0.50 0.31 0.76 0.75 0.82 1.13 0.78 1.13 1.28 1.05 1.10 Dy 2.75 1.66 3.88 4.55 4.54 6.70 4.38 5.84 7.54 5.95 5.99 Ho 0.53 0.30 0.76 0.96 0.89 1.43 0.83 1.16 1.54 1.17 1.14 Er 1.44 0.79 2.02 2.84 2.36 4.13 2.29 3.24 4.17 3.25 3.09 Tm 0.22 0.14 0.31 0.47 0.36 0.65 0.35 0.50 0.61 0.48 0.45 Yb 1.32 0.77 1.89 3.00 2.23 4.4 2.16 2.88 3.69 2.90 2.72 Lu 0.19 0.11 0.26 0.45 0.31 0.68 0.30 0.41 0.52 0.42 0.37 V 103.80 51.35 170.02 234.01 164.30 167.70 114.30 227.70 308.90 259.60 215.60 Co 8.26 6.61 30.44 19.48 18.85 20.38 13.36 27.16 42.49 39.07 28.97 Ni 2.45 4.22 45.05 1.27 15.90 10.15 1.60 61.81 41.92 32.21 28.05 Ga 20.85 21.97 15.23 19.73 20.70 20.29 20.80 18.35 20.62 18.13 20.10 Rb 85.73 70.83 26.43 39.83 85.22 54.30 46.98 53.60 36.50 58.36 55.66 Sr 673.47 461.41 749.30 412.02 544.87 831.62 707.88 755.55 364.93 399.98 719.08 Y 13.86 7.90 18.99 24.76 22.30 35.85 21.15 29.3 36.33 28.08 29.46 Zr 522.7 148.30 71.10 101.20 112.50 332.90 226.8 87.00 79.90 65.60 142.30 Nb 12.11 3.47 6.80 8.26 12.20 10.52 10.21 11.62 11.26 7.54 12.70 Cs 4.63 1.87 1.03 4.80 5.62 4.60 2.72 4.50 1.88 4.28 4.51 Ba 649.2 537.00 229.64 420.71 402.50 729.80 769.50 254.74 135.60 131.30 472.90 Hf 20.99 7.26 3.38 7.93 8.77 18.61 14.79 5.41 4.55 3.47 9.16 Ta 0.63 0.20 0.44 0.83 0.95 0.64 0.42 0.68 1.00 1.12 0.62 Pb 13.69 12.74 7.11 7.91 11.21 8.54 10.67 6.46 4.99 4.53 7.41 Th 0.46 0.36 0.90 0.53 0.86 0.88 0.55 0.91 0.40 0.37 0.54 U 0.17 0.26 0.28 0.11 0.33 0.10 0.09 0.21 0.26 0.13 0.14 注:主量元素单位为%,微量元素和稀土元素单位为×10-6 -
CAI J X, ZHANG K J, 2009. A new model for the Indochina and South China collision during the Late Permian to the Middle Triassic[J]. Tectonophysics, 467(1-4): 35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.12.003
CHEN X Y, WANG Y J, FAN W M, et al., 2011. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of granitic gneisses from Wuzhishan area, Hainan, and geological significances[J]. Geochimica, 40(5): 454-463. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAURE M, LIN W, CHU Y, et al., 2016. Triassic tectonics of the southern margin of the South China Block[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 348(1): 5-14. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2015.06.012
Hainan Geological Survey Institute, 2017. Regional geology of China·Hainan chronicle[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese)
HE H Y, WANG Y J, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2018. Fingerprints of the Paleotethyan back-arc basin in Central Hainan, South China: geochronological and geochemical constraints on the Carboniferous metabasites[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 107(2): 553-570. doi: 10.1007/s00531-017-1508-3
HE H Y, WANG Y J, CAWOOD P A, et al., 2020. Permo-Triassic granitoids, Hainan Island, link to Paleotethyan not Paleopacific tectonics[J]. GSA Bulletin, 132(9-10): 2067-2083. doi: 10.1130/B35370.1
HU Z L, WANG Y, ZHAO X M, et al., 2019. The identification of Jurassic stratigraphy in southern Hainan Island: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(10): 1740-1757 (in Chinese with English abstract).
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A, 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A, et al., 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27(3): 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
LI S G, 1993. Ba-Nb-Th-La diagrams used to identify tectonic environments of ophiolite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 9(2): 146-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302004.htm
LI S X, FAN Y, MO W M, et al., 2006. Characteristics of arc structure zones in the Paleozoic Era of Hainan Island, and its geological implications[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 20(3): 232-236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI S X, GAO L Z, CHEN M L, et al., 2013. Zircon SHRIMP age constraints of the Mesoproterozoic migmatization age in Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 37(4): 635-636. (in Chinese)
LI W P, LU F X, 1999. New progress of the study of geologic setting for calc alkline volcanic rocks[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 18(2): 15-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI X H, ZHOU H W, DING S J, et al., 2000. Sm-Nd isotopic constraints on the age of the Bangxi-Chenxing ophiolite in Hainan Island: implications for the tectonic evolution of eastern Paleo-Tethys[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(3): 425-432. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU J L, TRAN M D, TANG Y, et al., 2012. Permo-Triassic granitoids in the northern part of the Truong Son belt, NW Vietnam: Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 628-644. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.10.011
LIU X C, CHEN Y, WANG W, et al., 2021. Carboniferous eclogite and garnet-omphacite granulite from northeastern Hainan Island, South China: Implications for the evolution of the eastern Palaeo-Tethys[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 39(1): 101-132. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12563
LIU X C, HU J, CHEN L Y, et al., 2021. Oceanic-type high-temperature eclogites from Hainan Island, South China: General characteristics and unsolved problems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(1): 143-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.01.10
LIU X C, HU J, CHEN L Y, et al., 2022. The Mulantou metamorphic complex from northeastern Hainan Island, South China: compositions, ages and tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(9): 3051-3083. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al., 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al., 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
LONG W G, ZHOU D, KE X Z, et al., 2022. Early Paleozoic tectonics of Hainan Island: Constraints from the detrital zircons U-Pb geochronology on Early Silurian sandstones[J]. South China Geology, 38(1): 79-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MALUSKI H, LEPVRIER C, LEYRELOUP A, et al., 2005. 40Ar-39Ar geochronology of the charnockites and granulites of the Kan Nack complex, Kon Tum Massif, Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 25(4): 653-677. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.07.004
MEHNERT K R, 1968. Migmatites and the origin of granitic rocks[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company.
METCALFE I, SHERGOLD J H, LI Z X, 1993. IGCP 321 Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: fieldwork on Hainan Island[J]. Episodes, 16(4): 443-447.
METCALFE I, 1996. Gondwanaland dispersion, Asian accretion and evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 43(6): 605-623. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728282
PAN G T, XIAO Q H, 2015. Tectonic Map of China(1 ∶ 2500000)[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese)
REN L D, GENG Y S, DU L L, et al., 2011. Anatexis and migmatization of the Fuping Complex, North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1056-1066 (in Chinese with English abstract).
REN L D, WANG Y B, YANG C H, et al., 2010. Metamorphism, migmatization and granites of the Mashan Complex in Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2005-2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
REN L D, 2021. Anatexis and enrichment mechanism of the Fe-Ti oxide minerals in the quartzofeldspathic gneisses from the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica. Journal of Geomechanics, 27 (5): 736-746. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SAWYER E W, 1999. Criteria for the recognition of partial melting[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 24(3): 269-279. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1895(99)00029-0
SIMONEN A, 1953. Stratigraphy and sedimentation of the Svecofennidic, early Archean supracrustal rocks in southwestern Finland[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Finland, 160: 1-64.
SUN S S, MCDOUGALL W F, 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition of the earth and mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 35: 429-448.
WANG R M, HE G P, CHEN Z Z, et al., 1987. Graphical discriminance of the protolith of metamorphic rocks[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese)
WANG X S, JIANG T, GAO J, et al., 2019. Contrasting migmatites in the southern Chinese Central Tianshan: Petrogenesis and geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(10): 3233-3261. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.16
WANG Y J, QIAN X, CAWOOD P A, et al., 2018. Closure of the East Paleotethyan Ocean and amalgamation of the Eastern Cimmerian and Southeast Asia continental fragments[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 186: 195-230. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.013
WEN S N, LIANG X Q, FAN W M, et al., 2013. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic composition of Zhizhong granitic intrusion in Ledong area of Hainan Island and their tectonic implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(2): 294-307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A, 1977. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 20: 325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
WU F Y, WAN B, ZHAO L, et al., 2020. Tethyan geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(6): 1627-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.06.01
XIA B D, REN Z P, 1979. Stratigraphy and sedimentary formation in Shilu and surrounded area in Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(1): 43-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA M M, HU J, HU D G, et al., 2019. The discovery of eclogite-high-pressure granulite association from Hainan Island, South China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(10): 1591-1594. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA M M, LIU X C, CHEN Y, et al., 2022. New U-Pb zircon and geochemical constraints on Late Devonian Back-arc basin origin of eclogite protoliths from northeastern Hainan Island, South China[J]. Lithos, 418-419: 106677. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2022.106677
XIAO L L, JIANG Z S, 2010. Geochemistry and tectonic environment of Amphibolites of the Zanhuang metamorphic complex[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 29(4): 339-347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU D R, XIA B, LI P C, et al., 2007. Protolith natures and U-Pb sensitive high mass-resolution ion microprobe (SHRIMP) zircon ages of the metabasites in Hainan Island, South China: Implications for geodynamic evolution since the late Precambrian[J]. Island Arc, 16(4): 575-597. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2007.00584.x
XU Y J, CAWOOD P A, ZHANG H C, et al., 2020. The Mesoproterozoic Baoban Complex, South China: A missing fragment of western Laurentian lithosphere[J]. GSA Bulletin, 132(7-8): 1404-1418. doi: 10.1130/B35380.1
YANG S F, YU Z Y, GUO L Z, et al., 1989. The division and palaeomagnetism of the Hainan Island and platetectonic significance[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Earth Sciences Edition), 1(1-2): 38-46. (in Chinese)
YAO W H, LI Z X, LI W X, et al., 2017. Proterozoic tectonics of Hainan Island in supercontinent cycles: New insights from geochronological and isotopic results[J]. Precambrian Research, 290: 86-100. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.01.001
ZHANG L M, WANG Y J, QIAN X, et al., 2018. Petrogenesis of Mesoproterozoic mafic rocks in Hainan (South China) and its implication on the southwest Hainan-Laurentia-Australia connection[J]. Precambrian Research, 313: 119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.05.002
ZHANG R Y, LO C H, LI X H, et al., 2014. U-Pb dating and tectonic implication of ophiolite and metabasite from the Song Ma suture zone, northern Vietnam[J]. American Journal of Science, 314(2): 649-678. doi: 10.2475/02.2014.07
ZHANG Y Z, YANG X, WANG Y J, et al., 2021. Rifting and subduction records of the Paleo-Tethys in North Laos: Constraints from Late Paleozoic mafic and plagiogranitic magmatism along the Song Ma tectonic zone[J]. GSA Bulletin, 133(1-2): 212-232. doi: 10.1130/B35537.1
陈新跃, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 等, 2011. 海南五指山地区花岗片麻岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 40(5): 454-463. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201105006.htm
海南省地质调查院, 2017. 中国区域地质志·海南志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
胡在龙, 王勇, 赵小明, 等, 2019. 海南岛南部侏罗系的发现: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素的证据[J]. 地质通报, 38(10): 1740-1757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201910016.htm
李曙光, 1993. 蛇绿岩生成构造环境的Ba-Th-Nb-La判别图[J]. 岩石学报, 9(2): 146-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302004.htm
李孙雄, 范渊, 莫位明, 等, 2006. 海南岛古生代弧状构造带的特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 20(3): 232-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200603005.htm
李孙雄, 高林志, 陈沐龙, 等, 2013. 海南岛中元古代混合岩化作用时代的锆石SHRIMP年龄制约[J]. 地层学杂志, 37(4): 635-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201304099.htm
李伍平, 路凤香, 1999. 钙碱性火山岩构造背景的研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 18(2): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ902.006.htm
李献华, 周汉文, 丁式江, 等, 2000. 海南岛邦溪-晨星蛇绿岩片的时代及其构造意义: Sm-Nd同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 16(3): 425-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200003016.htm
刘晓春, 胡娟, 陈龙耀, 等, 2021. 海南洋壳型高温榴辉岩: 基本特征及待解问题[J]. 岩石学报, 37(1): 143-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202101013.htm
刘晓春, 胡娟, 陈龙耀, 等, 2022. 海南岛东北部木栏头变质杂岩的组成、时代及其区域大地构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 96(9): 3051-3083. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202209006.htm
龙文国, 周岱, 柯贤忠, 等, 2022. 海南岛早古生代大地构造格局: 来自志留纪早期碎屑锆石年代学的约束[J]. 华南地质, 38(1): 79-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC202201005.htm
潘桂堂, 肖庆辉, 2015. 中国大地构造图(1 ∶ 2500000)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
任留东, 耿元生, 杜利林, 等, 2011. 华北克拉通阜平杂岩的深熔和混合岩化作用[J]. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1056-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201104016.htm
任留东, 王彦斌, 杨崇辉, 等, 2010. 麻山杂岩的变质-混合岩化作用和花岗质岩浆活动[J]. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2005-2014. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201007005.htm
任留东, 2021. 东南极拉斯曼丘陵长英质片麻岩的深熔作用与铁钛氧化物的聚集机制. 地质力学学报, 27(5): 736-746. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.05.060
王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等, 1987. 变质岩原岩图解判别法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
王信水, 江拓, 高俊, 等, 2019. 中天山地块南缘两类混合岩的成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 35(10): 3233-3261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201910017.htm
温淑女, 梁新权, 范蔚茗, 等, 2013. 海南岛乐东地区志仲岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素研究及其构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(2): 294-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201302014.htm
吴福元, 万博, 赵亮, 等, 2020. 特提斯地球动力学[J]. 岩石学报, 36(6): 1627-1674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202006001.htm
夏邦栋, 任震鹏, 1979. 海南岛石碌及其外围地区的地层和沉积建造[J]. 南京大学学报(地质专刊)(1): 43-55.
夏蒙蒙, 胡娟, 胡道功, 等, 2019. 海南岛发现榴辉岩-高压麻粒岩组合[J]. 地质通报, 38(10): 1591-1594. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201910001.htm
肖玲玲, 蒋宗胜, 2010. 赞皇斜长角闪片麻岩地球化学特征及其构造环境探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 29(4): 339-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201004002.htm
杨树锋, 虞子冶, 郭令智, 等, 1989. 海南岛的地体划分、古地磁研究及其板块构造意义[J]. 南京大学学报(地球科学版), 1(1-2): 38-36.
-



 下载:
下载: