Reconstructing the tectonics and paleogeography during the ocean-land transition of the "Sanjiang"orogenic belt in southwest China
-
摘要:
西南"三江"造山带包含消失的特提斯大洋及两侧大陆边缘"弧盆系"。采用大地构造相和盆地分析原理, 对"三江"造山带中的沉积地质体进行岩相刻画、复原古地理、再造古构造、推演洋陆转化。在中二叠世之前, 特提斯大洋持续扩张, 冈瓦纳、欧亚2个大陆边缘拉张裂离, 形成裂离地块(陆缘海台)与陆缘裂陷盆地, 构成"多岛洋"构造-地理格局。中二叠世, 特提斯大洋板块开始向北俯冲消减, 欧亚大陆边缘的东大山—临沧一线形成增生前锋弧, 前锋弧靠陆一侧转为弧后拉张环境, 继续保持"台盆相间"的古地理格局。晚二叠世末—早三叠世, 特提斯大洋板块继续向北俯冲消减, 金沙江-哀牢山和澜沧江弧后盆地洋壳也分别向西、向东俯冲于昌都-思茅地块之下, 使其转为双向弧后盆地; 而中咱-中甸地块、甘孜-理塘洋还保持拉张环境。晚三叠世, 特提斯洋、澜沧江和金沙江-哀牢山弧后盆地洋壳继续俯冲, 直到关闭; 昌都-思茅地块转为弧后双向前陆盆地, 中咱-中甸地块转为周缘前陆盆地; 中咱-中甸地块东部受甘孜-理塘弧后洋盆的俯冲, 形成弧-盆系。晚三叠世, 特提斯大洋板块开始向南西俯冲, 形成冈底斯-腾冲陆缘岛弧。保山地块东部在晚三叠世早期为陆缘岛弧, 晚期转为弧后前陆盆; 西部形成周缘前陆盆地。这样, 在大洋板块俯冲阶段形成冈瓦纳、欧亚2个大陆边缘与裂离地块上的2个级别的"多弧盆"构造-地理格局。
Abstract:The " Sanjiang " orogenic belt in the southwest contains the lost Tethys Ocean and the "arc-basin system" of the continental margins on both sides.Based on the principle of tectonic facies and basin analysis, lithofacies characterization, palaeogeography restoration, palaeostructure reconstruction and oceanic and continental transformation are carried out for the sedimentary geological bodies in the "Sanjiang" orogenic belt. Before the Middle Permian, the Tethys Ocean continued to expand, and the two continental margins of Gondwana and Eurasia were stretched and split apart, forming the detachment block(continental margin platform)and continental margin rift basin, which constituted the "multi-island ocean" structural-geographic pattern. During the Middle Permian, the Tethys oceanic plate began to subduct northward, and the Dongdashan-Lincang line of the Eurasian continental margin formed an accretive front arc.The front arc turned into a backarc stretching environment on the continental side, which continued to maintain the paleogeographic pattern of "platform and basin". During the Late Permian to Early Triassic, the Tethys oceanic plate continued to subduct northward, and the oceanic crust of Jinshajiang-Alao Mountain and Lancang River back-arc basins also subducted westward and eastward under the Changdu -Simao block, making them turn into bidirectional back-arc basins. And the Zhongza-Zhongdian block, Ganzi - Litang Ocean also maintained the stretching environment.During the Late Triassic, the oceanic crust of Tethys Ocean, Lancang River and Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan back-arc basin continued to subduct until it closed.The Changdu - Simao block turns into a backarc bidirectional foreland basin, and the Zhongzan - Zhongdian block turns into a peripheral foreland basin.The eastern part of the Zhongzan-Zhongdian block was subducted by the ocean basin behind the Ganzi - Litang arc, forming the arc-basin system.In the Late Triassic, the Tethys oceanic plate began to submerge southwestward, forming the Gangdis-Tengchong marginal island arc.The eastern part of the Baoshan block was a marginal island arc in the early Late Triassic and turned into a backarc foreland basin in the Late Triassic.In the west, peripheral foreland basins are formed.Thus, during the subduction stage of the oceanic plate, the tectono-geographic pattern of the Gondwana and Eurasian continental margins and the two-level "multi-arc basin" on the detachment block were formed.
-

-
图 4 西南“三江”造山带及邻区盆地构造演化示意图(据参考文献[13]修改)
Figure 4.
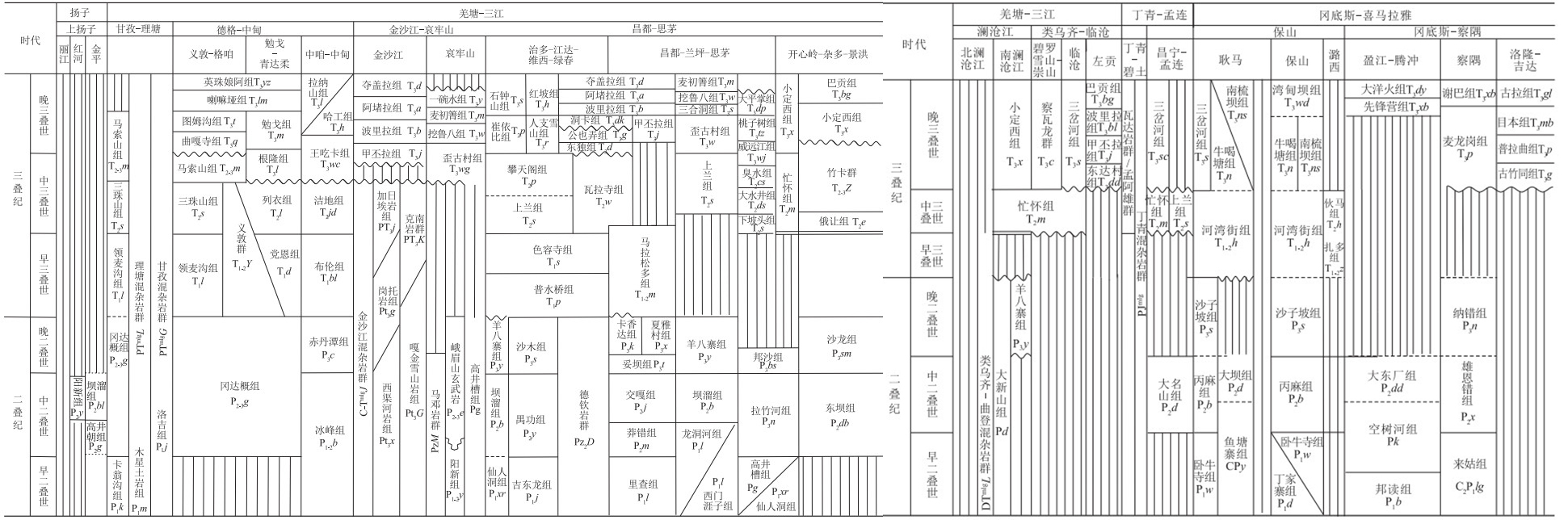
表 1 “三江”地区二叠纪—三叠纪地层划分对比
Table 1. Permian—Triassic stratigraphic division and correlation in Sanjiang area
-
[1] 吴根耀. 初论造山带古地理学[J]. 地层学杂志, 2003, 27(2): 81-98, 115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2003.02.002
[2] 吴根耀. 造山带古地理学——在盆地构造古地理重建中的若干思考[J]. 古地理学报, 2005, 7(3): 405- 416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.03.011
[3] 徐强. 造山带沉积学——以中国几个典型造山带为例[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2001.
[4] 蔡雄飞, 王国灿, 李德威. 造山带古地理恢复的反序方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.001
[5] 牟传龙, 王启宇, 王秀平, 等. 造山带岩相古地理研究与实践——以甘肃省奥陶纪为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 1: 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201601001.htm
[6] 张克信, 何卫红, 徐亚东, 等. 论从俯冲增生杂岩带中重建洋板块地层主要类型与序列——以青藏特提斯二叠系为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(2): 137-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202102002.htm
[7] Dickinson W R. Plate tectonics and sedimentation[M]. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication, 1974, 22: 1-27.
[8] Dickinson W R. Plate tectonic evolution of sedimentary basins[M]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Continuing Education Course Notes, Series, 1976, 1: 1-62.
[9] Ingersoll R V, Busby C J. Tectonics of sedimentary basins[C]//Busby C J, Ingersoll R V. Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 1995: 1-51.
[10] Ingersoll R V. Tectonics of sedimentary basins, with revised nomenclature[C]//Busby C J, Azor A. Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent Advances. Wilev-Blackwell, 2012: 3-43.
[11] 刘本培, 冯庆来, Chong L C, 等. 滇西古特提斯多岛洋的结构及其南北延伸[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(3): 161-171. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.03.020
[12] 潘桂棠, 陈智良, 李兴振, 等. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
[13] 潘桂棠, 徐强, 侯增谦, 等. 西南"三江"多岛弧造山过程成矿系统与资源评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003.
[14] 钟大赉. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.
[15] 尹福光, 潘桂棠, 万方, 等. 西南"三江"造山带大地构造相[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2006, (4): 33-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2006.04.005
[16] 李兴振, 刘文均, 王义昭, 等. 西南三江地区特提斯构造演化与成矿总论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999.
[17] 莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.
[18] 李兴振, 江新胜, 孙志明, 等. 西南三江地区碰撞造山过程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.
[19] 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦, 等. 西南"三江"多岛弧盆-碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.
[20] 王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 等. 三江昌宁-孟连带原-古特提斯构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8): 2527-2550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808001.htm
[21] 罗建宁, 张正贵, 陈明, 等. 三江特提斯沉积地质与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992.
[22] 罗建宁, 惠兰, 朱夔玉, 等. 西南三江地区沉积地质与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 1-173.
[23] 闫臻, 王宗起, 闫全人, 等. 造山带汇聚板块边缘沉积盆地的鉴别与恢复[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(7): 1943-1958. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201807009.htm
[24] 张克信, 何卫红, 徐亚东, 等. 中国洋板块地层分布及构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201606007.htm
[25] 段向东, 刘桂春, 冯庆来. 昌宁孟连构造带拉丁期放射虫动物群及构造演化意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 2: 67-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX2012S2014.htm
[26] 张翼飞, 段锦荪, 张罡. 滇西蛇绿岩带地质构造演化与澜沧江板块缝合线研究[J]. 云南地质, 2001, 4: 426-426.
[27] 严松涛, 吴青松, 李虎, 等. 甘孜-理塘蛇绿混杂岩带中段理塘地区混杂岩物质组成及其洋盆演化史[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(6): 1875-1895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202106015.htm
[28] 闫全人. 西南三江特提斯洋扩张与晚古生代东冈瓦纳裂解: 来自甘孜蛇绿岩辉长岩的SHRIMP年代学[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 2: 158-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB20050200A.htm
[29] 侯增谦, 杨岳清, 王海. 三江义敦岛弧碰撞造山过程与成矿系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003.
[30] 范承钧, 张翼飞. 云南西部地质构造格局[J]. 云南地质, 1993, 2: 139-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199302000.htm
[31] 王冬兵, 罗亮, 王保弟, 等. 滇西澜沧江构造带景谷地区团梁子岩组的时代与构造属性[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8): 2551-2570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808002.htm
[32] 王冬兵, 王保弟, 唐渊, 等. 西南三江特提斯研究进展与展望[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(11): 1799-1813. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211102&flag=1
[33] 刘昌实, 朱金初, 徐夕生, 等. 滇西临沧复式岩基特征研究[J]. 云南地质, 1989, 1: 189-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD1989Z1000.htm
[34] 张旗, 张魁武, 李达周. 横断山区基性-超基性岩的类型[J]. 岩石学报, 1987, (3): 46-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB198703005.htm
[35] 孙载波, 李静, 周坤, 等. 滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 4: 746-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201704009.htm
[36] 刘桂春, 孙载波, 曾文涛, 等. 湾河蛇绿混杂岩的形成时代、岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(2): 163-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201702003.htm
[37] 段向东, 张志斌, 冯庆来, 等. 滇西南耿马弄巴地区南皮河组正层型剖面地层层序、时代的重新认识[J]. 地层学杂志, 2003, 27(1): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200301011.htm
[38] 冯庆来. 滇西南海西—印支期放射虫古生物学及造山带地层学研究[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 1992.
[39] 罗亮, 王冬兵, 尹福光, 等. 云南保山地块香山组和丁家寨组沉积序列与碳同位素研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 2: 291-301 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201802007.htm
[40] 陈炳蔚, 王铠元, 刘万熹, 等. 怒江—澜沧江—金沙江地区大地构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.
[41] 王立全, 王保弟, 李光明, 等. 东特提斯地质调查研究进展综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(2): 283-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202102014.htm
[42] 范蔚茗, 彭头平, 王岳军. 滇西古特提斯俯冲-碰撞过程的岩浆作用记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 6: 291-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200906039.htm
[43] 孔会磊, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等. 滇西三江地区临沧花岗岩的岩石成因: 地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1438-1452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205010.htm
[44] 吴根耀. 初论造山带地层学: 以三江地区特提斯造山带为例[J]. 地层学杂志, 1998, 3: 3-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ803.000.htm
[45] 李再会, 林仕良, 丛峰, 等. 滇西腾-梁地块印支造山事件——花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石学证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(3): 298-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201003006.htm
[46] 李廷栋, 肖庆辉, 潘桂棠, 等. 关于发展洋板块地质学的思考[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(5): 1441-1451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201905003.htm
[47] 刘增乾, 李兴振, 叶庆同, 等. 中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报4矿床与矿产第34号三江地区构造岩浆带的划分与矿产分布规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.
[48] Sone M, Metcalfe I. Parallel. Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2008, 340(2/3): 166-179.
[49] Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66: 1-33.
[50] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 耿全如, 等. 班公湖—双湖—怒江—昌宁—孟连对接带时空结构——特提斯大洋地质及演化问题[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(3): 1-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202003002.htm
[51] 张翼飞, 段锦荪, 张罡, 等. 滇西蛇绿岩带地质构造演化与澜沧江板块缝合线研究[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2001.
[52] 沈上越, 冯庆来, 刘本培, 等. 昌宁—孟连带洋脊、洋岛型火山岩研究[J]. 地质科技情报. 2002, 21(3): 13-17 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200203002.htm
[53] 王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 等. 西南三江金沙江弧盆系时空结构及构造演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(2): 246-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202102012.htm
[54] 王保弟, 王立全, 周道卿, 等. 龙木错-双湖-昌宁-孟连结合带: 冈瓦纳大陆与泛华夏大陆的界线[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(11): 1783-1798. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211101&flag=1
① 西藏自治区地质调查院. 中华人民共和国1∶25万那曲县幅区域地质调查报告. 2006.
-




 下载:
下载:


