Geochemical characteristics of Late Triassic lamprophyres from the western Zhen'an, South Qinling and its indicative significance for tectonic environment
-
摘要:
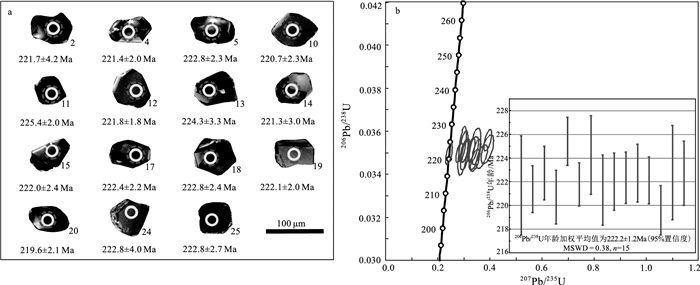
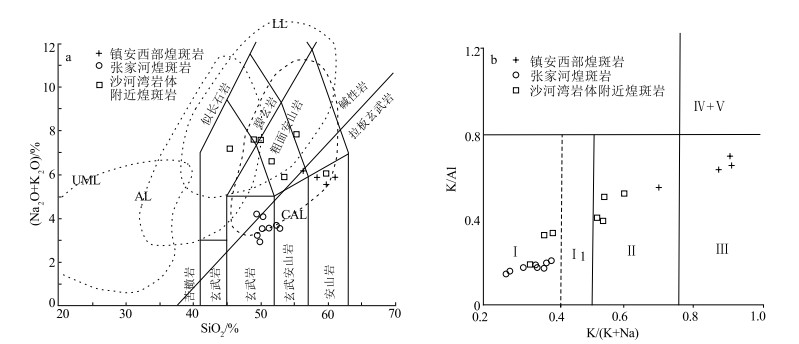
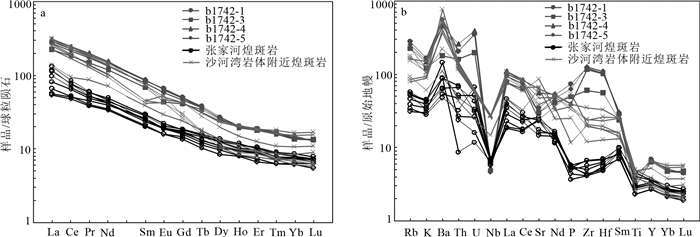
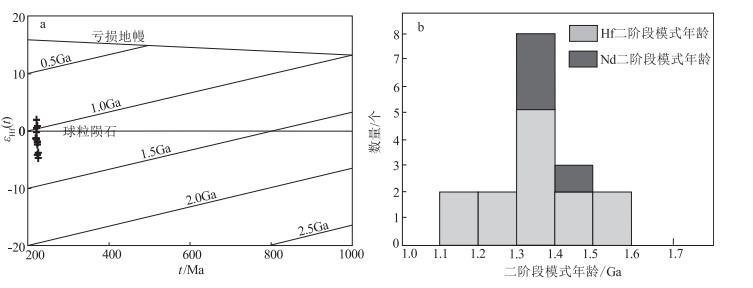
煌斑岩是反映深部构造-岩浆作用和源区地球化学性质的良好地质体。对南秦岭镇安西部地区出露的煌斑岩脉进行系统研究, 用LA-ICP-MS测定了煌斑岩中锆石U-Pb同位素, 得到其206Pb/238U年龄为222.2±1.2Ma(MSWD=0.38, n=15), 此年龄代表脉体的形成年龄, 属晚三叠世。地球化学分析表明, 岩石属钙碱性钾质-超钾质系列, 轻稀土元素和Rb、Ba等大离子亲石元素富集, 重稀土元素和Nb、Ti等高场强元素亏损, 具有俯冲带幔源岩石的成分特征; 岩石具有较高的(87Sr/86Sr)i值(0.7066~0.7076)和较低的εNd(t)值(-5.77~-4.62);锆石176Hf/177Hf值为0.28250~0.28287, εHf(t)值为-4.75~1.89, 锆石二阶段Hf模式年龄与全岩Nd二阶段模式年龄主要集中于中元古代(1.3~1.5Ga)。综合分析表明, 煌斑岩的源区为中元古代富集地幔, 形成于后碰撞伸展构造环境。在晚三叠世(220Ma左右)后碰撞伸展构造环境下, 勉略洋壳俯冲过程中形成的流体交代富集地幔在构造减压、深部物质上涌提供热和流体的共同作用下, 发生部分熔融, 形成具EMⅡ型同位素特征的镁铁质岩浆, 镁铁质岩浆沿后碰撞伸展阶段形成的裂隙上升侵位形成煌斑岩脉。
-
关键词:
- 煌斑岩脉 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 地球化学 /
- Sr-Nd-Hf同位素 /
- 南秦岭
Abstract:The lamprophyres are good geological bodies reflecting deep tectonomagmatism and geochemical properties of source.In this paper, a systematic study has been carried out on the lamprophyre veins in the west of Zhen'an, South Qinling Mountains.Zircon U-Pb isotopes of the lamprophyre have been determined by LA-ICP-MS.The 206Pb/238U age of the lamprophyre is 222.2±1.2 Ma(MSWD=0.38, n=15), which represents the formation age of the vein body and belongs to the Late Triassic.Geochemical data show that the rocks belong to the calc-alkaline potassium-superpotassic series, enriched in LREE and large ion lithophile elements such as Rb and Ba, and deficient in HREE and high field strength elements such as Nb and Ti, which have the composition characteristics of mantle derived rocks in subduction zones.The isotopic compositions of the rocks are characterized by high initial(87Sr/86Sr)i rations(0.7066~0.7076)and negative εNd(t)values(-5.77~ -4.62);Furthermore, the 176Hf/177Hf rations of zircons range from 0.28250 to 0.28287, with εHf(t)values from -4.75 to 1.89, The two-stage Hf model ages(TDM2)and the whole-rock Nd isotopic model ages, are mainly concentrated in mesoproterozoic(1.3~1.5 Ga).Comprehensive analysis shows that the source of lamprophyre is Mesoproterozoic enriched mantle and formed in post-collision extensional tectonic environment.At the Late Triassic(approximately at 220 Ma), the enriched lithospheric mantle experienced metasomatism by subduction fluid, which occurred to partial melting under the conditions of tectonic decompression, heat and fluid from the upwelling deep materials, and produced mafic magma, the magma emplaced to shallow crust along tectonic fracture and formed the lamprophyres.
-
Key words:
- lamprophyres /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating /
- geochemistry /
- Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes /
- South Qinling Mountains
-

-
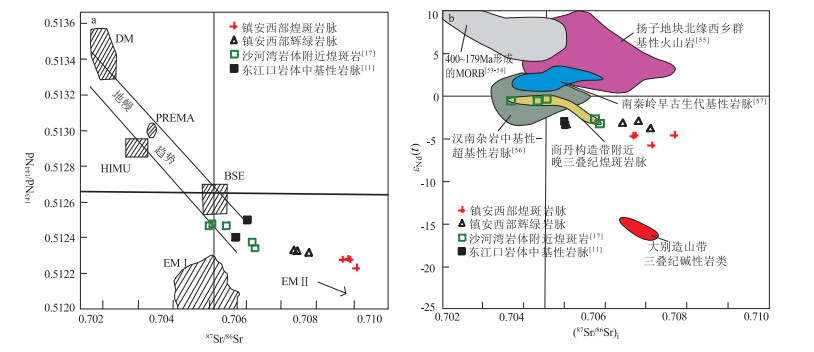
图 6 南秦岭镇安西部煌斑岩t - εHf(t)图解(a,底图据参考文献[39]) 和二阶段模式年龄值柱状图(b)
Figure 6.
表 1 南秦岭镇安西部煌斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1. U-Th-Pb isotopic data of zircon in the lamprohyres from western Zhen'an, South Qinling, as measured by LA-ICP-MS
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ RZ1742-02 739 2377 1547 1.5 0.0619 0.0023 0.2965 0.013 0.0350 0.00067 0.0199 0.0010 221.7 4.2 RZ1742-04 132 538 1499 0.4 0.0503 0.0017 0.2424 0.008 0.0349 0.00032 0.0116 0.0005 221.4 2.0 RZ1742-05 816 2317 3327 0.7 0.0680 0.0023 0.3283 0.009 0.0352 0.00036 0.0212 0.0008 222.8 2.3 RZ1742-10 501 1996 2020 1.0 0.0765 0.0030 0.3686 0.014 0.0348 0.00036 0.0153 0.0010 220.7 2.3 RZ1742-11 1216 3875 2062 1.9 0.0799 0.0022 0.3916 0.010 0.0356 0.00033 0.0201 0.0008 225.4 2.0 RZ1742-12 897 2727 2109 1.3 0.0585 0.0019 0.2823 0.009 0.0350 0.00029 0.0209 0.0008 221.8 1.8 RZ1742-13 587 1516 3788 0.4 0.0614 0.0028 0.2944 0.009 0.0354 0.00053 0.0217 0.0009 224.3 3.3 RZ1742-14 223 1052 1418 0.7 0.0628 0.0020 0.3042 0.012 0.0349 0.00048 0.0122 0.0005 221.3 3.0 RZ1742-15 193 698 1655 0.4 0.0717 0.0021 0.3481 0.011 0.0350 0.00039 0.0146 0.0007 222.0 2.4 RZ1742-17 288 1269 1985 0.6 0.0623 0.0021 0.3012 0.010 0.0351 0.00035 0.0129 0.0007 222.4 2.2 RZ1742-18 1115 3410 2129 1.6 0.0699 0.0027 0.3367 0.012 0.0352 0.00039 0.0220 0.0011 222.8 2.4 RZ1742-19 300 1317 2263 0.6 0.0629 0.0021 0.3038 0.010 0.0351 0.00032 0.0129 0.0006 222.1 2.0 RZ1742-20 421 2090 1848 1.1 0.0717 0.0025 0.3426 0.012 0.0347 0.00033 0.0128 0.0007 219.6 2.1 RZ1742-24 720 2236 1464 1.5 0.0716 0.0028 0.3417 0.015 0.0352 0.00064 0.0208 0.0010 222.8 4.0 RZ1742-25 701 1884 2482 0.8 0.0804 0.0032 0.3893 0.016 0.0352 0.00044 0.0236 0.0013 222.8 2.7 表 2 南秦岭镇安西部煌斑岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2. Major, trace elements and REE compositions of lamprohyres from western Zhen'an, South Qinling
样号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 K2O+Na2O K2O/Na2O Mg# TFe2O3 1742-1 51.05 0.805 11.25 2.4 3.23 0.0937 6.4 8.32 0.581 4.98 1.59 8.45 99.15 5.56 8.57 77.93 5.99 1742-3 56.23 0.653 10.38 2.25 3.2 0.0904 5.36 6.88 1.72 3.64 1.09 7.48 98.97 5.36 2.12 74.91 5.81 1742-4 53.52 0.607 10.65 3.36 2.42 0.0993 5.02 7.73 0.498 4.43 0.882 9.95 99.17 4.93 8.90 78.71 6.05 1742-5 52.89 0.744 11.38 2.45 2.93 0.0921 5.59 7.97 0.751 4.59 1.36 8.26 99.01 5.34 6.11 77.28 5.71 样号 Nb Zr Th U Ba Co Cr Ni Hf Rb Ta La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu 1742-1 3.29 1354 17.3 7.47 3945 22.8 273 183 32.3 177 0.17 69.7 142 17.9 69.4 13.0 3.84 1742-3 4.34 670 13.9 4.11 1239 25.6 205 123 17.2 144 0.21 53.4 113 14.1 55.6 10.6 2.52 1742-4 3.82 1309 21.9 8.18 3158 23.5 139 85.5 31.6 144 0.20 75.3 153 18.9 72.5 13.3 3.68 1742-5 3.61 1411 17.5 7.30 3189 21.1 279 151 34.0 161 0.18 64.6 132 16.5 62.9 12.0 3.40 样号 Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ∑REE LREE HREE LREE/HREE LaN/YbN LaN/SmN GdN/YbN δEu 1742-1 10.3 1.42 6.96 1.18 3.19 0.43 2.41 0.34 32.0 342.07 315.84 26.23 12.04 20.75 3.46 3.54 0.98 1742-3 8.55 1.28 6.40 1.13 3.02 0.43 2.34 0.35 28.9 272.72 249.22 23.50 10.61 16.37 3.25 3.02 0.78 1742-4 10.2 1.38 6.70 1.11 2.97 0.41 2.34 0.34 29.8 362.13 336.68 25.45 13.23 23.08 3.65 3.61 0.93 1742-5 9.52 1.36 6.48 1.17 3.04 0.42 2.55 0.33 30.3 316.27 291.40 24.87 11.72 18.17 3.48 3.09 0.94 注:Mg=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++ Fe2+),TFe2O3=Fe2O3+1.111×FeO,δEu =EuN /(SmN + GdN)1/2;主量元素含量单位为%, 微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 南秦岭镇安西部煌斑岩Sr-Nd同位素数据
Table 3. Sr-Nd isotopic results of lamprohyres from western Zhen'an, South Qinling
样品号 Rb /10-6 Sr/10-6 (87Sr/86Sr) ±2σ 87Rb/86Sr (87Sr/86Sr)i Sm /10-6 Nd /10-6 143Nd/144Nd ±2σ 147Sm/144Nd (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) TDM2 /Ga 1742-1 177 720 0.708876 0.000010 0.71 0.70663 13.0 69.4 0.512281 0.000006 0.1140 0.512115 -4.62 1.38 1742-3 144 628 0.709141 0.000010 0.66 0.70705 10.6 55.6 0.512225 0.000006 0.1160 0.512056 -5.77 1.47 1742-4 144 1179 0.708715 0.000008 0.35 0.70760 13.3 72.5 0.512276 0.000006 0.1117 0.512114 -4.65 1.38 1742-5 161 624 0.708946 0.000008 0.75 0.70659 12.0 62.9 0.512275 0.000005 0.1161 0.512106 -4.80 1.39 注:εNd(t)= {[(143Nd/144Nd)样品-(147Sm/144Nd)样品×(eλt -1)]/[(143Nd/144Nd)CHUR-(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR×(eλt -1)-1]}×10000; TDM=(1/ λ)×ln {1+[(143Nd/144Nd)样品-(143Nd/144Nd)亏损地幔]/[(147Sm/144Nd)样品-(147Sm /144Nd)亏损地幔]}; (143Nd/144Nd)CHUR=0.512638,(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR=0.1967,(143Nd/144Nd)亏损地幔=0.51315,(147Sm /144Nd)亏损地幔=0.2137 表 4 南秦岭镇安西部煌斑岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据
Table 4. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic results of lamprohyres from western Zhen'an, South Qinling
测点号 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ 206Pb/238U/Ma (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1 /Ga TDM2 /Ga fLu/Hf 1742-02 0.03738 0.00040 0.00110 0.000010 0.28260 0.000039 221.7 0.282591 -6.25 -1.54 0.93 1.35 -0.97 1742-04 0.01466 0.00012 0.00043 0.000003 0.28260 0.000043 221.4 0.282597 -6.12 -1.32 0.91 1.34 -0.99 1742-05 0.02554 0.00043 0.00079 0.000012 0.28266 0.000025 222.7 0.282660 -3.84 0.94 0.83 1.20 -0.98 1742-10 0.03345 0.00011 0.00107 0.000006 0.28265 0.000017 220.7 0.282648 -4.24 0.45 0.85 1.23 -0.97 1742-11 0.02177 0.00023 0.00071 0.000006 0.28250 0.000065 225.4 0.282498 -9.59 -4.74 1.05 1.56 -0.98 1742-12 0.06097 0.00046 0.00155 0.000006 0.28269 0.000033 221.8 0.282688 -2.75 1.89 0.80 1.14 -0.95 1742-13 0.00727 0.00004 0.00019 0.000001 0.28253 0.000021 224.3 0.282527 -8.63 -3.73 1.00 1.49 -0.99 1742-14 0.03868 0.00046 0.00131 0.000013 0.28263 0.000029 221.3 0.282628 -4.89 -0.22 0.88 1.27 -0.96 1742-15 0.00843 0.00008 0.00030 0.000002 0.28257 0.000018 222.0 0.282568 -7.16 -2.33 0.95 1.40 -0.99 1742-17 0.01063 0.00007 0.00034 0.000002 0.28258 0.000020 222.3 0.282577 -6.85 -2.01 0.94 1.38 -0.99 1742-18 0.01278 0.00007 0.00042 0.000003 0.28258 0.000022 222.7 0.282583 -6.63 -1.80 0.93 1.37 -0.99 1742-19 0.01617 0.00005 0.00050 0.000002 0.28252 0.000037 222.1 0.282515 -9.00 -4.20 1.03 1.52 -0.99 1742-20 0.03132 0.00009 0.00112 0.000002 0.28260 0.000021 219.6 0.282597 -6.02 -1.36 0.92 1.34 -0.97 注:εHf(t)={[(176Hf/177Hf)s -(176Lu/177Hf)s ×(eλt -1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0 -(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0×(eλt -1)]-1 }×10000; TDM1=(1/ λ)×ln {1+[(176Hf / 177Hf)s -(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu / 177Hf)s -(176Lu/177Hf)DM]}; TDM2=t+(1/ λ)×ln {1+[(176Hf / 177Hf)s , t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM, t]/[(176Lu / 177Hf)c -(176Lu/177Hf)DM]} ; fLu/Hf =(176Lu/177Hf)s /(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0-1; 其中(176Lu/177Hf)s和(176Hf/177Hf)s为样品测定值,(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0=0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0=0.282772, (176Lu/177Hf)DM =0.0384,(176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325,(176Lu/177Hf)c =0.015, λ=1.867×10-11/a,t为锆石结晶年龄 -
[1] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学城, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.
[2] 刘春花, 吴才来, 郜源红, 等. 南秦岭麻池河乡和沙河湾花岗岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素组成[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(5): 36-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201305004.htm
[3] 刘春花, 吴才来, 郜源红, 等. 南秦岭东江口、柞水和梨园堂花岗岩类锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学与锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(8): 2402-2420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201408021.htm
[4] 孙卫东, 李曙光, Yadong Chen, 等. 南秦岭花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29(3): 209-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2000.03.001
[5] 张国伟, 董云鹏, 赖绍聪, 等. 秦岭-大别造山带南缘勉略构造带与勉略缝合带[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(12): 1121-1135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200312000.htm
[6] 张静, 陈衍景, 舒桂明, 等. 陕西西南部秦岭梁花岗岩体的矿物成分研究和相关问题讨论[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2002, 32(2): 113-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200202002.htm
[7] 张成立, 张国伟, 晏云翔, 等. 南秦岭勉略带北光头山花岗岩体群的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 711-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503013.htm
[8] 张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞. 秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(3): 304-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.03.003
[9] 张成立, 王晓霞, 王涛, 等. 东秦岭沙河湾岩体成因——来自锆石U-Pb定年及其Hf同位素的证据[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3): 453-465. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200903015.htm
[10] 弓虎军, 朱赖民, 孙博亚, 等. 南秦岭地体东江口花岗岩及其基性包体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 3029-3042. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911033.htm
[11] 秦江锋. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D]. 西北大学博士学位论文, 2010.
[12] 卢欣祥, 尉向东, 肖庆辉, 等. 秦岭环斑花岗岩的年代学研究及其意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 1999, 5(4): 372-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX199904001.htm
[13] Sun W D, Li S G, Chen Y D, et al. Timing of Synorogenic Granitoids in the South Qinling, Central China: Constraints on the Evolution of the Qinling-Dabie Orogenic Belt[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2002, 110: 457-468. doi: 10.1086/340632
[14] 贾大成, 胡瑞忠, 卢焱, 等. 湘东北蕉溪岭富钠煌斑岩地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(4): 459-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200204002.htm
[15] 姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 等. 辽东半岛煌斑岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其对中国东部岩石圈减薄开始时间的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(19): 115-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200519016.htm
[16] 梁国科, 吴祥珂, 蔡逸涛, 等. 桂北罗城地区云煌岩成因-地球化学及U-Pb年龄约束[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(2/3): 267-278. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2020020310&flag=1
[17] Wang X X, Wang T, Jahn B M, et al. Tectonic significance of Late Triassic post-collisional lamprophyre dykes fron the Qinling Moutains(China)[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007, 144(5): 837-848. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003548
[18] 汪欢. 陕西双王金矿区岩浆岩特征及与金成矿的关系[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2012.
[19] 杨朝贵, 刘燊, 冯彩霞, 等. 南秦岭中生代张家河煌斑岩的地球化学特征及其岩石成因探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2013, 33(1): 119-128. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2013.01.017
[20] 王邢颖. 南秦岭晚三叠世东江口岩体岩浆混合机理研究[D]. 西北大学硕士学位论文, 2020.
[21] 陕西省地质调查院. 中国区域地质志·陕西志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
[22] 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(14): 1511-1520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008
[23] De Biévre P, Taylor P D P. Table of the isotopic compositions of the elements[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 1993, 123(2): 149-166. doi: 10.1016/0168-1176(93)87009-H
[24] Chu Nanchin, Taylor R N, Chavagnac V, et al. Calibration of the Lutetium-Hafnium Clock[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5530): 683-687. doi: 10.1126/science.1061372
[25] Scherer E E, Cameron K L, Blichert-Toft J. Lu-Hf garent geochronology: Closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusion[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(19): 3413-3432. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00440-3
[26] Albarède F, Blichert-Toft J. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1/2): 243-258.
[27] Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3/4): 237-269.
[28] Chen F, Satir M, Ji J, et al. Nd-Sr-Pb Isotopes of Tengchong Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks from Western Yunnan, China: Evidence for an Enriched-mantle Source[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00007-X
[29] Chen F K, Li X H, Wang X L, et al. Zircon Age and Nd-Hf Isotopic Composition of the Yunnan Tethyan Belt, Southwestern China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2007, 96(6): 1179-1194. doi: 10.1007/s00531-006-0146-y
[30] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
[31] Le Base M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkli-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27: 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
[32] Rock N M S. The nature and origin of the lamprophyres: anoverview[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1987, 30(1): 191-226. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1987.030.01.09
[33] 路凤香, 舒小辛, 赵崇贺. 有关煌斑岩分类的建议[J]. 地质科技情报, 55-62, 10(增1): 1991.
[34] Sun S S, McDonough W E. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implicaitons for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society of London, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[35] 马铁球, 陈俊, 郭乐群, 等. 湘东北临湘地区钾质煌斑岩40Ar-39Ar定年及其地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(1): 56-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201001009.htm
[36] 王治华, 郭晓东, 葛良胜, 等. 云南大坪金矿区煌斑岩的地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(4): 355-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.04.002
[37] Depaolo D J, Wasserburg G J. Inferences about magma sources and mantle structure from variations of 143Nd/144Nd[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1976, 3(12): 743-746. doi: 10.1029/GL003i012p00743
[38] Jacobsen S B, Wasserburg G J. Sm-Nd isotopic evolution of chondrites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1): 139-155. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90125-9
[39] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm
[40] 穆可斌, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 南秦岭白龙江群中花岗岩脉群年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3): 111-135. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.03.010
[41] Stille P, Oberhänsli R, Wenger-Schenk K. Hf-Nd isotopic and trace element constraints on the genesis of alkaline and calc-alkaline lamprophyres[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1989, 96(1): 209-219.
[42] Prelevic D, Foley S F, Cvetkovic V, et al. Origin of Minette by Mixing of Lamproite and Dacite Magmas in Veliki Majdan, Serbia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45(4): 759-792. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egg109
[43] 贾丽琼, 莫宣学, 董国臣, 等. 滇西马厂箐煌斑岩成因: 地球化学、年代学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(4): 1247-1260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201304012.htm
[44] 和文言, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 滇西北衙煌斑岩的岩石成因及动力学背景: 年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3287-3300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411014.htm
[45] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[J]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985, 94(4): 57-72.
[46] Weaver B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(2/4): 381-397.
[47] Frey F A, Green D H. The mineralogy, geochemistry and origin of iherzolite inclusions in Victorian basanites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1974, 38(7): 1023-1059. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(74)90003-9
[48] Rock N M S, Bowes D R, Wright A E. Lamprophyres[M]. Blackie: Glasgow, 1991: 1-285.
[49] Dupuy C, Liotard J M, Dostal J. Zr/Hf fractionation in intraplate basaltic rocks: Carbonate metasomatism in the mantle source[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(6): 2417-2423. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90198-R
[50] 吴鹏, 谭茂, 韩润生, 等. 滇中楚雄盆地六苴铜矿床煌斑岩地球化学、年代学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5): 1409-1425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005006.htm
[51] Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1/2): 33-45.
[52] Ayers J. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the mantle wedge of subduction zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 132(4): 390-404.
[53] Tribuzio R, Thirlwall M F, Vannucci R, et al. Origin of the gabbro-peridotite association from the Northern Apennine Ophiolites(Italy)[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45: 109-11124.
[54] Xu J F, Castillo P R. Geochemical and Nd-Pb isotopic characteristics of the Tethyan asthenosphere: implications for the origin of the Indian Ocean mantle domain[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 393: 9-27.
[55] Ling W L, Gao S, Zhang B R, et al. Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the northwestern Yangtze craton, South China: implications for amalgamation and break-up of the Rodinia Supercontinent[J]. Precambrain Research, 2003, 122: 111-140.
[56] Zhao J H, Zhou M F. Secular evolution of the Neoproterozoic lithospheric mantle underneath the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Lithos, 2009, 107: 152-168.
[57] 张成立, 高山, 袁洪林, 等. 南秦岭早古生代地幔性质: 来自超镁铁质、镁铁质岩脉及火山岩的Sr-Nd-Pb同位素数据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(7): 857-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200707000.htm
[58] Wolf M B, Wyllie P J. Dehydration-melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar: the effects of temperature and time[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 115: 369-383.
[59] 郑永飞. 超高压变质与大陆碰撞研究进展: 以大别-苏鲁造山带为例[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(18): 2129-2152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200818002.htm
[60] Zheng Y F, Gao T S, Wu Y B, et al. Fluid flow during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: zircon U-Pb age and O-isotope studies of a quartz vein within ultrahigh-pressure eclogite[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2007, 25(2): 267-283.
[61] 路应辉. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩地球化学研究[D]. 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2017.
[62] Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Neubauer F, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(3): 213-237.
[63] 罗照华, 魏阳, 辛后田, 等. 造山后脉岩组合的岩石成因——对岩石圈拆沉作用的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1672-1684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606024.htm
[64] 王凯, 胡海燕, 刘坤鹏. 北秦岭西段普洛河地区煌斑岩脉地球化学特征及成岩构造环境[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(12): 2906-2912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201912004.htm
① 陕西省矿产地质调查中心. 镇安西部金铜钨多金属找矿会战区地质矿产图, 2020.
-



 下载:
下载: