The genesis of glaucony in the lower Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation, southern Shaanxi: implication to seawater redox condition
-
摘要:
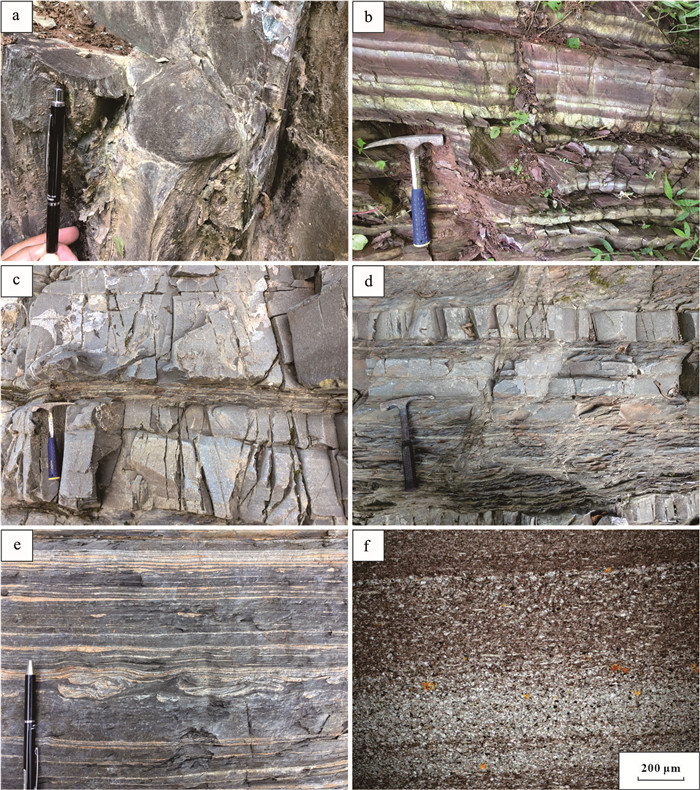
海绿石是海洋环境中一类重要的自生矿物,在古环境研究方面具有广泛的应用。基于中国陕南地区埃迪卡拉纪陡山沱组下部海绿石的分布特征,对其开展了综合的岩相学、原位微区成分定量分析、X-射线衍射(XRD)分析等研究,旨在探讨海绿石的形成机制,剖析研究区埃迪卡拉纪早期的氧化还原环境。偏光显微镜和扫描电镜(SEM)观察结果表明,海绿石多以胶体沉淀物的形式充填于石英、长石等碎屑矿物颗粒之间的孔隙中,为早期成岩阶段自生沉淀成因。由于海绿石的形成需要Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)的同时存在,Fe氧化还原界面附近(次氧化)最有利于海绿石的发育,因此研究区陡山沱组下部海绿石的形成指示了次氧化的孔隙水条件。能谱(EDS)定量分析表明,研究区陡山沱组的海绿石具有高K2O和Al2O3、低Fe2O3含量,该化学组分是前寒武纪海绿石的典型特征。碎屑矿物溶解及海水与孔隙水之间的物质交换提供了海绿石演化过程所需的元素。与贵州瓮安地区同时期的含海绿石地层相比,研究区海绿石的分布层位相对局限,表明古海水氧化还原环境和古地理环境对于海绿石分布位置具有共同调控作用。
Abstract:Glaucony is an important authigenic mineral in marine environment and has been widely used in palaeoenvironmental research.In this study, we report the occurrence of the glaucony in the lower Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation in southern Shaanxi Province for the first time.Integrated studies including petrography, in-situ microanalysis and X-ray diffraction(XRD)are carried out to constrain the diagenesis of the glaucony and the oceanic redox condition in the early Ediacaran of this area.Microscopic observations using polarizing microscope and scanning electron microscope(SEM)show that the glaucony mainly fills the pores of quartz, feldspar and other clastic minerals in the form of colloidal precipitates, suggesting authigenic precipitation during the early diagenesis.Since both Fe(Ⅱ)and Fe(Ⅲ)are simultaneously required for glauconitization, glaucony prefers to precipitate around the Fe redoxcline(suboxic conditions).Accordingly, the occurrence of glaucony in the lower Doushantuo Formation of study section implies suboxic pore water environments.The results of energy dispersive spectroscopy(EDS)show that the glaucony is characterized by high K2O and Al2O3 but low Fe2O3 contents which are typical of Precambrian glaucony.The dissolution of detrital minerals along with ion exchange between the seawater and pore-water supplied the elements required for glaucony formation.Compared with contemporaneous glaucony-bearing strata in Weng'an area, Guizhou, the limited vertical distribution of glaucony in the study area indicates that the marine redox condition and paleogeography may have played a joint role in regulating the formation and spread of glaucony.
-
Key words:
- palaeoceanography /
- Lianghekou /
- Doushantuo Formation /
- clay /
- redox
-

-
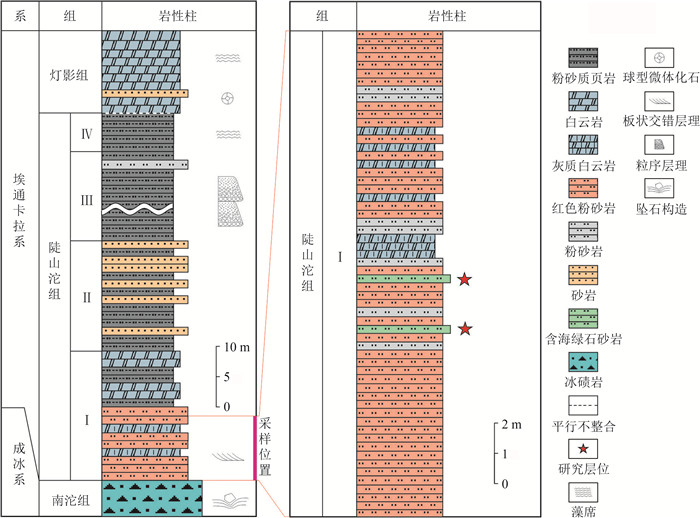
图 2 陕南两河口陡山沱组沉积地层柱状图(据Zhang et al., 2017修改)
Figure 2.
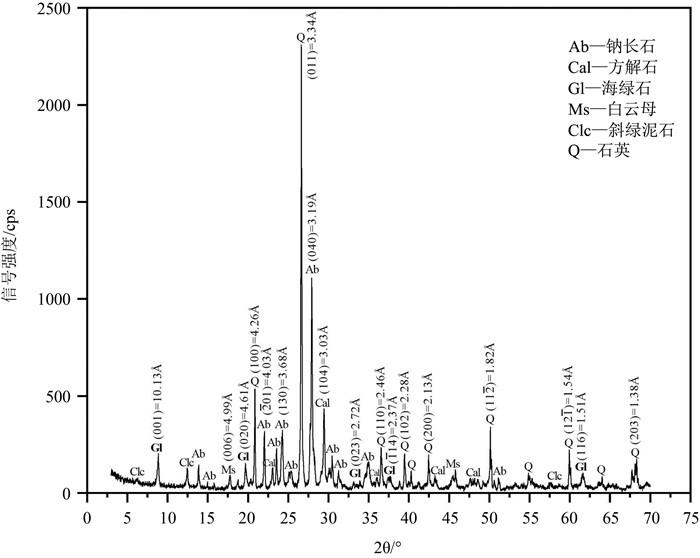
图 5 陡山沱组海绿石K2O与Fe2O3协变图(图中圆圈代表本研究所选取的陕南地区陡山沱组海绿石样品的K2O-Fe2O3数据点;三角形代表瓮安地区陡山沱组海绿石的K2O-Fe2O3数据点(Algabri et al., 2020);黑色闭合曲线代表其他作者发表的前寒武纪海绿石K2O-Fe2O3分布范围(Odin et al., 1981; Dasgupta et al., 1990; Dep et al., 1998; Guimaraes et al., 2000; Ivanovskaya et al., 2006; Banerjee et al., 2008; Mei et al., 2008; Drits et al., 2010; Banerjee et al., 2015; 汤冬杰等, 2016; Tang et al., 2017a; Bansal et al., 2020);图中的3个箭头代表海绿石的3种成因机制理论)
Figure 5.
-
[1] Algabri M, She Z B, Jiao L X, et al. Apatite-glaucony association in the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation, South China and implications for marine redox conditions[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 347: 105842. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105842
[2] Algeo T J, Liu J S. A re-assessment of elemental proxies for paleoredox analysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 540: 119549. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119549
[3] Amorosi A. Glaucony and Sequence Stratigraphy: A Conceptual Framework of Distribution in Siliciclastic Sequences[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1995, 65(4b): 419-425.
[4] Amorosi A. Detecting Compositional, Spatial, and Temporal Attributes of Glaucony: A Tool for Provenance Research[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1997, 109(1/2): 135-153.
[5] An Z H, Jiang G Q, Tong J N, et al. Stratigraphic position of the Ediacaran Miaohe biota and its constrains on the age of the upper Doushantuo delta C-13 anomaly in the Yangtze Gorges area, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 271: 243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.10.007
[6] Bailey S W. Summary of Recommendation of AIPEA Nomenclature Committee on Clay Minerals[J]. American Mineralogist, 1980, 65: 1-7.
[7] Banerjee S, Jeevankumar S, Eriksson P G. Mg-Rich Ferric Illite in Marine Transgressive and Highstand Systems Tracts: Examples from the Paleoproterozoic Semri Group, Central India[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 162(1/2): 212-226.
[8] Banerjee S, Chattoraj S L, Saraswati P K, et al. Substrate Control on Formation and Maturation of Glauconites in the Middle Eocene Harudi Formation, Western Kutch, India[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012a, 30(1): 144-160. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.10.008
[9] Banerjee S, Chattoraj S L, Saraswati P K, et al. The Origin and Maturation of Lagoonal Glauconites: A Case Study from the Oligocene Maniyara Fort Formation, Western Kutch, India[J]. Geological Journal, 2012b, 269(8): 259-269.
[10] Banerjee S, Mondal S, Chakraborty P P, et al. Distinctive compositional characteristics and evolutionary trend of Precambrian glaucony: Example from Bhalukona Formation, Chhattisgarh basin, India[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 271: 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.09.026
[11] Banerjee S, Bansal U, Thorat A V. A review on palaeogeographic implications and temporal variation in glaucony composition[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2016, 5(1): 43-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jop.2015.12.001
[12] Bansal U, Banerjee S, Nagendra R. Is the rarity of glauconite in Precambrian Bhima Basin in India related to its chloritization?[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 336: 105509. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2019.105509
[13] Bristow T F, Kennedy M J, Derkowski A, et al. Mineralogical constraints on the paleoenvironments of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(32): 13190-13195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901080106
[14] Burst J F, Houston T. "Glauconite" pellets Their mineral nature and applications to stratigraphic interpretations[J]. Bulletin of the American Association of Petroleum Geologist, 1958, 42(2): 310-327.
[15] Condon D, Zhu M Y, Bowring S, et al. U-Pb Ages from the Neoproterozoic Doushantuo Formation, China[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5718): 95-98. doi: 10.1126/science.1107765
[16] Dasgupta S, Chaudhuri A K, Fukuoka M. Compositional Characteristics of Glauconitic Alterations of K-Feldspar from India and Their Implications[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1990, 60: 277-281.
[17] Deb S P, Fukuoka M. Fe-Illites in a Proterozoic Deep Marine Slope Deposit in the Penganga Group of the Pranhita Godavari Valley: Their Origin and Environmental Significance[J]. Journal of Geology, 1998, 106(6): 741-749. doi: 10.1086/516057
[18] Drits V A, Ivanovskaya T A, Sakharov B A, et al. Nature of the Structural and Crystal-Chemical Heterogeneity of the Mg-Rich Glauconite(Riphean, Anabar Uplift)[J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2010, 45(6): 555-576. doi: 10.1134/S0024490210060040
[19] Fischer H. Glauconite formation: discussion of the terms authigenic, perigenic, allogenic and meta-allogenic[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1990, 83(1): 1-6.
[20] Guimaraes E M, Velde B, Hillier S, et al. Diagenetic/Anchimetamorphic Changes on the Proterozoic Glauconite and Glaucony From the Paranoá Group, Mid-Western Brazil[J]. Revista Brasileira de Geociências, 2000, 30(3): 363-366. doi: 10.25249/0375-7536.2000303363366
[21] Harris L C, Whiting B M. Sequence-stratigraphic significance of Miocene to Pliocene glauconite-rich layers, on- and offshore of the US Mid-Atlantic margin[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 134(1): 129-147.
[22] Hillier S, Velde B. Chlorite Interstratified with a 7-a Mineral - an Example from Offshore Norway and Possible Implications for the Interpretation of the Composition of Diagenetic Chlorites[J]. Clay Minerals, 1992, 27(4): 475-486. doi: 10.1180/claymin.1992.027.4.07
[23] Hoffman P F, Kaufman A J, Halverson G P, et al. A Neoproterozoic snowball earth[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5381): 1342-1346. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1342
[24] Hoffman P F, Abbot D S, Ashkenazy Y, et al. Snowball Earth climate dynamics and Cryogenian geology-geobiology[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(11): e1600983. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600983
[25] Ivanovskaya T A, Gor'kova N V, Karpova G V, et al. Phyllosilicates(Glauconite, Illite, and Chlorite)in Terrigenous Sediments of the Arymas Formation(Olenek High)[J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2006, 41(6): 547-569. doi: 10.1134/S0024490206060046
[26] Jiang G Q, Shi X Y, Zhang S H, et al. Stratigraphy and paleogeography of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation(ca. 635-551Ma)in South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(4): 831-849. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.006
[27] Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indexes used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129.
[28] Kitamura A. Glaucony and carbonate grains as indicators of the condensed section: Omma Formation, Japan[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 122(1/4): 151-163.
[29] Li C, Love G D, Lyons T W, et al. A stratified redox model for the Ediacaran ocean[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5974): 80-83. doi: 10.1126/science.1182369
[30] Li C, Cheng M, Zhu M Y, et al. Heterogeneous and dynamic marine shelf oxygenation and coupled early animal evolution[J]. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2018, 2(2): 279-288. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20170157
[31] Mei M X, Yang F J, Gao J H, et al. Glauconites Formed in the High-energy Shallow-Marine Environment of the Late Mesoproterozoic: Case Study from Tieling Formation at Jixian Section in Tianjin, North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(4): 146-158. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60048-2
[32] Meunier A, Albani A E. The glauconite-Fe-illite-Fe-smectite problem: a critical review[J]. Terra Nova, 2007, 19(2): 95-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2006.00719.x
[33] Murav'yev V I, Daynyak L G, Golovin B. Changes in the Composition of Glauconite in Contact with Sea Water[J]. International Geology Review, 1985, 27(7): 850-858. doi: 10.1080/00206818509466471
[34] Odin G S, Matter A. De glauconiarum origine[J]. Sedimentology, 1981, 28: 611-641. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1981.tb01925.x
[35] Odin G S, Fullagar P D. Chapter C4 Geological Significance of the Glaucony Facies[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1988, 45: 295-332. doi: 10.1016/S0070-4571(08)70069-4
[36] Planavsky N J, Rouxel O J, Bekker A, et al. The evolution of the marine phosphate reservoir[J]. Nature, 2010, 467(7319): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1038/nature09485
[37] Sahoo S K, Planavsky N J, Kendall B, et al. Ocean oxygenation in the wake of the Marinoan glaciation[J]. Nature, 2012, 489: 546-549. doi: 10.1038/nature11445
[38] Sahoo S K, Planavsky N J, Jiang G Q, et al. Oceanic oxygenation events in the anoxic Ediacaran ocean[J]. Geobiology, 2016, 14(5): 457-468. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12182
[39] Sarkar S, Choudhuri A, Banerjee S, et al. Seismic and Non-Seismic Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in the Proterozoic Bhander Limestone, Central India[J]. Geologos, 2014, 20(2): 89-103. doi: 10.2478/logos-2014-0008
[40] Tang D J, Shi X Y, Ma J B, et al. Formation of shallow-water glaucony in weakly oxygenated Precambrian ocean: An example from the Mesoproterozoic Tieling Formation in North China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017a, 294: 214-229. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.026
[41] Tang D J, Shi X Y, Jiang G Q, et al. Ferruginous seawater facilitates the transformation of glauconite to chamosite: An example from the Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling Formation of North China[J]. American Mineralogist, 2017b, 102(11): 2317-2332. doi: 10.2138/am-2017-6136
[42] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12-32.
[43] Xiao D, Cao J, Luo B, et al. Neoproterozoic postglacial paleoenvironment and hydrocarbon potential: A review and new insights from the Doushantuo Formation Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 212: 103453. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103453
[44] Xiao W Y, Cao J, Luo B, et al. Marinoan glacial aftermath in South China: Paleo-environmental evolution and organic carbon accumulation in the Doushantuo shales[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 555: 119838. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119838
[45] Zhang S H, Jiang G Q, Zhang J M, et al. U-Pb sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe ages from the Doushantuo Formation in south China: Constraints on late Neoproterozoic glaciations[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 473-476. doi: 10.1130/G21418.1
[46] Zhang Y, Zhang X L. New Megasphaera-like microfossils reveal their reproductive strategies[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 300: 141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.006
[47] Zhou C M, Huyskens M H, Lang X G, et al. Calibrating the terminations of Cryogenian global glaciations[J]. Geology, 2019, 47(3): 251-254. doi: 10.1130/G45719.1
[48] 程锦翔, 邓敏, 王正和, 等. 康滇古陆西侧早志留世古海洋氧化-还原环境及优质烃源岩发育模式——以盐源地区CYD2井为例[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(10): 1813-1828. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20221010&flag=1
[49] 李智武, 冉波, 肖斌, 等. 四川盆地北缘震旦纪—早寒武世隆-坳格局及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 59-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901008.htm
[50] 陕西省地质矿产局. 陕西省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989.
[51] 汤冬杰, 史晓颖, 马坚白, 等. 中元古代海绿石: 前寒武纪海洋浅化变层深度的潜在指示矿物[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 219-235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201606023.htm
[52] 汪泽成, 刘静江, 姜华, 等. 中—上扬子地区震旦纪陡山沱组沉积期岩相古地理及勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901004.htm
[53] 张琴, 梅啸寒, 谢寅符, 等. 不同类型海绿石的发育特征及分类体系探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6): 952-963. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201606020.htm
[54] 赵全基, 彭汉昌, 张壮域. 中国陆架海绿石分布特征及其意义[J]. 海洋科学, 1992, 16(5): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX199205018.htm
[55] 周传明, 袁训来, 肖书海, 等. 中国埃迪卡拉纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(1): 7-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201901003.htm
[56] 周晓峰, 杨风丽, 杨瑞青, 等. 扬子克拉通埃迪卡拉系陡山沱组构造-岩相古地理恢复及油气意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(4): 647-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202004005.htm
[57] 周锡强, 李楠, 梁光胜, 等. 天津蓟县中元古界铁岭组叠层石灰岩中原地海绿石的沉积学意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(7): 985-990. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090719&flag=1
-




 下载:
下载: